Gastroscopy is a modern examination method. Thanks to it, you can diagnose the duodenum, stomach, sphincter and much more. FGDS is prescribed if there is a suspicion of any pathology of an acute or chronic nature. Modern conditions provide patients with the opportunity to undergo gastroscopy without pain, despite the fact that it is performed invasively.
In order to conduct the study, the doctor uses a special flexible fiber gastroscope. It follows the curves of the esophagus, which makes it possible to carry out the procedure painlessly. For particularly fearful patients, the procedure can be performed in their sleep. When going for an FGDS, it is important to properly tune in and prepare, as well as follow the recommendations of specialists after the procedure. Only then can you get accurate and high-quality results, without experiencing painful and uncomfortable sensations. We will tell you more about what to do before, during and after FGDS below.
Preparation
If the examination is scheduled for the morning, then you need to completely stop eating in the evening. You should not eat even those foods that are quickly digested. This number includes any liquids, even plain water. Three to four hours before the procedure, you can drink half a glass of clean water. You should also quit smoking. This is explained by the fact that nicotine stimulates the activity of the gastrointestinal tract, which adversely affects the conduct of FGDS.
If the patient is taking any medicine, then it should also be abandoned. If this is impossible to do, you should notify the doctor about this in advance and come to a common decision with him. In some cases, medications may be given by injection. It is necessary to understand that only by strictly following all recommendations can you get the desired result.
In some cases, gastroscopy is prescribed after lunch. In this case, the patient can have breakfast. However, meals should be light. For example, it could be yogurt or unsweetened tea. The time interval between breakfast and FGDS is at least seven to eight hours. The doctor will give all the necessary recommendations in advance. You can coordinate your medication intake with him.
Diet food
A special diet is prescribed to the patient three days before the proposed gastroscopy procedure. This allows you to ease the work of the gastrointestinal tract and cleanse it. In addition, a special diet helps eliminate the possible occurrence of flatulence and inaccurate results.
The patient must follow the following rules:
- Eating in small portions;
- Overeating is prohibited;
- Eat four to five times a day;
- Eliminate foods that cause increased gas formation (beans, cabbage, drinks with gases, etc.);
- Drink at least two liters of water per day.
The diet allows you to relieve the gastrointestinal tract and not irritate its walls.
Prohibited and permitted foods
Patients who have been scheduled for gastroscopy should know what they can and cannot eat before undergoing the procedure. This issue worries many people, so it deserves special attention. In addition, if you prepare incorrectly for the FGDS, you will have to go through the procedure again, which you don’t want to do at all.
The day before the examination, you must completely avoid the following foods:
- Fatty meats and fish;
- Bread and other baked goods;
- Pasta;
- Chocolate and other sweets;
- Legumes;
- Milk and dairy products;
- Salo;
- Smoked meats;
- Sauces, spices and seasonings;
- Nuts;
- Alcoholic drinks;
- Coffee;
- Carbonated drinks.
Preference should be given to those products that do not irritate the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract.
The following products are allowed to be consumed:
- Dietary chicken meat;
- Oatmeal and buckwheat porridge with water;
- Low-fat dietary soups;
- Mashed potatoes;
- Steamed vegetables;
- Low fat sour cream;
- Light herbal teas without sugar.
What to do before the examination
Preparation for gastroscopy includes a list of laboratory tests and ECG - electrocardiography. Patients must submit the following:
- Clinical blood test;
- Analysis to determine the Rh factor and blood group;
- Coagulogram;
- Testing for HIV and other infections.
Before entering the gastroscopic office, you need to remove dentures from your teeth, go to the toilet, and remove glasses or contact lenses. If a person has a chronic disease, then the doctor must be warned about this in advance. It is possible that you will need to first consult with a specialist doctor. For example, a neurologist or someone else. It is also worth warning the specialist in advance if you suddenly have an allergic reaction to something.
Particular attention is paid to preparing a person for gastroscopy with taking a biopsy. The procedure includes examining the stomach followed by taking a piece of the mucous membrane. After this, it is examined for the presence of pathologies. The procedure is not difficult and is not painful for the patient. This is common practice for doctors. Taking a biopsy almost never leads to complications. However, in some cases this procedure is contraindicated.
It is not prescribed to people who have:
- Acute infectious diseases;
- Obstruction of the esophagus or intestines;
- High blood pressure;
- Mental disorders;
- Inflammatory processes;
- Exacerbation of bronchial asthma.
Typically, gastroscopy with biopsy is performed as an additional examination.
Gastroscopy under anesthesia
FGDS under anesthesia deserves a separate discussion. Typically this procedure is carried out for a fee. Those patients who are afraid of the procedure or have some factors that do not allow gastroscopy without anesthesia undergo it.
In order to conduct a high-quality FGDS under anesthesia, it is necessary:
- Examine the patient well to exclude the possible development of complications;
- Choose the safest type of pain relief;
- Eliminate possible risks of side effects.
As a rule, before performing this procedure, the patient undergoes a consultation with a gastroenterologist, therapist and anesthesiologist. If necessary, other highly specialized specialists are involved. This allows you to make the procedure as safe and effective as possible.
Is FGDS safe?
Complications after gastroscopy occur extremely rarely. This type of manipulation is worked out to the smallest detail, so specialists do not expose patients to any danger. The main difficulty is only the inappropriate behavior of the patient. Due to excessive fear and anxiety, the patient forgets about the importance of a high-quality procedure and begins to resist during probing. This leads to an undesirable result. If the patient behaves calmly and adequately, this will minimize discomfort. With a competent approach to gastroscopy, it will not cause any harm. The safety of FGDS is evidenced by the fact that it is prescribed even to children.
What to do after the examination
After FGDS, the patient must follow some recommendations from specialists. These include the following:
- The patient should rest for 10-15 minutes after the procedure is completed. There is no need to suddenly get up and run somewhere;
- You need to refrain from eating any foods for the first two to three hours;
- During the day, it is necessary to avoid excessive physical activity, rest more and spend time in the fresh air.
There are no strict restrictions. Long-term observations of patients show that everyone tolerates the procedure differently. Some are calm, some worry too much, and some behave violently and aggressively. Further recovery and the quality of the result depend on this. If you do not follow the recommendations, then repeat gastroscopy is possible. So it’s better to do everything right right away.
It is also not recommended to smoke in the first hour after the examination. It is worth understanding that the introduction of equipment irritates the mucous membrane of the throat. In turn, smoking only aggravates this condition. As a result, a person does not know what to do if his throat hurts after an FGDS. And this is precisely a sign that the patient did something wrong. For example, smoked after the procedure or strained too much during the study.
How long will it take?
Almost all patients are interested in when they can eat after FGDS. The main restrictions on the consumption of products were before the study. After the procedure, there are no serious prohibitions, but there are still some rules. Below are recommendations from experts that will help you understand how long you can eat after FGDS:
- You can eat food after the swallowing reflex appears and the feeling of numbness in the throat disappears;
- The first portions of food must be small (maximum 200 grams);
- Avoid drinking alcoholic beverages on the first day;
- Drink at least two liters of water per day;
- Avoid excessively hot foods. This is especially true for those patients from whom a biopsy was taken. It is enough that the food is warm, at a comfortable room temperature;
- Eliminate solid foods.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the table, which contains a list of prohibited and permitted products:
| Authorized Products | Prohibited Products |
| Liquid porridge on water | Coffee |
| Puree diet soups | Various sauces, spices and seasonings |
| Steamed vegetables | Spicy dishes |
| Lean meat | Fat meat |
| Herbal teas without sugar | Marinades |
| Bread and other baked goods |
The patient is asked when he can eat and drink after FGDS. This is allowed to be done two to three hours after the study. At the same time, it is important that the person feels good and does not experience pain in the throat.
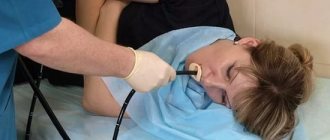
What to do during gastroscopy
The procedure does not last long, but during this time it is important not to swallow unless absolutely necessary. The accumulated saliva is removed by the nurse using a special suction. The total cost of gastroscopy includes anesthesia. A local anesthetic is sprayed onto the root of the tongue, making both the tongue and throat numb and inactive.
For some time it may seem to you that you are having difficulty breathing and the gastroscope is to blame. These sensations are false; in fact, the reason is the anesthetic. There is always enough air around the device, and the endoscope in no way impedes its passage into the lungs. The patient’s task in this case is to try to relax and take a few deep breaths.
If you cannot cope with the problem and pain is still present, give the medical staff a pre-agreed hand sign. But, as a rule, experienced doctors always make sure that the patient does not experience such discomfort and take the necessary actions.
Don’t be afraid of the noisy suction respirator: the operation of the device does not cause any pain. Biopsy of tissue samples is also painless. Another unpleasant feeling is belching and bloating immediately after the examination. The gases that inflated the stomach walls remain inside, so this is absolutely normal.
Possible complications
Despite the fact that FGDS is a safe type of examination, in extremely rare cases complications still arise. As a rule, this happens if a person has not properly prepared for the study and ignored the recommendations of specialists.
So, below is a list of possible complications:
- Painful sensations in the throat or epigastric area;
- Increased body temperature;
- Laryngotracheitis (minor injury);
- Vomiting with blood;
- Lack of air;
- Bleeding.
In old age, heart rhythm disturbances, heart attack or stroke are possible. There are objective reasons for this, because older patients tolerate this type of procedure less well. In any case, if an undesirable reaction occurs, you should immediately consult a doctor or call an ambulance. It is prohibited to ignore these complications, as they can lead to negative consequences.
In what cases should you seek medical help?
If, a short time after gastroscopy, you experience chest pain or difficulty breathing, you should immediately call a doctor. Alarming symptoms also include dizziness and sore throat, fever and chills as signs of infection, as well as the appearance of fresh or coagulated blood in the vomit.
If you have other symptoms that are unclear to you, contact your doctor and consult with him about further actions. But remember! If the procedure was performed in a good clinic by qualified personnel, the percentage of complications and side effects is always minimal.