Both examinations are highly informative diagnostic methods that make it possible to make a diagnosis in difficult cases when diseases of the lower parts of the digestive system are suspected.
Intestinal ultrasound or colonoscopy expands the possibilities of medical care for patients with signs of gastrointestinal pathology. The test helps make a diagnosis when symptoms have just begun and the disease is at an early stage. In such a situation, it is possible to completely cure almost any disease.
After questioning, examining and palpating the patient, the doctor prescribes a series of laboratory tests and also gives a referral for instrumental diagnostic methods (ultrasound of the intestines or colonoscopy). The choice of method is determined by the patient’s condition and the nature of the suspected pathology.
The fundamental difference between the methods is that when performing ultrasound, internal organs are studied through the surface of the body using sensors that emit ultrasonic waves that are reflected from anatomical structures. Colonoscopy allows you to see the walls of the gastrointestinal tract from the inside through direct inspection using a video camera attached to a probe that is inserted into the intestines.
For the patient, intestinal ultrasound is a more comfortable and painless procedure, but often diagnosis is only possible using colonoscopy. The methods cannot replace each other; in complex clinical situations, both procedures are required. The doctor decides which test will be ordered first - intestinal ultrasound or colonoscopy - based on the symptoms and manifestations of the disease.
Indications
Both methods have a common purpose - examination of the gastrointestinal tract for the purpose of diagnosing inflammatory diseases, neoplasms, internal bleeding, foreign bodies, and structural anomalies of organs. The specificity of each method provides an advantage in diagnosis when a specific disease is suspected.
Common symptoms for which an intestinal ultrasound or colonoscopy may be prescribed:
- prolonged constipation, alternating constipation and diarrhea;
- the presence of bloody, mucous, purulent impurities in the stool, change in the color of stool;
- bloating, increased gastrointestinal motility, increased gas formation;
- pain of any nature, localized in the abdomen, groin, near the anus;
- intestinal colic;
- weight loss;
- suspicion of cancer or the development of metastases in the gastrointestinal tract;
- the presence of a space-occupying formation when palpating the gastrointestinal tract.
In the diagnosis of gastrointestinal diseases, the manifestations of which are localized on the mucous membrane, colonoscopy is prescribed. The study has the advantage of being able to take a biopsy for histological examination of the material, as well as perform operations to remove detected tumors and stop bleeding.
Colonoscopy is performed for the following pathologies:
- bleeding from the lower gastrointestinal tract, manifested by traces of blood in the stool;
- nonspecific ulcerative colitis;
- gastrointestinal polyps;
- cancer or benign neoplasm;
- Crohn's disease;
- intestinal obstruction of unknown etiology.
Ultrasound is prescribed as a screening method, as well as after operations on the gastrointestinal tract to monitor the healing and recovery processes. As a method for diagnosing diseases, ultrasound allows one to study parts of the gastrointestinal tract and surrounding tissues and obtain information about the boundaries of pathological foci and formations.
Intestinal ultrasound is prescribed for the following indications:
- clarification of the localization of endometriosis in the presence of appropriate symptoms;
- inflammatory diseases – appendicitis, colitis, enteritis;
- suspicion of germination of pelvic tumors in the gastrointestinal tract;
- ischemic conditions of the gastrointestinal tract;
- injuries;
- elongated sigmoid colon;
- peritonitis;
- irritable bowel syndrome;
- gastrointestinal deformations, fecal stones;
- Hirschsprung's disease.
Intestinal ultrasound is an absolutely safe and painless examination that can be performed an unlimited number of times. Colonoscopy is more traumatic and unpleasant for the person being examined.
Contraindications
When deciding which study will be performed - intestinal ultrasound or colonoscopy, the doctor makes a decision in each case individually, depending on the patient’s health condition and the presence of contraindications.
Ultrasound examination is not dangerous for healthy people and for patients with poor health. Ultrasound is a universal method with a small number of limitations that are associated with the condition of the patient’s external integument and his mental health.
Contraindications to intestinal ultrasound:
- open wounds,
- acute phase of infectious diseases;
- inappropriate behavior of the patient due to mental illness.
Unlike intestinal ultrasound, colonoscopy is an invasive procedure - it is introduced into the internal environment of the body. The examination is quite traumatic and painful.
There are a number of contraindications when colonoscopy is not performed:
- intestinal bleeding;
- bronchial asthma in exacerbation;
- high-grade arterial hypertension;
- coronary heart disease, heart attack, heart failure;
- stroke, shock;
- pregnancy;
- epilepsy and other mental illnesses;
- exacerbation of inflammatory bowel diseases.
The high information content of colonoscopy is determined by the possibility of direct examination of the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract and taking material for further examination. The procedure has a number of relative contraindications: menstruation, infectious diseases, hernia, decreased blood clotting. Once these conditions are eliminated, colonoscopy becomes possible.
Preparation
Normally, the gastrointestinal tract is filled with feces and air inclusions. This state of the organ makes it difficult to obtain informative images reflecting the condition of the walls of the gastrointestinal tract, which reduces the diagnostic value of the study. Before conducting any examination of the gastrointestinal tract, preliminary preparation is necessary.
General principles of preparation:
- For several days before diagnosis, it is necessary to follow a diet aimed at reducing the load on the gastrointestinal tract and reducing gas formation;
- limit as much as possible the consumption of legumes, cabbage, onions, mushrooms, dairy products, eggs, sweets, carbonated drinks;
- exclude alcohol;
- drink at least 2 liters of fluid per day;
- It is recommended to include lean meat, chicken, cereals, and vegetable broths in the diet;
- meals are taken in small portions 5-6 times a day;
- You must come for the study at least 6 hours after your last meal;
- if diet is not enough to reduce the amount of gases in the gastrointestinal tract, you should take activated charcoal and espumizan on the day before the examination;
- if constipation occurs, you should use laxatives;
- On the eve of the procedure, it is necessary to cleanse the large intestine with an enema.
Neglecting the preparation rules leads to insufficient cleansing of the stomach, which is a relative contraindication for the procedure. If an examination is carried out in such a condition, then there is a high probability of missing a small pathological formation, and the diagnostic value of the study will be reduced.
When visiting a doctor, you must take a referral for testing and medical documentation related to your current state of health - an advisory opinion from the attending physician with a preliminary diagnosis, laboratory test results. If an intestinal ultrasound or colonoscopy is repeated, you must have the results of previous examinations with you. The maximum amount of information about the patient’s health status helps the doctor make an effective diagnosis.
Examination for certain categories of patients
Preparation for ultrasound for men and women is not fundamentally different, with the exception of pregnant women.
Pregnant
Metabolic processes in pregnant women are more intense than in other people. They need to eat more often to ensure that they and the baby are receiving nutrients. Their meal intervals are reduced to two hours, and they must eat in small portions. Therefore, they need to eat their last meal two hours before the test.
Children
Infants stop feeding 3 hours before the ultrasound scan. Older children should not eat 4 hours before the procedure. You are only allowed to drink a little water, but the reliability of the study results may be reduced.
Patients with diabetes
A long gap between meals for diabetics can negatively affect their well-being and cause glycemic coma. For such patients, ultrasound is prescribed in the morning. If this is not possible, then you are allowed to have breakfast and undergo an examination after 3-4 hours. They should take sweet tea and crackers with them to have a snack after the procedure.
How is an ultrasound of the intestines performed?
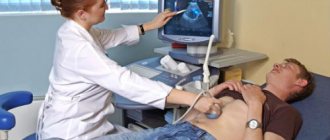
The procedure is carried out by several types of sensors with different purposes and depth of penetration of ultrasonic waves. The patient enters the doctor's office, takes off his clothes, then lies down on his back. The main method of examination is transabdominal. A transparent gel is applied to the abdomen, which is necessary to conduct the signal from the sensor to the body. The doctor examines the projection area of the gastrointestinal tract, receiving visual information on the device monitor.
Inspection of the rectum during a transabdominal examination is difficult, since the organ is deeply located and protected by the pubic bone. To diagnose possible pathology of the rectum, a transrectal sensor is used with insertion directly into the rectum. The patient is asked to turn on his side and bend his legs. In women, a transvaginal sensor is sometimes used for better access to the gastrointestinal tract.
When performing an ultrasound, a liquid can be injected into the large intestine, which allows you to examine the walls of the straightened tract. The technique allows you to evaluate peristalsis and absorption capacity of the mucous membrane.
Carrying out an ultrasound
How the research is conducted depends on its type.
The duration of transabdominal analysis is no more than 30 minutes. Before the examination, the patient is placed on his back so that the knee joints are bent, which will allow the abdominal region to relax.
The doctor applies a special product in the form of a gel to the abdomen, which improves the interaction of the device’s sensor with the skin and increases the ultrasound signal.
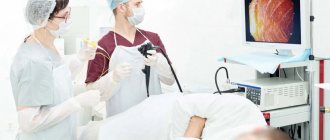
How is a colonoscopy performed?
The success of the procedure depends on the quality of the patient’s preparation and the accurate implementation of the doctor’s instructions. The examination is carried out using local or general anesthesia.
The patient undresses, lies on the table on his left side and pulls his legs to his chest. The tip of the colonoscope is inserted into the anus, to which a flexible tube is attached. The advancement of the tube into the large intestine occurs gradually, with the injection of a small amount of air, which ensures a moderate expansion of the walls of the gastrointestinal tract and easier passage of the tube.
Through the tube, a video camera and instruments can be brought to the walls of the tract to perform operations, stop bleeding, and take a biopsy. During the procedure, the mucous membrane is examined. The detected polyp can be removed using a surgical instrument inserted through a tube. The presence of a neoplasm or ulcer means taking the material with special forceps for examination in the laboratory.
The duration of the examination depends on the volume of manipulations, on average – 20-60 minutes. After the procedure, the patient may experience discomfort - accumulation of gas, the urge to defecate. The condition normalizes on its own within a few hours; to speed up the process, you can take espumizan or activated carbon.
Virtual colonoscopy
The method is the construction of a model of the gastrointestinal tract with the ability to study the relief of the walls of the tract, neoplasms, defects of the mucous membrane, and developmental anomalies. The image is obtained as a result of a computed tomography scan of the abdominal cavity with preliminary expansion of the gastrointestinal tract cavity with air.
Indications and preparation for the procedure are similar to other instrumental examination methods. The advantage of virtual colonoscopy is that it is non-invasive, painless for the patient, and the ability to build a detailed three-dimensional model of the gastrointestinal tract. The method is used when an oncological process in the gastrointestinal tract and adjacent tumors of the abdominal cavity and pelvis is suspected, as well as to monitor postoperative changes in the large intestine. The examination is prescribed when an intestinal ultrasound or colonoscopy cannot be performed due to contraindications.
The disadvantage of this method is the inability to perform surgery or take material for research. Due to the use of ionizing radiation, the method has limited use in pregnant women and children.
Types of intestinal ultrasound
Two ultrasound methods are used to visualize the intestines: transabdominal and rectal. The transabdominal method involves ultrasound examination through the abdominal cavity. This method is used without filling the intestines, while contrast is introduced, and the bladder must be full.
The rectal method uses a rectal sensor. You can also do an intracavitary examination using a vaginal probe. This method is optional and is only possible for women.
Content:
- Types of intestinal ultrasound
- Indications for ultrasound diagnostics
- Preparing for an ultrasound examination
- Carrying out an ultrasound
- What can you find?
- Ultrasound examination of the intestine in children
- Preparing a child for an ultrasound
- Advantages of intestinal ultrasound
To maximize coverage of the intestines, most often 2 methods are used at once. Transabdominal ultrasound does not always give 100% results, since in 15% of cases the bladder is not full enough. Rectal ultrasound is more informative, but may be contraindicated in some people. Such a study is not carried out for people who have been diagnosed with stenosis of the terminal part of the gastrointestinal tract. Based on this, it becomes clear that none of the methods is ideal, so only their combination can give the most accurate result.
Ultrasound diagnostic results
On the monitor during the examination, you can see and record the size, shape of the organ, the thickness of the tract walls, and the presence of pathological formations several millimeters in size.
How does pathology manifest itself on ultrasound diagnostics:
- There is normally no fluid in the abdominal cavity. The accumulation of fluid appears as an anechoic area. The presence of fluid indicates peritonitis, internal bleeding, inflammatory processes, and tumors. Based on the location of the liquid, one can judge the reasons for its appearance;
- intestinal obstruction manifests itself as increased visualization of intestinal loops filled with gas or liquid. The reason for this condition is the closure of the lumen by a foreign body or tumor;
- appendicitis is manifested by thickening of the appendix, accumulation of gases in the lumen of the gastrointestinal tract, and a small amount of fluid in the abdominal cavity;
- tumors and neoplasms are characterized by an increase in the thickness of the intestinal wall due to hypoechoic areas of round or irregular shape. Ultrasound shows the size of the tumor, the degree and depth of the lesion, and invasion into neighboring organs;
- adhesions are high-density strands, often combined with deformation of nearby sections of the tract.
The conclusion is drawn up by the ultrasound doctor and given to the patient. The document contains a detailed description of the state of the gastrointestinal tract and all pathological changes and neoplasms. The information allows the attending physician to make the correct diagnosis.
What to do before the study
Before performing an ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity, it is necessary to consult a gastroenterologist. He collects anamnesis, finds out the presence of chronic diseases, genetic predisposition, and allergies to drugs. If necessary, prescribes additional studies and tests.
Ultrasound is a non-invasive diagnostic method and does not require additional tests. You only need to undergo chest fluorography (FLG), donate urine and blood for a general analysis. However, in order to make an accurate diagnosis, other studies are prescribed along with ultrasound, the number and list of which depends on the preliminary diagnosis.
Not only a gastroenterologist, but also other specialists can prescribe an examination. For example, an ultrasound examination helps a neurologist monitor the condition of the liver during long-term use of drugs that affect this organ; an allergist prescribes a prescription to identify pathologies of the liver and gallbladder that can cause an autoimmune disease; a hematologist is interested in the condition of the hematopoietic organs: the spleen and liver. They also prescribe a whole range of additional tests and studies.
Consultation with a gastroenterologist before performing an ultrasound of the abdominal organs
Colonoscopy results
A healthy large intestine has a smooth, shiny, pink mucous membrane, without areas of hyperemia or edema. Cicatricial changes, diverticula, pathological narrowing or expansion of the intestinal lumen, ulcers, and polyps are normally absent.
What some diseases look like:
- with nonspecific ulcerative colitis, the mucous membrane becomes bright red, swelling, granularity, and areas of hemorrhage appear;
- intestinal diverticula look like branches of the gastrointestinal tract with an entrance diameter of up to 2 mm, at the site of the lesion the tone of the intestinal wall is increased, the folds are thickened;
- cancer looks like a heterogeneous neoplasm of irregular shape with a granular surface, surrounded by an area of edema, and bleeds when touched.
The results of examining the intestinal walls with a video camera can be obtained shortly after the procedure. Based on the results of the conclusion, the attending physician makes a diagnosis or refers the patient for further diagnostics. If a biopsy was performed, the result of the examination of the fragment will be issued within two weeks. Microscopic examination allows you to make the most accurate diagnosis.
What can be detected on an ultrasound
Ultrasound is best combined with other diagnostic methods to provide a comprehensive picture of intestinal health.
During diagnosis, pathologies such as:
- Inflammatory process in the appendix area;
- Colitis (inflammation of the large intestine);
- Diseases of the sigmoid colon;
- Helminthic infestation and negative changes caused by it;
- Hemorrhages;
- Hemorrhoids and their inflammation;
- Bowel displacement;
- Obstruction.
In representatives of the fair sex, pathologies of the reproductive system can be detected during rectal diagnostics.