Many women, while carrying a child, experience difficulty in bowel movements. Constipation during pregnancy not only creates discomfort, but also becomes a cause of constant anxiety. When pushing on the toilet, a woman is afraid of harming herself and her unborn child.
Can this unpleasant situation be avoided or should we accept the state of affairs? What traditional methods of eliminating constipation are suitable for pregnant women and is there a reliable recipe with which you can get rid of stool retention once and for all?
Why do problems with bowel movements occur during pregnancy?
The problem of stool retention during pregnancy is quite relevant. Between half and two-thirds of expectant mothers suffer from constipation. Factors that cause constipation include:
- Hormone. Elevated progesterone levels cause many reactions in the body, one of which is smooth muscle relaxation. The result of this is decreased intestinal motility and constipation.
- Insufficient food and fluid intake. This phenomenon is characteristic of early toxicosis, when everything eaten and drunk comes back with vomiting. Some women deliberately cut back on their meals in an attempt to get rid of the feeling of nausea.
- Physical inactivity. A growing belly limits movement, or the woman, out of fear for the child, tries to be more at rest.
- Taking iron tablets. They are prescribed to prevent anemia in pregnant women. The iron contained in the preparations is only partially absorbed into the blood, and a large proportion of it settles in the intestines, binding to food masses and causing a fixing effect.
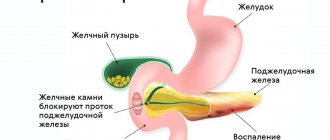
- Anatomical factors. The growing uterus with the fetus puts pressure on the pelvic organs, including the colon, causing congestion.
Third trimester
In the third trimester of pregnancy, the same causes of constipation persist as in the second. Naturally, the compression of the intestines by the grown fetus increases. Unfortunately, constipation can persist not only before childbirth, but also in the future. It is fair to say that for some women, symptoms of constipation may subside at the end of pregnancy. This is associated with the readiness of the uterus to contract before childbirth. Intestinal activity may also be restored5.
Reduced bowel function during pregnancy is a protective reaction of the body aimed at preserving the child4.
Why does constipation receive so much attention? When intestinal function is disrupted, its microflora changes. This can have a bad effect on the composition of the microflora of the birth canal, which is especially important during natural childbirth3. In addition, the intestines are considered not only a digestive organ, but also part of the body's immune system.
Particular attention to the problem of constipation and irregular bowel movements should be paid to those women who faced the problem of constipation even before pregnancy. During pregnancy, they should pay more attention to bowel function and think through an action plan in advance, since the use of laxatives during pregnancy is limited.
Other possible causes include the following1:
- insufficient fluid and fiber intake;
- forced restriction of mobility to maintain pregnancy;
- taking iron supplements for the prevention and treatment of anemia;
- using medications for other problems (for example, to lower blood pressure);
- constipation before pregnancy.
After childbirth, constipation can be caused by6:
- a long period of restoration of the tone of the abdominal wall and pelvic floor muscles;
- taking painkillers;
- sometimes it’s just fear that the tension will damage the seams;
- disruption of the usual biorhythms of intestinal function due to lack of sleep, night feedings, and irregular daily routine.
Constipation can negatively affect the health of both mother and baby, which is why it is so important to approach the issue of treating constipation correctly.
Is it possible to push on the toilet during pregnancy?
To empty the intestines, a pregnant woman suffering from constipation has to make considerable efforts. The woman pushes for a long time, straining the muscles of the perineum, abdominals and diaphragm. At this time, intra-abdominal and general blood pressure increases, which is harmful for the mother and child. Tense abdominal muscles put pressure on the uterus, which leads to its hypertonicity and impaired blood circulation in the circumuterine vessels.
Constant tension also affects the condition of the rectum, causing complications such as its prolapse and the appearance of hemorrhoids. In addition, intestinal contents during constipation have a dense consistency and injure the delicate mucous membrane of the rectum during defecation.
In the early stages
The appearance of constipation in the early stages of pregnancy is often associated with toxicosis. Due to constant nausea and vomiting, a woman does not receive the amount of food and liquid necessary for normal digestion. Feces become dense and dehydrated, requiring great effort to get rid of them. When visiting the toilet, a woman has to push hard and strain her stomach.
The resulting muscle tension is dangerous, as it can lead to uterine hypertonicity and embryo rejection. It is especially harmful to push for pregnant women who are at risk, for example, women with isthmic-cervical insufficiency or a history of miscarriage.
In the later stages
At the end of the second and third trimesters, the large uterus compresses the final sections of the large intestine. This leads to decreased motility, fecal stagnation and constipation. The situation is aggravated by the fact that during this period it becomes more difficult for women to move and they prefer a sedentary lifestyle to movement. A very common complaint accompanying constipation in later stages is hemorrhoids. Its appearance is associated with stagnation of blood in the veins and increased pressure in the rectum. With strong straining in the later stages, the development of hemorrhoids accelerates, and the tone of the uterus increases, which can lead to premature birth.
Push correctly
While passing through the birth canal, the baby squeezes the internal organs, and it is not strange that during pushing and the birth of the child, the intestines and bladder may empty
Compared to the labor period, which lasts on average 9–11 hours, pushing is a quick process. On average, it takes from 20 minutes to an hour (rarely longer) to push the baby to the exit during the first birth. With repeated births, the pushing period is even shorter
It is necessary to follow the commands of the doctor and midwife. If it is not clear what they want, you need to ask for an explanation.
Why are efforts needed?
During childbirth, the uterus begins to contract, these contractions are called contractions, they are needed so that the cervix opens completely and can release the baby. But dilation of the cervix alone is not enough, the baby still needs to somehow come out into the world. And here pushing joins the contractions –
reflex contractions of the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall. They increase intra-abdominal pressure and, together with contractions, push the baby out. Attempts occur because the baby's head, thanks to uterine contractions, moves down and compresses the nerve endings in the cervix, vagina, pelvic floor and rectal muscles. The receptors of these organs are irritated, and as a result, the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall and diaphragm reflexively contract.
How to recognize them
At some point during contractions, a woman begins to feel that she wants to go to the toilet in a big way - this indicates that pushing begins. These sensations gradually increase, and it seems that “trouble” is about to happen. In fact, pushing occurs because the baby’s head puts pressure on the pelvic floor and rectum of the expectant mother, and not at all because she really wants to go to the toilet.
The average duration of each push is 10–15 seconds. Typically, during one contraction, a woman feels the need to push an average of three times. And although contractions are the strongest at this point, most women say that when pushing joined the contractions, they became less painful.
What will you feel
In addition to physiological manifestations (pressure on the rectum), the psychological state of a woman in labor also changes. Attempts begin when the strongest and longest contractions occur, but the interval between contractions is already short. A woman has very little time to rest, and then there’s pushing. In the midst of pushing, most often the woman in labor withdraws from what is happening around her: she is only interested in her own sensations and experiences. The expectant mother no longer cares how she looks and behaves. On the one hand, this is the right state, since it allows you not to waste energy on external stimuli, but to use it for its intended purpose, for pushing. On the other hand, a woman may have difficulty understanding the words of the doctor and midwife.
Emotional stress is possible, because you still have to work - push, but you already have little strength.
What to do
As soon as attempts begin, you must definitely call a doctor or midwife. From this period they will constantly be near the woman. In general, even if there is a desire to push, you cannot do this without the command of a doctor or midwife. Sometimes the expectant mother feels that she is being “pushed” (there is a desire to go to the toilet, but it is not yet strong), and begins to try to push on her own. But these may not be real attempts yet. Plus, the woman does not know how much the cervix has dilated, and if the dilation is not yet complete, and the mother begins to push, there is a high risk of cervical rupture. Another option is that the baby’s head has not yet moved far enough, and the woman in labor begins to push; then the mother may quickly get tired and have no strength left for the main push. Therefore, we wait for the midwife or doctor and listen to what they say.
Important point:
pushing, unlike contractions, can be controlled - a woman can delay pushing or, conversely, intensify it. If the doctor or midwife still prohibits pushing, then the “doggy style” breathing technique will help to restrain the efforts. Usually the midwife says: “Don’t push, just breathe!” Then you need to breathe shallowly with short inhalations and exhalations.
How to push correctly
When starting to push, you should always listen to your doctor or midwife. If the midwife says: “Push!”, you need to:
1. Gather all your strength, take a deep breath, hold your breath, push and gently exhale while pushing. The most important
–
the pushing movement and all the woman’s efforts should be directed towards the perineum
.
2. During each contraction, you need to push three times.
3. You need to push smoothly, and between pushes you need to rest and prepare yourself for work.
Important point:
the mother must understand that pushing is the main moment of childbirth, when she needs to work the most. The outcome of the birth for her child depends on this. Therefore, even if you no longer have the strength, you need to gather your will into a fist and start pushing.
NO NEED
1. You cannot disconnect from the ongoing process and stop pushing. You can’t shout “I can’t do it anymore!”, and there’s no need to shout at all: this way you’ll only waste energy on screaming, and it should go towards pushing.
2. There is no need to close your eyes and push your face (make grimaces, etc.) - this will not help the child’s progress in any way, because the forces will go not to the perineum, but to the face. Plus, you will get tired, you will not help the child, in addition, you will have a headache, blood vessels on your face and on the mucous membranes of the eyes will burst.
3. You can’t sit down while pushing, because the baby’s head is already at the exit from the genital tract.
4. There is no need to be embarrassed if feces or urine pass involuntarily; this happens to almost all women, and doctors and midwives do not see anything indecent here.
The ability to give birth is in a woman’s genes, but it just needs to be applied correctly. No one - not your husband, not your doctor, not your midwife - can give birth for you. This means that you need to be determined to complete your work to the end, because the duration of the pushing period and, in general, the outcome of childbirth for the newborn depend on this.
Why is straining dangerous for a pregnant woman?
Why shouldn't pregnant women push hard on the toilet? The process of straining is equivalent to lifting weights, since it tenses all the muscles of the abdominal press and perineum. Straining these muscle groups can lead to the following complications:
- increasing the tone of the uterus;
- bleeding;
- placental abruption;
- miscarriage;
- rupture of the membranes and leakage of amniotic fluid;
- premature birth;
- the appearance of a hernia;
- hemorrhoids;
- rectal prolapse;
- cracks in the rectal area.
Constipation in pregnant women and nursing mothers
From an interview: From 20 to 60% of women during pregnancy experience intestinal dysfunction in the form of constipation. Today, doctors identify “constipation during pregnancy” as a separate problem. So why does constipation occur during pregnancy and how can you help the expectant mother?
Why does constipation occur in pregnant women and mothers who have already given birth? What is this connected with? Constipation occurs in pregnant women for several reasons. Firstly, an ever-increasing level of progesterone leads to water retention in the body, tissue swelling and suppression of intestinal motility. If you remember the premenstrual days, then almost every woman notices bloating, heaviness in the lower abdomen, the appearance of “extra” pounds, and constipation. Secondly, few women eat right. In other words, the diet is very poor in fiber, which is very important for intestinal motility. Many women limit their water intake for fear of swelling of the legs, but this is a misconception, since the nature of edema of the lower extremities depends least of all on the amount of fluid taken. Therefore, a pregnant woman should take enough fluids. Thirdly, and this is probably the most common reason – inactivity. Especially in pregnant women. The problem for pregnant women is that as soon as they find out about their pregnancy, they suddenly immediately become almost “paralyzed” and go straight to bed. And immediately oohs and aahs, because the doctor said that there is a threat, although in 90% of cases there is no smell of a threat. But they all lie there and swallow progesterone drugs, aggravating the situation, although neither the first nor the second pregnancy is preserved. In the postpartum period, the reasons are the same - an unbalanced diet and a sedentary lifestyle, but progesterone decreases to normal. However, often after childbirth, women continue to experience menopause (since menstruation may not occur for 6-12 months, especially in breastfeeding women), and therefore a state of physiological hypoestrogenia occurs, when the level of estrogen decreases, which is normal, not scary, but due to This may be due to decreased intestinal motility.
How can you suspect that this is constipation? Very simple. Normally, bowel movements should be 1-2 times a day. If it happens less often, it means constipation.
Why is the problem of constipation so relevant specifically for pregnant women? The problem of constipation is relevant not only for pregnant women, but also for the entire modern society, which eats refined foods and leads an extremely sedentary lifestyle.
Are there any specific treatment options for constipation in pregnant and breastfeeding mothers? Does not exist. The recommendations are simple - a balanced diet and exercise. Yes Yes Yes! Pregnant women should not lie in bed, but move as much as possible, so that the baby can receive as much oxygen as possible, and so that there is no stagnation of venous blood in the pelvis and lower extremities, and so that the intestines work well. Most laxatives cannot be used during pregnancy, especially those that cause increased intestinal motility. Nursing mothers can use many medications, most of them are not transmitted through milk.
What products have fixing properties? Poor in fiber, containing a lot of fats of animal origin, as well as chemically processed (including now very fashionable low-fat products): semi-finished products, sweets, canned food.
What can you take if you have bloating? First of all, it is necessary to establish nutrition, i.e. introduce fiber into your diet. Additional intake of food enzymes helps. There are many such drugs on sale in the form of tablets or powders (the same festal, for example). A gastroenterologist can help in selecting such drugs. Nutritional enzymes are very safe for pregnant women. It is often recommended to lie on your side, changing body position frequently. Enemas for constipation in pregnant women are not recommended, however, if bloating is accompanied by pain and fecal retention, then an enema can be used. A woman should also use enough fluids (water, not juices).
How not to treat constipation during pregnancy and breastfeeding. There are several groups of laxative drugs, and not all drugs can be taken during pregnancy. The group of disintegrating substances, which includes derivatives of cellulose and polysaccharides, is very safe for a pregnant woman. Stool softeners also do no harm, because most often they are not absorbed and do not enter the blood, and are very neutral in their effect on the entire body. Another group of carryover substances act as irritants to the intestines, causing them to produce more mucus and increasing intestinal motility and contractions. This group includes bisecodil, senna preparations, aloe, phenolphthalein, castor oil and others. The problem is that these drugs have too pronounced side effects in the form of increased mucus production, pain and intestinal spasms, loss of fluid and salts (electrolytes) when diarrhea occurs, and loose stools. This group of drugs should not be taken frequently or for a long period of time, as they significantly disrupt the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and destroy the normal intestinal flora. Since these laxatives can be partially absorbed, most of them can enter the mother’s bloodstream, and possibly through the placenta into the fetus. This aspect of the issue has not been fully studied, so doctors avoid prescribing this group of laxative drugs for pregnant women. Of particular danger are saline solutions that have a laxative effect - solutions of magnesium (magnesium), sodium and potassium, as well as fatty lubricants (mineral oils). Their use is contraindicated during pregnancy, as they disrupt the water-salt (electrolyte) balance of a pregnant woman and can lead to serious side effects. Eliminating constipation is the number one preventative measure against hemorrhoids. A big mistake is made by women who, if they have constipation, strain very hard during bowel movements. Both pregnant and non-pregnant women should not push, because this can lead to worsening of hemorrhoids, rectal fissures and pain. On the contrary, it is important to learn to relax during the act of defecation.
If during pregnancy, in addition to constipation, hemorrhoids are tormented, what should you do in this case? In addition to what is said above, use suppositories for hemorrhoids. A very simple folk method for treating hemorrhoids helps. Take one onion and boil it in 300-350 ml of milk. Then, when the broth has cooled to an acceptable temperature, it is used for sitz baths, i.e. sit on a small bowl or saucepan with only the “back part”, immersing the anus in this broth. They sit like this for 15-20 minutes. Baths can be done every day.
Can constipation cause increased uterine tone and the threat of miscarriage? No, it cannot, but it significantly worsens blood circulation in the pelvic organs. In fact, feces are waste products, and if there is stagnation, all this “chemistry of life” is absorbed back into the woman’s body, and since the rectum is located in the pelvis next to the uterus, the child will begin to suffer from a lack of oxygenated blood. Therefore, women should understand that prevention of fetal hypoxia begins with regulating intestinal function and eliminating immobility.
Can constant constipation negatively affect the course of pregnancy and the general condition of the mother and child? Of course they can.
What medications can be used to treat constipation during pregnancy? Laxatives are discussed above. There is no drug treatment for constipation, unless, of course, constipation is associated with some kind of hereditary or acquired disease of the gastrointestinal tract. In such cases, appropriate treatment should be prescribed by a gastroenterologist.
Source: https://www.uaua.info/planirovaniye-semji/oslozhnenia-beremennosti/article-11396-zaporyi-u-beremennyih/
Share link:
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
- Click here to share content on Facebook. (Opens in a new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Skype (Opens in new window)
- Send this to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
By
What to do when you can't push?
No one can answer this question more accurately than the doctor managing the pregnancy. There are many affordable and safe ways to get rid of constipation without straining, including both medicinal and traditional ones.
The easiest way to combat constipation is to correct your diet. Most likely, the doctor will first of all advise you to diversify the menu with plant fiber, which is rich in fresh vegetables, fruits and grains. Fermented milk products deserve special attention: kefir, fermented baked milk, natural yogurt.
Among food products, it is also worth highlighting dried fruits, honey and lemon juice, black or bran bread, oatmeal, buckwheat, and barley.
Drinking regime also plays an equally important role. Excessive drinking does cause swelling in the lower extremities, but not drinking enough fluids can be even more dangerous during pregnancy.
Walking in the fresh air for 1 hour a day can also improve the situation. Swimming in the pool and light morning exercises can help.
If all the above methods do not help, harmless medications come to the rescue. The doctor may prescribe lactulose (Duphalac, Prelax, Normaze), mild laxatives (Mukofalk, Fiberlex), glycerin rectal suppositories or Papaverine. In severe cases, it is recommended to resort to microenemas.
It is permissible to use folk remedies if they are agreed upon with a doctor. The most common of them are prepared on the basis of the food products mentioned above: beets, carrots, oatmeal, dried fruits.
Folk remedies for constipation during pregnancy
Prunes for constipation can be eaten pure or prepared as an infusion.
Natural remedies have long been known, with regular use of which you can get rid of unwanted problems with stool without any side effects.
One of the most effective, safe and accessible remedies is a glass of warm water on an empty stomach, about 30 minutes before breakfast.
If you drink cold water in the morning, it leads to shock to the digestive system. While a morning portion of warm water will help the gastrointestinal tract begin its work, collect waste and toxins that have accumulated overnight, and cleanse the blood and intestines.
From dried apricots, raisins, prunes and natural honey, you can make a sweet cure for constipation, which feeds beneficial intestinal bacteria, stimulating the growth of their numbers. The composition includes the listed dried fruits, 100 g of each type in crushed form, and 2 tablespoons of honey. The resulting mixture is taken daily, 2 teaspoons in the evening before going to bed.
Symptomatic therapy
In 95% of cases, constipation during pregnancy is associated with physiological changes in the patient’s body; they are usually eliminated by adjusting the diet and increasing physical activity. To normalize peristalsis, it is recommended to eat food frequently and in small portions, avoiding feelings of hunger and excessive overeating. In order to increase the volume of stool and improve the passage of stool through the intestines, it is necessary to include foods rich in fiber in the diet - fresh vegetables and fruits, whole grain bread.
Women are advised to perform feasible physical exercises, specially selected taking into account the duration of pregnancy, stimulating the smooth muscles and facilitating bowel movements. For constipation caused by nervous overstrain, psychotherapy methods help well. The use of herbal or synthetic laxatives without a doctor’s prescription is prohibited, since the drugs can harm the child’s body or cause increased uterine tone.
Is it possible to push a little during pregnancy?
In general, any effort in the toilet during pregnancy is undesirable. Experts recommend abandoning such amateur activities, reporting the problem to your doctor and finding another way out of this situation.
However, some doctors claim that minimal efforts cannot harm either the expectant mother or the fetus, provided that the pregnancy is easy and the woman feels well. The presence of various threats is an absolute contraindication to attempts. Contraindications are:
- Uterine tone;
- Threat of miscarriage;
- Threat of premature birth;
- Dilatation of the cervix;
- Any pathological discharge, the cause of which has not been established;
- The onset of contractions or the breaking of amniotic fluid.
In any case, the need for constant effort during bowel movements should not be present during pregnancy. If such a problem occurs once, you need to inform your doctor about it and find a solution in case of repeated constipation.
What medications can be used for constipation during pregnancy?
Defenorm is a drug for constipation, of herbal origin, safe for pregnant women
Strong laxatives containing buckthorn bark or senna extract are prohibited for use by pregnant women.
However, in cases where following a diet does not help to cope with the problem of constipation, gentle remedies can be prescribed:
- Duphalac, the main active ingredient is lactulose, which increases the number of lactobacilli in the colon. Beneficial microorganisms dilute the intestinal contents, absorb ammonia, and reduce the formation of toxic substances containing nitrogen. The positive qualities of the supplement are its low absorption, it does not reduce the absorption of vitamins and is not addictive.
- A drug of natural origin called Defenorm contains dried flea plantain husk. Available in capsules. Taking the product is accompanied by a large amount of clean water, at least 1.5 liters per day, since the husk swells under the influence of intestinal temperature and a humid environment, many times exceeding its original weight. At the same time, the substance remains soft, which promotes normal intestinal motility and the passage of feces.
- Phytomucil, in addition to plantain seed husks, also contains dried plum fruits. A large amount of fiber, which actively swells in the stomach and then in the intestines, helps to increase the volume of feces while maintaining their soft consistency; the plant sponge absorbs undigested food particles and removes them from the body, preventing them from penetrating into the blood through the intestinal walls.
- Glycerin suppositories are classified as irritant laxatives and are used rectally, preferably 20 minutes after a morning meal. In response to the stimulus, intestinal motility reflexively increases, thanks to the softening of the mucous membrane, emptying occurs painlessly.
- Microlax is a small enema for one-time use. The drug is multi-component, characterized by a quick effect; emptying can occur a quarter of an hour after the procedure for administering the medication orally. Refers to drugs with low absorption into the blood.
- Fortrans is a prescription drug and can only be prescribed by a doctor. Contains the active ingredient macrogol, which greatly swells in the intestines, while maintaining softness and promoting increased peristalsis. Not absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract.
Modern drugs make it possible to normalize the process of bowel movement and maintain the balance of microflora without harm to the baby’s health.