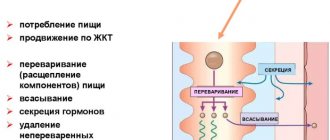
Abdominal pain can occur for a number of reasons. Dividing the abdomen into quadrants, or nine areas, can help preliminarily determine the cause of pain or discomfort. How to do this can be found in our guide below.
Abdominal pain is caused by a variety of gastrointestinal disorders, from gas accumulation (flatulence) and constipation to gallstones and duct stones or peritonitis. Understanding which area of the patient's abdomen is hurting can be extremely helpful during a remote consultation with a gastroenterologist. Knowing exactly where the stomach hurts, the doctor will be able to quickly determine the cause of the disease and prescribe the correct treatment.
Right upper quadrant
Organs in this quarter: liver, gallbladder, duodenum, head of the pancreas (the part of the pancreas firmly attached to the duodenum), part of the colon.
Pain in the right upper quadrant can be caused by hepatitis (inflammation of the liver), cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder), inflammation of the bile ducts (cholangitis), inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis), or peptic ulcers of the stomach and duodenum.
Regardless of the cause of the disease, liver inflammation is called hepatitis. Many cases of hepatitis are viral, but the disease can also be caused by alcohol, drugs and other toxic substances.
Liver inflammation can be acute or chronic. With chronic hepatitis, a person usually does not experience any symptoms. During acute hepatitis, abdominal pain, nausea, jaundice (yellowing of the skin, mucous membranes, eyes) may occur, and in more severe cases, liver problems may occur.
The most common types of hepatitis are:
- The hepatitis A virus causes acute inflammation of the liver, which in many cases resolves spontaneously without residual effects. The infection is transmitted through the feces of an infected person (due to poor hygiene conditions and habits), contaminated food and water that has not been properly cooked. Sun-dried tomatoes, fish, shellfish, and frozen berries are the most common sources of infection.
- Hepatitis B is the most common chronic asymptomatic form of abdominal pain. Hepatitis B is transmitted through blood or other body fluids. The hepatitis B virus damages the liver, causing chronic inflammation that can progress to cirrhosis and primary liver cancer. In acute hepatitis B, the course is usually violent - abdominal pain, yellowing of the skin, liver problems. Requires hospital treatment.
- Hepatitis C is also the most common chronic asymptomatic form. Transmitted through blood (highest risk for people before 1990 who donated blood or had a blood transfusion and had any surgery or dental procedures).
Types of hepatitis
Types of pain in the left side
Pain manifests itself in different ways, and the correct diagnosis depends on this. The intensity and duration of pain most often indicates its cause.
Table. Types of pain:
| Type of pain | Preliminary diagnosis |
| Sharp pain | He talks about diseases of the pelvic organs, about inflammatory processes occurring in the bladder. |
| Blunt pain | May become an indicator of gynecological ailments. In less dangerous cases, it occurs simply from bruises and is eliminated by applying cold. |
| Stitching pain | Often manifests itself during inflammation of the vertebral discs and other skeletal-related ailments. If the abdomen is hard and swollen, then this symptom may indicate inflammation of the ovarian cyst. |
| Nagging pain | It is most characteristic of purulent infectious diseases. In men it can occur due to pathology of the scrotum. Often indicates the presence of cancer at a late stage. |
If the temperature rises sharply and is accompanied by pain, then this is a manifestation of infectious diseases of the internal organs of the pelvis. If the patient suffers from constant nausea and vomiting, this may indicate the presence of a stomach or duodenal ulcer, inflammation of the intestines, pancreatitis and other diseases.
In case of sudden pain attacks, you cannot hesitate: you must immediately call an ambulance so that doctors can help immediately.
Life-threatening symptoms:
- incessant pain along the entire left side, which intensifies and does not subside even after taking painkillers;
- a hard and swollen abdomen, which can be seen even without palpation;
- severe vomiting with blood clots or blood found in the stool.
Peptic ulcers
Peptic ulcers are lesions of the inner lining (mucous membranes) of the gastrointestinal tract that can occur anywhere in the gastrointestinal tract, but most commonly in the stomach and duodenum. The most common symptom of an ulcer is abdominal pain.
Peptic ulcers are usually associated with the following:
- The bacterium Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori). Helicobacter pylori is a gram-negative spiral-shaped bacterium that causes chronic inflammation of the stomach and duodenum and is a common cause of infectious ulcers worldwide.
- Frequent use of NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), such as aspirin, ibuprofen, ketanov, etc.
- Risk factors: smoking, alcohol abuse, stress, irregular and unhealthy diet.
Peptic ulcer
Organs of the human thoracic region
The thoracic region is composed of the following important organs:
- Light.
- With my heart.
- Bronchi.
- Trachea.
- Esophagus.
- Diaphragm.
- Thymus gland.
We present in the table the features of their location and purpose:
| Organ | Location | Functions |
| Heart | In the middle between two lungs | The heart pumps blood through the system of blood vessels |
| Lungs | Fill almost the entire chest area. Consist of two halves | Production of oxygen by processing it into carbon dioxide, saturation of the blood with the isolated component |
| Bronchi | In the area of the 5th and 6th vertebrae. Include two parts (both sides) | They transmit oxygen from the trachea to the alveoli of the lungs. Protects against penetration of foreign bodies |
| Trachea | From the bronchi to the larynx. Divided in two at the bottom | Transfers air from the larynx to the bronchi and in the opposite direction - carbon dioxide |
| Esophagus | From the larynx through the diaphragm to the stomach | Moves food to the stomach |
| Diaphragm | Between the chest cavity and the peritoneum | Controls lung volume during breathing. The chest and abdomen are separated |
| Thymus gland (thymus) | Below the sternum | Affects immunity and growth, blood composition (lymphocyte production) |
Lower left quadrant
The organs in this quarter are the left kidney, part of the large and small intestine, and in women, the left ovary and fallopian tube.
Abdominal pain in this quarter can be a symptom of colitis, colonic diverticulosis or kidney stones, and in women can also be a sign of ovarian or pelvic inflammation.
Microflora
The intestinal tract is inhabited by the following bacteria:
- lactobacilli;
- bifidobacteria;
- bacteroides;
- enterococci;
- coli;
- Proteus;
- staphylococci;
- fungi.
The first three names refer to the main group of microorganisms present in the intestines. In addition to beneficial bacteria, the microflora also consists of opportunistic microorganisms. Under the condition of strong immunity, these bacteria do not cause any disturbances in the body, but when the immune forces are weakened, these same microorganisms get out of control, begin to actively multiply and can cause serious abnormalities in the body.
Interesting! The human intestine is inhabited by microorganisms that are seventy times more numerous than the number of inhabitants of the globe.
Bacteria present in the intestines are divided into two main groups: anaerobes (do not require oxygen) and aerobes (live on oxygen). The overwhelming number of microorganisms in the intestinal tract are anaerobes: lactobacilli, bifidobacteria, bacteroides. And, for example, E. coli and enterococci are aerobes.
Colon diverticulosis
Diverticula are projections on the outside of the wall of the colon, commonly called “pockets.” The causes of colonic diverticulosis are not fully known. It is believed that the pathology may be associated with a congenital predisposition and constipation. Diverticulosis itself does not usually cause pain, but it can interfere with bowel movements, make bowel movements difficult, cause air to accumulate in the area, and cause bowel spasms, which can be painful.
Another cause associated with severe pain is inflammation of diverticulitis (diverticulosis). With inflammation, the pain is acute, severe discomfort, bloating, cramps, blood, mucus or pus in the stool may occur, and the temperature may rise. Antibiotics are usually prescribed and surgery is rarely required.
Pain in women
In men and women, some organs of the reproductive system are located in the lower left, the defeat of which provokes painful sensations. In the fairer sex, this is the ovary:
- During inflammatory processes occurring in the organ, a nagging pain occurs, which intensifies with movement.
- A formed cyst can also cause discomfort, including nausea, vomiting, and fever. The nature of menstruation also changes - they become abundant and are accompanied by pain.
- Rupture of the follicle during ovulation can cause severe pain.
A woman may also experience an ectopic pregnancy, when a fertilized egg remains in the fallopian tube and begins to divide. The fallopian tube enlarges, discomfort and vaginal bleeding appear. When a rupture occurs, a sharp, severe pain appears, internal bleeding begins, against the background of which the pressure drops and loss of consciousness is observed. Pathological discharge, menstrual irregularities, and the appearance of various types of pain in the anterior lower abdomen may indicate the development of fibroids or malignant neoplasms.
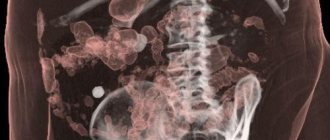
Kidney stone disease
This is a disease in which stones (calculi) form in the ducts and glands of the kidneys. This is a fairly common disease. Kidney stones usually do not cause symptoms until they begin to “move” and interfere with the flow of urine.
Kidney stone disease
If small stones get into the peritoneal fluid, the pain is especially severe (colic), the person sweats, gets cold, and a high temperature may rise. In such cases, the patient is hospitalized, given painkillers and antispasmodics, and given intravenous fluid infusions. If signs of infection appear, antibiotics are prescribed. If stones cannot be removed with medications, surgery is performed.
Where to go for help?
If there is pain under the ribs on the left, what should you do? Often a person, faced with such problems, simply does not know which specialist to turn to. However, delay can lead to a worsening of the condition, so you can go to any doctor who will refer you to the right address. In addition, sometimes a person knows that he has certain diseases. Therefore, during the period when these diseases worsen, you should go to your doctor.
If the pain occurs suddenly, then the best option would be to contact an emergency medical service. Then the doctor or emergency paramedic, having provided you with first aid, will decide on hospitalization or recommend contacting a specialist. Only a complete examination and clinical tests will allow the doctor to get a complete picture of the disease, and therefore correctly prescribe treatment. Thus, it is possible to determine exactly what caused the pain under the ribs, its nature, causes, treatment, only in a hospital setting.
Summarizing the above, we can conclude that pain in the left hypochondrium often indicates the presence of serious diseases. Therefore, the sooner the cause is identified, the sooner you can begin to eliminate it. In addition, the speed of decision-making on treatment issues often prevents the transition of diseases to the chronic stage.
Treatment for pain on the left, under the ribs, front and back
Treatment for pain on the left, under the ribs, in front and behind.
To relieve the condition, you need to lie down on a flat surface, remove constrictive clothing, relax and open the window. The following medications will help alleviate the condition:
- Antispasmodics - Drotaverine, No-Shpa
- Anti-inflammatory tablets - Ibuprofen, Nurofen
- Analgesics - Analgin, Pentalgin
It is important to remember: If the patient is bothered by acute, sudden pain on the left, or girdle pain, with nausea, vomiting, dizziness and fever, it is necessary to urgently call an ambulance. Such an acute condition may indicate a rupture of an internal organ, peritonitis, intestinal obstruction, ulcer perforation, or internal bleeding.
Treatment for pain on the left, under the ribs, in front and behind should only be prescribed by a doctor.
Pain on the left under the ribs in front and behind: what is it, associated symptoms
The cause of pain in the left side of the abdomen in front or behind, on the same side, can be a serious pathology, as well as some kind of malfunction in the activity of a specific part of the body. So what is it?
- This may indicate the beginning of a number of health problems.
- To find out what kind of illness is hidden in the body, you need to feel the nature of the pain on the left under the ribs, understand its duration and frequency, how often and how much it bothers you.
- Based on this, we can make assumptions about the source and causes of pain.
- It is necessary to understand in which organ the pathology appeared and look for ways to cure it.
Having determined the nature of the pain symptoms, we can assume what is wrong with health, which organ needs to be examined and treated. In addition, the following accompanying symptoms often appear:
- My head is spinning
- Feeling weak
- The person may be unconscious
- Skin hyperemia may occur
- Body temperature rises
- Feels like it's freezing
It is possible to finally establish which system failed and what caused it only after an in-depth study and accurate diagnosis. The causes of deviations can be injuries, chronic pathological conditions and even oncology.
Which doctor should I contact: diagnosis
A doctor who treats pathologies on the left under the ribs.
If there is pain, it is forbidden to endure and self-medicate. In this case, the patient requires doctor’s intervention and appropriate diagnosis. Which doctor should I contact? First of all, go see a therapist. He will conduct an initial examination and give a referral to a specialist
- To the traumatologist
- Infectious disease specialist
- Gastroenterologist
- To the surgeon
- Oncologist, etc.
The doctor will prescribe a more detailed study:
- Analyzes
- Ultrasound
- MRI
- Radiography
After identifying the disease, you will have to observe a doctor for several months and follow his recommendations. Perhaps, after diagnosis, the doctor will write a referral to a hospital. If the pain is sharp and acute, then diagnostic measures are performed directly in the emergency department or in a specialized department - surgery, traumatology or infectious diseases.
It is important to strictly follow everything that the specialist advises and monitor your well-being. If there is any deterioration, you need to contact the clinic again.