Vitamin composition of citrus
Grapefruit can rightfully be called a valuable storehouse of vitamins and nutrients. Its fruits are rich in:
- vitamin complexes A, B, C, E, PP;
- pectins;
- bioflavonoids;
- organic acids;
- essential oils;
- calcium, potassium, phosphorus, magnesium, and also contains iron, zinc, and selenium in small quantities.
88% of the fruit consists of water, 6.5% are saccharides, another 6.5% are carbohydrates, 1.8% are dietary fiber, 5% are organic acids, 0.7% are proteins, 0.2% are fats, 0.5% - ash.
Calorie content
Grapefruit is a low-calorie product: 100 grams of pulp contains only 35 kcal. Therefore, the fruits are very popular among those who want to get rid of extra pounds.
Mango in remission
You can indulge in an exotic delicacy only if stable remission of the disease is established. The delicious fruit not only brings pleasure to gourmets, but also has a positive effect on many complex processes. The advantages of mango are:
- antioxidant activity (due to phenolic compounds and vitamins);
- the presence of beta-carotene, which transforms into vitamin A and helps improve twilight vision and protect against harmful ultraviolet radiation;
- mild laxative and diuretic effect;
- the content of plant pepsin - papain, which breaks down animal proteins and increases the absorption of meat products and egg whites;
- immunomodulatory effect;
- stimulation of the proliferation of beneficial intestinal bacteria;
- a large amount of useful ascorbic acid (up to 175 mg per 100 g of mango);
- stabilizing effect on the nervous system (improved sleep, reduced irritability, etc.);
- the presence of a number of essential amino acids;
- positive effect on altered cholesterol metabolism (reduction of “bad” cholesterol).
Beneficial properties of grapefruit
The fruit has a wide range of beneficial properties:
- Enriches the body with vitamins (one fruit can satisfy the daily dose of vitamin C).
- Helps strengthen the immune system.
- It is an effective antioxidant, neutralizes the negative effects of free radicals, and helps eliminate toxins and other harmful substances from the body.
- Lowers cholesterol levels.
- Helps strengthen blood vessels and improve their elasticity.
- Improves mood, relieves irritation, anxiety, and promotes better sleep.
- Improves digestion and metabolism.
- Improves appetite.
- Activates intestinal motility and prevents constipation.
- Helps burn excess calories.
- Lowers blood glucose levels, thereby allowing people with diabetes to reduce the need for insulin.
- Normalizes fat metabolism, prevents the accumulation of fats in the body.
- Normalizes liver function.
- Prevents the formation of gallstones.
- Promotes the resorption of swelling of the tissues of internal organs.
- Strengthens bone tissue, improves the condition of joints, nails, and hair.
- Has a beneficial effect on the skin, improves its tone and elasticity.
- Reduces bleeding gums.
- Nourishes the retina of the eye, maintaining visual acuity.
- Helps reduce the severity of symptoms of toxicosis during pregnancy.
Thus, grapefruit has a beneficial effect on the entire human body, helping to prevent the development of many types of serious diseases or cope with them.
In addition, eating this fruit is a good prevention of cancer, as it is a powerful antioxidant and helps remove free radicals from the body.
Disease prevention
To prevent exacerbations of chronic pathology, the following rules should be followed:
- Sausages and fatty foods are completely removed from the diet - they do not contain the vitamins and microelements necessary for the body;
- It is allowed to eat porridge cooked in water or low-fat milk;
- Fruit consumption is reduced to a minimum.
Inflammatory processes in the pancreas are incompatible with alcoholic and low-alcohol drinks. Complete abstinence from alcohol will reduce the frequency of exacerbations of the disease and prevent its development.
Nicotine addiction, self-medication with medications (antibacterial, diuretic, to reduce high blood pressure, anti-diabetes, etc.), lack of necessary physical activity lead to the formation of inflammation in the digestive organs. Elimination of predisposing factors reduces the risk of developing pancreatitis several times.
Possible harm of sour fruit
Basically, the possibility of causing harm to the human body is due to the fact that the fruit contains a large amount of acids. For this reason, grapefruit is contraindicated for:
- Increased acidity of gastric juice.
- Gastritis, which is accompanied by high acidity.
- Peptic ulcer disease.
- Exacerbation of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (including pancreatitis), if they are not accompanied by low acidity.
- Personal intolerance.
By increasing the acidity of gastric juice, grapefruit will lead to even greater irritation and inflammation of the tissues of the digestive tract. In turn, this can cause the development of severe pain in the epigastric region, intestinal and stomach colic, nausea, vomiting, and spasms of the pancreas.
In addition, increased acidity leads to the activation of digestive enzymes. During the period of disruption of the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, such exposure entails injury to pancreatic tissue and disruption of its performance. Due to the significant amount of organic acids in the product, its consumption in large quantities leads to damage to tooth enamel.
It is also contraindicated to eat fruit if you have cholecystitis. The product activates the production of hydrochloric acid and bile enzymes, so its use can significantly aggravate the course of the disease.
With personal intolerance, as well as consumption of the fruit in large quantities, an allergy may develop. It usually manifests itself as a small skin rash, burning, itching of the skin, and difficulty breathing.
For this reason, it is not recommended to eat fruit during lactation in order to protect the baby from the risk of allergic reactions and intestinal colic.
Interaction with food
The fruits should not be eaten with milk, mushrooms, rice, or baked goods made from white flour. Combining such products can lead to diarrhea, bloating, and flatulence.
Interaction with medications
The fruit should not be consumed while taking:
- antibiotics;
- anticoagulants;
- antidepressants;
- hormonal;
- antiviral;
- antihistamines;
- antifungal;
- antitussives;
- antitumor drugs.
This is explained by the fact that the fruits contain furanocoumarin, which blocks the antioxidant abilities of the liver and also prevents it from removing drugs from the body. Therefore, when taking such medications and grapefruit at the same time, there is a high risk of drug intoxication.
It should also be noted that grapefruit can reduce the effectiveness of contraceptive medications.
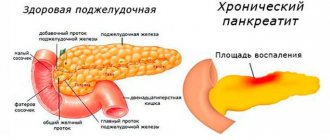
Symptoms of pancreatitis
The disease occurs in two variants: acute and chronic. In the first case, clinical signs appear:
- Pain syndrome - of a specific nature, with dull or cutting sensations, localized in the area of the right or left hypochondrium;
- Increased body temperature - along with it, the level of blood pressure can sharply increase or decrease; such a manifestation serves as a sign of an inflammatory process rapidly developing in the pancreas;
- Changes in skin color - pallor, a grayish tint to the face; attacks of nausea - accompanied by constant dryness in the mouth;
- Severe vomiting - inclusions of bile in the secretion is considered the main symptom of pancreatitis.
The main principle of treating the disease is to reduce the load on the gallbladder and pancreas. The chronic form of the pathology develops over a long period and can be asymptomatic for several decades.
The initial stages of the disease are manifested by discomfort in the hypochondrium, lumbar region or on the left side of the chest after each meal - for 1-2 hours.
Unpleasant sensations arise:
- After a lot of fatty, spicy food;
- Consumption of alcoholic beverages, coffee;
- Chocolate and confectionery.
The problem is associated with the impossibility of normal processing of these products by the pancreas and the gradual development of the inflammatory process. After the disease progresses into an exacerbation, the patient feels heaviness in the abdomen, nausea, weakness, and pain.
An advanced form of pancreatitis leads to the gradual death of organ tissue and its complete dysfunction. Insufficient production of enzymes provokes the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus at the last stage of the disease.
Is it possible to eat grapefruit when diagnosed with pancreatitis?
Grapefruit in small quantities is beneficial for the pancreas and other digestive organs when they are not damaged and function without disturbances. Has the following effect:
- It improves appetite, normalizes fat metabolism, improves digestion and metabolism.
- The product lowers sugar and cholesterol levels, which greatly facilitates the work of the pancreas.
- In addition, the fruit activates intestinal and pancreatic peristalsis, improving the outflow of digestive enzymes from the gland into the duodenum.
- Thanks to the large amount of vitamin C, fruits strengthen the protective functions of internal organs, inhibit the activity of pathogenic microorganisms and prevent the development of infectious and inflammatory processes.
On the other hand, grapefruit contains a significant amount of organic acids, and its consumption leads to an increase in the acidity of gastric juice. This is the main reason for excluding fruit from the diet of people suffering from gastrointestinal diseases.
Whether it is possible to eat grapefruit with pancreatitis depends on the form, severity of the disease, as well as the type of fruit.
At the acute stage
Grapefruit is strictly contraindicated for acute pancreatitis. The fruits contain a lot of acid. During diseases of the digestive tract that are not associated with low acidity of gastric juice, eating any acidic berries and fruits leads not only to irritation of the mucous membranes of the stomach, but also to an increase in the activity of digestive enzymes. With pancreatitis, the passage of these enzymes from the pancreas to the intestine is difficult, so most of them remain in the gland and begin to digest its tissue.
In case of inflammation of the organ, the activity of pancreatic secretions should be minimized, which grapefruit does not contribute to at all.
In addition, the fruit contains fiber, which, if the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract is disrupted, irritates the intestines. This leads to the development of symptoms such as flatulence, bloating, stool upset, intestinal or stomach colic.
Grapefruit is prohibited for pancreatic diseases also because it inhibits the liver’s ability to remove drugs from the body. Treatment of pancreatitis, especially its acute attacks, requires the mandatory use of medications (for example, antibiotics, enzyme preparations, antacids). If drugs are not cleared from the body in a timely manner, there is a high risk of patient intoxication, which can be fatal.
In remission
Many nutritionists, given the increased acidity of grapefruit, are of the belief that it should not be consumed even if remission occurs. It is believed that the fruit can cause a relapse of exacerbation of the disease. However, today the choice of such fruits has expanded significantly and slightly acidic varieties of fruit can be found on sale, for example:
- Sweetie.
- Oroblanco.
- Chandler.
- Star Ruby.
Therefore, upon the onset of stable remission, as well as in the chronic form of pancreatitis outside the stages of exacerbation, grapefruit is allowed to be eaten periodically, but only in small quantities.
Fruits and acute pancreatitis
In the first few days of the period of exacerbation of pancreatitis, the patient is recommended to undergo therapeutic fasting. All food products are prohibited, including fruits and berries. At the recovery stage of therapy, some of them are allowed to be introduced into the menu. The main condition is that to reduce the additional load on the digestive system, it is recommended to remove the skin from the fruit and extract the seeds.
To avoid unwanted reactions of the body, berries and fruits should be consumed after appropriate heat treatment (baking, adding to casseroles, making purees and other dishes or drinks).
List of healthy fruits and berries for acute process
Some berries and fruits, when consumed during the treatment of acute pancreatitis, can produce a therapeutic effect. For example, rosehip decoction or currant compote have a number of beneficial properties for the immune system, the digestive system and replenishing the supply of vitamins in the body. Berries and fruits are introduced into the diet in minimal portions (preferably after heat treatment).
Useful fruits:
- currant;
- rose hip;
- strawberry;
- raspberries;
- sweet apples;
- bananas.
Rules for the use and introduction of the product into the diet
You can start trying grapefruit for pancreatitis no earlier than three months after acute attacks of the disease have stopped, provided there is a positive dynamics of treatment, there is no need for drug treatment and there is no pancreatic pain.
It is recommended to choose slightly acidic and ripe varieties of fruit so that the fruits are not too sour.
- You are allowed to eat no more than three slices of fruit per day.
- Grapefruit can be consumed no more than 2-3 times a week.
Under no circumstances should you eat fruit on an empty stomach. It is best to eat a slice of fruit after a meal. On the day grapefruit is included in the menu, it is not recommended to consume other sour dishes and foods.
If, after eating the fruit, signs of irritation of the digestive tract begin to appear (pain in the abdomen, intestines or hypochondrium, nausea, vomiting, bloating, flatulence, diarrhea), the fruit should be completely excluded from the diet for another month. Afterwards, you can try one slice of fruit and see how your body reacts. If it responds with a worsening of the condition, it is better to avoid eating such fruit altogether.
Dietary requirements
Damage to the pancreas requires changes in the usual diet, a transition to a gentle menu. A diet for pancreatitis is a prerequisite for normalizing the body’s functioning; it is recommended for patients at any form and stage of the disease.
The slightest deviation from the prescribed diet leads to an exacerbation and requires the following rules:
- During the first three days, the patient must remain in bed;
- At this time you cannot eat, you are only allowed to drink in sufficient quantities: still mineral water, green tea, liquid jelly and rosehip decoction;
- After the pain disappears, the patient is gradually transferred to a strict diet with low-fat foods.
For pancreatitis, the menu consists of lean meat, soups cooked in vegetable broths, cottage cheese, and cheeses with minimal fat content.
How to choose a fruit?
People suffering from pancreatitis are advised to buy only the ripest fruits of slightly acidic varieties. These grapefruits have rich orange-red skin. Varieties with pale yellow, green skin are the most sour.
- A high-quality fruit should not have damage, signs of spoilage, rotting, or black spots.
- The aroma of ripe good fruit is rich and pleasant. If the fruit has no smell at all, it is most likely not ripe.
- The grapefruit skin should be smooth and elastic. And if the peel is very soft, fingerprints remain on it when pressed, most likely the fruit has already begun to deteriorate.
If the purchased fruit is not ripe, it does not need to be put in the refrigerator. This fruit should be placed in a sunny window to ripen for several days. Obviously unripe fruit should not be cut, since after this it will no longer ripen and will simply deteriorate if stored for a long time.
Before eating, be sure to remove the peel and skin from the fruit. If you have pancreatitis, it is also strictly forbidden to eat fruit seeds, as they contain a lot of acid and bitterness.
Article rating: (total 1 votes, rating: 5.00 out of 5)
Livestock products
The disease does not require complete exclusion of fish and meat products. They must contain a minimum amount of fat; for preparing dishes in their dietary section, the following is used:
- Rabbit, chicken;
- Veal, turkey, beef;
- Pike, zander;
- Bream, pollock, cod.
Eating baked skin or crust, classic scrambled eggs is strictly prohibited. To diversify your diet, you can eat steamed omelettes and boiled chicken eggs. Fermented milk products are also an integral part of the diet.
Allowed low-fat foods are:
- Sour cream, yoghurts;
- Cottage cheese, fermented baked milk;
- Kefir, goat milk.
Classic whole milk is prohibited as a drink - it provokes dyspeptic disorders and increased gas formation. It can be used in cooking. A small amount of unsalted butter will not harm the diseased pancreas, but you need to eat it in reasonable quantities.
Pancreas-safe recipes for quince dishes
These are, as mentioned above, fruits that have gone through several stages of culinary processing. Moreover, an integral part of the fruit itself - pectin - a jelly-forming compound, will help in creating marmalades or jellies. Quince juice can be diluted with cherry, pear, and apple juice.
Recipe No. 1: Quince marmalade
This dish is widespread in the Old World. For example, in Spain, marmalade is traditionally poured into carved wooden dishes, in Italy - from ceramics, and in Great Britain it is cut into cubes and eaten with sharp cheese and buns.
Ingredients:
- 2 kg of quince fruits,
- sugar (to taste),
- 3 tablespoons lemon juice.
The fruits are peeled, cut into two parts, and the membranes and seeds are removed. The halves of the fruit are placed in boiling water and cooked until they acquire the required softness. After this, the quince is placed in a colander to drain the water.
The fruit halves are weighed and pureed using a food processor. The resulting puree is mixed with an equal weight of sugar.
A small amount of lemon juice is added to the mixture, and the container with it is placed on medium-intensity heat. The puree is cooked with regular stirring for one and a half hours until thickened. Checking readiness is carried out as follows: a small amount of puree is placed on a plate, and a line is drawn along its surface using the handle of a wooden spoon. The puree is ready if there is a trace left on it.
A baking tray up to 30 mm deep is lined with parchment paper, and the resulting puree is poured into it. The surface is leveled using a special spatula. The baking sheet is placed in a cool place for a day.
After hardening, the resulting marmalade is cut into small cubes, which are laid out on a sheet of parchment paper so that they do not touch each other. Dry in this way for three days. The cubes should be turned over regularly.
On the fourth day, the marmalade is sprinkled with granulated sugar and placed in an airtight container. The product can be stored for six months.
How to eat cherries without causing harm?
Cherry is a sweet, juicy berry that is prohibited during the acute phase of pancreatitis, and during remission of pancreatitis it is advisable to consume it, following a number of simple rules:
- It is undesirable to eat fresh fruits, since fiber and acids provoke an exacerbation of pancreatitis.
- The best option is considered to be the use of thermally processed berries - in the form of jelly, compote, pudding, jelly, mousses.
- Doctors recommend consuming dishes and drinks containing cherries only after meals: on an empty stomach they can cause a deterioration in well-being.
- Eating fresh berries becomes possible at the stage of long-term stable remission of the disease (at least 1 year). Before this, they must be peeled and pitted. You should start with 2-3 berries at a time. If well tolerated, the daily amount of cherries is increased to approximately 100 g.
Cherries and cherries are very healthy and tasty berries that bring many benefits to a patient with pancreatitis if used correctly and with prior consultation with a nutritionist or gastroenterologist. During an exacerbation, this product is strictly prohibited for use in order to avoid an increase in the symptoms of acute inflammation and the development of life-threatening complications. When the stage of remission of the disease is reached, cherries are introduced into the menu of a sick person as part of many healthy drinks or desserts.