Acute pathologies of the abdominal cavity are a reason to immediately consult a doctor. After all, many conditions require urgent surgical intervention. These include abdominal diseases such as:
- Strangulated hernia;
- Acute appendicitis;
- Acute pancreatitis;
- Intestinal obstruction;
- Cholecystitis;
- Ulcerative bleeding of the duodenum and stomach.
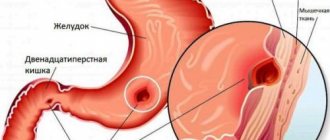
In abdominal surgery, it is very important to correctly determine the localization of pain, but since pain can radiate to other parts of the body, in order to make a correct diagnosis, it is not enough to rely on the clinical picture of what is happening. Laboratory tests of blood, urine, and additional studies are required. But the most informative are hardware diagnostic methods. One of the most modern is abdominal CT, which helps to examine the tissues of the peritoneal organs, as well as adjacent vessels and lymph nodes.
CT allows you to obtain a three-dimensional image of the area under study in different planes. This method takes X-ray images layer by layer, and the thickness of each in this case is about several microns. A ring-shaped circuit with sensors emits X-rays at different angles, so when they arrive on a computer monitor, they are superimposed on each other, forming a three-dimensional model of the organ being studied.
If there is a suspicion of neoplasms, inflammatory or purulent processes in the abdominal organs, the specialist will prescribe an abdominal CT scan with contrast. X-ray contrast, most often iodine-based preparations, moves along with the bloodstream to the desired area, increasing the contrast of blood vessels and tissues, maximizing differences in the absorption of x-rays. Thanks to this, it is possible to detect pathologies in the initial stages, as well as accurately determine their shape, size, structure and location.
What can be detected with an abdominal CT scan?
Firstly, this method helps to most accurately identify the source of the disease, determine the volume and boundaries of the pathology, and examine the state of the circulatory and lymphatic systems. Excellent visualization of tissue structure and uniformity. CT helps to see:
- Ulcerative bleeding;
- Polyps;
- Fibroids;
- Adenomas;
- Abscesses, foci of inflammation;
- Tumors of malignant and benign nature;
- Secondary foci of cancer;
- Dropsy;
- Atherosclerosis;
- Lymphadenopathy;
- Lymphadenitis;
- Cholecystitis;
- Tissue necrosis;
- Cysts;
- Congenital structural anomalies;
- Hepatosis;
- Cirrhosis;
- Cholangitis;
- Pancreatitis;
- Gallbladder diseases;
- Aneurysms;
- Parasitic lesions;
- Chronic and acute hepatitis;
- Acute appendicitis.
MRI and CT with and without contrast - what is the difference?
Check the possibility of treatment in this area at the moment
Magnetic resonance and computed tomography are considered the most informative, safe and fast diagnostic methods in modern medicine. With their help, pathologies of various organs and systems are identified, the condition of the body is monitored during the rehabilitation period, and congenital anomalies are found. At CDC-24 you can undergo examinations using new generation tomographs, including MRI and CT with and without contrast
. The difference lies in the need to use medications that are administered intravenously or orally. Enhanced examinations are safe, but require certain preparation and are done exclusively as prescribed by a specialist: cardiologist, neurologist, gastroenterologist, oncologist, traumatologist, etc.
Why is contrast used in MRI?
In most cases, diagnostics using radio waves and magnetic fields is sufficient to detect abnormalities in internal organs, joints, brain structures and the spine. But sometimes there is a need to obtain the most accurate and detailed image, and then the doctor recommends a contrast method. The injected substance influences the properties of water molecules in the area under study, thereby improving visualization and making it possible to find the smallest anomalies due to the amplified signal.
Some people think that the main difference between an MRI with and without contrast is
is that enhanced diagnostics are harmful, but conventional magnetic resonance imaging is not. In fact, both procedures are safe, and the substances used do not affect the body in any way; their purpose is to “illuminate” the picture. They are quickly eliminated from the body and do not cause a hypersensitivity reaction (with rare exceptions). As for adverse reactions, they occur infrequently and disappear within 1-2 hours - as a rule, they are a slight headache, rashes and dizziness.
Depending on the area under study, enhancer substances may differ in composition (with iron oxide, manganese compounds, gadolinium, etc.) and method of use. Most drugs are administered by intravenous injection, but when studying the state of the gastrointestinal tract, oral varieties are used.
Does MRI without contrast show tumors?
It is possible to detect neoplasms without introducing special drugs into the patient’s body. However, in some cases, for example, with a small tumor or its complex location, amplification is required in order to most accurately determine the type and stage of the pathology. The study is also prescribed to determine malignancy and when deciding on surgical intervention.
Indications and contraindications
Enhanced MRI is performed on patients with suspected cancer, aneurysms, pituitary gland pathologies, as well as nerve damage and disorders of the cardiovascular system. Diagnostics allows us to identify necrotic lesions of soft tissues of any location, injuries of the musculo-ligamentous apparatus, diseases of the reproductive organs, lungs, liver, gallbladder and spleen, as well as degenerative changes in the central nervous system.
Indications for the examination include:
- convulsions, migraines, frequent fainting;
- decrease or loss of hearing, vision;
- palpable neoplasms in the neck area;
- arthrosis of joints, hernias, protrusions;
- multiple sclerosis;
- joint pain;
- muscle atrophy, paralysis, paresis of the lower and upper extremities;
- infectious lesions of the brain or spinal cord;
- neoplasms in the chest, pelvic organs and gastrointestinal tract;
- infertility in men and women.
There are no restrictions on the frequency of the procedure - it is prescribed as many times as required for effective treatment of the patient. Before conducting diagnostics at CDC-24, it is mandatory to check for contraindications, which include:
- pregnancy, regardless of trimester;
- individual intolerance to contrast agent;
- chronic heart failure;
- serious diseases of the kidneys and other organs of the urinary system;
- the presence of metal objects and devices in the body;
- fear of closed spaces.
MRI with and without contrast: which is better?
Both methods are effective and safe, and their differences are due to the use of drugs that enhance the signal. Compared to conventional magnetic resonance imaging, enhanced MRI:
- Lasts longer - the patient will have to stay 30-40 minutes longer inside the tomograph.
- Allows you to get more detailed pictures.
- May cause minor allergic reactions.
- Provides additional information about the state of the structures under study.
- Requires large financial costs.
- Assumes compliance with additional training recommendations.
PET CT, CT with and without contrast: what studies show, what are their differences
If we are talking about injuries and diseases of dense structures, then patients are prescribed computed tomography and PET CT, and CT can also be performed with the introduction of a contrast agent. In the first case, the radiologist studies the anatomical features of organs and tissues, using signal-enhancing drugs if necessary, and in the second, he determines deviations in dynamics by examining functional activity. Positron emission tomography is considered the most advanced method and provides more information than CT with contrast. The disadvantages of the examination include its duration (and the patient must remain motionless during the entire diagnosis) and high cost.
Conclusion
To summarize, we can say that the difference between MRI, CT with and without contrast
lies in the quality of visualization. Enhanced examination makes it possible to detect pathologies at the initial stage and is indispensable in differential diagnosis. Most often, the procedure is performed on patients with cardiac, neurological symptoms, as well as malignant and benign neoplasms. When contrast is administered, the examination takes longer and in some cases may be accompanied by side effects.
Indications for CT scan of the abdomen
Computed tomography shows the condition of parenchymal and tubular organs. It is prescribed in preparation for a planned or emergency operation, as a control for the success of surgery, to clarify the effectiveness of drug therapy. In addition, CT is necessary if:
- The patient suffers from chronic or acute pain in the abdominal area;
- Sharp weight loss not related to diets occurs;
- Hyperbilirubinemia is observed, that is, yellow staining of the mucous membranes and skin, which occurs due to the increased content of bilirubin in the blood plasma;
- There are signs of internal bleeding;
- There are symptoms of gastrointestinal dysfunction: flatulence, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation;
- Diseases of the urinary system were diagnosed;
- There is a suspicion of neoplasms of various etiologies;
- The pancreas suffers;
- There was a closed abdominal injury;
- A strangulated abdominal hernia has occurred;
- Interloop abscesses are suspected;
- History of injury or disease of the spleen.
Contraindications to CT
Computed tomography is an x-ray method that carries radiation exposure to a person. It has a number of contraindications:
- Scans are not performed on patients under 14 unless absolutely necessary. X-rays have an adverse effect on a child's body.
- CT scans are not prescribed to pregnant women throughout the entire period of expecting a child. Fetal cells divide at tremendous speed, forming all systems, so any, even small changes at the cellular level can lead to severe congenital pathologies.
- Depending on the model of the tomograph, the camera of the device can withstand a weight of 150-200 kilograms. If a person's weight exceeds these values, the examination cannot be carried out for technical reasons.
- The state of drug and alcohol intoxication, mental illness, accompanied by confusion and lack of control over one’s actions, are an obstacle to examination. Since during the tomography process the patient will have to follow the instructions of the radiologist;
- The characteristic noise produced by the tomograph during operation can provoke panic attacks in people prone to this type of disorder. In this case, it is advisable to first take sedatives or be examined under sedation.
Contraindications to CT with contrast
Contraindications to CT with contrast include:
- presence of a confirmed allergy to iodine;
- acute or chronic renal failure due to the possibility of complications due to the administration of a contrast agent;
- blood creatinine level above 100 µmol/l;
- severe diabetes mellitus (risk of complications from contrast enhancement while the patient is taking medications containing metformin);
- some thyroid diseases.
It is possible to do a computed tomography scan with contrast during breastfeeding. You just need to exclude lactation within 48 hours after the study.
Questions
Is it possible to do a CT scan during pregnancy?
Any form of X-ray diagnostics is contraindicated at any stage of pregnancy. Computed tomography uses well-known x-rays, which have a negative effect on the fetus. Therefore, CT scanning for pregnant women is performed only in exceptional cases when it comes to saving the life of the mother. If there is a threat to the life of a pregnant woman, they will try to carry out a tomography using a low-dose program, covering the tummy as much as possible with a special lead blanket that reflects X-rays. But even these precautions cannot exclude the possibility of the development of abnormalities in the fetus. The likelihood of this threat depends on the stage of pregnancy. The use of computed tomography in the early stages of pregnancy is strictly undesirable, since this may be fatal to the embryo, and the woman will have to terminate the pregnancy. According to the observations of expert radiologists:
- in pregnant patients who were irradiated at 1-2 weeks due to radiation from CT scans, in 98% the fetus died or stopped developing;
- in women irradiated at 2-5 weeks of pregnancy, in 70% of cases there was a miscarriage or frozen pregnancy, and in 20% the fetus had malformations of the liver, heart, and thyroid gland;
- In pregnant women who underwent computed tomography at 6-12 weeks, in 80% of cases the child developed multiple pathologies of organ development.
Is it possible to do a CT scan after x-rays and fluorography?
In case of medical necessity, an X-ray or fluorography examination can be combined with a computed tomography session on the same day. The main thing is to ensure that the total radiation dose does not exceed 15-20 mSv. On average, X-rays provide 0.2 mSv of radiation exposure per scanning session. The level of radiation exposure on MSCT is significantly higher and depends on the scanning area. It can range from 1 mSv to 15 mSv per examination.
Is it possible to do CT scans for children?
Computed tomography is a radiological form of diagnosis. It is not recommended for children under 14 years of age unless absolutely necessary. X-rays have a negative impact on the formation of the central nervous system in a child and increase the chances of cancer in children under 5 years of age. The dose of radiation that a child receives during a tomography session leads to an increase in the number of cells with mutations in the P53 gene, which is responsible for the development of cancer, and increases the chance of developing leukemia and brain cancer by 35%. Therefore, a child’s CT scan is performed only as prescribed by a doctor and in the presence of compelling medical reasons, when the benefits of the examination outweigh the health risks associated with it. Doctors strive, whenever possible, to replace computer scans with safer forms of diagnostics - ultrasound or MRI.
Is it possible to do a CT scan at a temperature?
Temperature is not a contraindication to native tomography, but it may be a limitation for contrast-enhanced CT. Changes in a person's temperature may indicate an inflammatory process in the body, and in such a state, the introduction of iodine-containing contrast can provoke a crisis.
Can I do a CT scan with dental implants and braces?
The short answer is yes. X-rays do not in any way affect dental implants, crowns and braces, no matter what material they are made of. Dental implants also cannot affect the quality of the tomograms obtained. They do not produce any artifacts on CT images.
Is it possible to do CT with titanium and metal plates?
Metal in the body is not a contraindication to CT, regardless of the alloy composition of your metal inclusion. Therefore, computed tomography can be used as an alternative form of diagnosis when, due to the metal in the patient’s body, magnetic resonance imaging cannot be performed on the patient.
Is it possible to do a CT scan with a pacemaker?
If you have a pacemaker of any model, you can do a CT scan. CT scans use X-rays and they do not have any negative effect on any artificial pacemakers. Therefore, CT is used as an alternative to MRI if the patient has a pacemaker, neurostimulator, or insulin pump, which can fail in the magnetic field of the magnetic resonance imaging scanner. But it is safe for such patients to undergo examination with a CT scanner.
Is it possible to do a CT scan after chemotherapy?
A CT scan may be ordered after a series of chemotherapy treatments to assess the effectiveness of the treatment. The decision about when control images need to be taken is made by the attending physician. Chemicals used in oncological treatment are not a contraindication to CT. The only thing you should always remember is that X-rays tend to accumulate in the human body, so the recommended interval between CT examinations for an oncological diagnosis should be 2-3 months. For diagnostics, you should also choose spiral low-dose units.
In what cases is an abdominal CT scan with contrast prescribed?
This scanning method allows specialists to study the smallest structures or identify oncology in the early stages. An abdominal CT scan with contrast helps determine:
- Degeneration of atypical cells;
- Presence and localization of secondary cancer foci;
- Vasoconstriction and other vascular pathologies;
- Ureteral obstruction;
- To clarify the success of anticancer therapy.
Tomography allows you to examine the aorta in detail.
Contraindications
An absolute contraindication to MSCT is pregnancy. In other cases, the doctor considers the conclusion about the admissibility of examination using X-ray irradiation in each situation individually. Relative limitations to computed tomography include:
- the patient’s body weight is more than 200 kg, which is associated with the maximum load on the tomograph table;
- age up to 5 years due to radiation exposure;
- mental illness and other conditions that do not allow the patient to lie still during a CT scan.
Computed tomography of the abdominal cavity with contrast may be complicated by:
- patients with renal failure;
- patients with diabetes mellitus.
In what cases is it not possible to have a CT scan of the abdominal cavity with contrast?
The introduction of radiocontrast also has a number of contraindications:
- Diabetes mellitus with a blood glucose level of more than 6.5 mmol on an empty stomach, pathologies of the thyroid gland and other serious autoimmune diseases;
- It is not advisable to use contrast in patients with renal or hepatic impairment. Their ability to eliminate drugs is reduced, and the use of the substance can lead to intoxication. To exclude these pathologies, before the procedure you need to take a biochemical blood test to determine the level of creatinine;
- Scanning is not carried out for people with cardiovascular diseases;
- A malignant brain tumor, placetoma, is also an obstacle to tomography.
- People suffering from allergies of any form need to warn the radiologist about this. In some cases, iodine-containing substances can cause allergic reactions. If this happens, the scan must be stopped;
- CT scanning with X-ray contrast is not done for nursing mothers, since the iodine-containing drug easily passes into breast milk. Therefore, if the procedure is necessary for emergency reasons, lactation is interrupted for a time, it is necessary to completely remove the dye from the body. To preserve milk during this period, you will have to express. There is no need to introduce formula to your baby if you prepare a supply of breast milk a few days before the scan. It is stored in the refrigerator in sterile containers.
In some cases, despite the presence of contraindications to computed tomography, the need for it exceeds the possible harm from the procedure. Then a council of doctors gathers to prescribe a CT scan of the abdominal cavity. This is most relevant for examination of the abdominal aorta, which is not done without the introduction of radiocontrast, since without its use the procedure is not sensitive enough.
Contraindications to the procedure with contrast
To avoid complications, abdominal CT is not performed in patients with:
- allergy to iodine;
- severe renal failure with elevated creatinine levels in the blood (creatinine testing is included in the services of our diagnostic center);
- hyperthyroidism and other thyroid diseases.
Children over 12 years of age have their internal organs checked with contrast only according to indications with a doctor’s referral.
For women breastfeeding, the procedure is not prohibited. Radiation exposure does not affect milk, but the dye partially penetrates into it. Therefore, you will have to give up at least two consecutive feedings. Before the study, the woman must express and store the milk. After CT or MSCT with contrast, you must wait until the drug leaves the body and after two pumpings, feed the baby as usual.
Any questions you may have and the price for contrast examinations can be clarified with the administrator.
How to prepare for an abdominal CT scan
Tomography of the peritoneal organs is one of the few types of tests that require careful preparation from patients. It is the preliminary actions that will determine how well all organs will be visualized in the images.
Additional examinations will be required before the procedure. The specialist may prescribe an ultrasound of the peritoneum, x-ray or colonoscopy. You also need to consult with an allergist and anesthesiologist about possible risks from the introduction of X-ray contrast. If the urinary system is to be examined, laboratory tests must be done for the presence of creatine, urea, ALT and AST enzymes.
Most of all, diagnostic information reduces intestinal bloating and fullness. Therefore, it is necessary to normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract in advance. To do this, three to five days before the tomography you need to switch to a gentle diet. Need to exclude:
- Heavy and fatty foods;
- Products that cause increased gas formation;
- Cabbage;
- Legumes;
- Beetroot;
- Celery;
- Dried and fresh fruits;
- Dairy products;
- Cereal dishes;
- Fresh baked goods;
- Confectionery products;
- Kvass;
- Carbonated drinks;
- Strong coffee and tea;
- Alcohol.
It is allowed to eat lean meat and steamed fish, omelettes, light non-rich broths, boiled chicken, rolled oats with water.
The scan is done on an empty stomach, so they try to schedule a CT scan of the abdominal cavity in the first half of the day. 18 hours before, you can drink enterosorbents: activated carbon, smecta. The day before, they give a cleansing enema, take a mild laxative, or administer a suppository with glycerin.
A few hours before the scan, you should stop drinking drinks so as not to increase intestinal motility.
Administration of a contrast agent without appropriate preparation may cause vomiting and nausea. If the patient had a CT scan of the abdominal cavity with contrast, then after it it is advisable to drink a liter of clean drinking water. This will help remove the drug from the body faster.
Computed tomography of OBP without contrast
Computed tomography without contrast is used much more often than computed tomography with contrast. Why? SCT ABP without intravenous contrast is much cheaper and the study itself is much faster and easier, in one phase and without the manipulation of a nurse or an injection syringe. For this study, the patient only needs to undergo special training and, before the study itself, drink a portion of a contrast agent diluted in water, so that the stomach and intestines do not interfere with “seeing” other abdominal organs, and the condition of the gastrointestinal tract can also be assessed separately.
When performing SCT without intravenous contrast, you can assess the general condition of the abdominal cavity, determine whether there are developmental anomalies, understand the general condition of the organs, differentiate the presence of stones in the kidneys, gall bladder, ureters, bile ducts, identify those organs that do not correspond to the norm: enlarged or pathologically reduced organs with altered tissue density (for example, this is how fatty hepatosis can be diagnosed - a pre-cirrhotic condition of the liver). With a conventional (native/non-contrast) scan of the aneurysm, you can evaluate the number and density of calcifications in large arteries (abdominal aorta, renal and iliac arteries, splenic and hepatic arteries, others), exclude or suspect the presence of an aneurysm, visualize calcifications in the pancreas, which will immediately indicate for pathology, as well as identify pathological and atypical calcifications in organs, which can confidently indicate the presence of a tumor with malignant features.
It can also be used if there are contraindications to the intravenous administration of iodine-containing X-ray contrast agents. Sometimes this allows you to obtain important diagnostic information, which is especially important if there is a risk of conditions that threaten the patient’s life. it is often not possible to identify the cause of the disease and assess the condition of vital organs (liver, kidneys, pancreas, adrenal glands) .
How is an abdominal CT scan performed?
The examination lasts from 15 minutes to an hour.
- The patient must undress to the waist, remove all jewelry, glasses and other wardrobe items containing metal.
- You will need to turn off your cell phone and other mobile devices.
- During CT scanning of the abdominal cavity with contrast, the dye is introduced in different ways depending on the area of examination. If it is necessary to check the liver, kidneys or pancreas, a person takes a solution of an iodine-containing substance orally in small sips. To clarify the condition of hollow organs and vessels, intravenous administration of the drug is used. To identify diseases of the large intestine, the dye is administered rectally. In some cases, the diagnostician may suggest a bolus administration of radiocontrast, that is, it will enter the body through an automatic drip injector.
- After this, the person lies down on the retractable table of the device.
- He is placed in the tomograph tunnel and the scan begins.
- At the end of the scan, the diagnostician prepares a transcript of the results.
MRI or CT scan of the abdominal cavity - which is better?
Diagnostics of the abdominal organs in St. Petersburg clinics can be carried out using the following methods:
- Ultrasound (ultrasound waves) of the abdominal cavity;
- MRI of the abdominal cavity with and without contrast;
- CT scan of the abdominal organs with and without contrast.
Most often, ultrasound is used for the initial examination of organs located in the peritoneum and retroperitoneal space. The doctor usually prescribes an MRI or CT scan of the abdominal cavity as an expert diagnostic method when examination or ultrasound data show alarming symptoms. In terms of information value and price, MRI and CT of the abdominal cavity are comparable to each other, and which one is better is usually determined by the doctor based on the purpose of the scan. The CT method is based on the action of x-rays. MRI equipment works by applying a magnetic field and radiofrequency pulses to the organs being examined. Based on the peculiarities of the physics of image acquisition, MRI of the abdominal organs better visualizes soft tissues and organs with a high water content - liver, spleen, pancreas. Computed tomography clearly shows hollow organs, for example, the gallbladder, stomach, and intestines.
Computed tomography of the abdominal cavity is considered the most informative method of urgent diagnosis, which allows you to obtain a comprehensive picture of the condition of the abdominal organs and retroperitoneal space in a matter of minutes. It is a priority form of diagnosis for traumatic injuries and emergencies. Limitations and contraindications for each type of examination depend on the method of exposure. Computed tomography is associated with radiation exposure to the body. On average, it is 7-9 mSv with computed tomography of the abdominal cavity. The radiation dose from MSCT poses a potential danger to pregnant women and the fetus, as well as infants, so this study is not performed on pregnant women, nursing mothers and young children. Magnetic resonance imaging does not carry any burden and is comparable in safety to ultrasound. However, the powerful magnetic field of the CT scanner can be a health hazard for patients with electronic pacemakers, such as pacemakers.
Author: Telegina Natalya Dmitrievna
Specialization: Therapist
Make an appointment: MC RIORIT
Decoding
Based on the images obtained, the radiologist enters into the examination protocol information about the size, shape, structure and relative position of organs, notes congenital anomalies and detected disorders. Enters his observations into a research protocol, which, together with the images, is transferred to the attending physician or given to the patient. Many diagnostic clinics can record the results on a computer disk, flash card, or send them by email. It is worth considering that the final diagnosis is made by a doctor of the appropriate profile based on the results obtained.
Alternative examination methods
An X-ray or MRI can replace a CT scan. The advantage of CT scanning of the abdominal cavity over them is the ability to check the structure of hollow organs, including the intestines and stomach. In addition, magnetic resonance imaging, unlike CT, is not indicated for patients using pacemakers, insulin pumps and metal implants. X-ray is less informative compared to CT scan of the abdominal cavity.
Another examination option is ultrasound. Due to its high safety and almost complete absence of contraindications, ultrasound diagnostics is prescribed quite often. Especially if primary diagnosis is required. CT is used if ultrasound turns out to be uninformative.
Examination safety
Computed tomography is a safe method that does not cause discomfort to the patient, but the recommendations of the radiologist must be followed. Scanning does not harm your health. Radiation exposure with CT is present, but it is minimal. And yet, after the tomography, a recovery period is necessary. In this case, the procedure will not have delayed consequences. Experts recommend, if possible, not to resort to this type of hardware diagnostics more often than once every six months. If it needs to be carried out for emergency reasons, and it is impossible to replace it with alternative methods, then you should not neglect such protective measures as a lead apron, taking absorbents and observing an increased drinking regime.
It is worth considering that when performing an abdominal CT scan with contrast, the danger is not so much the procedure itself as a possible reaction to the injected drug. Side effects on X-ray contrast may include:
- Joint spasms;
- Increase in temperature to subfebrile levels;
- Cephalgia;
- Damage to the kidneys and urinary canals by toxins;
- Allergic reactions, the signs of which are: acute burning in the stomach, swelling of the mucous membrane, difficulty breathing, itching, rash.
What to take with you to an abdominal CT scan
Diagnostic clinics licensed to perform computed tomography are asked to bring with them:
- Identity document: passport or birth certificate for minors;
- Medical history, results of laboratory tests and previous examinations;
- Referral from a specialist.
We must remember that timely diagnosis can not only preserve health and improve the quality of life, but also avoid death. After all, the effectiveness of therapy depends on the accuracy of the diagnosis.
Price for CT scan of the abdomen in Moscow
The cost of the examination averages 3000-4000 rubles. It is influenced by many factors: the model of the tomograph, the qualifications of the radiologist, the distance of the clinic from the metro. It is worth considering that for an abdominal CT scan with contrast, the price will be 20-30 percent higher. To save your money, you need to spend some free time and study the cost of the procedure in various medical centers, as well as find out about the promotions and discounts taking place there. This can be done easily and quickly using the service. And also on the website you can immediately sign up for any diagnostic center at a suitable time.
How is an abdominal CT scan performed?
The abdominal computed tomography procedure is performed in many public and private medical centers in St. Petersburg. Its distinctive features:
- convenience for the person being examined;
- high degree of information content;
- quick results.
Typically, a CT scan is performed with a doctor’s referral, which specifies the protocol and focus of the examination. The procedure is performed by a radiologist and a radiation technologist (laboratory assistant). The patient is placed on a special table, which during the examination will move and slide into the tomograph ring. While the X-ray tube is operating, the person must lie still and follow the doctor’s commands regarding inhalation, exhalation or holding his breath. Medical staff watches the process through the window and on the monitor. The entire procedure takes an average of 5-7 minutes, a little more time (20-30 minutes) will be needed when performing a CT scan of the abdominal cavity with contrast. After completing the study, it will take 30-40 minutes to process the images and record the received information on electronic media (disk or flash drive). The prepared package of documents should be submitted to your attending physician for diagnosis and treatment. If a CT scan with contrast was performed, after the examination it is necessary to drink large amounts of still water to quickly remove the contrast agent from the body.