- home
- >
- Useful articles
FGDS (fibrogastroduodenoscopy) is a modern instrumental method for studying the esophagus, stomach, and intestines.
During the procedure, an endoscope is used, which allows you to obtain the most accurate research results. Conducting an FGDS requires mandatory preparation, which should be known in advance. Features of psychological preparation for FGDS
Psychological attitude is an important factor that often hinders the timely completion of the procedure. Patients often feel afraid when they are told about the need for this study and refuse it. The doctor must convince of the need for the procedure, give an objective assessment of the current state of health, and explain how the results of the study will affect the effectiveness of treatment.
The doctor also needs to be given complete information about how the manipulation will take place so that the patient understands what to expect. During the FGDS study itself, it is better to mentally distract yourself from what is happening, but do not forget to listen to the doctor. Correct behavior allows diagnosis to be made quickly and with minimal discomfort.
Particularly sensitive patients are offered the procedure under general anesthesia. The duration of the study is short-term, and the discomfort lies only in the irritant that stimulates the gag reflex. Physiological preparation and compliance with all rules and recommendations given by medical specialists help ensure maximum psychological comfort during the procedure.
Is it painful to do FGDS?
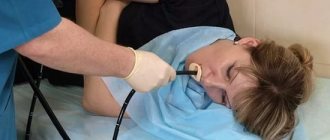
Gastroscopy cannot be called a painful procedure. Most often, discomfort is associated with gagging. To reduce the severity of the gag reflex, a local anesthetic is used, which is used to treat the oropharynx. But this does not help all patients.
Most often, when undergoing FGDS, people complain about:
- severe attacks of nausea;
- discomfort in the places where the probe passes;
- copious amounts of saliva;
- burping;
- panic attacks caused by a feeling of lack of air.
Severe pain during the examination can occur due to exacerbation of a stomach ulcer, perforation of the walls of the organ, or violation of the rules of the procedure. To avoid the appearance of unpleasant symptoms, it is necessary to properly prepare for gastroscopy and strictly follow all the doctor’s recommendations.
Reasons why FGDS is prohibited
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy has a number of contraindications. These include:
- diseases of the esophagus, with signs of dysphagia;
- cerebrovascular accident;
- myocardial infarction;
- acute inflammation of the pharynx;
- some mental illnesses.
The possibility of performing an FGDS on a pregnant woman cannot be ruled out, but only on the recommendation of a doctor if there are serious indications.
How to do FGDS, you will learn from the video:
What you can and cannot do before gastroscopy
How is it easier to undergo an FGDS of the stomach? You need to prepare properly - follow a diet, refuse to eat and drink before the procedure, and prepare yourself mentally.
You need to start following a diet 2 days before the examination, you must exclude heavy and gas-producing foods from your diet.
List of prohibited products:
- alcoholic, carbonated drinks;
- cocoa, sweets with chocolate, tea, strong coffee;
- spicy dishes;
- any types of nuts;
- legumes;
- black bread;
- milk;
- fatty meat and rich broths;
- fast food, smoked meats.
In order for the stomach to have time to cleanse itself, before FGDS it is necessary to eat food that is quickly digested. This includes boiled lean meat and fish, rice and buckwheat porridge, vegetable soups, eggs, fermented milk products with a low fat content, and thermally processed vegetables.
To make it easier to tolerate FGDS, the last meal should be 12 hours before the procedure. You can drink water 2 hours before. If these rules are followed, even if a gag reflex occurs when the probe is inserted, only drool will come out.
Before gastroscopy, you should not smoke, take any medications, chew gum or brush your teeth. FGDS is not performed for a runny nose, elevated body temperature, inflammation of the tonsils of the pharynx, mucous membrane of the larynx or trachea. With these pathologies, the tissues swell, their sensitivity increases, and when the endoscope is inserted, unpleasant sensations will occur.
How to prepare for the procedure?
A gastroenterologist will tell you in detail about all the rules for preparing for an FGDS of the stomach, and here we will focus on the most important of them. So, two days before the procedure you should completely avoid alcohol and spicy foods. But smokers can breathe a sigh of relief, since this rule does not apply to their habit. You only need to quit smoking a few hours before your visit to the doctor. Smoking immediately before the procedure provokes the release of gastric juice, which may cause an incorrect diagnosis.
Another important rule: FGDS should be performed on a completely empty stomach. If the procedure is scheduled for the morning, the patient cannot eat after 20.00 the previous day, and if it is planned after lunch, a light breakfast is allowed in the morning. Neglecting this rule can cause discomfort and vomiting in the patient, and for the doctor it will make it difficult to study the walls of the stomach. The optimal food is considered to be dishes made from vegetables, fruits, fish and chicken. It is not recommended to eat nuts and chocolate, as they take a very long time to be processed in a sick stomach.
How to undergo an FGD easier - psychological preparation
To make it easier to undergo gastroscopy, you need to choose a qualified doctor. A good specialist will help reduce feelings of anxiety; correct implementation of the procedure reduces the intensity and frequency of negative effects.
So that the patient is not afraid, the doctor explains all the nuances of the study. It is the lack of reliable information and reviews from friends that leads to the fact that patients refuse to undergo gastroscopy, because they are sure that it will be painful and unpleasant.
There is no need to be ashamed if during the procedure you burp, drool, or begin to feel sick. These symptoms bother almost all people; they do not indicate that something is going wrong. Medical personnel constantly encounter such manifestations, so they do not pay attention to them.
How to behave during FGDS
You must bring a medical card or a doctor’s referral and two disposable diapers to the office where the gastroscopy will take place. Before entering the office, change your shoes or put on shoe covers and take off your outerwear.
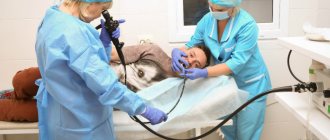
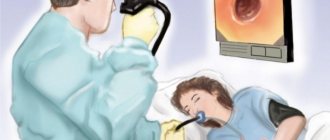
After a preliminary conversation, the specialist places the subject on his side, with his legs bent at the knees. A mouthpiece is inserted into the mouth to facilitate the passage of the probe. An anesthetic is applied to the root of the tongue. The doctor begins to slowly insert the endoscope tube, which passes through the mouth into the oropharynx, down the larynx and esophagus into the gastric cavity. The specialist examines the condition of the mucous membrane, measures the pH of gastric juice, and does a test to detect the bacteria Helicobacter pylori. If necessary, tissue particles are taken for histology.
It is important to relax as much as possible, breathe deeply and slowly through your nose only, and try not to swallow saliva. The duration of FGDS is 5-30 minutes.
It is necessary to make an appointment with a gastroenterologist and have a gastroscopy if you are often bothered by attacks of nausea and vomiting, or have problems with swallowing. Dangerous symptoms include lack of appetite, flatulence, chronic cough without other manifestations of diseases of the respiratory system. In case of stomach pathologies, pain in the epigastric region, belching and heartburn are a concern, a feeling of heaviness occurs after eating, and weight loss occurs for no reason.
Procedure
FGDS of the stomach takes very little time - no more than 10 minutes. If there is a need to take material for research (biopsy), this time increases to 15 minutes. Before the procedure, the patient must undergo testing for resistance to the injected material (it should not cause allergic reactions).
It all starts with the doctor placing the patient on their side and spraying the mouth with an anesthetic, which helps minimize the gag reflex and relieve discomfort. Then the doctor inserts a plastic mouthpiece into the mouth, which is needed in case the patient suddenly reflexively clenches his teeth. After this, an endoscope is inserted into the opening of the mouthpiece, which the doctor gradually moves into the esophagus and then into the stomach. As a rule, the patient tolerates the procedure calmly, although discomfort is, of course, present. In extreme cases, the doctor may prescribe anesthesia, but this issue is discussed in advance.
During an FGDS, the doctor observes an image of the inner walls of the stomach on a monitor screen in real time. Modern diagnostic equipment makes it possible to obtain high-quality, high-resolution images, which can then be printed and attached to the patient’s medical record. An endoscope can also be used to administer medications, remove growths, and stop internal bleeding on the walls of the esophagus. In this case, the procedure takes a little longer. After removing the endoscope, the patient feels fine and can go home immediately.
Alternative options
One way to avoid the gag reflex during FGDS is to insert a probe through the nose. This method is more convenient for patients, allows maintaining vocal contact with a specialist, and does not interfere with normal breathing. The examination can be carried out if there are problems with swallowing or narrowing of the esophagus. Disadvantages - not all clinics have the necessary equipment; the nasal mucosa can be injured. Contraindications: neoplasms in the nasopharynx, deviated nasal septum, swelling of the nasal mucosa. The study is not carried out if there is a tendency to nosebleeds, after traumatic brain injury and myocardial infarction, with unstable angina, or the acute phase of a stroke.
How to do FGDS painlessly:
- Intravenous administration of benzodiazepines. The drug removes fear and relaxes muscles. After sedation, the person falls asleep. The method is often used when performing FGDS of the stomach in children and especially excitable adults. 5-10 minutes after the end of the examination, the patient wakes up and remains under the supervision of medical personnel for an hour. Side effects are rare.
- General anesthesia. Rarely used, usually before a planned operation the anesthesiologist administers a mixture of several painkillers; connection to a ventilator is not required.
- Capsule endoscopy. A new method for painless FGDS. The patient needs to swallow a small capsule with a camera that will pass through all parts of the digestive tract. Disadvantages - it is impossible to carefully examine the affected areas of the mucosa, do a biopsy or test to detect Helicobacter pylori infection.
Some pathologies of the stomach can be detected using ultrasound, radiography, CT and MRI of the abdominal organs, and electrogastroenterography. But if there are signs of gastrointestinal bleeding, exacerbation of varicose veins of the esophagus, or a foreign body in the stomach or esophagus, FGDS cannot be avoided.
Can complications occur after FGDS?
Negative consequences after gastroscopy rarely occur. Most often, nausea and discomfort in the stomach bother you for 2-3 hours. Some patients experience pain when swallowing. When collecting biomaterial for histological examination, minor internal bleeding may occur. If the probe is not properly disinfected, the walls of the organs become infected and become inflamed.
If you behave restlessly during the examination and do not listen to the doctor’s advice, injuries to the stomach and larynx may occur.
All complications are short-term and no specific treatment is required. But if after gastroscopy the temperature rises, blood appears in the stool and vomit, or abdominal pain intensifies, you should immediately consult a doctor.
FGDS is an informative and safe method of examining the stomach and has a minimal list of contraindications. The procedure is not contraindicated for children, pregnant women, or the elderly. By following simple preparation rules, you can significantly reduce discomfort during the study.
Indications for the purpose of the study
FGDS is done when there is a complaint about the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
FGDS is carried out for any complaints about the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Thanks to her, I diagnose the causes of pain, nausea, vomiting, bitterness in the mouth, bloody spots in the vomit, a feeling of fullness in the stomach and other symptoms.
Using this technique, diseases such as stomach ulcers, gastritis, polyps in the stomach, and cancer of the digestive organs are successfully detected.
The FGDS method is also convenient for performing targeted treatment with medications. For example, it is used to apply medications to stop bleeding from an ulcer.
For purely diagnostic purposes, the use of FGDS does not end. Through fibrogastroduodenoscopy, it is also possible to remove swallowed foreign bodies and even perform a minor operation (remove a polyp, for example).
Despite the need for this method of diagnosing diseases, many people are in a state of panic before going to the doctor. Considering that the procedure is not pleasant, they can be understood. But it should be remembered that the speedy determination of the correct diagnosis and prescription of treatment depends on it.