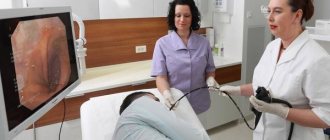
FGDS stands for fibrogastroduodenoscopy. It means diagnostics of the digestive organs, which is carried out using a gastroendoscope.
This device displays a clear image of the internal state of the abdominal organs, thereby allowing you to make the correct diagnosis and formulate the necessary treatment. When an FGDS procedure of the stomach is necessary, it is also called “gastroscopy,” which refers to an examination of the stomach.
What does FGDS mean?
FGDS is a method of examining the stomach.
What does this procedure include, based on its name:
- The word "fibro" implies a characteristic of the probe that is used in this procedure. It is made of optical fiber. A videoscope can also be used for research, with the help of which a photograph of the digestive tract organs will be displayed on the monitor.
- The name "gastro" implies an examination of the walls of the stomach.
- The word particle “duodeno” indicates that the study will be carried out on the duodenum, that is, the base of the intestine.
- The last prefix of the name “scopy” means that the doctor, using a probe, can examine the internal state of the abdominal organs.
- Also, this procedure may also be called fibroesophagogastroduodenoscopy. By the name of this procedure, you can indicate that the esophagus is also examined.
Preparation for gastroscopy
Preparation for the study begins 2-3 days in advance. Foods rich in nitrogen compounds and fiber - meat products, bread, fresh fruits and vegetables - are excluded from the diet. On the eve of the examination, the last meal is at 19-00 (do not overeat). At 6 am you are allowed to drink a glass of clean water without gas (if thirsty), you can take prescribed medications. Taking anticoagulants and smoking on the day of gastroscopy is prohibited. You need to take the results of previous examinations with you Gastrointestinal tract (endoscopic, x-ray, ultrasound), general blood test.
FGDS diagnostic
The FGDS procedure will help make a diagnosis.
The gastroenterologist also talks about the need to perform an FGDS procedure in a situation where you need to see what the mucous membrane of the stomach, the walls of the esophagus, and the duodenum look like.
Without the FGDS procedure, it is impossible to clearly make a diagnosis, and therefore it is not possible to prescribe treatment. This procedure must be completed in order to identify diseases with symptoms:
- Inflammatory conditions of the walls of the stomach, which also include acute and chronic gastritis with varying acidity in the stomach;
- Inflammatory processes of the duodenum of various origins and degrees of complications;
- Esophagitis;
- Reflux esophagitis;
- The presence of ulcers on the walls of the stomach, as well as the duodenum;
- The likelihood of developing tumors of various origins in the intestines.
This procedure must also be carried out for prevention, so as not to miss serious changes in the functioning of organs. The people most at risk are:
- Those who are over 40 years old or people who are constantly bothered by pain in this area;
- People who are genetically prone to various serious diseases, including cancer, chronic diseases, or simply often consume harmful foods, alcohol, and other things.
- This procedure is also indicated for those who suffer from nausea, constant heartburn, belching and other unpleasant moments.
- People who have had gastric surgery in the past.
- People who have previously taken glucocorticosteroids or non-steroidal drugs that have an anti-inflammatory effect.
If the patient develops gastroesophageal reflux disease.
Duration of the procedure?
FGDS is done after special preliminary preparation, including diet, giving up bad habits and stopping taking certain medications. As a rule, it is necessary to adhere to these preparatory measures several days before the scheduled day of the diagnostic procedure. This is a mandatory measure to obtain the most informative and accurate data. If we talk directly about gastroscopy, then its duration is approximately 5-10 minutes. This medical procedure is carried out exclusively by a qualified diagnostician in a specially equipped office with the necessary amount of endoscopic equipment.
This time is enough to assess the condition of the esophagus and gastric wall. If it is necessary to perform a biopsy (taking biomaterial for further microscopic examination) or obtain images, the duration of diagnosis may increase. Since FGDS involves swallowing and further advancement of the probe, some patients may experience discomfort and activation of the gag reflex. To prevent unwanted effects or pain, local anesthesia may be used. Taking into account pain relief, the procedure takes about 15-20 minutes.
.
The process of conducting FGDS
The probe must be inserted with extreme caution.
This procedure should only take place in a doctor's office. You must have a fiberscope, as well as a monitor on which the image will be displayed.
The patient should lie on his left side on a special couch. After which the doctor begins to slowly insert the probe into the patient’s mouth.
The probe is a thin cable that should not cause damage to the mucous membrane. There are cases when this examination is carried out through the nose.
In standard situations, the probe passes through the mouth, then into the esophagus, then into the stomach and only then into the duodenum. This procedure does not take much time, usually it lasts up to 15 minutes.
Upon completion, the doctor carefully removes the tube from the stomach. A patient who comes for such a procedure should not be afraid, since he will not experience pain.
In some cases, this procedure may be accompanied by unpleasant sensations. But in such situations, the doctor can numb the throat so that they don’t exist.
In certain situations, the doctor may use anesthesia. Thus, while in a dream, a person will undergo this procedure without feeling any unpleasant symptoms.
It is mainly done for children and restless patients.
The following video will tell you how to conduct gastroscopy examinations:
What is the difference?
Let us note the main differences between gastroscopy of the stomach and FGDS - we present them in the table below.
| Criterion | FGS | FGDS |
| Scope of study | Only stomach | Stomach and duodenum |
| Discomfort during the procedure | Moderate | May be more pronounced |
| Possibility of complications | Less | More |
| Comprehensive assessment of the initial part of the digestive tract | Absent | Present |
| Volume of readings | Small | Wide |
FGDS involves examination of the stomach and duodenum , which can increase the time of the procedure, but this point largely depends on the practical skills of the doctor.
During FGDS, the device passes through the pyloric sphincter into the duodenal bulb, which increases discomfort during the procedure.
With FGDS, it is possible to conduct a comprehensive assessment of the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum. Such a comparison expands diagnostic capabilities and makes the technique more valuable.
FGDS of the stomach can reveal
Gastroscopy is an effective method for examining the walls of the stomach.
Gastroscopy implies an effective method for examining the walls of the stomach.
During the procedure, the surface of the stomach will be displayed on the monitor, its pathological changes will be visible:
- Changes that may occur in the mucous membrane.
- Since this procedure allows you to obtain a clear image of the walls of the stomach, it will not be difficult to identify gastritis. In this case, the doctor will need to create a specific treatment for the patient.
- Before the probe passes through the esophagus, it is necessary to find out whether there are any formations or polyps in it.
- It is also worth finding out how the mucous membrane is deformed during the development of the disease. Where are the formations located and what are they by nature? Where is the gastric mucosa affected by Helicobacter pylori bacteria? How likely is it to get a stomach ulcer?
- What is the condition of the pylorus?
- Is there erosion on the gastric mucosa?
- The images that can be seen after undergoing the FGDS procedure are considered correct, as they can show even the slightest changes, which will allow the doctor to make the correct diagnosis. Based on this, it will be much easier to cure the disease.
Alternative Methods
Sometimes situations arise in which the use of a gastroscope is impossible - due to intolerance to discomfort, the presence of contraindications and other reasons.
In such cases, additional methods may be prescribed. Let's display them in table form and compare them with gastroscopy - note the pros and cons.
| Research method | Advantage | Flaw |
| Ultrasound | Painless examination, minimal contraindications | The mucous membrane is displayed worse than with gastroscopy |
| MRI | Painless examination, minimal contraindications | It is impossible to conduct a study if you have claustrophobia, pacemakers or metal implants |
| CT with contrast | The procedure is faster, less discomfort | The study is accompanied by radiation |
| Using the video capsule | Painless examination, minimal contraindications | The quality of the images depends on intestinal motility; there is no possibility of directed examination. |
safety for the patient’s health and information content are primarily taken into account . Sometimes it is better to endure discomfort for the sake of an accurate diagnosis than to treat complications later.
FGDS - when not to do it
The FGDS procedure also has contraindications.
This examination cannot be carried out if the patient has a sore throat or has an acute respiratory disease. When is it necessary to sign up for an FGDS procedure:
- Body temperature remains at 38 degrees Celsius.
- Constant nausea, as well as vomiting, with which blood clots come out (in this situation, the color resembles dark chocolate).
- Defecation is difficult, and the stake is black (that is, there is a trace of blood in it).
- My stomach hurts all the time.
All this suggests that some abnormalities are developing in the body. To find out, you need to urgently visit a doctor who will prescribe this procedure.
Contraindications
Before conducting a study, it is important to take into account the limitations - ignoring contraindications is dangerous for the health, and sometimes even for the life of the patient.
We list when gastroscopy cannot be done:
- problems with blood pressure are noted;
- history of stroke or heart attack;
- there is a risk of bleeding ;
- the patient has bronchial asthma ;
- mental disorders are noted.