The article was prepared by a specialist for informational purposes only. We urge you not to self-medicate. When the first symptoms appear, consult a doctor.
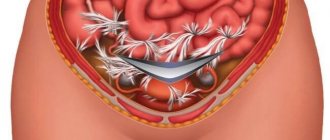
Intestinal adhesions are formations of connective tissue (cords) between the abdominal organs and intestinal loops, leading to fusion or gluing of the serous membranes of the organs to each other. As a result, they merge with each other, which entails a wide variety of functional disorders. The cords themselves consist of the same tissue as the outer wall of the intestine. Most often, this pathological process is caused by a previous surgical intervention.
According to statistics, if a primary laparotomy intervention was performed on the intestine, then adhesions will form in 14% of cases, and if this is the third operation, then they occur in 96% of cases.
What are adhesions in gynecology
Adhesive disease of the pelvic organs in women is a complication after which fibrinous connective tissue grows between the pelvic and abdominal organs.
In this way, the body tries to protect the source of inflammation - due to excess tissue, the fallopian tubes, uterus, ovary and intestinal loops stick together, pull tightly together, which disrupts their functions. Adhesive processes can be of several types, depending on the “neglect”:
- Formation of single thin adhesions (synechia).
- Synechiae become denser, covering up to 50% of the surface of the ovary.
- The adhesions are dense and numerous, changing the position of organs or causing their deformation.
Adhesions cause pain and disturbances in the functioning of the pelvic organs. They appear after gynecological diseases or operations and can lead to serious complications: ectopic pregnancy, infertility, frequent inflammation and more.
To prevent the occurrence of adhesions, avoid complications and prescribe competent treatment, make an appointment with the doctors of the Doctor A clinic. We employ gynecologists of the first and highest qualification categories
Surgical treatment of adhesions
Watch a video of operations for abdominal adhesions performed by Professor K.V. Puchkov. You can visit the website “Video of operations of the best surgeons in the world.”
Video from the operating room. Laparoscopic cystadnexectomy for severe adhesions
In most cases, adhesions do not cause symptoms or discomfort, and such situations do not require treatment. Surgical intervention to separate adhesions is used in cases of pain, the threat of intestinal obstruction, and infertility in women.
The operation to separate adhesions is performed using laparoscopy. It is precisely these minimally invasive surgery techniques that allow for accurate and gentle dissection of adhesions.
During the operation, modern anti-adhesive barriers are used, which minimize the loss of fibrin (a protein that promotes clotting) in the area of intervention and several times reduce the likelihood of relapse of adhesive disease.
If open (laparotomy) surgery cannot be avoided, we use special anti-adhesion membranes that are located between the organs and prevent adhesion and adhesions. These materials spontaneously dissolve in the abdominal cavity without leaving a trace within 7–10 days.
The operation usually takes about one hour. After surgery, the patient spends on average 2–3 days in the clinic. It is advisable to spend another three days in Moscow (relatives, a hotel are nearby). We perform a follow-up examination and make recommendations for further treatment. Then you can safely return home.
An operation to separate abdominal adhesions must be performed by a surgeon with extensive experience in such operations, both open and laparoscopic methods. I have been performing similar operations since 1993 and currently have experience in more than 900 similar interventions for various forms of adhesive disease of the abdominal and pelvic organs.
What causes adhesions to form in the pelvis
Inflammation of the pelvic organs. The disease is diagnosed in women who have suffered acute inflammation or suffer from chronic:
- colpitis;
- endometritis;
- andexite;
- parametritis and other diseases.
Operations. Adhesive disease appears in 16% of those operated for the first time and in 96% of women after the third operation. The percentage is high for laparotomy operations:
- appendectomy;
- C-section;
- removal of appendages;
- hysterectomy;
- supravaginal amputation.
Pelvic hemorrhages. The trigger is ovarian apoplexy, bleeding due to a ruptured tube during an ectopic pregnancy.
Endometriosis. The formation of fibrinous ties is provoked by endometrioid growths, which spread to the organs and peritoneum of the pelvis.
Pelvic injuries. Open and closed damage after accidents, falls from a height received at work are one of the reasons for the appearance of adhesions.
Predisposing factors. The occurrence and development of the disease is influenced by:
- invasive gynecological interventions;
- promiscuous sex life;
- late visit to the clinic.
How osteopathy affects adhesions
An osteopathic doctor is able to feel with his hands where the adhesions are located and where they lead, where they are attached and what they are pinching. He is also able to loosen their tension in a few sessions, and can restore, balance and balance damaged organs, and therefore restore their function to the fullest possible extent.
An osteopathic doctor is also able to interrupt the chains of damage and pain in parts of the body that seem to be unrelated to the operated area. After all, our body is an integral system where everything is interconnected. The osteopath acts on the adhesions directly, without violating the integrity of the body tissues, and therefore without an additional factor stimulating the formation of connective tissue. By restoring and harmonizing the function of the suffering organ, the body releases energy to initiate complete recovery in possible individual conditions for the entire organism.
Any surgical intervention, no matter how minimally gentle it may be, leaves behind a lot of negative changes, injuries and stress, which the body is forced to fight alone. What the body will do to heal itself, what it will sacrifice, how it will limit itself is always individual. But within the framework of self-preservation, this is always expressed in loss of function to one degree or another, and therefore subsequent suffering of the entire organism with loss of compensation and the expenditure of much greater effort on normal functioning throughout life.
Therefore, if you have had surgical interventions on the abdominal organs in your life, consult an osteopathic doctor. It does not matter whether the operation was conventional or performed using a gentle laparoscopic method. Any discomfort has a reason, which means there is an opportunity to solve it.
An osteopathic doctor can use pulse diagnostics to determine the significance of adhesions or scars on the body. This means that if, when pressing on a postoperative scar, the properties of your pulse change, then this zone is important and significant for the whole organism, and this adhesion or scar must be worked with.
Adhesions and scars have the following significance and prevalence of influence:
- local (the effect is limited to the area where the scar or adhesions are located);
- regional (the effect extends to the entire thoracic or abdominal region where the commissure is located);
- global (affects the entire body, even to the point of disturbing its position in space).
How long does osteopathic treatment last?
If the patient has undergone surgery, then the osteopathic doctor will tactically act as follows. 10 days after the operation, when the stitches are removed, the doctor will work with the scar itself layer by layer, work with the tissues directly around the scar itself and restore that independent mobility of the organ, which does not depend on the movement of the diaphragm. This period of work ranges from 10 days to 3 months after the operation.
If the duration after surgery is 3 or more months, then the doctor will pay attention to all surrounding organs and tissues in the operation area, influence the mobility of all internal organs in general and directly to the localization of the adhesions themselves.
The information was prepared by the leading specialist of the osteopathy and family medicine clinic Osteo Poly Clinic Gulyants Maria Alexandrovna, osteopathic doctor, chiropractor, endoscopist surgeon.
Adhesions in gynecology: symptoms
The adhesive process can be both acute and chronic, or have a periodic nature (with periodic exacerbation of symptoms). Often, women do not notice any symptoms of adhesions in the pelvis, and the disease is discovered only when examining the possible causes of infertility.
Signs of adhesions in the pelvic cavity:
- Painful sensations in the lower abdomen, lower back, above the pubis or in the sacral area;
- Discomfort during physical activity, before menstruation, after stressful situations;
- Pain during sexual intercourse or urination;
- Intestinal disorders: diarrhea, constipation, flatulence;
- Periodic attacks of nausea and vomiting.
Symptoms may worsen when consuming foods that increase gas formation.
Symptoms of intestinal adhesions
Symptoms of intestinal adhesions depend on when a person experiences intestinal obstruction. It can develop either in the early period after surgery or injury, or a little later - several months or even years after exposure to the provoking factor.
Symptoms of early adhesive bowel disease
- Symptoms indicating the formation of adhesions in the first days after an injury or surgery are often veiled by the intervention itself. A person complains of periodically increasing pain in the abdominal area, which is present to one degree or another on an ongoing basis. As the pathological process progresses, the pain becomes cramping.
- Vomiting occurs, which becomes very frequent and profuse.
- If the patient has a probe inserted, the amount of fluid discharged will increase.
- Abdominal bloating is observed, but it is not uniform, as usual, but asymmetrical. This is explained by the fact that certain parts of the intestine become overfilled with gases.
- On palpation the patient complains of pain. Even stroking the abdominal wall causes increased intestinal perilstatics and discomfort.
- There is no chair. Conducted enemas allow for the removal of only small volumes of feces.
A simple form of adhesive obstruction develops against the background of improvement after surgery. As a rule, this happens 5-14 days after its completion. Its symptoms are clear and do not raise diagnostic questions. Sudden sharp pain appears, vomiting of gastric contents with bile begins. The abdomen is distended unevenly, gases and stool at the initial stage of formation of adhesions can pass on their own.
It is typical that after a few hours the patient’s condition will worsen, vomiting will intensify, signs of dehydration will appear, the tongue will become dry and covered with a white coating. The gases stop passing and the stool disappears.
If early adhesive intestinal obstruction develops against the background of an inflammatory process, then in addition to all the symptoms, body temperature rises. An inflammatory infiltrate, which is represented by a compacted area, can be palpated in the intestine.
Separately, it is worth noting early delayed adhesive intestinal disease, which manifests itself 21-30 days after exposure to the provoking factor. Symptoms develop gradually, with a tendency to intensify. Often this occurs even against the background of a successfully completed operation after discharge home.
Symptoms of late adhesive intestinal obstruction
- Symptoms develop months or years after the intervention. It is possible that the acute process will be preceded by pain in the lower abdomen.
- Suddenly, a person experiences severe cramping pain. As the process progresses, they appear more often and become stronger.
- Vomiting begins. There is no stool or gas production.
- The abdomen takes on an asymmetrical shape, this is especially noticeable in the place where there are adhesions. The intestinal loop becomes full of gases.
- The patient's condition will worsen as dehydration and intoxication increase. Subsequently, intestinal paresis will occur if emergency assistance is not provided.
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnosis of adhesions in the pelvis is carried out using various studies:
- Diagnostic laparoscopy. This method can most accurately see adhesions and assess the severity of the process. Diagnosis is carried out under local (or general) anesthesia; a small incision is made through which a camera is inserted.
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- Hysterosalpingography (performed using X-rays or ultrasound and contrast agents);
- MRI of the pelvic organs.
The necessary examination (or set of examinations) will be prescribed to you by your attending physician.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of intestinal adhesions is based on examining the patient and identifying characteristic symptoms. The doctor may suspect the formation of cords when collecting anamnesis. The indicator is previous surgical interventions on the intestines and the presence of infectious pathology.
To clarify the diagnosis, the following research methods are used:
- Plain radiography of the abdominal cavity. Thanks to this method, it is possible to visualize the presence of inflammatory exudate, the presence of a large amount of gases in the intestines, and its bloating. Often, radiography is performed with the introduction of a specialized dye. This provides additional information about its cross-country ability. This procedure is called irrigography; in this case, barium is used as a contrast agent.
- Electrogastroenterography allows you to measure electrical impulses that come from parts of the intestine during peristalsis.
- Ultrasound and MRI allow you to accurately determine the location of the adhesions, as well as determine their number.
- The most informative method for detecting adhesions is laparoscopic examination. However, it is a small operation that requires making incisions in the abdomen and inserting instruments equipped with a camera into its cavity. The undoubted advantage of this procedure is that if the doctor sees a problem, he can fix it immediately. That is, intestinal adhesions can be removed during diagnosis.
As for laboratory tests, you will need to donate blood to rule out the presence of inflammation. It is important to carry out a differential diagnosis with other types of acute intestinal obstruction, which can be caused by intestinal strictures or large tumors.
How to treat adhesions in the pelvis
What to do if adhesions are found in the pelvis? Depending on the severity of the adhesive process, the doctor will select the appropriate treatment for you.
To treat single thin adhesions in the pelvis in women, drug therapy is used. What is usually prescribed:
- Antibiotics and antimicrobial agents (to relieve inflammation);
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (as a pain reliever);
- Fibrinolytic agents (for resorption of adhesions);
- Vitamins and immune system regulators (to restore immune balance);
- Hormonal drugs (in cases where adhesions are caused by endometriosis).
Additionally, physiotherapy, balneotherapy and mud therapy may be prescribed as auxiliary measures.
In more severe forms of adhesive disease, a surgical method is used to treat adhesions in the pelvis, i.e. their dissection. The most gentle surgical procedure is manipulative laparoscopy. To prevent re-formation of adhesions, hyaluronic acid is injected into the surgical area.
Proper nutrition and diet
If the diagnosis of “adhesive disease” is confirmed, the patient should seriously think about healthy nutrition. Basic rules of diet:
- Frequent meals in small portions
. It is better to eat about 5 times a day, eating simple dishes with a minimum of spices in them. Fasting with such a diagnosis is unacceptable. - After eating, you should not take a horizontal position
. Walking will help food digest much faster. - It is not recommended to eat before going to bed
. At night, all body systems should rest. - It is worth including a sufficient amount of liquid in the daily menu
. This will help not only the digestion process, but also improve the condition of the body as a whole. - Constipation should not be allowed
. They provoke an exacerbation of the disease.
| Healthy | Harmful |
| dishes made from boiled or steamed fish | any types of canned food |
| lean (low-fat) decoctions and broths | mushroom, as well as fatty meat and fish broths |
| yoghurts, kefir, cottage cheese | citrus |
| boiled poultry meat | smoked products |
| butter in small doses. | strong tea and coffee. |
Nutrition and diet are the basis of conservative treatment of intestinal adhesions.
Is it possible to get pregnant during adhesions?
Adhesions disrupt the proper functionality of the reproductive organs, which greatly reduces the chance of getting pregnant. There is a chance of pregnancy and its successful gestation, especially in cases where the adhesive process affected only one tube. But the likelihood of conception decreases, and the risk of ectopic pregnancy and miscarriage also increases.
In this case, IVF may help. The fallopian tubes are not involved in such fertilization, and a 3-5-day-old embryo is immediately implanted into the uterine cavity.
Is it possible to do a colonoscopy if there are intestinal adhesions?
Colonoscopy for intestinal adhesions can be done, since their presence is not an absolute contraindication to the procedure. However, some experts recommend the study be performed under intravenous anesthesia. This is explained by the fact that adhesions can cause severe pain during the procedure.
If a patient requires a colonoscopy, but there is a suspicion of adhesive disease, then it is better to do an irrigoscopy first. A study using a colonoscope should be carried out only in case of low information content of irrigoscopy.
Prevention of adhesions
For the prevention and treatment of adhesions, enzyme preparations based on hyaluronidase are used. Perhaps the most popular drug for the treatment of adhesions in gynecology is Longidaza suppositories.
Prevention is mostly aimed at preventing relapses of the disease or before an upcoming operation (since adhesions often appear after them).
Remember that the best prevention is regular visits to the doctor and timely diagnosis. Don’t delay until later and sign up for a pelvic ultrasound or a consultation with a gynecologist.
If you feel acute pain in the abdominal cavity or pelvic organs, do not delay visiting a doctor - prevent the development of the disease. Doctors at the Doctor A clinic will conduct an expert examination and prescribe competent treatment. Call or make an appointment online.
FAQ
Abdominal adhesions - symptoms
At the initial stage, the disease is asymptomatic, but over time, nausea, problems with the passage of gases appear, and vomiting often occurs. Over time, pain appears: either as a result of sudden movement, lifting weights and even sexual intercourse, or having a permanent nature. The pain disappears either under the influence of painkillers or on its own. In severe situations, intestinal obstruction may develop, requiring emergency surgical care.
Diagnostics
Due to the lack of specific symptoms, adhesions in the abdominal cavity can only be detected using modern diagnostic methods. In our clinic you can undergo an ultrasound examination, MRI or CT scan - the most effective non-invasive examination methods today. One of the informative diagnostic methods is laparoscopy - a minimally invasive micro-surgery during which internal organs are examined using video endoscopic equipment inserted into the abdominal cavity. In addition to diagnostic manipulations, adhesions can also be separated during the operation.
Is conservative therapy possible for adhesions?
In case of moderately severe pain syndrome, but in the absence of intestinal obstruction, conservative therapy can be used: anti-inflammatory and antispasmodic drugs, diet, limitation of physical activity, etc. If drug treatment is ineffective, surgery is indicated, since the presence of adhesions for a long time is accompanied by the involvement of internal organs, which is fraught with serious complications.
Can adhesions cause infertility?
The presence of adhesions can cause deformation of the fallopian tubes, a decrease in their lumen or closure, impaired mobility of the fibrils and other abnormalities, which will make conception impossible. Also, one of the complications of adhesive disease is the development of ectopic pregnancy, when a fertilized egg attaches outside the uterine cavity. If fertilization does occur, there is a risk of miscarriage.
Prevention of adhesions formation
Since the cause of adhesions is most often a violation of the surgical technique, resulting in inflammatory and destructive processes leading to the appearance of adhesions, minimally invasive interventions using anti-adhesive barriers are most justified. In our Center, all types of highly effective products are used to prevent adhesive disease: gels, liquids, aerosols, self-absorbing membranes.
Sign up for a consultation: +7 (495) 782-50-10
Folk remedies and adhesive disease
Folk remedies in the presence of cage elements are also quite relevant. The following plants are considered beneficial:
- Linen
. Place 3 tablespoons of flax seeds in a canvas bag. The bag is dipped in boiling water, wrung out, cooled and applied to the problem area. This recipe is suitable for eliminating pain from adhesive disease. - St. John's wort
. Dried St. John's wort flowers in the amount of 1 teaspoon are poured with a glass of boiling water and infused for a quarter of an hour. Next, the liquid is filtered, divided into three parts and taken throughout the day. This decoction must be taken for a month. The remedy will alleviate the general condition of the body susceptible to adhesive disease. - Rose hip
. Rose hips (2 tablespoons) are mixed with lingonberries (1 tablespoon) and dried nettle leaves (2 tablespoons). Take 1 teaspoon of the resulting mixture and pour a glass of boiling water over it, leave for 3 hours, strain and take 30 minutes before meals. You need to use the product for 45 days. The components of the decoction are consumed to prevent adhesive disease and its exacerbations.
Before using any folk remedy, you should consult your doctor.
The prognosis for the treatment of intestinal adhesive disease is positive. Taking good care of your health, systematically visiting a doctor and carefully selecting food products will help avoid the formation of adhesions or reduce their number.
Gymnastics in the presence of adhesions
Excessive physical activity during adhesive disease is unacceptable. However, simple gymnastics will benefit the patient.
If exercise causes discomfort and pain in the intestinal area, the exercise should be stopped immediately.
A special complex of exercise therapy is prescribed by a doctor. Examples of some exercises:
- “scissors” with legs in a supine position (about 20 times);
- lifting straightened legs while lying on their side, fixing them at one point, lowering them to the floor (4-6 times);
- bending and arching the back in the lumbar region while standing on all fours and so on.
[media=
https://youtu.be/fM7GVy2VjIA
]
Treatment of adhesive disease of the abdominal cavity
When a sick person has gone through all types of examinations, but still has not found out the exact diagnosis, he still has a way out - diagnostic laparoscopy. Just a couple of punctures are made in the abdominal wall and the surgeon examines the entire abdominal cavity, all its organs and formations.
If the presence of an adhesive process is confirmed, then the detected adhesions are immediately intersected. Sometimes the intersection of just one or several adhesions is enough to stop the patient’s many months, and sometimes many years of suffering.
Our clinic is equipped with the most modern laparoscopic equipment. Our surgeons have extensive and many years of experience performing such operations.
Hospitalization in a hospital will take you only 2 days in comfortable conditions with an individual observation post.
Contraindications to the use of folk remedies
When using a particular drug, it is necessary to take into account the composition of its ingredients and some of its properties. An incorrect dosage of medication may not only fail to cure the disease, but may also worsen the symptoms.
For clarity, the main contraindications of folk remedies used in the treatment of adhesive disease are presented in table form:
| Name of medicinal plant | Possible contraindications |
| nettle | thrombosis, thrombophlebitis, varicose veins, pregnancy |
| sweet clover | poor blood clotting, liver disease, pregnancy |
| yarrow | tendency to low blood pressure, increased number of platelets in the blood |
| coltsfoot | pregnancy, lactation period, liver cirrhosis, children under 12 years of age |
| bergenia | increased blood clotting, tendency to hypotension, tachycardia |
| Morinda | pregnancy |
| St. John's wort | photodermatitis, pregnancy, lactation, children under 12 years of age |
| marin root | gastritis, tendency to low blood pressure, pregnancy, lactation, children under 12 years of age |
| milk thistle | epilepsy, asthma, diseases of the cardiovascular system, cholelithiasis, cholecystitis, pancreatitis, children under 12 years of age |
In addition, when using any product, individual intolerance to its constituent components may occur. When taking medications based on folk remedies, you should carefully monitor the body’s reactions and strictly follow the recipe and dosage.
Causes of abdominal adhesive disease
Adhesions form due to various reasons. It can be:
- Inflammatory diseases of the abdominal organs (cholecystitis, adnexitis, etc.).
- Systemic diseases (Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis).
- Abdominal injuries.
Often the cause of adhesions is previous surgical operations. And here it is not always the surgeon’s fault (for example, the abdominal cavity was not drained of blood well enough).
The fact is that during operations, a wound surface most often forms on organs (the place of suturing of the intestines, stomach, appendix stump, etc.). Any wound heals by going through the stage of inflammation. Inflammation is the cause of the formation of adhesions.