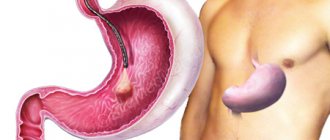
The essence of this most common endoscopic examination is to examine the upper parts of the gastrointestinal tract, namely the esophagus, stomach and duodenum.
Many patients believe that gastroscopy is “something old and only looks at the stomach,” and esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) is “something new and a more complete examination.” In fact, we are talking about the same procedure (gastroscopy is just a shortened version of a long word).
To perform esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD, gastroscopy), two types of devices can be used:
- fiber endoscopes (devices of the previous generation, with fiber optics, while the doctor looks through the “eye” on the device itself, and the image is no longer visible to anyone). The clarified, more complete name of such a study is fibroesophagogastroduodenoscopy, or fibrogastroscopy, or FEGDS, or FGDS;
- video endoscopes (devices of the latest generation, with digital optics, with an enlarged image transmitted to the monitor). The clarified, more complete name of such a study is video esophagogastroduodenoscopy, or video gastroscopy, or VEGDS.
The difference is not only in the names of the devices, but also in their capabilities.
VEGDS is the most informative method. Modern equipment allows you to conduct an examination with multiple magnification, in a special spectrum of light, examine the acidity of the stomach, determine the presence of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, and also perform a biopsy (taking small pieces of the mucous membrane for histological examination).
High image clarity and the use of additional techniques significantly expand the diagnostic capabilities of the procedure - this helps to identify even the earliest changes.
At the National Medical Research Center for Surgery named after. A.V. Vishnevsky VEGDS is carried out using the latest generation equipment.
- If the study is carried out in the morning or afternoon, then you need to have dinner the night before no later than 18-19 hours.
- You cannot have breakfast on the day of the study.
- If the study is scheduled for the daytime, then 6 hours before the test you can drink a glass of sweet tea.
- After the study, you can drink and eat no earlier than half an hour later.
How to prepare for an endoscopy at home?
If the patient is taking medications that slow down blood clotting, he should consult with his doctor two weeks before the test.
A patient with diabetes must notify the doctor in advance. In this case, the study is carried out in the morning, and you can eat food 30 minutes after its completion.
If the patient knows about the infectious diseases identified in him (hepatitis, syphilis, HIV), it is necessary to inform the doctor about this. We will maintain your privacy. The infection safety of our patients and medical staff must remain at a high level.
Pregnancy is also a reason to inform your doctor.
Endoscopy needs to be postponed for several days if an x-ray was taken immediately before it using barium as a contrast agent.
Before the study, it is important to clarify the type of anesthesia and inform the doctor about any allergic reactions to anesthetics.
It is necessary to inform the doctor if you have: respiratory failure, aortic aneurysm, epilepsy, recent stroke, heart failure.
You must start following the diet prescribed by your doctor 2 days before the test.
If endoscopy is scheduled for the first half of the day:
The study is carried out on an empty stomach. The last meal for adults is allowed no later than 12 hours before the procedure, and no later than 8 hours for children. This time is necessary to completely empty the stomach of food and allow the doctor to examine the mucous membrane without difficulty.
On the day of the study, it is prohibited to take medications (tablets) orally.
If you have removable dentures, you need to take a container to store them.
It is better to wear comfortable, non-restrictive clothing on the day of the examination (no tight collars, belts, or ties).
You can take wet wipes and a towel with you.
Before the examination, you need to remove your glasses and contact lenses.
To make you feel more comfortable, it is recommended to empty your bladder before the procedure.
If EGD is scheduled for the afternoon:
A light breakfast is allowed 8-10 hours before the study.
The remaining points do not differ from the preparation for the procedure scheduled in the morning.
Performing endoscopy of the stomach
The process of endoscopic diagnosis of the stomach, not combined with medical manipulations, takes 10–20 minutes. If a minimally invasive operation is required, the procedure time depends on the indications.
Carrying out endoscopy:
- application of local anesthetic;
- installation of a mouthpiece;
- insertion of an endoscope through the oral cavity;
- swallowing of the tube by the patient;
- guiding the tube through the esophagus into the stomach;
- examination of the mucous membrane;
- removing the endoscope and mouthpiece.
Immediately after the procedure, the patient can return to normal life. Unpleasant sensations may persist for 30 minutes to 1 hour. The cost of gastric endoscopy depends on the characteristics of the study and the need for additional manipulations.
The most typical questions about preparing for endoscopy
Is smoking allowed before the procedure?
Nicotine increases the production of gastric juice, complicating the study. Smoking is strictly prohibited 3 hours before endoscopy.
Can I brush my teeth before the procedure?
Brushing your teeth is prohibited. During an endoscopy, the doctor measures the acidity of gastric juice. Brushing your teeth and drinking water can change the acidity and the measurements will be erroneous.
What can you drink before an endoscopy?
On the day of the study, you should not drink coffee, tea, juices, or carbonated drinks. If you are very thirsty (no later than 3 hours before the test), you can drink no more than 100 ml of pure water without gas.
How many hours should you not eat before the test?
If the procedure is scheduled for the morning, then the last meal should be the night before no later than 18:00. Only easily digestible foods are allowed. If an endoscopy is scheduled for the afternoon, then a light snack is allowed early in the morning. During the examination, the doctor carefully examines the gastric mucosa, so it should be free of food.
What food and when can you take before endoscopy?
The last meal of the day before the study should be no later than 6 pm. Food can be taken in small portions, warm, preferably with a puree-like consistency.
Allowed are oatmeal and buckwheat porridge, potato soup without fried ingredients, mashed potatoes, soft-boiled eggs, boiled lean fish, steamed white poultry cutlets, baked vegetables and fruits, and dried white bread.
How to get ready for research psychologically?
A calm psychological state and the right attitude on the day of the procedure are an important component of a successful study. Modern equipment allows you to perform EGDS as comfortably and painlessly as possible. Taking tissue samples (biopsy) will also not cause pain.
If during the procedure the patient experiences nervous tension, panic increases, and there is a feeling of lack of air, it is important for him to calm down, take a deep breath, and concentrate on breathing evenly. The gastroscope cannot prevent the flow of air; it is too thin for this. The examination will go faster if the patient tries to relax as much as possible during the procedure.
If the patient cannot cope with anxiety and this interferes with the study, at the discretion of the doctor, he can be put into medicated sleep. For 24 hours after sedation, the patient will not be able to drive a vehicle and will need an accompanying person to get home.
How long does the study last?
If endoscopy is performed using local anesthesia, the patient is relaxed, does not feel anxious and follows all the doctor’s recommendations, the endoscopic examination will take 3-5 minutes. Along with the preparation, the patient will stay in the endoscopy room for about 15 minutes.
When using medicated sleep, the procedure will take approximately 30 minutes.
The main criterion for the effectiveness of esophagogastroduodenoscopy is not the time spent on the procedure, but the thoroughness of the examination!
What anesthesia is usually used for endoscopy?
The insertion of an endoscope is often accompanied by a gag reflex. If the patient does not have an allergic reaction to anesthetics (lidocaine), then the endoscopist uses it to irrigate the upper part of the pharynx and the root of the tongue a few minutes before the procedure. The drug has a bitter taste and does not alter consciousness. The patient is awake, he sees and hears everything that happens during the examination, he may have a feeling of discomfort when swallowing.
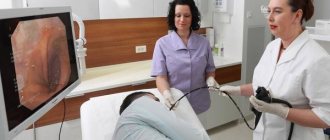
How is endoscopic examination performed?
EGD is performed by a certified endoscopist.
Before the examination, the doctor treats the upper part of the pharynx and the root of the patient’s tongue with an anesthetic to reduce gagging during insertion of the gastroscope.
The patient is then asked to clamp the mouthpiece between his teeth, which facilitates insertion of the sensor and protects the teeth from possible injury.
The patient is asked to breathe through the mouth and, if possible, not to swallow - this helps reduce the urge to vomit.
If the patient cannot cope with anxiety and interferes with the procedure, he may undergo endoscopy “in his sleep.”
After inserting the gastroscope, the endoscopist gradually moves the device through the mouth and pharynx towards the esophagus and stomach. When the gastroscope reaches the area required for diagnosis, the doctor straightens and cleans the mucous membrane, supplying air and water through a special channel of the device. This allows you to better visualize possible changes in the mucosa. The supply of air and water may be accompanied by a feeling of tension in the stomach.
If necessary, the doctor takes a biopsy. To do this, special forceps are used to take tissue samples from suspicious areas on the mucous membranes of the esophagus and stomach, after which they are submitted for histological examination. Taking samples is painless.
At the end of the study, the doctor removes the gastroscope, and his assistant frees the patient from the mouthpiece.
When can you drink and eat after endoscopy?
The patient may experience a feeling of numbness after using the anesthetic, so it is advisable to postpone drinking water and food for a while to avoid choking. 1-2 hours after the procedure, you can drink a few sips of water; if swallowing is restored and the process does not cause discomfort, you can start eating and drinking as usual.
If a biopsy was performed, then during the day after the procedure you can only eat chilled food.
What is revealed during gastric endoscopy?
The use of an endoscope equipped with a “flashlight” and a camera allows a specialist to examine the stomach in full detail. The doctor has the opportunity on the monitor screen to examine in detail the entire surface of the organ for the presence of pathological formations or processes.
During an endoscopic examination of the stomach, pathology can be detected:
- inflammation of the mucous membrane;
- signs of gastritis;
- ulcers or erosions of the mucous membrane;
- changes in vascular pattern;
- neoplasms of benign or malignant type;
- changes in the structure of the walls of the organ.
Diagnostics is also used to monitor the dynamics of the results of therapy. Monitoring treatment makes it possible to timely adjust therapeutic tactics or take more radical measures.
Side effects after endoscopy
Sometimes the patient complains that after the examination he is bothered by pain and a feeling of numbness in the throat, discomfort when swallowing, and his voice becomes hoarse. These phenomena are associated with the passage of a gastroscope; they go away on their own. There is no need to worry about this. To relieve discomfort and pain, your doctor may recommend using soothing lozenges.
What to do if your stomach hurts after endoscopy?
The pain may be caused by air being pumped into the stomach to smooth out the lining. It usually does not require treatment and goes away on its own.
Indications for gastric endoscopy
Gastric endoscopy is a complex procedure performed according to indications for diagnostic purposes or as a joint method during surgery or minimally invasive treatment.
Indications for endoscopic examination of the stomach:
- penetration of a foreign body into the gastrointestinal tract;
- detection of polyps during a previous endoscopic examination;
- suspicion of ulcers or erosions of the stomach walls;
- obstruction of the esophagus;
- control of the treatment.
Diagnostics can be combined with endoscopic treatment of the stomach for bleeding and biopsy of tumor tissue. Features of the procedure depend on the indications and the chosen method.
SIGROMANOSCOPY (RRS)
Sigmoidoscopy is an examination of the rectum and sigmoid colon using a rectosigmoid endoscope or colonoscope, which is inserted through the anus.
INDICATIONS for undergoing this procedure are:
- regular pain in the anus, throughout the lower abdomen
- bloody and mucous discharge from the anus
- frequent changes of constipation and diarrhea
- past and chronic diseases of the rectum and sigmoid colon
Often, sigmoidoscopy is performed for prophylactic purposes to prevent the development of serious diseases, before operations on the rectum. Numerous inflammations and the most minor tumors are diagnosed with the help of this study.
CONTRAINDICATIONS to sigmoidoscopy may include:
- acute inflammation in the anus - paraproctitis or thrombosis of hemorrhoids
- anal tumors
- chemical, mechanical and thermal damage to the rectum.
The question is often asked - what is the difference between sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy, which study is less painful? It is impossible to answer unambiguously, since the goals of these procedures differ.
Sigmoidoscopy helps to examine 2 sections of the large intestine - a smaller area of the human intestine, therefore it brings less discomfort, but also provides less information, and during colonoscopy the entire large intestine is examined, which gives a greater opportunity to view the condition of the intestine from the inside, therefore it is more painful, but always passes with the help of painkillers or under anesthesia, as the tube is inserted deeper; is more informative.
PREPARATION is the same as for colonoscopy (see below).
Diet
It is mandatory to adhere to a slag-free diet, food and drinking regimen. Preparation for intestinal endoscopy (colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy) begins 3 days before the study. It is forbidden to go hungry!
Authorized products:
Meat: lean (beef, veal, chicken) boiled, in the form of meatballs/cutlets. Fish: lean (cod, pike perch, perch). Dairy products: low-fat cottage cheese, milk, sour cream, kefir, cheeses, butter, yogurt without additives. Soups with low-fat, non-rich (“second”) broth; vegetable broths (without vegetables). Flour products: sponge cake without cream, crackers, bagels, bagels (without poppy seeds and sesame seeds). Durum flour noodles, white bread. Eggs: omelet, boiled, steamed eggs. Sweets: sugar, honey, jelly, syrup. Liquids: water, juices without pulp, clear compotes and jelly (without berries, pulp and grains), broths, tea. Liquid intake is not limited.
Exclude products:
Meat: fatty varieties (lamb, pork, duck), sausages, frankfurters. Fish: fatty varieties (herring, mackerel, trout). Fatty dairy products: sour cream, yogurt with fillings, cream, full-fat cottage cheese, ice cream, pudding. Soups: cabbage soup, borscht, okroshka, milk soup and cream soup. Flour products. Brown bread and bread with additives. Grain-containing products: whole grains, all cereals, nuts, poppy seeds, legumes, lentils, peas, coconut flakes, etc. Vegetables, fruits, berries: fresh and dried, raisins, prunes, cabbage, herbs. Spicy seasonings: horseradish, pepper, mustard, vinegar, sauces with grains and herbs. Mushrooms. Canned food. Pickles. Fast food. Chips. Sweets. Chocolate. Liquids: alcohol, carbonated drinks and kvass, jelly and compote with berries, pulp and grains. Drinks made from prunes.
Endoscopic Department of Toksovo Hospital
Since 2016, the endoscopic department has been separated as an independent structural unit of the Toksovo district hospital. The department is staffed by qualified personnel and equipped with modern digital video endoscopic equipment made in Japan (Olympus, Pentax).
Particular attention is paid to infection safety for the patient. The endoscopy department is equipped with automatic washing machines that use modern disinfectants. This allows you to minimize the risk of possible infection during the study.
Techniques
- gastroscopy (FGDS, esophagogastroduodenoscopy);
- rapid reaction to Helicobacter pylori infection;
- colonoscopy;
- sigmoidoscopy;
- bronchoscopy;
- taking material for microscopic examination (biopsy);
- chromoscopy (the use of dyes during the examination, which makes it possible to enhance the relief of the image and achieve clearer visualization of the smallest pathological areas);
- stopping gastrointestinal bleeding;
- endoscopic polypectomy;
- sigmoidoscopy;
- removal of foreign bodies;
- performing research under medicated sleep conditions;
Modern equipment, qualified and friendly staff allow us to quickly and accurately make timely diagnostics.
Patients who want to undergo research on a paid basis will be pleasantly surprised by the affordable prices.
The endoscopy department employs a well-coordinated team with many years of experience.