An examination by a doctor and the medical history collected during an appointment are often not enough to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment. Especially when it comes to the abdominal cavity. The location of internal vital organs does not make it possible to make an accurate diagnosis, or confirm it without instrumental diagnostics. To obtain the most informative results from the study, it is necessary to properly prepare for the examination procedure. We tell you how to do this.
In what cases is ultrasound of the abdominal organs prescribed?
In comparison with other studies - x-rays and CT scans, ultrasound is completely safe and can be prescribed to children from birth, and in adults it can be carried out without time intervals between diagnostics. Ultrasound gives an idea not only of pathologies in a specific organ, but also allows you to measure it, assess the condition of tissues and structure. Referrals for this study are issued by therapists, general practitioners and almost all specialized specialists: from gynecologists and urologists to neurologists.
Ultrasonic waves allow you to determine:
- size;
- shape;
- integrity;
- compliance with anatomical standards;
- location;
- contractility;
- level of peristalsis of the abdominal organs.
Ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs may be required in the process of comprehensive diagnosis of the following systems of the human body:
| Functional systems of the body | Organs examined using abdominal ultrasound |
| hepatobiliary system | gallbladder bile ducts liver |
| urinary system | kidneys renal tubules collecting ducts ureter bladder |
| digestive system | small and large intestine rectum pancreas duodenum |
| hematopoietic and circulatory system | spleen veins arteries |
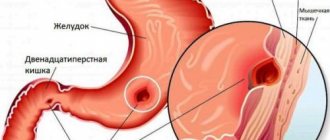
Ultrasound of the stomach and intestines is an auxiliary diagnostic method that is used in gastroenterological practice to detect pathology. In order for the procedure to be as informative as possible, proper preliminary preparation is necessary. This will allow the entire surface of the intestine to be examined as much as possible.
What preparation is needed for the procedure?
Flatulence, impaired peristalsis and feces can disrupt the examination. The presence of solid components in the intestine is a risk of missing existing lesions. For this reason, preparation plays an important role. You need to cleanse the intestines with a slag-free diet, laxatives or an enema.
Diet
Before the examination, 3-4 days before the examination, you need to start following a special diet and drink a lot of clean water. Heavy foods that contribute to gas formation are excluded from the diet. Prohibited products:
- whole milk;
- bakery products;
- mushrooms;
- fat meat;
- sausages, sausage;
- legumes (lentils, peas, beans);
- nuts;
- sweets;
- dried fruits;
- greens (sorrel, spinach);
- berries with seeds;
- fresh vegetables (especially white cabbage).
Also, you should not drink strong coffee, alcohol or carbonated drinks.
List of permitted products:
- lean varieties of fish and meat;
- soft-boiled eggs or omelet;
- buckwheat and rice porridge;
- low-fat yoghurts and cottage cheese;
- jelly;
- boiled potatoes;
- crackers, biscuits;
- light vegetable soups;
- vegetable oils (in small quantities);
- some fruits (as recommended by a doctor);
- kefir;
- cheese (low-fat varieties).
The last meal should be the evening before. The examination is performed on an empty stomach (this is important for examining the stomach, but it may be necessary to fill it with liquid during the examination).
How to prepare for an ultrasound of the stomach and intestines at home
There are two methods used to cleanse the intestines: medications or enemas. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages.
The best drugs
Before using any medicine with a laxative effect, you should carefully read the instructions. In case of overdose, there is a risk of complications. Some medications are taken only on an empty stomach. Others are allowed to be drunk 2 hours after a light breakfast.
Contraindications:
- individual sensitivity;
- significant water load (heart failure, childhood and old age);
- suspected intestinal obstruction.
More information about the most common drugs:
- Duphalac. A mild, fast-acting lactose-based drug. It is a thick syrupy liquid. It is not absorbed into the blood, so it is actively used in children and pregnant women. The contents of the bottle are diluted in two liters of water. Preparation begins 4 days before the examination.
- Picoprep. Powdered medicine with a pleasant orange scent. Contains sodium picosulfate, anhydrous citric acid and magnesium oxide. The laxative effect occurs a couple of hours after consumption. It has a comprehensive cleansing effect ─ retains water, softens feces and promotes their rapid movement.
- Lavacol. Designed for deep cleansing of the intestines. To dissolve, a small volume of liquid is required ─ one sachet per glass of water. The action begins 2-4 hours after consumption. It disrupts the microflora, so after using it it is better to drink bifidobacteria.
- Movieprep. It is a combination of macrogol, sodium sulfuric acid and other laxatives. Contains lemon flavor and synthetic sweeteners.
- Fleet Phospho-soda. Ready-made laxative. Promotes increased peristalsis, retains fluid in the small intestine. The dose is for 2 doses (morning and evening). The expected effect occurs after half an hour.
- Endofalk. The composition contains macrogol, potassium and sodium chlorides, sodium bicarbonates. The product has a pleasant taste thanks to the addition of flavorings.
- Fortrans. The main active ingredient is Macrogol 4000. The drug ensures rapid emptying of the entire intestine. Contains electrolytes that correspond to the osmotic pressure of saline solution. Thanks to this, the body fluids do not change in composition.
The degree of readiness of the patient can be determined by two criteria:
- Feces. They are transparent, light yellow in color, and have the consistency of water.
- Feeling of emptiness in the gastrointestinal tract.
Espumisan is often prescribed to relieve flatulence. This drug eliminates gas formation and helps avoid pneumatization of the intestine.
Enema
An enema can also be used to properly prepare for a colonoscopy. The method allows you to effectively cleanse the intestines and remove residual feces. This is an old and proven method. The main advantages are simplicity and accessibility. In particular, manipulation is indicated for people suffering from frequent constipation. The disadvantage is the need to control the flow of fluid and retain it in the intestines for a certain time.
To perform an enema you will need an Esmarch mug. It is recommended to do the procedure two evenings in a row. The water should be warm. The required amount of liquid is 1.5-2 liters. It is not recommended to use saline solutions, as they have an irritating effect on the intestinal walls. Rinsing is done with warm water.
The method is contraindicated for people suffering from hemorrhoids and anal fissures.
Preparation for ultrasound of the intestines with Fortrans
One sachet of the drug is designed for 20 kg of weight and is diluted in 1 liter of water. For example, a patient weighing 60 kg will need 3 sachets.
The prepared solution is divided into 2 parts. The first part should be drunk between 14-16 hours. Every 15 minutes, 250 ml, then a break (1 hour). The second part is drunk between 17-19 hours.
To improve the taste of the solution, it can be placed in the refrigerator and cooled the day before the test. Another option is to add a little orange juice.
If the procedure is carried out in the morning, then preparation begins the day before. Last meal around 13:00. Three hours later ─ use the first portion of Fortrans. The first urge will begin an hour after this. Next, the solution is taken for another 4 hours.
Fortrans is the drug of choice for the patient in the following cases:
- presence of heart or kidney failure, diabetes mellitus;
- the presence of symptoms of nonspecific diseases of the large intestine (Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis);
- taking certain medications (for example, drugs from the angiotensin receptor blocker group).
Preparation for ultrasound of the intestines with Moviprep
The total dose of Moviprep depends on the patient’s weight, but does not exceed two liters.
If the procedure is carried out in the morning, then the night before you should first drink one liter of solution (about 8 pm), and a little later the second liter (about 10 o’clock).
If an intestinal ultrasound is performed in the afternoon, then preparation is meant only on the day of the study. The entire solution must be drunk between 8 and 11 am.
Contraindications for bowel cleansing with Moviprep:
- childhood and adolescence (up to 18 years);
- hemolytic anemia;
- atony of the colon;
- fermentopathy;
- through defects in the gastrointestinal organs;
- intolerance to the components of the product.
What is better to prepare for an ultrasound of the intestines Lavacol, Moviprep or Fortrans
All three medications contain the same active substance, so the mechanism of action will be similar.
The following differences can be distinguished:
- Fortrans has an unpleasant taste, but Lavacol is quite acceptable (similar to mineral water).
- Price. The cost of imported drugs is always higher.
- Manufacturer. Lavacol is produced in Russia, and Fortrans in France.
TRUS of the lower intestines is an additional ultrasound endocavity (internal - through the anus) examination of the rectum and sigmoid colon, as well as surrounding tissues of the male or female pelvis.
Preparation is minimal - a small cleansing enema of up to 500 ml. In case of increased sensitivity of the rectum, suppositories with anesthesin should be used 1 hour before the examination.
How is an abdominal ultrasound performed?
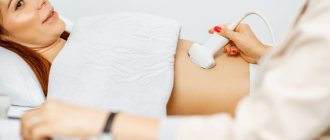
Ultrasound diagnostics allows you to visualize internal organs and tissues on the screen. To do this, the patient lies down on the couch. A hypoallergenic gel, safe for health, is applied to his stomach, which ensures a stable connection between the ultrasound sensor and the human body, prevents the penetration of air and allows the device to move unhindered over the skin. The doctor moves the sensor across the abdomen and records the data in an electronic protocol. The procedure takes from 20 minutes to an hour.
The main difficulty that specialists face when conducting ultrasound diagnostics of the abdominal cavity is gas bubbles that prevent the penetration of ultrasonic waves to the examined organ. Reducing gas formation allows you to obtain reliable data about the organs and tissues of the abdominal cavity.
Some important nuances
12 hours before the diagnosis, you should cleanse the intestines by doing an enema - using an Esmarch mug, 1.5 liters of cool water are injected into the rectum. An alternative to an enema can be microenemas or laxatives.
If necessary, your doctor may prescribe medications to improve digestion and prevent flatulence. It is advisable to avoid other medications, especially antispasmodics. If this cannot be done, then you must inform your doctor.
You must refrain from smoking for two hours before diagnosis, as nicotine provokes spasms of the gallbladder and stomach. In addition, smoking promotes air absorption.
Before going to the clinic, you should not use refreshing lollipops or chewing gum.
If an examination of the genitourinary system is planned, an hour and a half before the procedure you need to drink a liter of gas-free water and not urinate.
If the patient has undergone colonoscopy, fibrogastroduodenoscopy, or radiography with contrast, then an ultrasound examination can be done only after two days.
Bladder examination
Diagnosis of the bladder is carried out when the organ is filled with fluid. It is necessary not to overdo it with fluid intake, otherwise the doctor will not be able to assess the situation. When examining a congested organ, diseases such as pyeloecstasy and residual urine may be revealed. Sometimes these diagnoses are false. In this case, it is optimal to drink 0.5 liters of liquid half an hour before the test. In rare cases, diuretics may be used.
Indications
An ultrasound of the gallbladder is prescribed by a gastroenterologist, therapist or surgeon in the following cases:
- frequent pain in the right hypochondrium that is not relieved by painkillers;
- a feeling of heaviness or discomfort in the liver area;
- feeling of bitterness in the mouth;
- yellowness of the skin and visible mucous membranes;
- severe nutritional disorder: abuse of spicy, fatty, fried, smoked foods;
- irregular meals;
- excessive passion for low-calorie diets;
Note: patients with a removed gallbladder undergo a specialized ultrasound - dynamic echo-choledochography (ultrasound examination of the ducts with a food load).
Contraindications
Apart from severe damage to the skin in the area of study (open wounds, burns, infections), there are no contraindications to the procedure.
Why preparation is needed
Before performing an ultrasound, you need to complete a training course.
Strict adherence to recommendations for preparation for diagnosis is necessary to eliminate a number of factors that may interfere with clearly visualizing the desired organ. This is important not only for the doctor, but the patient will have confidence that the results obtained are reliable. The study can begin only after the patient has completed all instructions, namely:
- Followed a special diet
- Didn't do any other research the day before
- Did not take medications that may interfere with the study
- Did not abuse alcohol or smoking
- Complied with fluid intake standards
Research may be hindered by:
- Spasms of the intestinal muscles resulting from previous endoscopic examination or overeating.
- Overflow of intestinal gases
- Remains of contrast agent after an x-ray
- Large fat layer on the abdomen, preventing deep penetration of ultrasound
- Wound in the examined area
- Motor activity during diagnosis
Of course, it is quite difficult to exclude some factors, but the patient can correct many of them by taking the necessary measures to eliminate them.
Decoding the results
During the procedure, the doctor evaluates the following indicators:
- organ location and mobility;
- shape, size, thickness of the walls of the gallbladder;
- diameter of the bile ducts;
- contractile function of the organ;
- the presence of stones, polyps, neoplasms.
The size of the gallbladder is normal
- length 7-10cm;
- width 3-5cm;
- transverse size 3-3.5 cm;
- volume from 30 to 70 cubic meters. cm;
- wall thickness up to 4mm;
- common bile duct with a diameter of 6-8 mm;
- the internal diameter of the lobar bile ducts is up to 3 mm.
The shape of the gallbladder is pear-shaped or oval, the contours are clear, the bottom of the bladder can protrude from under the lower edge of the liver by 1-1.5 cm. However, it is worth noting that the size of the organ largely depends on the build of the patient himself. Therefore, a competent doctor pays attention to the overall picture, rather than simply measuring individual structures.
Photo: one of the projections of the gallbladder on ultrasound
Method of implementation
A sensor is used to determine the condition of the organ with further diagnostics. It is adjusted to the abdominal wall to make the ultrasound procedure easier. In order for the research to be carried out efficiently, it is necessary to free up space where the sensors will be installed. It is also necessary to get rid of the air that has formed between the body and the sensor so that there are no failures. In this case, the accuracy of the readings increases.
There are times when loops in the abdomen interfere with the correct diagnosis. You need to take a deep breath, or turn on your side. Ultrasound examination of internal organs is often necessary, since it is difficult to determine the extent and main nuances of the disease just by symptoms.