Timely treatment of hernias of the anterior abdominal wall, including inguinal, femoral, umbilical, and linea alba, helps to avoid the development of such serious complications as acute intestinal obstruction and improve the quality of life of patients.
Hernias of the anterior abdominal wall, especially hernias of the white line of the abdomen, occur in cancer patients as a consequence of previously performed operations on the abdominal organs, as a result of long-term ascites, as well as with weakness of the connective tissue, as in any other patients who do not suffer from cancer.
- Hernia of the anterior abdominal wall as a disease
- How do hernias develop?
- Why is hernia repair necessary?
- Tests to confirm the diagnosis
- Is surgery always necessary?
- Contraindications for surgery
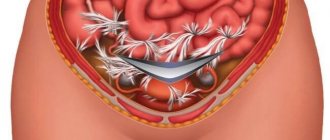
- Progress of hernia repair operation
Euroonco clinics employ highly qualified surgeons with extensive experience in reconstructive and aesthetic medicine. The use in our clinic of modern methods and materials for hernia repair, the timeliness of surgical intervention allows us to minimize the number of complications, minimize relapses and ensure a comfortable postoperative period for the patient. Using modern endovideosurgical equipment, surgical treatment is carried out in accordance with the principles of aesthetic and cosmetic surgery. New techniques make it possible to perform combined (simultaneous) operations for an individual patient.
Hernia of the anterior abdominal wall as a disease
A hernia itself is a protrusion of internal organs or parts thereof without violating the integrity of the skin and the membrane lining the cavity. The opening through which this occurs is called the hernial orifice. The anatomical structure of the anterior abdominal wall is such that there are several “weak” places, which, due to the features of their structure, are predisposed to be hernial orifices. The most common hernial orifice is the inguinal ring (66% of hernias) and the adjacent area called the medial inguinal fossa. The contents of the hernial protrusion in this case may include the small intestine, omentum, occasionally the cecum, appendix, bladder, sigmoid colon, and internal female genital organs. Over time, the hernial sac descends into the scrotum in men, and into the labia majora in women. Inguinal hernias are divided into direct and oblique according to the location of the hernial canal.
Less common are femoral, umbilical hernias, and hernias of the white line of the abdomen.
In addition, the following types of hernias are distinguished: congenital and acquired, traumatic, postoperative; complete and incomplete, reducible and irreducible, complicated and uncomplicated.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Our doctors
Prokhorov Yuri Anatolievich
Surgeon, head of the surgical service of CELT, candidate of medical sciences, doctor of the highest category
33 years of experience
Make an appointment
Gordeev Sergey Alexandrovich
Surgeon, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
42 years of experience
Make an appointment
Fedorova Elena Vladimirovna
Surgeon, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
22 years of experience
Make an appointment
Lutsevich Oleg Emmanuilovich
Chief Surgeon of CELT, Honored Doctor of the Russian Federation, Chief Specialist of the Moscow Department of Health in Endosurgery and Endoscopy, Corresponding Member of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Head of the Department of Faculty Surgery No. 1 of the State Budgetary Educational Institution BPO MGMSU, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Doctor of the Highest Category, Professor
43 years of experience
Make an appointment
How do hernias develop?
As a rule, patients who develop hernias have certain characteristics of the physique and structure of connective tissue, which already loses its elasticity with age. The general name for these changes is “connective tissue weakness syndrome.” Modern studies have confirmed metabolic disorders of collagen, the main framework protein of connective tissue, in such patients.
Factors contributing to the clinical manifestation of a hernia are a decrease (hypotrophy) of the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall, an increase in intra-abdominal pressure with ascites, obesity, pregnancy, and intestinal dyskinesia. The occurrence of umbilical hernia in women is facilitated by multiple pregnancies and difficult childbirth. The holes and gaps between the muscles of the abdominal wall can increase with sudden weight loss.
Postoperative hernias occur at the site of a tissue defect, thinning of a postoperative scar, more often after various complications in the area of a postoperative suture (suppuration, infiltration, etc.). In patients with cancer, postoperative hernias can develop in later stages due to a sharp decrease in body weight, including the development of cancer cachexia.
Conservative treatment
Removal of this type of hernia is possible when it is necessary to relieve the patient from complications. Thus, the pathology stops growing, and the symptoms become less severe. This type is suitable only for those patients who are contraindicated for surgery due to age, another disease, or pregnant women.
The following measures are being taken:
- treatment with medications;
- combating the causes that provoke pressure inside the womb;
- diet food;
- special gymnastics;
- indication for wearing a bandage;
- special massage.
Why is hernia repair necessary?
In addition to the cosmetic defect and the discomfort caused by the hernia, there is a good reason not to put the operation on hold. This reason is the danger of infringement, i.e. sudden compression of the contents of the hernia in the hernial orifice. This usually happens after lifting something heavy, straining hard, or during a strong cough, i.e. with increased intra-abdominal pressure. Most often, the mobile small intestine is strangulated; in the strangulated part of the intestine, blood circulation is disrupted, which after a short time leads to necrosis of the intestine and even perforation (perforation) of its wall with the development of inflammation of the peritoneum (peritonitis) - a life-threatening condition.
Clinically, strangulated hernia is accompanied by a significant increase in hernial protrusion, its non-reduction, tension and severe pain. Pain can be localized only in the area of the hernia or spread over the entire surface of the anterior abdominal wall. The temperature rises, sometimes to a high level of 38-39'C. In some patients, blood pressure drops sharply with a decrease in the systole-diastolic interval, for example, to 80/60 mmHg. Some patients may vomit bile and even feces. Acute intestinal obstruction develops.
Risk factors
— Hereditary genetic factor. - Chronic cough and sneezing. - Tuberculosis. - Chronic constipation. - Enlarged prostate. - Obesity. - Liver diseases, such as cirrhosis. - Lack of protein. - Lifting weights. — Smoking (increases the risk of developing the disease). —Patients suffering from polio or paraplegia are prone to the disease due to muscle weakness. — Weakness of muscles due to old age. — Postoperative infection in a wound with poorly fused muscles, which leads to weakness of the abdominal wall and, accordingly, to a hernia. — Accidental nerve damage during appendicitis surgery. - Certain yoga or aerobics exercises. At the same time, cycling or exercising on an exercise bike does not lead to the formation of pathology.
Tests to confirm the diagnosis
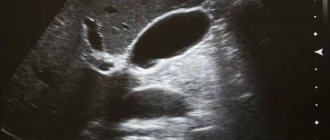
In uncomplicated cases of hernia, a standard preoperative examination is usually sufficient. The diagnosis is made during a routine clinical examination by a surgeon. In doubtful cases, the surgeon tries to insert a finger into the suspected hernial canal and asks the patient to strain or cough. At the same time, a push is felt, indicating the presence of a hernia. Carrying out an ultrasound examination of the patient in an upright position can detect thinning of the tissues of the anterior abdominal wall in the area of the hernial orifice.
In complicated cases, an ultrasound scan can reveal the corresponding organs in the hernial sac - the intestines, bladder and others.
In the presence of nausea, vomiting, pain and the absence of organ strangulation in the hernial orifice, other diseases with similar symptoms must be excluded. It happens that hernias of the white line of the abdomen accompany peptic ulcers, stomach cancer, cholecystitis, etc.
Self-diagnosis
It is important to remember that it is impossible to independently determine the presence of a hernia with high accuracy - one can only assume the development of pathology. So the information below is for informational purposes only.
- Palpation and examination - doctors do the same thing, but they know what, where and how to look. They usually notice a reflex contraction of the back muscles.
- Behavior - you need to observe how you want to sit or lie down. Sometimes poses can be completely unnatural; a person takes them in order to reduce pain or discomfort. Also, all the patient’s movements will be smooth and accurate.
- Nature of pain. For example, the pain is aching - there is no compression of the nerve roots. Here it is just relevant to use the table above.
How to identify an intervertebral hernia yourself
Contraindications for surgery
Acute infections, late pregnancy, dermatitis and eczema in the hernia area.
Since the herniotomy operation is performed under general anesthesia, the presence of decompensation of severe diseases of the internal organs, including coronary heart disease, stroke, diabetes, is a contraindication to the operation due to the high degree of anesthetic risk.
In cancer patients, a hernia of the anterior abdominal wall is treated according to the same principles as in other patients.
Diagnosis of the disease
When you suspect a pathology, you must urgently seek advice from a specialist who will prescribe an examination in combination with ultrasound and tests. It is very easy to identify the disease when it appears in standard, familiar places of its formation. It could be the navel, groin, thigh. If the hernia is of the ventral type, then it can be recognized based on the symptom of a cough impulse. A hand is placed on the tubercle, the patient must cough. At that moment, the doctor may feel tremors. The disease can be detected by palpation. Sometimes the doctor may feel or tap the affected area.
Types by degree of protrusion
Another classification distinguishes hernias according to the degree of their extension beyond the intervertebral space and the integrity of the fibrous ring. There are such types - protrusion, prolapse, extrusion, sequestration.
Protrusion
A type of minor spinal hernia, when only the internal fibers of the fibrous ring are damaged, the ring itself does not rupture. The reason is deformation and dehydration of the intervertebral disc, which reduces its elasticity. Cracks appear in the ring, and the fixation of the vertebrae with each other deteriorates.
Bulging occurs under vertical loads. Therefore, if the patient was lying down during the examination, the defect may not be noticed. The formation often occurs in the lumbar spine, less often in the neck and chest. The compression of the nerve endings disappears quickly. The nature of the pain depends on the location of the protrusion:
- thoracic region
- the heart, lungs, and other organs inside the sternum ache; - lumbar zone
- discomfort in the back, numbness in the legs, groin area; - cervical spine
– neck pain, decreased blood pressure, headache, tinnitus.
Prolapse
Prolapse is a medium-sized hernia of the spine, which is characterized by partial release of the nucleus into the spinal canal. The ring may simply stretch too much or tear. The nucleus compresses the nerve roots, causing inflammation and swelling of the tissue.
The appearance of a protrusion is accompanied by chronic pain, impaired sensitivity in the lower back, neck, legs and arms. Discomfort intensifies with sudden movements (coughing, sneezing), and can put a person to bed for several days.
Prolapse usually appears in the lower back. The main reason is spinal injury due to heavy lifting, sudden straightening and turning, working in an awkward position, hypothermia, and stress.
Extrusion
Extrusion is a hernia in which the fibrous ring is torn, but the longitudinal ligament remains intact. Discomfort appears if the nucleus pulposus touches the nerve roots.
Pain symptoms may vary, depending on the size and displacement of the protrusion. With a strong shift, a dull spasm occurs in the neck, which moves to the head and shoulder. Possible numbness, tingling, and loss of skin sensitivity. With breast extrusion, the heart, ribs, stomach, and intestines hurt. When the lumbar region is affected, problems appear in the lower back, groin, and legs. The development of pathology is fraught with impaired urination and erection in men.
Protrusion, prolapse, extrusion, severstration - types of hernias according to the degree of their extension beyond the intervertebral space
Severstration
Sequestration is a severe form of hernia, which is characterized by the formation of a sequester - the prolapse of the nucleus or part of the disc into the spinal canal. Due to rupture of the longitudinal ligament, the nucleus pulposus is completely or partially separated from the disc. It falls into the canal, squeezing the nerves. The mass may remain in place or migrate up or down, simulating a herniation of another vertebra.
The diagnosis is usually made in older people. A striking symptom is lumbago in the back, which radiates to the legs or arms, followed by numbness, sometimes paralysis.
Approach to the treatment of different types of hernias at the Paramita clinic
If lumbago occurs frequently, buy an anesthetic ointment (Indomethacin, Diclofenac). You can apply a piece of ice to the affected area, after wrapping it in a towel, to avoid damaging the skin. Keep for 15 minutes, then remove. But, if the intervertebral hernia is not treated, the pain will last for several weeks and may become permanent. Depending on the dislocation, the patient is unable to bend normally, turn his neck, raise his arm, leg, stand, or sit.
Don't ignore the pain. Paramita Clinic specialists use in their work:
- exercise therapy exercises;
- proven methods of alternative medicine - acupuncture, manual therapy, massage, reflexology, etc.;
- physiotherapy - electrophoresis, Darsonval, laser therapy, shock wave therapy.
We use non-surgical hernia treatment techniques
Read more about our unique technique
Before prescribing treatment, the doctor prescribes diagnostics - x-rays, CT, MRI. They allow you to assess the condition of soft and bone tissues, the size and location of the hernia, and accurately determine its type.
Surgery for any type of hernia should be resorted to only if the analysis shows the impossibility of another solution - severe constant pain from a spinal hernia, the risk of paresis, paralysis.
Themes
Intervertebral hernia, Spine, Pain, Treatment without surgery Date of publication: 09.17.2020 Date of update: 01.12.2020
Reader rating
Rating: 5 / 5 (2)