Today we would like to discuss a sensitive issue. The functioning of the gastrointestinal tract largely determines our well-being, vigor and good mood. Moreover, it is important not only proper nutrition, but also stable emptying so that the body does not waste waste products. It’s very good if you have never encountered such problems, and morning toilet does not cause unpleasant associations. But most people know firsthand what a spasm of the rectal sphincter is. The symptoms are extremely unpleasant; they include pain and distension in the lower abdomen, which are difficult to cope with without taking antispasmodic drugs. Today we will talk about this phenomenon and ways to combat it in a little more detail.
A little about physiological characteristics
What is the rectal sphincter? This is a muscle element. It is located directly in the rectum and is designed to regulate the excretion of feces. On the one hand, it performs a locking function, and when sufficient mass accumulation occurs, it opens. This is usually a controlled process. The rectal sphincter opens only in the right place (in the toilet), and not on the way home from work.
In order for the sphincter to work smoothly, its surface is lined with a large number of receptor cells, and the inner part is smooth muscle, which forms a ring. While the child is small, it works in a natural mode, that is, immediately after the emerging need, bowel movement follows. As you get older and potty trained, your rectal sphincter becomes more trained to effectively hold back stool and gas.
The main causes of pain in the anus can be:
- Oncological disease,
- Anal fissure (small tear in the lining of the anus),
- Anal itching,
- Anal sex,
- Anorectal fistula (an abnormal passage between the anus or rectum, usually leading to the skin near the anus),
- Coccydynia or coccydynia (pain in the tailbone),
- Constipation,
- Crohn's disease (inflammatory bowel disease),
- Diarrhea causing anal irritation
- Fecal impact (a mass of hardened stool in the rectum caused by chronic constipation),
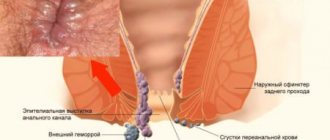
- Hemorrhoids (swollen and inflamed veins and venous nodes located in the anus or rectum),
- Levator anus syndrome (spasm in the muscles surrounding the anus)
- Perianal abscess (pus in the deep tissues around the anus),
- Perianal hematoma (collection of blood in the perianal tissue caused by a ruptured vein, sometimes called external hemorrhoids),
- Proctalgia fugax is a transient, transient proctalgia (an attack of sharp pain that suddenly occurs in the rectum, which can last for several minutes or hours,
- Proctitis (inflammation of the rectal mucosa),
- Solitary rectal ulcer syndrome (rectal ulcer),
- Thrombosis of hemorrhoidal node,
- Injury,
- Ulcerative colitis,
- Ulcerative proctitis (inflammatory bowel disease).
You should seek medical help immediately if:
- there is intense rectal bleeding that cannot be stopped, especially if it is accompanied by dizziness or a feeling of general weakness;
- anal pain progresses, spreads to other areas or is accompanied by anal discharge, as well as fever or chills;
A scheduled visit to the doctor is necessary if:
- the pain lasts for several days and painkillers do not help;
- if pain is accompanied by changes in bowel function or bleeding.
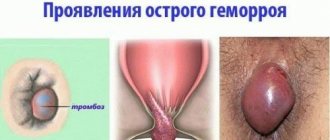
With hemorrhoids that develop quickly or are particularly painful, a blood clot (thrombus) may form inside the venous node. A hemorrhoidal clot, although painful, cannot break loose and travel through the bloodstream, so it will not cause serious complications such as stroke, pulmonary embolism, or coronary embolism—commonly associated with blood clots that have formed in other parts of the body.
Be sure to see your doctor for advice about rectal bleeding if you are over 40 years of age. Goal: to rule out a serious disease such as colon cancer.
What is a sphincter spasm?
This is not a disease, but only its manifestation, so doctors will have to conduct a full diagnosis to determine what causes this phenomenon. And we will start by telling you what characterizes a spasm of the rectal sphincter. Symptoms are primarily pain. It is not caused by inflammation, but by painful muscle contraction, which has a psychological or somatogenic nature.
This picture is typical for most proctological pathologies, so if doctors talk about spasm of the rectal sphincter, they mean that there are no organic lesions in this section of the intestine. That is, there is pain of unknown etiology.
More about symptoms
How can you suspect that your rectal sphincter is spasming? Simple enough. Severe, paroxysmal pain will not allow you to make a mistake. In this case, the following signs are observed:
- Acute paroxysmal pain that radiates to the perineum. In this regard, patients tend to attribute symptoms to chronic kidney diseases and problems of the pelvic organs.
- Please note that pain may accompany the act of defecation or occur separately from it.
- Most often, after taking a bath, the pain subsides significantly, although it may not go away completely.
- The important point is the reason why the spasm occurs. This is the key to the solution, as well as to the appointment of adequate treatment. Most often, it is provoked not even by somatogenic diseases, but by psycho-emotional ones: worries, chronic stress and neurological problems, as well as inadequate physical activity.
Diagnosis of anal fissure
Pain in the anus is a symptom not only of anal fissure, but also of many intestinal diseases, including malignant neoplasms. For this reason, doctors at the proctology department conduct a comprehensive examination for patients who come to the Yusupov Hospital. Initially, pain from anal fissure is relieved using a blockade with local anesthetics or ointment applications with painkillers. Then the following examinations are carried out:
- Digital examination of the rectum;
- Anoscopy;
- Sigmoidoscopy;
- Ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs.
If indicated, patients undergo magnetic resonance or computed tomography. After establishing an accurate diagnosis, proctologists collectively select the optimal treatment option for anal fissure, which would not only eliminate pain, but also achieve healing of the mucosal defect and avoid re-rupture of the anoderm.
What everyone needs to know
We have already touched on this issue a little, but it is extremely important to understand this point in more detail. Treatment of rectal sphincter, or rather its effectiveness, directly depends on how well the doctor understands the causes. What causes the spasm? This is a contraction of smooth muscle. This may involve the external or internal sphincter. But that's half the problem. When smooth muscles contract, nagging, sometimes pulsating pain occurs, varying in duration and intensity, as nerves and blood vessels are compressed.
Most often, this pathology occurs in middle-aged people. At the same time, there is no division between men and women; everyone is susceptible to the disease. Why is this particular area of the intestine prone to spasms? This is due to good innervation. What can be included here:
- constipation;
- inflammation;
- violation of the integrity of the mucous membrane;
- varicose veins or blood vessels.
As a result, the patient feels severe pain, which is difficult to correct with medication.
Anal sphincter spasm (transient proctalgia)
Characteristic manifestations of anal sphincter spasm are pain of varying duration and intensity, radiating to the tailbone, perineum, hip joints or lower abdomen. Pain during spasm is paroxysmal, can appear during defecation or occur without any visible connection with the condition of the rectum (emptied or not emptied) and other circumstances. There is a low effectiveness of analgesics, while the pain syndrome often disappears or weakens after completing a bowel movement or taking a warm bath.
Spasm of the anal sphincter can be provoked not only by the act of defecation, but also by chronic stress, acute emotional and psychological stress, overwork, heavy physical exertion and some neurological diseases. At the same time, spasm of the anal sphincter often itself becomes an impetus for the occurrence of long-term stress, increased emotional instability and the development of mental disorders of a neurotic level.
Depending on the type of pain syndrome, there are two forms of anal sphincter spasm: with long-term and short-term proctalgia. With short-term proctalgia, the pain is strong, pulling or stabbing. Due to the high intensity of the pain syndrome and its irradiation to neighboring anatomical areas, patients suffering from anal sphincter spasm often find it difficult to determine the location of the pain and may regard this symptom as a manifestation of diseases of the reproductive or urinary system. With prolonged proctalgia, the pain is usually less intense and difficult to relieve with analgesics.
With secondary spasm of the anal sphincter, which occurs against the background of hemorrhoids, anal fissure and other diseases, as a rule, there is a clear connection between proctalgia and the act of defecation. The pain appears with the urge to stool, intensifies with straining and persists for several hours (sometimes up to a day or more) after the end of defecation. Constant pain negatively affects the quality of life of patients suffering from anal sphincter spasm, and can cause fear of defecation, due to which patients “postpone” going to the toilet. This further aggravates the violations that have arisen.
With primary spasm of the anal sphincter, the connection with the act of defecation is less clearly visible. Pain often appears at night or in the morning. Patients develop insomnia. The causelessness of the appearance of pain, sleep disturbances, initial emotional instability and predisposition to neurotic disorders create a psycho-emotional mood that contributes to the emergence of cancerophobia and hypochondriacal spectrum disorders.
Risk group
Before we talk about how to relieve spasm of the rectal sphincter, we will dwell on one more point. There is a certain group of patients in whom the risk of this pathology is more likely. These are the people:
- mentally unstable;
- suffering from central nervous system pathology.
As a result of the above pathologies, spasm of the anus develops, which increases emotional lability and, as a result, pain. In addition, this syndrome may be caused by various innervation disorders. This is a consequence of injury or difficult childbirth. Often, spasm of the anal sphincters develops in emotionally unstable women. Men fall into this category less often, although gender, as we have already mentioned, is not predominant.
What causes pain with anal fissure?
Initially, an anal fissure is accompanied by short-term acute pain that occurs during bowel movements, and the appearance of a streak of blood on the surface of the stool or bloody spots on toilet paper. If in this case complex treatment was not carried out or pain therapy was inadequate, the pathological process enters the chronic stage. The pain becomes constant, and vasospasm of the anal area occurs. The mucous membrane of the rectal canal suffers from oxygen starvation, and healing of the resulting defect does not occur.
The edges of the fissure are calloused; at its bottom, doctors find fibers of the internal anal sphincter. A vicious circle arises: pain with anal fissure causes ischemia of the mucous membrane, which increases the severity of the pain syndrome. Patients have a fear of defecation. They retain stool, and during defecation they feel severe pain when a hard fecal lump passes through the spasmodic sphincter. With persistent spasm of the anal sphincter, a painless act of defecation with anal fissure becomes impossible. In this case, proctologists prescribe drugs that have an antispasmodic effect or perform an injection of botulinum toxin into the anal sphincter.
The main complication of anal fissure is inflammation of the rectum, acute paraproctitis. It develops due to the entry of pathological microorganisms through a defect in the mucous membrane into the tissue surrounding the rectum. When an anal fissure hurts, the process of urination may be disrupted.
Types of spasms
Most often, problems arise when the internal sphincter of the rectum spasms. First of all, they can be divided according to the time of the attack:
- quickly passing;
- long-term
Typically, mild pathology is simultaneously and quickly passing. At the same time, the use of serious drugs is not required to alleviate the condition. The disorder manifests itself in the form of sudden pulling or stabbing pain. Very often, patients feel severe discomfort in the perineal area. Moreover, some of them begin to treat fictitious diseases of the prostate gland, kidneys and uterus to no avail. Once again I would like to remind you that any therapy begins with an adequate diagnosis. Without this, it is not only ineffective, but also dangerous.
Prolonged pain of unknown etiology practically does not respond to pain relief, and attacks can last for several days. Moreover, it is characterized by an uneven course; after some time, the frequency of attacks increases. However, the factors that cause exacerbation of pain are not fully identified. However, doctors have long noted that the patient’s emotional state greatly affects the condition of his intestines. Stress and anxiety instantly make the situation worse.
There is a classification according to the etiological factor. In this case, the following are distinguished:
- Primary spasm. If you compare two photos of the rectal sphincter - spasmodic and absolutely healthy - you will notice that they are not much different. In our case, it is simply a muscle spasm, which most often develops against a background of stress and goes away after the situation returns to normal.
- Secondary. This disorder does not appear on its own, but develops against the background of certain pathologies of the rectum. These include hemorrhoids and fissures, Crohn's disease and tumors in the anal canal.
Any problems with the intestines require attention and timely consultation with specialists. The sooner the cause is determined, the more effective the therapeutic effect will be.
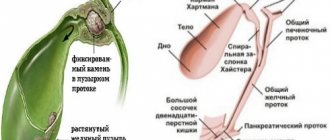
Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction (postcholecystectomy syndrome)
Features of diagnostics. To exclude organic pathology of the oily system, a number of screening and clarifying methods are used. Indirect methods that suggest dysfunction of the sphincter of Oddi include blood tests of bilirubin content, alkaline phosphatase activity, aminotransferases, amylase and lipase, carried out during or no later than 6 hours after the end of a painful attack, as well as over time. Sphincter dysfunction is confirmed by a transient increase of 2 times or more or at least during two consecutive pain attacks. The provocative morphine-prostigmine test is of great importance in diagnosing dysfunction. Dilatation of the common bile duct and main pancreatic duct, indicating a disturbance in the flow of bile and pancreatic juice at the level of the sphincter of Oddi, is determined by ultrasound of the abdominal organs. At the same time, it is necessary to remember that 34% of people who have undergone cholecystectomy, in the absence of clinical symptoms, have an enlargement of the common bile duct. In the diagnosis of sphincter of Oddi dysfunction, dynamic ultrasound of the diameter of the common bile duct is used with the use of fatty breakfasts, which stimulate the production of endogenous cholecystokinin and increase choleresis. In this case, after a test breakfast, measurement of the common bile duct is carried out for 1 hour every 15 minutes. An increase in its diameter by 2 mm or more may indicate the presence of incomplete obstruction of the common bile duct as a result of dysfunction of the sphincter of Oddi or organic pathology of the biliary system.
Changes in the diameter of the pancreatic ducts are determined by performing a test with secretin. In a healthy person, after administration of 1 mg/kg of secretin, ultrasound for 30 minutes shows dilation of the pancreatic duct, followed by its decrease to the initial level. Dilatation of the duct for more than 30 minutes indicates a violation of its patency. Computed tomography of the hepatoduodenal gastrointestinal tract is important in the diagnosis of sphincter dysfunction. Invasive indirect methods for assessing the function of the sphincter of Oddi include endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP). Indirect signs of an increase in its tone are an increase in the diameter of the common bile duct by more than 12 mm and a delay of contrast in the common bile duct for more than 45 minutes. Dysfunction of the sphincter of the main pancreatic duct is indicated by its expansion of more than 5 mm, as well as slower evacuation of contrast from the duct.
A direct method to confirm sphincter dysfunction is manometry. When performing manometry, it is possible to separately cannulate the common bile duct and Wirsung duct with manometry of their sphincters. This makes it possible to identify the appropriate type of disorder and establish the cause of recurrent pancreatitis after cholecystectomy and papillotomy.
At the same time, manometric examination of the sphincter of Oddi is not available to all medical institutions where ERCP is performed. This has stimulated interest in the use of non-invasive methods to study the function of the sphincter of Oddi.
To exclude organic pathology of the sphincter of Oddi, a test with a smooth muscle relaxant is used. The presence of functional disorders is indicated by a decrease in basal pressure after the administration of relaxants. At the same time, sphincter manometry is not always informative, which was the reason for developing criteria that are taken into account when choosing treatment tactics for this condition.
Signs of sphincter of Oddi dysfunction
- Classic attack of biliary or pancreatic pain
- Changes in the activity of liver and/or pancreatic enzymes (twofold increase)
- Delay in the removal of contrast agent from the common bile duct during ERCP (more than 45 minutes)
- Dilation of the common bile duct (more than 12 mm) or main pancreatic duct
There are several variants of sphincter of Oddi dysfunction, which must be taken into account when choosing management tactics for this category of patients.
In the pancreatic type, great importance is given to a twofold increase in the activity of pancreatic enzymes in the blood serum during two consecutive attacks of pain, as well as an expansion of the pancreatic duct of more than 5 mm.
Patients with the first type of sphincter of Oddi dysfunction and a high probability of developing stenosis (more than 70%) are shown endoscopic sphincterotomy without preliminary manometric examination, which helps reduce the incidence of complications.
Patients with the second option are prescribed drug therapy. If there is no effect, a manometric study is necessary.
In persons with signs of dysfunction of the sphincter of Oddi in the third option, the causes of pain are more often due to dyskinesia. Manometric examination of the sphincter in this case is not indicated.
In the diagnosis of intestinal pathology, X-ray examination of the stomach, duodenum and small intestine, endoscopic examination of the gastrointestinal tract with the collection of bioisic material from the mucous membranes are used.
To confirm excessive bacterial growth in the intestine, aspiration and culture of intestinal contents, stool, testing the concentration of hydrogen ions in the air released on an empty stomach, and breathing tests with lactulose or glucose are used. The simplest and most informative test is the improvement of the patient's condition after antibiotic therapy.
First trip to the doctor
It all starts with an examination. Taking an anamnesis plays an important role. Quite often, patients are diagnosed with primary diseases that led to such developments. These include previous injuries and various operations. Even more often, the root cause is diseases of the rectum and genitourinary system. Do not forget that the smooth muscle muscles of our body are interconnected, therefore primary proctology is combined with muscle spasms of other organs. What does diagnostics include:
- visual inspection;
- palpation of the anus;
- examination of the walls of the rectum;
- examination of the colon using colonoscopy.
What to do
Since it will not be possible to relieve spasm of the rectal sphincter overnight, you will have to follow a number of doctor’s recommendations in order to achieve an improvement in the condition. The choice of treatment methods will depend on the general and psychological state of the patient, the presence of somatic diseases.
But the doctor’s first task is to relieve spasm of the rectal sphincter. Treatment should begin with eliminating the disorder and eliminating inflammation. For this purpose, antispasmodics and painkillers are prescribed. If necessary, antibacterial agents are prescribed, and for constipation, laxatives are prescribed.
Hemorrhoidal thrombosis - symptoms and treatment
Acute hemorrhoids is a disease, with adequate treatment of which, in 98 - 100% of cases, complete relief from the manifestations of thrombophlebitis is possible.* With conservative management of an exacerbation after the signs of inflammation subside, the disappearance of edema, further treatment of hemorrhoidal disease is indicated using numerous methods (minimally invasive: latex ligation, sclerotherapy, laser vaporization or classic hemorrhoidectomy). Correcting changes in chronic hemorrhoidal disease is necessary, among other things, to exclude relapses of thrombophlebitis of the nodes and improve the quality of life.
The choice of method for removing pathologically altered cavernous plexuses in chronic headache depends on their location, size, degree of dystrophic changes in the underlying tissues (stage of the disease), the availability of modern medical equipment in the medical institution and the surgeon’s preferences.
Prevention of the disease consists of eliminating factors that provoke exacerbation of hemorrhoidal disease:
- Normalization of stool;
- Drinking enough fluids throughout the day;
- Increasing physical activity**, combating physical inactivity;
- Nutrition correction - increasing the diet of plant fiber, vegetables and fruits, fermented milk products***;
- Limiting the intake of strong alcohol and spicy foods;
- Treatment of chronic inflammatory processes in the perianal area (proctosigmoiditis, chronic hemorrhoids);
- Reducing body weight to optimal parameters (BMI 20-23);
- Treatment of concomitant diseases - arterial hypertension, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
*if in complex therapy surgical aids with coagulation of the vessels feeding the node were used.
**dosed physical activity helps normalize weight, metabolism, and strengthen the pelvic floor muscles. However, they should exclude activities that lead to a sharp increase in intra-abdominal pressure (deadlifts, squats with loads, weightlifting, powerlifting).
***if diet correction is not enough, for persistent constipation, regular use of probiotics and prebiotics, laxatives - lactulose (Lactusan, Duphalac), oval plantain seeds (Mucofalka, Fitomucila) is appropriate. Typically, the side effects of lactulose - bloating, flatulence - are eliminated by reducing carbohydrate intake, which prevents excessive growth of intestinal microflora.
Prevention of acute hemorrhoids in pregnant women
Even at the stage of pregnancy planning, girls need to consult a proctologist, because in the presence of hemorrhoidal disease, stage 1. manifestations may be minimal and unnoticeable to a young woman. However, when carrying a child, all minor problems can become quite painful for the expectant mother, and their effective treatment during pregnancy will be extremely difficult.
Repeated examination of pregnant women is indicated in the 2nd–3rd trimester. Even before the onset of birth, some pregnant women experienced some degree of exacerbation of hypertension, which is associated with impaired venous outflow from the pelvis, an increase in intra-abdominal pressure and changes in blood coagulation parameters. And during natural childbirth, thrombophlebitis occurs in almost half of women in labor due to direct compression of the nodes by the fetal head passing through the birth canal.[13]
For natural delivery, the diagnosis of hemorrhoids is not a contraindication, but the condition requires dynamic monitoring by a specialist and the implementation of certain recommendations.
Sphincter relaxation
This is the goal of the patient and the doctor, which is not always easy to achieve with drugs alone. Thermal procedures, as well as physiotherapeutic methods of treatment, help very well in this case. At the same time, it is necessary to carry out pain relief with the help of antispasmodics and analgesic suppositories. It is best to use “Relief Advance”, “Procto-glivenol”, “Venoruton”, “Ultraprokt”, “Prosterizan Forte”, suppositories with belladonna and sea buckthorn oil. Of the antispasmodics, No-spa is most often used, as well as warm sitz baths.
Solving problems with constipation
It is very important to pay close attention to the toilet. It is extremely important to keep the anal area perfectly clean. Every morning you need to wash yourself using the shower. It is good to repeat the procedure after each act of defecation so as not to irritate the mucous membrane by friction. Proper diet is one of the most important factors. Food should be as gentle as possible in order to reduce the load on the gastrointestinal tract. Everything here is quite simple: fatty, sweet, fried and spicy foods should be excluded from the diet. The basis is soups and lean porridges, baked fruits and vegetables. Maintain drinking regime.
Surgery
If alternative treatment does not work, then more radical measures will have to be chosen. First, doctors use various drugs, as well as conservative treatment methods. If attacks become more frequent, and severe complications arise, then there is no choice left. In this case, they resort to surgical intervention - sphincterotomy. It involves partial excision of the anal sphincter muscles. This causes the smooth muscles to relax and pain is significantly reduced. The cause is not eliminated, but the patient still gets a good result.
Traditional methods of treatment
If the situation has not yet gone too far, then you can use herbal medicine recipes. In this case, it is recommended to treat spasms of the anal sphincter with decoctions of medicinal herbs or a solution of potassium permanganate. The treatment regimen includes enemas and microenemas, tampons and suppositories.
Sitz baths are very easy to prepare. To do this, take some warm water into a basin and add potassium permanganate. The procedure must be repeated for at least 7-10 days. Baths with a decoction or infusion of medicinal plants, which have an antispasmodic or calming effect, are quite helpful. These are chamomile and yarrow, St. John's wort and oak bark, calendula. Plants can be mixed or alternated. A decoction of medicinal herbs is used to prepare enemas and tampons.
Sphincter weakness
This is exactly the opposite situation to the one we discussed above. If before this we discussed how to relax the sphincter of the rectum, normalize the passage of gases and feces and relieve pain, now we need to pay attention to what to do when loosening the same locking ring. A weak rectal sphincter leads to incontinence of gases, liquid or solid feces.
Treatment requires taking into account the individual characteristics of the person, as well as the disorders. As a rule, if the rectal sphincter is relaxed, a special diet, electrical stimulation and physical therapy are prescribed. Drug therapy in this case should be aimed at treating inflammatory diseases and dysbiosis.
If the sphincter is weakened due to organic reasons, surgical intervention is necessary, namely sphincteroplasty. After this operation, long-term rehabilitation treatment with mandatory diet is required.
How to relieve pain with anal fissure
In order to remove acute pain that has arisen for the first time with an anal fissure, you can take a sitz bath with a solution of potassium permanganate or chamomile decoction, and introduce 2% lidocaine gel into the anus. Proctoglivenol, Ultraproct, Anestezol, Relief suppositories effectively reduce pain with anal fissure. Pregnant women who have severe pain with anal fissure are prescribed natalsid and methyluracil suppositories. They do not contain local anesthetics, but help reduce pain due to wound healing and immunostimulating effects.
Second-line therapy is topical application of 0.2% nitroglycerin ointment to the internal sphincter. It relaxes the internal anal sphincter and reduces pain, increases blood flow in the mucous membrane of the anal canal. The use of nitroglycerin ointment is sometimes accompanied by side effects: headache and dizziness. Also, proctologists, in the presence of sphincter spasm, which causes pain with anal fissure, prescribe 1% isosorbide dinitrate ointment. gels of nifedipine 0.2% and diltiazem 2%. Pain from anal fissure is relieved by taking calcium channel blockers orally or sublingually, which reduce the tone of the internal anal sphincter. Injection of botulinum tocaine into the internal anal sphincter effectively reduces the severity of pain and promotes healing of the anal fissure. The effect lasts about three months, until the nerve endings are regenerated. This time is sufficient for the healing of the defect in the mucous membrane of the rectal canal. If, at the beginning of treatment, patients experience relief, and after three months the symptoms of the disease resume, proctologists offer the patient a surgical sphincterotomy.
Lateral internal sphincterotomy is today the operation of choice for anal fissure. Proctologists at the Yusupov Hospital perform this surgical procedure on an outpatient basis. For pain relief, anesthesiologists use anesthesia, spinal or local anesthesia. During the operation, the surgeon crosses the hypertrophied internal anal sphincter, which relieves the patient of pain and promotes healing of the anal fissure.
Doctors at the proctology department perform sphincterotomy in the lateral quadrants. Surgeons are fluent in surgical techniques, so after the operation the external sphincter remains intact. Proctologists perform sphincterotomy in an open or closed manner. The surgeon inserts a pointed scalpel blade into the intersphincteric recess and crosses the internal anal sphincter towards the mucous membrane. Sometimes proctologists make an incision up to one centimeter in this area and cross the internal anal sphincter under visual control. To avoid the formation of a fistula, the integumentary mucosa is left intact. For chronic anal fissure, sphincterotomy is performed in combination with excision of hypertrophied papillae and skin outgrowths. Sometimes, with a long-standing crack, doctors at the proctology department perform plastic surgery - they close the defect by moving a flap of the mucous membrane.
The intensity of pain after surgery does not exceed the pain that was caused by the crack before surgery. In the postoperative period, proctologists prescribe medications that increase the volume of stool and, to prevent constipation, a diet rich in plant fiber. If an anal fissure reoccurs after surgery, proctologists perform a sphincterotomy on the opposite side of the anal canal. To find out how to relieve pain from anal fissure, make an appointment with a proctologist by phone.