- Gastritis of various etiologies
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
- Duodenitis
- Chronic Helicobacter gastritis
- Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum
Symptoms Classification Diagnostics Treatment Information
Pathologies of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum play a leading role in diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. This directly affects the quality of life of patients.
Disturbances in the functioning of the esophagus are associated mainly with failures of its motor function. Pathologies of the stomach, esophagus, and duodenum are most often caused by the activity of bacteria (Helicobacter pylori), inflammatory processes, congenital characteristics of the body, and neoplasms.
THE INSTITUTE OF ALLERGOLOGY AND CLINICAL IMMUNOLOGY has:
- range of services for accurate diagnosis of diseases
- special treatment programs
- consultations are carried out by doctors with academic degrees.
When identifying concomitant diseases, consultations are held with specialists in related fields (otorhinolaryngologists, endocrinologists, neurologists, gastroenterologists, dermatovenerologists), consultations with Doctors of Medical Sciences.
Attention!
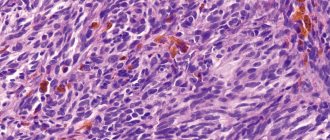
Helicobacter pylori is a causative agent of cancer in the gastrointestinal tract.
1.Structure of the esophagus
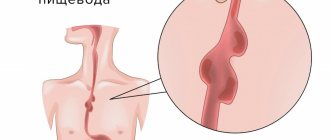
Esophagus
- a muscular tube connecting the throat (pharynx) to the stomach. The length of the esophagus is about 20 centimeters, and its inner surface is a pink mucous membrane. There is a part of the esophagus called the upper esophageal sphincter (UES). This is a group of muscles at the top of the esophagus that work during breathing, eating, belching and vomiting. A person can consciously control this muscle group. The upper esophageal sphincter muscle also holds food and secretions that may come from the windpipe.
The lower esophageal sphincter (LES) is a group of muscles at the lower end of the esophagus where it connects to the stomach. When the lower esophageal sphincter is closed, it prevents acid and stomach contents from moving back out of the stomach. The muscles of the LES are not subject to conscious control.
Diseases of the esophagus
, in fact, not so little. Some of them are quite serious, some do not require complex and long-term treatment. Depending on the severity of the disease, it may be treated by gastroenterologists or thoracic surgeons, who perform operations on the esophagus when necessary for treatment.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Types of GERD, manifestations of the disease and complications
In the medical classification, two types of the disease are distinguished - acute and chronic esophagitis. It differs in the type of inflammatory process. In the acute phase, the walls of the esophagus are exposed, and in the chronic phase, the mucous membrane is affected, with the duration of the disease lasting more than 6 months. Reflux esophagitis begins to develop due to improper nutrition, exposure to chemicals, and extensive infections. In the acute phase, there may be an increase in temperature, general malaise, and discomfort as food moves through the esophagus. Patients experience drooling during attacks, belching, and pain. With alcohol abuse, spicy or rough foods, the inflammatory process progresses. The disease enters the chronic phase. If left untreated, the esophagus changes and scars form.
2. The most common diseases of the esophagus
- Heartburn
. Heartburn occurs when the lower esophageal sphincter does not close completely. As a result, the acidic contents of the stomach enter the esophagus. This is called reflux. This reflux may cause heartburn, coughing, or hoarseness, or cause no symptoms at all. - Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
. If reflux occurs frequently or is accompanied by unpleasant symptoms, it is called GERD. - Esophagitis
. Esophagitis is inflammation of the esophagus. Esophagitis can be associated with irritation of the esophagus, either as a result of reflux or infection. - Barrett's esophagus
. Regular reflux of stomach acid causes irritation of the esophagus, which can result in changes in the structure of its lower part. In very rare cases, Barrett's esophagus progresses to esophageal cancer. - Esophageal ulcer
. With an esophageal ulcer, erosions form in the mucous membrane of the esophagus. This is often the cause of chronic reflux. - Esophageal strictures, or narrowing of the esophagus
. Chronic irritation from reflux is a common cause of esophageal strictures. - Achalasia of the esophagus
. Achalasia is a rare condition in which the lower esophageal sphincter does not relax. Difficulty swallowing and regurgitation of food are the most common symptoms of the disease. - Esophageal carcinoma
. Esophageal cancer is a serious disease, which, however, is not so common. Risk factors for the development of esophageal cancer are smoking, alcoholism and chronic reflux. - Mallory-Weiss syndrome, or gastroesophageal rupture-hemorrhagic syndrome
, occurs when tears occur in the surface of the esophagus due to frequent vomiting. Such ruptures are accompanied by internal bleeding and subsequent vomiting of blood. - Varicose veins of the esophagus
. In people with cirrhosis, the veins in the esophagus may become enlarged and protruding. These veins can cause life-threatening bleeding. - Ring-shaped formations in the lower parts of the esophagus
. This is a benign collection of tissue in the form of a ring around the lower end of the esophagus. Typically, these rings do not cause any symptoms, but in some cases they can cause difficulty swallowing. - A collection of tissue at the top of the esophagus
. A disease that develops in a similar way to ring-shaped formations in the lower part of the esophagus, which also usually does not cause unpleasant symptoms. - Plummer-Vinson syndrome
. This is a disease of the esophagus accompanied by chronic iron deficiency anemia, ring-shaped formations in the upper part of the esophagus and difficulty swallowing. Iron therapy and expansion of esophageal tissue are the main methods of treating the disease.
Visit our Gastroenterology page
People's Councils
They do not replace drug treatment; for this reason they are used as an addition to the main therapy. To reduce discomfort and protect the mucous membrane, use:
- Flax seeds with honey. The medicine is prepared in advance, stored in the refrigerator and taken a teaspoon at a time.
- Decoctions of rose hips, chamomile, calendula and plantain. You can take infusions in combination, in the form of herbal tea or tea.
- A little oregano, as well as mint: suitable for lubricating the throat, will help eliminate an attack of hiccups.
If a person has been diagnosed with an esophageal disease, he will have to take medications and follow a diet throughout his life. Folk remedies will speed up the effect of medications, but, alas, they cannot replace them.
3.Diagnosis of diseases
Of course, depending on the symptoms of which disease the doctor sees during the initial examination and consultation, methods for further diagnosing diseases of the esophagus will be selected individually. Let's talk about some of them:
- Upper endoscopy, FGDS (esophagogastroduodenoscopy)
. In this procedure, a flexible, thin tube with a camera on the end (endoscope) is inserted into the esophagus through the mouth. An endoscope allows you to examine the stomach and duodenum (small intestine). - pH monitoring of the esophagus
. A probe that monitors pH levels is inserted into the esophagus. This method is used to diagnose GERD and monitor the progress of GERD treatment. - X-ray examination
with preliminary administration of drugs containing barium. This method is usually used to determine the causes of difficulty swallowing. - Biopsy
. A method for diagnosing diseases of the esophagus, in which a sample of esophageal tissue is taken using endoscopy, which is then examined under a microscope. - Confocal laser endomicroscopy
. This is a new procedure in which a microscope is inserted into the patient's esophagus. Endomicroscopy can be a good alternative to biopsy.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
How to diagnose
In gastroenterology, a number of objective diagnostic methods are used to determine the patient’s condition and the extent of damage to the esophagus. Esophagitis manifests symptoms to a pronounced degree, which is a reason to consult a doctor. Diagnosis and treatment are carried out by a gastroenterologist. The patient examination consists of:
- collecting anamnesis about health, presence of diseases;
- contrast x-ray (with barium);
- endoscopic gastroscopy;
- pH-metry and manometry;
- laboratory tests of gastric juice.
4. Treatment of diseases of the esophagus
Just like the diagnosis of esophageal diseases, treatment depends on what specific disease is diagnosed. Among the treatment methods include:
- Use of H2 blockers
. The release of acid in the stomach is stimulated by histamine. Some antihistamines are called H2 blockers. They can reduce acid content and improve the condition of a patient with GERD and esophagitis. - Proton pump inhibitors
. These medications block many of the acid production processes in the stomach and also help with GERD. In addition, inhibitors help heal ulcers or esophagitis. - Esophagectomy, or removal of the esophagus
. This is a surgical procedure performed by thoracic surgeons. As a rule, it is performed for esophageal cancer. - Dilatation of the esophagus
. A special device is passed down the esophagus and then expands on its own, causing the esophageal ring, stricture, and other formations that prevent swallowing to widen. - Ringing of esophageal varices
. This procedure is performed endoscopically and involves wrapping rubber band-like devices around the esophageal varices. This reduces the chance of bleeding.
Presentation of symptoms and signs
Reflux esophagitis manifests symptoms and signs with varying degrees of severity, which depends on the stage of the disease:
- heartburn (the most common manifestation);
- pain in the chest near the heart;
- lump in throat and difficulty swallowing;
- frequent cough and inflammation of the respiratory tract;
- weight loss;
- hoarse voice;
- poor sleep;
- nausea and belching;
- bloating;
- vomit.
Are you experiencing symptoms of reflux esophagitis?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
Methods of treating the disease
In case of esophagitis, treatment is prescribed taking into account the patient’s condition and pathogenesis. The most important condition is a change in lifestyle and a systematic reduction in the amount of acid entering the esophagus. The treatment system includes:
- taking medications to reduce stomach acidity;
- antibacterial therapy in the presence of infection;
- diet therapy on an ongoing basis;
- surgical intervention for complicated forms of the disease.
Diagnosis of Barrett's esophagus
The main and most effective method for diagnosing Barrett's syndrome is endoscopic. Its purpose is to obtain biopsy material. In this case, the morphological study is aimed at:
- confirmation of metaplasia of the esophageal mucosa;
- detection of dysplasia;
- detection of malignant cells, most often adenocarcinoma.
To determine more precise boundaries of the changed mucosa during endoscopic examination, chromoscopy is used; this is the coloring of the mucosa. Lugol's solution is usually used; if you are allergic to iodine, use methylene blue or acetic acid.
What is diet therapy for reflux esophagitis
A diet for reflux esophagitis helps maintain body weight within normal limits and eliminates provoking factors for increasing the level of stomach acidity. The patient must adhere to a meal schedule of 4-5 times a day. Portions should be small. It is recommended to exclude carbonated drinks, coffee, chocolate, citrus fruits, and strong tea from the diet. It is important not to create reasons for increasing intra-abdominal pressure. For this purpose, you should avoid wearing tight belts and tight clothing, and do not lift heavy things (more than 8-10 kg). The place to sleep should be organized in such a way that the head and neck are above the level of the abdomen. This will prevent gastric contents from refluxing into the esophagus during rest.
How to understand that esophageal esophagitis has begun to develop
The severity of symptoms in the acute course of the pathology depends on the severity of inflammation of the organ. In the catarrhal form, esophagitis may not cause symptoms, only occasionally it is manifested by increased sensitivity of the esophagus to cold or hot foods. Severe forms of the pathology are accompanied by severe pain in the chest, radiating to the back and neck, dysphagia due to severe pain, heartburn and increased salivation. In especially severe cases, vomiting with blood may occur, leading to shock. After a week, the patient may feel imaginary well-being and notice the disappearance of unpleasant symptoms, but without proper treatment, after a few weeks, esophagitis will lead to the formation of rough scars and stenosis, which will provoke the progression of swallowing disorders and regurgitation of food.
The main symptom of chronic esophagitis is heartburn, which worsens after eating spicy and fatty foods, coffee and highly carbonated drinks. Overeating can also cause a burning sensation in the epigastric area. At night, the patient may experience regurgitation.
Often other pathologies are associated with esophagitis:
- Bronchial asthma;
- Laryngospasm;
- Breathing disorders;
- Frequent pneumonia.
In children under 1 year of age, esophageal sphincter insufficiency is diagnosed with repeated heavy regurgitation in a horizontal position immediately after feeding. At an older age, children complain of paroxysmal pain in the epigastrium, especially after eating hot food. The pain syndrome intensifies when bending the body, performing physical exercises and at night. Young children are often bothered by nausea and vomiting, while older children are often bothered by heartburn and belching. After waking up, a wet, colorless or yellowish spot may be found on the child’s pillow due to regurgitation. If the disease is not treated in childhood, it threatens bleeding, scarring and stenosis of the esophagus, the development of aspiration pneumonia and anemia.
Why is it better to seek treatment from us?
Early detection of esophageal diverticulum and a complete assessment of the risk of the disease for a particular patient allows doctors at the Kuntsevo Treatment and Rehabilitation Center to fully assess the person’s condition and choose the most effective treatment tactics in each individual case. In addition, modern diagnostic methods available at the Kuntsevo Treatment and Rehabilitation Center (gastroscopy, MRI of the esophagus, MRI of the esophagus “in sleep”) allow the doctor to monitor the patient’s dynamics, evaluate the effectiveness of therapy and make changes to speed up the person’s recovery process.
IMPORTANT! You should not self-medicate if you discover this symptom. Cold hands can be a manifestation of both the physiological norm of your body and a pathological process that develops in the body.
The Kuntsevo Multidisciplinary Center has doctors of the highest category and doctors of medical sciences. Using modern equipment and high-tech devices, diagnosing esophageal diverticulum has become easier and more effective. You will be pleasantly surprised by the best prices and friendly staff. Don't delay treatment - make an appointment!
The contents of this article have been checked and confirmed for compliance with medical standards by gastroenterologist-nutritionist Tatyana Vladimirovna Lucheninova