Many people believe that the spleen is not such an important organ to focus on. The reason lies in the fact that a person can live without this organ. But, despite this, a person’s life becomes no better, and in some cases even worse, because he performs a number of very important functions, such as controlling the level of elements in the blood, regulating the clotting process and maintaining balance in the body. That is why it is worth paying close attention to when pain in the spleen area appears, as it can be caused by serious diseases. What are the symptoms of spleen disease?
Indications
The main indications for performing an abdominal ultrasound include:
- pain localized in the abdominal area;
- pain in the hypochondrium;
- abdominal trauma;
- bitterness in the mouth, belching, feeling of heaviness and bloating;
- problems with stool, increased gas formation;
- control in the presence of chronic or acute diseases of acute respiratory disease;
- nausea with fever, vomiting;
- pain on palpation or abnormalities on palpation;
- symptoms of neoplasms (tumors);
- the period before surgery or to mark the biopsy procedure;
- developmental abnormalities of the abdominal organs;
- burning and pain during urination;
- inflammatory and infectious processes.
How often should an abdominal ultrasound be done?
It is recommended to undergo an ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs for the purpose of preventive monitoring of health status once every 2 years. For those patients who have chronic diseases of internal organs, ultrasound examination should be performed at least once every six months. In some cases, screening is carried out more frequently to monitor the dynamics of changes in organs. There is no need to be afraid of this. Ultrasound is an absolutely safe and harmless diagnostic method and does not harm the patient’s health.
Previous Next
What organs are included in an abdominal ultrasound?
An ultrasound scan of the abdominal cavity can clearly assess the condition of the following organs:
- liver, porta hepatis, lobe sizes;
- gallbladder, duct of Wirsung;
- biliary tract;
- pancreas;
- spleen;
- kidneys and adrenal glands;
- retroperitoneal space;
- lymph nodes;
- portal vein.
Unfortunately, ultrasound of the abdominal cavity does not visualize the intestine well. Diagnosis of this organ using ultrasound is not very informative, and it is better for the patient to undergo an MRI of the gastrointestinal tract, virtual colonoscopy or enterography.
What will an ultrasound of the abdominal organs show?
Ultrasound of OBP will show well:
- inflammatory and necrotic liver lesions;
- hepatitis;
- cysts and tumors of organs, polyps;
- formation of stones, inflammation or scarring in the gallbladder and ducts;
- cholecystitis;
- damage to the kidneys and adrenal glands;
- acute and chronic pancreatitis of the pancreas;
- enlarged lymph nodes in the abdominal cavity;
- enlarged spleen;
- abnormal arrangement of organs.
Unfortunately, ultrasound examination is not informative enough to judge 100% the malignancy and benignity of a space-occupying lesion. Therefore, if tumors are detected, the doctor will refer the patient for further examination using an MRI of the abdominal cavity with contrast.
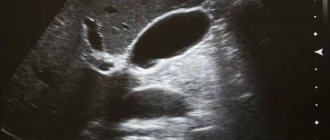
What do the abdominal organs look like on an ultrasound?
Spleen pain
General information
The spleen is an unpaired parenchymal organ that performs immune, filtration and hematopoietic functions, taking part in the metabolism, in particular iron and proteins. The spleen is located in the abdominal cavity, in the left hypochondrium.
On average, the length of the spleen in adults is 80-150 mm, width 60-90 mm, thickness 40-60 mm, weight 140-200 g. The place where arteries and nerves enter the organ and veins and lymphatic vessels exit it is called the hilum of the spleen.
The peritoneum, covering the spleen on all sides, with the exception of the gate and the area to which the tail of the pancreas is adjacent, forms ligaments. Due to them and intra-abdominal pressure, the spleen is fixed.
The spleen is also covered by a capsule. The section reveals numerous trabeculae, which diverge radially from the hilum of the spleen. They contain arteries, veins, lymphatic vessels and nerve fibers. This connective tissue skeleton and a few smooth muscle cells make up the musculoskeletal apparatus of the spleen, capable of withstanding a significant increase in its volume.
Immune diseases
One of the most important functions of the spleen is immune function. Phagocytic mononuclear cells of the spleen capture harmful substances and cleanse the blood of bacteria, viruses and other foreign agents. In addition, lymphocytes and plasma cells of the spleen participate in the immune response, promoting the elimination of antigens foreign to the body.
In some autoimmune diseases (eg, thrombocytopenic purpura, autoimmune hemolytic anemia), autoantibodies are produced in this organ. These may be the following diseases:
- thrombocytopenic purpura;
- autoimmune hemolytic anemia.
Spleen cells produce immunoglobulins. The spleen controls circulating blood cells, primarily aging and pathologically altered red blood cells, which are destroyed by phagocytes of the spleen (filtration function).
The spleen not only destroys, but also accumulates formed blood elements :
- red blood cells;
- leukocytes;
- platelets.
In particular, the spleen contains up to 50% of platelets, which, if necessary, are released into the bloodstream. The spleen (as well as the liver) has no pain receptors; it cannot hurt. Pain occurs only from stretching of its capsule, as a result of rapid enlargement.
Pain in the spleen in diseases
Injuries to the spleen can be open or closed . Open injuries occur when penetrating cut, stab or gunshot wounds of the abdomen or left half of the chest with simultaneous injury to the diaphragm. The causes of closed injuries are most often a blow to the left hypochondrium, a fall on the stomach, compression of the abdomen and left half of the chest with a simultaneous fracture of the lower ribs on the left.
Possible cracks and wounds of the spleen of varying depth and extent, separation of part or the entire spleen. Splenic ruptures are often complicated by bleeding into the abdominal cavity and shock. Immediately after the injury, the following symptoms appear:
- sharp pain in the spleen in the left hypochondrium;
- pale skin;
- cold sweat;
- frequent small pulse;
- drop in blood pressure;
- nausea, vomiting;
- strong thirst.
The victim takes a characteristic position on the left side with the hips brought to the stomach or in a semi-sitting position. Abrasions may be found on the skin of the abdomen . Respiratory excursions of the left half of the abdominal wall are limited, it is painful, tense, the Shchetkin-Blumberg sign is positive. Percussion reveals dullness in the left hypochondrium. With significant accumulation of blood in the abdominal cavity, the zone of dullness of percussion sound moves with a change in the position of the patient’s body.
Pain in the spleen can occur with various diseases. The spleen is involved in the pathological process in many infectious diseases, namely:
- typhoid and typhus;
- sepsis;
- anthrax;
- infectious mononucleosis;
- acute viral hepatitis;
- infectious lymphocytosis;
- cytomegalovirus infection;
- malaria;
- visceral leishmaniasis;
- tularemia;
- listeriosis;
- brucellosis;
- syphilis
Infarction and abscess of the spleen
Splenic infarction can develop as a result of thromboembolism of the branches of the splenic artery or its local thrombosis in leukemia, diffuse connective tissue diseases, a number of infections, atherosclerosis, lymphosarcoma.
The clinical picture of splenic infarction depends on its size. It is important to consider that small heart attacks are asymptomatic. With more extensive lesions as a result of the development of perisplenitis (inflammation of the spleen capsule), pain appears in the spleen in the left hypochondrium, often radiating to the back and intensifying with inspiration. A splenic abscess can develop due to bacteremia due to endocarditis or salmonellosis, as well as due to infection of splenic infarctions and subcapsular hematomas; for hemoglobinopathies, sickle cell anemia, rupture of a subdiaphragmatic abscess into the spleen.
Symptoms are often characterized by:
- fever;
- pain in the upper left half of the abdomen and chest;
- Tension of the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall.
Other diseases of the spleen
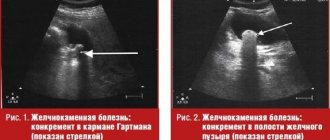
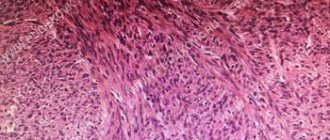
Splenic tuberculosis may be a manifestation of miliary tuberculosis. Isolated tuberculosis of the spleen is not very common; it occurs with scant clinical symptoms. Echinococcus is one of the parasitic diseases of the spleen. The most common lesion is unilocular echinococcus. Possible rupture of the echinococcus bladder and contamination of the abdominal cavity with daughter scolex. Recognizing the disease is quite difficult. Ultrasound and computed tomography play an important role in diagnosis. Primary tumors of the spleen, both benign and malignant, are quite rare. Of the benign tumors found in the spleen:
- hemangioma;
- lymphangioma;
- fibroma.
Among primary malignant tumors of the spleen, lymphomas are most often observed . At the beginning of the development of spleen tumors, as a rule, there are no clinical manifestations. As tumor nodes and the organ enlarges, patients feel heaviness and dull pain in the spleen in the left hypochondrium.
If you have severe pain in the spleen, contact your physician. Having established a preliminary diagnosis, the therapist will refer you to the appropriate professional: an infectious disease specialist, hematologist, traumatologist, surgeon or oncologist. If treatment does not give the expected results, then the issue is resolved through surgery. Many doctors recommend eating right and leading a healthy lifestyle to prevent such serious consequences.
Ultrasound of the abdomen and bladder
A conventional ultrasound examination is sufficient to evaluate the structure of the liver, pancreas, gallbladder, bile ducts, spleen, and if there is a need to examine the kidneys, then the structure of the kidneys and adrenal glands. If there is a need to assess the presence of urinary excretion disorders and the condition of the bladder, then you should sign up for a comprehensive ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, kidneys and bladder. Then the sonologist will be able, in addition to the organs of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space, to evaluate the structure of the bladder:
- does it contain salts, stones;
- unevenness of some wall;
- the presence of neoplasms and inflammatory processes.
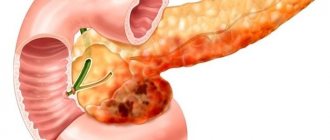
Connection between the spleen and pancreas
Basically, the tandem of these organs is responsible for metabolism and is also associated with the purification channels of our body, which are the kidneys and liver. The spleen and pancreatic gland play an important role in the energy circuit of the reproductive system. The production of sperm is their quality and quantity in men, as well as the functions of the uterus in women.
If this energy channel undergoes changes of deficiency or excess, it can cause anxiety, feelings of depression and a feeling of threat to life. A person develops various kinds of phobias, wariness and dreams that put pressure on the psyche. When this channel is damaged, thoughts of death come to a person’s head and this leads to energy depletion of the body. Eastern medicine believes that the pancreas and spleen are one and the same. In Western medicine, they are interpreted as two independent organs, working in pairs, responsible for different functions of our body.
What will an abdominal ultrasound not show?
When the question arises about the need to examine the intestines, stomach, duodenum, or colon, it is best to use endoscopic methods such as gastroscopy, endosonography, colonoscopy or virtual colonoscopy using MRI or CT instead of abdominal ultrasound. These forms of diagnostics make it possible to more accurately determine the condition of the walls and mucous membranes of these organs. An ultrasound examination can only indicate indirect signs that the patient has disorders of the mucous membrane, and its informativeness and diagnostic value of data is significantly lower than that of colonography or gastroscopy.
| Ultrasound service | Price according to Price, rub | Promotion price, rub |
| Ultrasound of the abdominal organs and retroperitoneal space (liver, gall bladder, pancreas, spleen) | 1500 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of one organ (liver, gall bladder, spleen, pancreas, bladder, adrenal glands) | 800 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of the abdominal organs and kidneys | 1700 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of the abdominal organs + ultrasound of the kidneys + ultrasound of the bladder | 2000 rub. | |
| Kidney ultrasound | 800 rub. | |
| Comprehensive kidney examination with a 20% discount (kidney ultrasound + tests) | 3530 rub. | 2999 rub. |
| Comprehensive ultrasound with a 20% discount (ultrasound of the abdominal organs + ultrasound of the kidneys + ultrasound of the thyroid gland) | 3200 rub. | 2599 rub. |
| Comprehensive ultrasound for women with a 20% discount (ultrasound of the abdominal organs + ultrasound of the kidney + ultrasound of the thyroid gland + pelvic ultrasound with an abdominal probe + ultrasound of the mammary glands) | 5800 rub. | 4599 rub. |
| Comprehensive ultrasound for men with a 20% discount (ultrasound of the abdominal organs + ultrasound of the kidneys + ultrasound of the thyroid gland + ultrasound of the prostate with an abdominal probe) | 4700 rub. | 3699 rub. |
Diseases of the pancreas and spleen
For this disease, it is possible to use traditional medicine. Medicines for the spleen and pancreas have been known to people for a long time. For this purpose, propolis, which has antimicrobial properties, is often used. Tincture from it 30 minutes before meals. The recommended dosage is 20 drops three times a day.
Hops have a great effect in reducing pain. A tablespoon of pine cones is poured into 200g of boiling water. Let it infuse for half an hour and take 2 tablespoons every day before meals. Treatment for these organs depends on what caused the disease. If the spleen and pancreatic gland have undergone an inflammatory process, antibiotics and other medications are used to eliminate the infection. For leukemia, chemotherapy is used.
Enlargement of these organs is observed with cirrhosis of the liver, anemia, any types of infections in various stages and with blood diseases. Most often this process occurs during palpation. When the spleen is not enlarged, it is almost impossible to palpate. If this organ is enlarged, it is able to capture more blood. But this process has negative effects, since the filtering capacity of the spleen is reduced. As a result, many cells are released from the blood, and this causes anemia.
Important. Enlargement of the pancreas occurs with congenital injuries, infectious diseases and damage to the abdominal cavity.
Contraindications
Ultrasound diagnostics of the abdominal organs has a number of contraindications for which such examination is not recommended. Such contraindications include:
- acute infectious diseases;
- open wounds;
- various skin lesions;
- after endoscopy of the gastrointestinal tract;
- after pneumoperitoneum;
- after colonoscopy.
If there are such contraindications, the abdominal ultrasound procedure should be postponed for several days - 2-5 days.
How to properly prepare for an abdominal ultrasound?
The main task when preparing for an abdominal ultrasound is to try to remove excess air from the intestines. Before undergoing the procedure, you must follow some nutritional rules. In order to prevent gas formation, you need to:
- A few days before the examination, stop eating bread and dairy products, and avoid carbonated drinks.
- Legumes or peas must be excluded.
- Vegetables and fruits should also be removed from the diet.
- It is worth giving up juices, confectionery and, of course, eliminating alcohol intake.
The presence of gases in the body will interfere with a clear image and make it difficult for the doctor to make a correct diagnosis.
If you want to properly prepare for an abdominal ultrasound, you should introduce some foods into your diet. The following will be useful: beef, chicken, low-fat fish, porridge cooked in water without adding butter. It is advisable to steam the food or eat it boiled. You can take some enterosorbent if there are no contraindications. It is advisable to empty your bowels naturally 2 hours before the procedure or do a small cleansing enema at home. The procedure itself is best done on an empty stomach or at least 6 hours after eating. Smoking patients must abstain from their bad habit for 4 hours before the examination. Author: Telegina Natalya Dmitrievna
Therapist with 25 years of experience
>
How to achieve energy balance
To balance the energy in the spleen and pancreas channel, emetics are usually used. This is due to the fact that energy moves upward. Classically, medium cardamom is used for this. If there is more energy in the channel than needed, products for cooling are used - celery and green tea. If there is a large excess, lotus roots and tomatoes help well. If the channel lacks energy, then together with medium cardamom, ginger, garlic, red pepper and other warming seasonings are used to balance.
Maximum channel activity is from 9 to 11 o'clock. Based on this, the time for second breakfast is determined. If the channel is in normal condition, then a light breakfast is needed. It is needed for the channel's enzyme system to work.
There are problems with the channel. Due to these problems, fluid cannot leave the body and is deposited. In such cases, diuretic tea can help. People suffering from various anemias are recommended to eat lamb or beef liver. You should also include vegetable juices in your diet. Beetroot, fennel and celery juices are good for this.