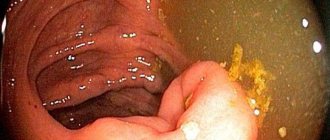
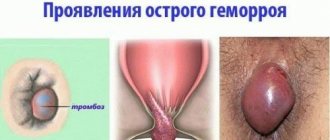
Anal polyps are usually the consequences of a person having hemorrhoids.
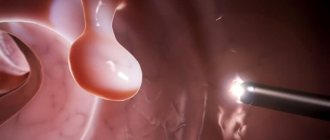
Rectal polyps (anal polyps) are benign formations that are shaped like a mushroom, a ball or a hemisphere, with or without a stalk.
The most common are glandular polyps. They usually reach from 2-3 mm to 2-3 cm in diameter and are located on a stalk. Often the leg grows large, for this reason the polyps become very mobile. This also threatens the fact that they fall out of the anal canal.
Anal polyps are peculiar skin growths in the anus. They appear with hemorrhoids, anal fissures, often during pregnancy and after childbirth. They are usually soft and painless, but can sometimes cause itching and irritation. Over time, polyps may increase in size.
Anal polyps must be removed.
The fact is that these benign formations may well turn into malignant ones. Risk factors are a large number of polyps and the age of the patient.
A proctologist treats anal polyps. The clinic employs male and female proctologists.
Briefly about the main thing
Surgery to remove rectal polyps ( polypectomy ) is necessary because colorectal cancer in 95% of cases develops from such formations.
The degree of risk of malignant transformation depends on the size, type of structure and cellular composition of the pathological growth. Timely diagnosis makes it possible to remove potential cancer using a low-traumatic method, which implies: • minimal risk of complications; • slight severity of postoperative symptoms (pain, weakness, dizziness, etc.); • short recovery period.
In the clinic of City Clinical Hospital No. 31, such operations are common practice. We recommend seeking help in a timely manner in order to get rid of the disease quickly and relatively painlessly.
The essence of the problem
Polyp is a medical term adopted to designate a formation that rises above the surface of the mucous membrane of a hollow organ. Polyps can grow in the stomach, intestines, gall bladder, sinuses, bladder, and on the inner surface of the cervix and body of the uterus.
The term “polyp” implies a benign process, but the exact nature of a suspicious neoplasm can only be determined through histological examination of its cells.
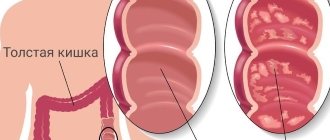
The large intestine is a favorite location for such neoplasms. Preventative colonoscopy detects polyps in 3% of patients; 70% of neoplasms are localized in the rectum.
Men suffer from this pathology 2-3 times more often than women.
The risk of development depends on age (78% of patients have crossed the age line of 55 years).
Methods for removing anal polyps
Depending on the severity of the disease, AP is removed on an outpatient basis, in a day or 24-hour hospital setting. In public clinics, removal is performed surgically using a scalpel. For this:
- The patient is asked to sit in a special chair and given local or general anesthesia.
- A rectal speculum is inserted into the AC to view the AP.
- The upper part of the AP is grabbed with a special tool and pulled outward.
- The growth is cut off with a scalpel to healthy tissue. It is taken to the laboratory for histological analysis and identification of its nature.
- A gas outlet tube is inserted into the anus to reduce the risk of damaging the walls of the anal canal in case of possible gas formation. It is removed only the next day.
The patient is discharged from the hospital after the first successful bowel movement without the use of laxatives. In the postoperative period, the patient is prescribed a diet. It prohibits the consumption of hot, salty and spicy foods, as they cause irritation of the intestinal mucosa. It is not allowed to consume alcoholic beverages, as well as foods that cause constipation, diarrhea or increased gas formation. To normalize stool, the patient is recommended to diversify the diet with vegetables, fruits, cereals and dairy products. To prevent complications, the proctologist prescribes him a course of antibiotics.
If you suspect anal polyps, contact your doctor. We employ qualified doctors with extensive experience. Our proctologists will conduct a thorough diagnosis and identify the cause of the alarming symptoms. If the diagnosis is confirmed (AP), we will remove the polyps using a laser or radio wave method. These methods of removing tumors are more preferable than the traditional use of a scalpel, since they injure tissue less and cause complications less often.
Appearance
The appearance of polyps is varied: most grow on a thin stalk, hanging into the intestinal lumen. Less common are neoplasms with a wide base, and even less common are tumor-like forms that slightly rise above the surface of the rectal mucosa. The size of a typical polyp is from 0.5 to 2 cm, but there are also giant forms that can block the intestinal lumen. As the size of the formation increases, the risk of transformation into a malignant tumor increases. Small formations (up to 0.5 cm) are represented predominantly by hyperplastic polyps , the cells of which differ little from normal epithelial cells and are characterized by a minimal risk of cancer transformation.
Large pathological elements (more than 2 cm) often have a villous surface, which is easily injured and bleeds. Such neoplasms are especially dangerous in terms of transformation into rectal cancer .
Prognosis and prevention
The development of rectal polyposis can be predicted conditionally, taking into account the nature of the formations, for example:
- anal canal adenoma - re-growth of polyps is possible;
- cloacogenic formations - high risk of cloacogenic cancer;
- hyperplastic - the pedunculated structure makes it possible to identify the disease at an early stage due to a clearer clinical picture (external manifestations);
- fibrous - the prognosis is favorable.
Preventive measures do not have a specific color. Proctologist specialists can only offer a general list of recommendations to reduce the risk of morbidity: a healthy balanced diet, an active lifestyle, a minimum of thermal procedures and excessive stress associated with frequent movement of heavy objects.
Causes
The causes of polypoid formations are disclosed only for certain types of pathology (familial polyposis). The risk groups for developing polyps in the intestines are calculated statistically. • The age factor is of great importance. WHO recommends regular colonoscopy after age 55. • In second place in importance is hereditary predisposition (benign tumors and/or rectal cancer in close relatives). • Doctors believe that additional factors are necessary for the genetic defect to occur: chronic inflammatory processes in the large intestine and/or congestion associated with stool retention. • The nature of nutrition matters: dairy and plant foods reduce the risk of benign and malignant formations. The presence of carcinogens in food, including smoked foods, can trigger the development of cancer.
Recovery phase
In the period after surgery, experts give some recommendations for a speedy recovery.
- Daily treatment of the anal canal with medications is recommended. Anti-inflammatory and wound-healing ointments based on the active ingredients fluocortolone, dioxomethyltetrahydropyrimidine, and chloramphenicol are used.
- The attending physician prescribes a diet after intestinal surgery with a large amount of plant fiber.
- Avoid eating spicy foods and drinking alcohol.
- Regular visits to the doctor to monitor recovery. This must be done until the anal canal is completely healed.
- After surgery, undergo a control endoscopy every 3 years.
It is important to monitor your health, undergo regular examinations, and visit your doctor. If polyps are found in the intestines, the symptoms of which should not be ignored, then timely surgical intervention will eliminate this problem without the development of complications. It is not recommended to self-prescribe treatment with any medications, suppositories, ointments, or folk remedies. To decide on treatment or surgery, you need to visit a specialist doctor.
If you need treatment for hemorrhoids without surgery, contact the specialists of our medical center.
Make an appointment
Symptoms
Rectal polyps are characterized by an asymptomatic course. In typical cases, formations are discovered accidentally during examinations that were prescribed for preventive purposes or for the diagnosis of another disease. Symptoms appear with significant growth sizes, as well as with multiple polyposis. • Formations consisting of fibrous tissue are prone to inflammatory reactions, which are manifested by signs of proctitis: frequent painful urge to defecate, loose stools, mucus and pus on the surface of the stool. • Adenomatous (glandular) polyps secrete a lot of mucus into the intestinal lumen, which can cause loose stools. • Villous formations often bleed, so blood may be released in the stool. • growing on a long stalk can “fall out” from the anus, attracting the attention of patients.
How are polyps diagnosed?
Patients usually come to the proctologist with complaints when the AP has reached a large size, has begun to fall out or cause discomfort. To make an accurate diagnosis, the doctor visually assesses the condition of the anus and probes the anal canal with his fingers. If deviations from the norm are detected, he performs an anoscopy - an instrumental examination of the AV using an endoscope.
Since anal polyposis has similar symptoms to other proctological diseases, the following pathologies should be excluded:
- haemorrhoids;
- Crohn's disease;
- ulcerative colitis;
- anal fissure;
- prolapse of the rectum or its mucosa;
- malignant neoplasm in the lumen of the rectum or AC.
Complications
• Large polyps can block the intestinal lumen and cause a fatal condition - acute intestinal obstruction. • Bleeding from villous growths contributes to the development of anemia. • Secretion of mucus by adenomatous tumors leads to dehydration and symptoms of hypokalemia : ___• increased fatigue; ___• muscle weakness up to the development of paralysis; ___• heart rhythm disturbances. • The inflammatory process associated with fibrous formations depletes the body and can be complicated by purulent inflammation of the perirectal tissue and sepsis. • Adenomatous and villous polyps inevitably develop into rectal cancer 5-15 years after their occurrence. Treatment for rectal cancer often involves “life with a colostomy bag” and painful courses of chemotherapy. High mortality is associated with early liver metastases, in such cases the prognosis becomes hopeless.
How to recognize a polyp
In most cases the disease is asymptomatic, but some patients may experience certain symptoms, e.g.
- pain - aching, bursting, cramping, localized in the lower or lateral part of the abdomen; after defecation, the intensity of the manifestations weakens or disappears;
- digestive dysfunction - constipation alternates with diarrhea;
- mucus or blood in the stool - this sign is characteristic of villous polyps located in the lower intestines.
Large polyps can block the intestinal lumen, which causes intestinal obstruction. The patient experiences intense pain, nausea, vomiting, lack of stool and passing gas. With this development of events, the patient needs urgent help from a surgeon.
To determine the type of polyp, its location and indications for surgery, as well as select the correct surgical treatment tactics, you must send me a complete description of the colonoscopy, histology data, and, if possible, MSCT data of the cavity with contrast, by email to my personal email address, indicate your age and main complaints. Then I will be able to give a more accurate answer to your situation.
Conservative treatment
Polyps are a surgical disease that cannot be treated with conservative methods . However, every rule has its exceptions. For small hyperplastic polyps, dynamic observation may be prescribed. The fact is that very small formations are difficult to remove without causing harm to the intestinal wall. Therefore, they are allowed to “ripen.”
Epithelial hyperplasia is associated with an inflammatory process. Therefore, conservative treatment with dynamic observation is aimed at eliminating diseases that provoke an inflammatory reaction.
Such pathologies include: • proctitis, • sigmoiditis, • hemorrhoids, • as well as inflammatory processes in the “neighboring” organs of the genitourinary system.
Types of surgical interventions
All types of surgical interventions can be divided into two large groups: traditional operations and minimally invasive techniques. Intervention using a minimally invasive method involves the use of endoscopic techniques and the latest technologies: • radio wave radiation, • laser, • electrocoagulation loop.
Such techniques are called “treatment without surgery” because they: • do not involve opening the abdominal cavity and intestinal cavity; • carried out using a bloodless method; • have a short recovery period with minimal severity of unpleasant side effects (pain, weakness, etc.).
traditional interventions to for impressively sized polyps, as well as for malignant neoplasms. If the growth is located in close proximity to the anus (up to 10-12 cm), then the operation is performed through the rectum. Otherwise, surgeons obtain surgical access by opening the abdominal cavity.
Treatment of polyps: suppositories, ASD, other means, how to get rid of them forever
Polyps are benign neoplasms formed from the mucous membranes of internal organs. Such tumors should be removed, as they can provoke the development of dangerous complications. Experts distinguish several methods for treating polyps.
Medications
The main goal of drug therapy is to reduce the growth of polyps, normalize the patient’s hormonal levels and generally reduce the severity of symptoms.
Among the assets of adenoids, experts highlight
- antibacterial - they should eliminate inflammation in the acute phase;
- atropic - with rectal bleeding;
- 7 antiseptic - their action is aimed at suppressing the activity of pathogenic microorganisms;
- vitamin complexes ;
- black - to increase the concentration of hemoglobin in blood fluid;
- hormonal - used for severe dysplastic processes in the intestines.
When diagnosing distant localization of damage, the disease should be treated with systemic drugs intended for oral use.
When a polyp bleeds, the doctor prescribes anti-polyp drugs such as hepatrombin (for bleeding accompanied by swelling and inflammation of the mucous membrane), heparin liniment (for a pathological condition accompanied by necrosis), heparoid jaw (reduces inflammation and the size of tumors).
In case of a strong decrease in hemoglobin concentration, experts recommend iron-containing drugs against polyps. These may be Ferlatum, Maltoferrin, Actiferrin, Feniuls.
Vitamins are necessary to strengthen the human body’s immune system and accelerate the restoration of mucous membranes.
When using drug treatment as a preparatory stage of a surgical procedure, to reduce the likelihood of complications in the postoperative phase and speed up the patient’s recovery time, hormonal drugs, antiseptics and antibiotics are used, and peristalsis is improved (in case of intestinal damage).
Candles
Recently, specialists are increasingly using suppositories from polyps to cure growths. The most common funds include the following.
Chistobolin
This suppository contains hemoc extract. It is absorbed into the circulatory system within a few minutes.
In addition, suppositories contain a large number of therapeutic components of plant origin, the action of which is aimed at softening the mucous lumen of the rectum. In this case, the volume of the tumor decreases and the severity of the pain syndrome decreases. A disinfection effect is also observed.
Phytocandles
It is noted that more and more patients are becoming effective in forming single tumors from the use of this drug.
^12 Thanks to the presence of herbal components, it is possible to prevent malignant neoplasms of cellular structures and reduce the severity of pain.
The drug contains substances such as thuja and cocoa butter, celandine, orange macula extract. In combination, there are positive results from using this drug.
Due to the fact that the composition also includes plantain extract, calendula, wormwood and suppositories have an antiseptic, anthelmintic and antitumor effect.
Relief
The drug is well known in the treatment of hemorrhoids. However, its effectiveness is also observed in polypoid lesions of the intestine. Used to remove clinical signs of a tumor formed from a hemorrhoid.
Hepazolon
This product belongs to a combination containing components such as lidocaine, heparin, prednisolone. Prescribed as a complex treatment for lesions of the rectal polyp and pain during bowel movements.
Operation
If a person is diagnosed with polypoid neoplasia, surgery is recommended in most cases. The choice of surgical tactics depends on the location of the polyps. The following methods are distinguished.
Surgical loop, scalpel, forceps
These methods are older and rarely used nowadays. In addition, their use is only suitable for the formation of growths on exposed surfaces, such as the cervix or nasal cavity. In addition, with such treatment, the possibility of relapse of the disease cannot be completely excluded.
Endoscopy
Used for damage to mucous internal anatomical structures. This technique is optimal for excision of polypoid tumors located in the uterus, gastrointestinal tract or bladder.
To perform surgical operations, a special device is used - an endoscope. After removal of the formation, its place is cauterized, which minimizes the risk of relapse of the disease.
Laser removal
Refers to more modern methods of processing polyps. The main advantage of this method is the non-contact effect on the pathological area. Thanks to the laser, it is possible to remove not only the tumors themselves, but also their deeper parts as they grow into an organ.
You might be interested in: Cardiac asthma. Causes, symptoms, signs, diagnosis and treatment of pathology
Diet
Special nutrition plays an equally important role in the treatment of polyps. Experts recommend removing fatty, spicy, salty and fried foods, sweets, sugar, confectionery, dairy products, and preservatives from the diet. It is advisable to eat more fresh vegetables and fruits (cabbage, spinach, raspberries, onions, garlic, pumpkin and others).
You should eat small portions at least four times a day. Don't eat food that is too cold or too hot.
ASD
No less positive recent results are shown by the use of the Dorogov antiseptic stimulant (DAS). The drug is produced as a solution.
This drug is a biogenic stimulant with an antimicrobial effect. Thanks to its use, the function of the nervous system is restored, tone increases, and the severity of general poisoning of the patient’s body decreases.
To treat polypoid formation, a small dose of the drug is prescribed. In addition, the specialist develops a special administration regime that must be followed.
Treatment of polypoids can be carried out using several methods.
However, to achieve the most positive result, experts try to give preference to the endoscopic procedure and laser removal of excrement.
To reduce the risk of relapse of the disease, it is also recommended to carry out drug therapy as a preparatory procedure before surgery.
Preoperative diagnosis
The proctologist diagnoses formations located near the anus during a digital examination. However, the main method for diagnosing rectal polyps is a hardware examination using sigmoidoscopy, which will provide a volume of information sufficient to select a treatment method: • localization, size and morphological appearance of growths; • presence of complications (bleeding, suppuration); • histological type of tumor (tissue sampling is carried out according to indications); • condition of the rectum.
If the doctor decides to undergo surgery, it will be necessary to undergo a standard preoperative examination, which includes: • a general blood and urine test; • blood chemistry; • determination of blood group and Rh factor; • coagulogram + determination of blood sugar levels; • tests to detect blood-borne infections (hepatitis B and C, HIV, syphilis); • ECG; • fluorography; • consultation with a therapist, and for women – consultation with a gynecologist.
Additionally, you may need: • gastroscopy (EGD); • colonoscopy; • CT scan of the abdominal cavity; • Doppler ultrasound of the veins of the lower extremities; • ECHO-KG.
Diagnostics
Since symptoms are not typical for the initial stage, when an intestinal polyp develops, the disease can be discovered by chance during a routine examination. Diagnosis is based on patient complaints, results of instrumental and other examination methods. Endoscopic examinations of the intestines are used.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity.
- Retroscopy.
- Irrigoscopy.
- Sigmoidoscopy.
- Finger examination.
- Colonoscopy.
- CT scan.
- Endoscopic biopsy and histological examination.
If necessary, fibrogastroduodenoscopy is prescribed.
Contraindications
There are no absolute contraindications to the removal of rectal polyps. It is recommended to postpone the operation in case of acute inflammatory processes and exacerbation of chronic diseases, as well as in case of blood clotting disorders and during the recovery period after injuries, strokes, heart attacks, operations, etc.
Endoscopic operations have their own contraindications: • significant size of the growth; • flat form of education; • malignant nature; • conditions that make it difficult to perform sigmoidoscopy.
There are also contraindications to certain types of endoscopic polypectomy. So, for example, electrocoagulation is contraindicated in patients with a pacemaker, since the high-frequency generator can disrupt the operation of the artificial pacemaker.
General information and classification of rectal polyps
Being tumor-like neoplasms, polyps are attached with a stalk to the wall of the intestine or any other hollow organ of the gastrointestinal tract. They can be called a fairly common pathological condition of a benign nature, affecting patients of various age groups, including children. Often the disease is inherited from parents - and in the vast majority of these cases, polyps are prone to malignancy, that is, to degenerate into malignant ones.
Most often, removal of a polyp in the rectum
required for male patients. The disease affects them one and a half times more often than women. According to medical statistics, about 10% of patients over the age of 45 suffer from polyps. In 1% of cases they become malignant. Early diagnosis, detection of signs of malignancy and treatment significantly increase the chances of recovery: almost 85 percent of patients survive.
| Classification of polyps | |
| Type/type of polyps | What is it characterized by? |
| By number and prevalence | |
| Single | There is one neoplasm of large diameter. |
| Multiple | Groups of tumors are diagnosed in different parts of the intestine. |
| Diffuse | They are hereditary and it is almost impossible to count their number. |
| According to morphological structure | |
| Ferrous | They are considered the most common: they account for 90% of all cases of detection of rectal polyps. They are characterized by a round shape, a smooth surface, and have a stem with a wide base. When the diameter reaches more than 20 mm, they are prone to degeneration in half of the cases. |
| Villous | They are found in 5% and are characterized by a velvety surface due to the large number of fine fibers. They have a wide base and protrude into the intestinal lumen, often covering large areas along its entire circumference. The diameter of the villous polyp ranges from 15 to 50 mm, the tendency to malignancy is up to 90%. |
| Granulating | Most often it affects pediatric patients. They grow on the mucous membrane and look like a vine. They are distinguished by a smooth surface and a brighter color than the healthy surface of the mucosa. Not prone to degeneration. |
| Hyperplastic | They are distinguished by their cone-shaped shape and small size: the diameter does not exceed 2 - 4 mm. They are able to maintain the normal structure of the mucosa with a significant increase in the number of glands, which creates the impression of thickening of the mucosa. They are reborn extremely rarely. |
Preparing for surgery
2-3 days before surgery, you should avoid coarse fiber, as well as foods that stimulate gas formation in the intestines. The ban includes black bread, products made from wholemeal flour, cabbage, legumes, fresh fruits and vegetables, milk and dairy products, juices, carbonated and alcoholic drinks.
1-2 days before surgery, care should be taken to “put off” bowel movements for several days. To do this, switch to a slag-free diet: • lean chicken and/or turkey; • cracker; • mashed potatoes; • vegetable soups; • boiled rice.
On the eve of the operation, dinner should be light and early; breakfast will have to be abandoned.
At this stage it will be necessary to cleanse the intestines. To ensure the success of the operation, the procedure is carried out twice – in the morning and in the evening.
You can use a regular medical enema (rinsing to clean water), but most patients prefer saline laxatives such as Fortrans (it should be used according to the instructions) or Microlax microenemas.
The use of rectal anti-inflammatory suppositories in gynecology
Rectal suppositories with anti-inflammatory activity are widely used to treat various inflammatory processes of the reproductive system, including endometritis and andexitis.
In addition, such suppositories have analgesic and antipyretic effects. It should be remembered that in gynecology, rectal suppositories with anti-inflammatory effects, as a rule, are only an addition to basic therapy.
Thanks to suppositories, the effect of other antibacterial drugs is enhanced and the healing process is accelerated.
In the treatment of various diseases of the female reproductive system, the following suppositories are most often used: Voltaren, Diclofenac, Flamax, Movalis.
Voltaren. A product based on the active component diclofenac sodium. This substance belongs to the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that have analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic effects.
The dosage of the drug is determined by the attending physician, usually using the minimum effective dose to avoid the development of side effects. Suppositories are inserted directly into the rectum. The use of the drug is recommended after bowel movement. The standard starting dose is up to 150 mg of the drug every 24 hours. It can be divided into two or three applications.
Voltaren is not recommended for stomach ulcers, gastric ulcers, urticaria, bronchial asthma, and acute rhinitis. It is also prohibited to use it to treat children under 18 years of age. This can cause thrombocytopenia, anaphylactic reaction, diplopia, depression, headache, myocardial infarction, vasculitis.
Diclofenac. A product based on the active component diclofenac sodium. It has moderate antipyretic, analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects.
The following dosage is used for treatment: up to 50 mg of the drug is used no more than three times within 24 hours. It is not recommended to use Diclofenac in the case of the aspirin triad, gastric ulcers and hematopoiesis. It should be used with caution when treating pregnant women.
Diclofenac can cause diarrhea, vomiting, liver disease, anemia, hair loss, paresthesia, edema, allergies, photosensitivity, headache.
Flamax. A product based on the active component ketoprofen. A non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug that also has antipyretic and analgesic effects. Inflammation usually subsides within a week after starting therapy.
The dose is determined by the attending physician depending on the patient’s condition and the severity of the disease. The standard dose is as follows: 100-200 mg of the drug should be divided into several doses over one day. This drug can be combined with other drugs to achieve effective results.
Flamax is not recommended for the treatment of patients with rhinitis, bronchial asthma, peptic ulcer, Crohn's disease, diverticulitis, hemophilia, gastric ulcer, kidney disease, hyperkalemia.
Pregnant women and children under 6 years of age should also not take the drug.
May cause allergies, dyspepsia, stomatitis, headache, insomnia, dizziness, conjunctivitis, myalgia, exfoliating dermatitis.
Movalis. A product based on the active component Meloxicam. This substance is a derivative of phenolic acid, therefore it has antipyretic, anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects.
Movalis suppositories are usually used 7.5 mg of the drug once a day. If the patient's condition is more severe, the dose may be increased to 15 mg. To avoid the development of side effects of suppositories, it is recommended to take the minimum effective dose.
It is not recommended to use the drug for stomach ulcers, Crohn's disease, acute and chronic liver diseases, bronchial asthma, gastric bleeding, hyperkalemia, pregnancy. Taking Movalis can cause nausea, gastritis, colitis, hepatitis, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, bronchospasm, photosensitivity, headache, and kidney dysfunction.
[7], [8], [9], [10], [11], [12]
Anti-inflammatory rectal suppositories for the intestines
Rectal suppositories with antibacterial action are often used to treat intestinal diseases, especially colitis. They can quickly eliminate the pathogens that cause the disease. The most popular anti-inflammatory suppositories for the treatment of inflammatory bowel diseases are Hexicon, Polygynax, Meratin-Combi, Mikozhinax.
Hexicon. A drug based on the active component chlorhexidine bluconate. It is characterized by an antibacterial effect against gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms (Nisseria gonorrhea, Treponema pallidum, Gardnerella vaginalis, Chlamydia spp., Ureaplasma spp.).
The dosage of hexicon depends on the patient’s condition, so it is determined solely by the attending physician. In addition, the dose and duration of therapy also depend on the disease itself.
Doctors do not recommend the drug for dermatitis and allergies; it is also worth using Hexicon when caring for children. Taking this medicine may cause itching, allergies, dermatitis, photosensitivity and taste disturbances.
Polygynax. A drug based on the active components of polymyxin B sulfate, neomycin sulfate, nystanin. It is an effective antibacterial agent, which is characterized by its activity in the fight against: Corynebacterium spp., Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Proteus vulgaris, Ureaplasma urealyticum.
The dosage of the drug is individual, so it is determined by the attending physician. In addition to intestinal inflammation, polygynax is also used to treat vaginal infections in women. Therapy lasts up to twelve days. It can be used as a prophylaxis (6 days).
There are no specific contraindications for the use of these suppositories, but their use may cause allergies.
Suppositories Meratina. A product based on the active components nystanin, ornidazole, prednisolone and neomycin sulfate.
It is recommended to administer once daily (preferably at night) at a fairly low dose. It is worth lying down for a while after the injection (at least fifteen minutes). On average, therapy takes about ten days.
There are no contraindications to the use of the drug, but it should be noted that in some cases Meratin-Combi can cause allergic reactions or irritation.
Mikozhinax. A drug based on the active components nystinin, chloramphenicol, metronidazole, dexamethasone acetate.
The standard dose of the drug is as follows: One suppository is administered once a day. The duration of therapy is determined by a specialist, but should not exceed ten days.
- The following diseases are absolute contraindications for the use of these suppositories: Breastfeeding, treatment of pregnant women, allergies to any of the ingredients of the medicine, treatment of children.
- Mikozhinax can cause diarrhea, oral inflammation, hepatitis, pancreatitis, encephalopathy, agranulocytosis, pustules, rash, nystagmus, diplopia and headache.
- [13], [14]
Anti-inflammatory rectal suppositories in proctology
The most common disease for which rectal suppositories with anti-inflammatory effects are used is hemorrhoids.
You might be interested in: Loratadine. instructions for the drug, use, price, release forms
They are usually made from synthetic and natural ingredients. The most popular plant components: calendula, propolis, sea buckthorn oil.
Among the effective suppositories in proctology, the following should be highlighted: Proctosan, neo-anusol, anusol and procto-livenol.
Proctosan. A product based on the active components of titanium dioxide, bufexamac, lidocaine hydrochloride monohydrate, bismuth subgallate. It is characterized by astringent, analgesic, anti-inflammatory and moisture-absorbing effects.
The dosage of suppositories is as follows: One suppository is inserted deep enough into the anus, up to two times within 24 hours. It is very important to take medications after a bowel movement. Therapy lasts up to ten days; there is no need to stop treatment after the disappearance of visible symptoms of the disease and improvement in general condition.
Proctosan is not recommended for tuberculosis or syphilis. Hemorrhoids should not be treated with these tablets during pregnancy or lactation. They should not be used to treat children. Taking proctosan can cause allergies, itching and burning.
Neo-Anusol. A drug based on the active components of tannin, bismuth nitrate, resorcinol, zinc oxide, iodine, methylthionide chloride. It is characterized by an astringent and antiseptic effect.
The standard dose consists of a suppository once or twice a day. There are practically no contraindications to the use of the drug, but it is worth noting that Neo-Anusol can cause allergies.
Anusol. A product based on the active components of zinc sulfate, bismuth tribromine phenate, and a thick beauty extract. It has antiseptic, anti-inflammatory, analgesic, astringent, antispasmodic, and desiccative effects.
The standard dose is one suppository no more than twice a day. Please note that you can use a maximum of seven suppositories per day (only if prescribed by a specialist).
Anusol is not recommended for use in cases of tachyarrhythmia, intestinal atony, glaucoma, myasthenia gravis, prostate adenoma. It should not be used in children, pregnant women, or women while breastfeeding. May cause loose stools, headache, dry mouth, constipation, rapid heartbeat.
Proto-Glivenol. A drug based on the active ingredients lidocaine and tribenose. Quite quickly eliminates the main symptoms of hemorrhoids.
The standard dose is one suppository twice within 24 hours (preferably morning and evening). If symptoms improve, it can be used once a day. Not recommended for pregnant women and children. Should not be taken if you have liver disease.
Procto-Glyvenol may cause allergic reactions, bronchospasm, anaphylactic reactions, swelling and skin irritation.
Let's consider the pharmacodynamics and pharmacological effects of rectal anti-inflammatory suppositories based on procto-glivenol.
How is the operation performed?
The operation can be performed either under local anesthesia or general anesthesia. The choice of anesthesia depends on the type of surgery, the size and number of polyps to be removed, as well as the health and sensitivity of the patient’s nervous system.
Most often, benign tumors of the rectum are removed using minimally invasive methods. Such operations can be performed under local anesthesia. Anesthesia is necessary to ensure painless access to the pathological element. The actual removal of the growth does not cause any discomfort.
Low-traumatic operations are performed using a bloodless method (blood vessels are cauterized during polyp removal). In one procedure, the doctor can remove up to four pathological elements, so if there is a significant number of formations, the operation will have to be repeated after 2-3 weeks.
Recovery period
The duration of the recovery period depends on the method of surgical intervention and can range from 2 weeks to 2 months.
Postoperative dietary restrictions also vary widely.
If the operation was performed on an outpatient basis or you were in the hospital for a short time, we recommend that you carefully monitor your own health and immediately consult a doctor if suspicious symptoms appear: • increasing fever; • blood in stool; • persistent pain syndrome; • swelling of the extremities.
Even in cases where the injuries received during surgery are minimal, doctors recommend sticking to a slag-free diet 1 week
During the recovery period, you should avoid increased physical activity, thermal procedures, alcohol and drugs. Smokers are advised to reduce their nicotine intake to a minimum.
Polyps in the rectum: symptoms
Polyps do not have specific clinical manifestations indicating that they are the cause of their appearance. Their severity and general presence are determined by the diameter of the neoplasms, their number, location, coverage and morphological structure. The presence/absence of malignant development also plays an important role. As a rule, the development of small polyps occurs almost unnoticed by the patient, and they are diagnosed accidentally during examinations. As for large specimens, the symptoms characteristic of them also appear in other pathological conditions.
| Symptom | How is it manifested? What is it characterized by? |
| Feeling of discomfort and presence of a foreign object in the rectum | The most specific clinical manifestation for polyps, developing as a result of their pressure on the intestinal wall. Appears only when their formation is of medium or large diameter and is periodic due to peristalsis. It can take on a bursting character when large in size due to constipation. |
| Painful sensations | They occur when large polyps close the intestinal lumen and cause fecal stagnation, which stretches the walls of the organ, causing pain. |
| Stool disorders | They manifest themselves at the initial stage in the form of rare, prolonged constipation, followed by diarrhea. As the polyp develops, constipation appears more often and lasts longer. |
| Impurities of blood and mucus in stool | The appearance of mucus is provoked by increased secretion of the glands of the mucous membrane, which produce mucus to facilitate the passage of feces through the intestines. It develops due to the presence of a polyp, which acts as an irritant. As for blood, its presence indicates that the integrity of the intestinal blood vessels is impaired or there is pinching/death of the polyp. |
Reviews from patients and recommendations from doctors
We analyzed patient reviews of operations performed to remove polyps. There is practically no negativity. Surgical interventions are well tolerated, the postoperative period goes smoothly.
Some patients consider the “short-term” effect of the operation and the need to undergo annual preventive examinations as a disadvantage.
In most cases, recovery occurs without the need for further surgery. However, for example, adenomatous and villous polyps are today considered as precancerous conditions, and patients who have undergone surgery require constant medical supervision. In other cases, a repeated consultation with a proctologist once every 1-3 years is sufficient.
The likelihood of relapse and the time frame for re-application can only be determined by your attending physician after the initial rehabilitation period has passed.
Reviews of the work of doctors at City Clinical Hospital No. 31 can be read here.
Treatment of polyps in the large intestine with traditional methods
On the Internet you can find many recipes for treating polyps in the large intestine using traditional methods. We hasten to warn our readers that many of the recipes provided (celandine and other poisonous plants) can cause significant harm to your health.
Colon polyps usually occur against the background of an inflammatory process. By experimenting with your own body, you can significantly increase the inflammatory response and cause the formation of new pathological growths.
By postponing surgery, you risk missing your chance to use low-traumatic methods that allow you to remove polyps relatively painlessly.
Methods for diagnosing polyps
According to proctological literature, most of the detected malignant formations in the intestines are the consequences of polyps. Therefore, at the slightest suspicion of an imbalance, you must contact a proctologist who will find out the cause of the ailment. In addition to collecting information about symptoms and family history, the following diagnostic methods are used:
- Physical examination - a visual external examination to assess the shape and gaping of the anus, the condition of the surrounding skin, as well as palpation (digital examination allows you to identify the presence of polyps in the anal canal and exclude other pathologies).
- Instrumental diagnostics - anoscopy and rectoscopy (sigmoidoscopy) give a more detailed picture of the inner surface of the intestine 25 cm from the anus, colonoscopy allows you to examine all parts of the colon and exclude oncological and inflammatory diseases.