The amount of mucus secreted that our body produces to help the muscles of the rectum depends on many reasons and factors, but if excessive fluid secretion occurs, this may indicate the presence of serious proctological diseases.
If you find yourself secreting an excessive amount of mucus from the anus, then this is a sure sign that you have a proctological disease. Most often, this symptom occurs together with others, such as constipation, bloating (flatulence) and others.
In order not to aggravate the situation and not to miss the transition of the disease to a chronic form, it is necessary to undergo an examination by a proctologist.
Mucus secretion
Mucous discharge appears due to increased production by goblet cells on the intestinal villi. Mucus facilitates the passage of feces and serves as a lubricant for the mucous membrane.
Mucous discharge from the anus appears when the digestive system is disrupted.
They can be called:
Causes of discharge
- gastrointestinal infections;
- vascular diseases;
- haemorrhoids;
- irritable bowel syndrome (Crohn's disease);
- venereal diseases;
- damage to the intestinal mucosa;
- neoplasms;
- intestinal polyps;
- damage to the rectal sphincter (surgery, trauma);
- helminthic infestations;
- condylomas, rectal papillomas;
- colitis;
- colds;
- errors in nutrition (unusual, unusual food).
The color of the discharge depends on the functional system causing its formation.
The color of anal mucus:
Anatomy of the gastrointestinal tract
- Inflammatory processes that cause mucus (mucus) excessive formation in the intestines - white or grayish mucus.
- Infections (gastroenteritis) or systemic autoimmune diseases of the intestines have clear or colorless mucus.
- Problems with the liver, pancreas and excessive production of bile that colors the discharge from the anus orange.
- Inflammatory processes (hemorrhoids, fissures, polyps), as well as helminthic infestations cause damage to the mucous membrane. Violating the mucous membrane and damaging the integrity of the blood vessels, which, during bowel movements, turn the mucus pink.
- Black mucus and feces indicate bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract.
Mucus, as a sign of disease, can be released regardless of the act of defecation and cause discomfort.
Causes of mucus discharge in stool
The intestines of an adult are a fairly resistant system to external influences, and the appearance of a large amount of mucus in the stool indicates a serious pathology that the body itself is not able to cope with. A small amount of mucus is always present in the human intestine; it is formed from dead intestinal epithelial cells, ingested nasal and nasopharyngeal secretions, leukocytes and microorganisms destroyed by them.
The reasons for the appearance of a large amount of mucus in feces can lie in a variety of diseases, and can also be caused by non-pathological processes. They can be divided into five main groups. We will consider which ones in the table below.
Table 1. Main groups of diseases causing the appearance of mucus in stool
| Diseases of infectious-inflammatory etiology | Diseases of the oncological category | Hereditary diseases | Problems associated with malnutrition | Infestation by parasites |
| 1. Hemorrhoids. 2. Various infections. 3. Diverticulitis. 4. Dysbiosis. | 1. Bowel cancer. 2. Formation of polyps. | 1. Cystic fibrosis. 2. Irritable bowel syndrome. | 1. Eating insufficient fiber. 2. Failure to comply with the water regime. 3. Other violations related to diet and nutrition. | 1. Helminthic infestation of the intestines. |
Let us move on to a detailed consideration of the phenomena that are representatives of each of the sought groups.
Haemorrhoids
Such formations on the intestinal walls provoke the occurrence of long-term constipation, accompanied by intense painful sensations in the anal passage during the passage of feces. The inflammation characteristic of this disease leads to the formation of mucus, which is released along with the feces. The inflammatory process that develops with hemorrhoids provokes irritation of the goblet cells responsible for:
- secretion of mucous lubricant;
- its quantity.
Due to the desired process, the amount of secreted mucus increases, it begins to be released from the anus not only during bowel movements, but also at normal times, remaining on the underwear.
The desired reaction of the body also falls into the category of protective. Mucus can also be released simultaneously with:
- blood;
- pus.
At the same time, it is not at all necessary that this mixture will be released during the act of defecation, since with hemorrhoids the sphincter muscles become more relaxed due to the development of inflammation, and therefore retain the contents of the intestine worse.
So, the shade and composition of mucus with hemorrhoids can change as follows:
- cloudiness of the mucus indicates the development of complications of hemorrhoids;
- provided that the mucus released is mixed with blood, this means that the inflamed hemorrhoidal node has ruptured, which requires immediate contact with a proctologist;
- green-yellow discharge mixed with mucus indicates the development of suppuration in inflamed areas, which increases the risk of consequences of the disease.
The following pathological and other conditions of the human body provoke the development of hemorrhoids:
- too heavy physical exercises performed regularly, as a result of which the pressure inside the peritoneum increases, which causes further prolapse of hemorrhoids;
- provided that you experience difficulties with constant constipation, and strain very hard to push out feces, the nodes receive a serious influx of blood, as a result of which they increase in size and fall out;
- drinking alcohol in large quantities leads to dilation of blood vessels, which are also located in the anal area, and therefore provokes bleeding;
- bearing a child is another common cause of hemorrhoids, since as the uterus enlarges, the pressure inside the abdomen increases;
- a sedentary lifestyle also causes the development of the desired disease.
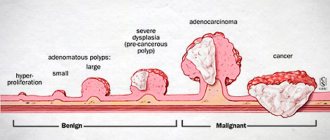
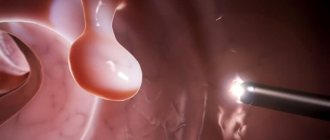
Polyps in the intestines
Benign neoplasms, so-called polyps, which attach to the internal mucous walls of the organ, can grow in the intestines. The desired formations consist of glandular epithelium. They can be formed:
- on a wide base;
- grow on a leg.
In fact, the formation of polyps is considered a pathological process that precedes the development of cancer, since the degeneration of the desired benign tumor quite often results in a malignant one.
Since the desired formations are formed by glandular epithelium, they secrete a huge amount of mucus that exits through the anus along with feces. The more abundant the impurity you are looking for, the more likely it is that you suffer from polyposis.
Along with the secretion of mucus during polyposis, the following symptoms may appear:
- profuse diarrhea;
- intestinal obstruction;
- blood in stool;
- constipation.
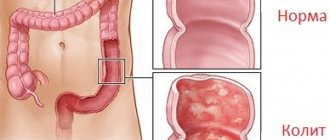
Membranous colitis
The disease in question is also called mucoid colic, and is one of the most common pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract. The disease is accompanied by the following clinical manifestations:
- loose stools;
- constipation;
- pain in the abdominal area;
- mucous discharge of an unusual shape.
This disease often accompanies mental disorders, however, it is not cured by eliminating mental trauma. Typically, pain and discomfort are accompanied by:
- discharge of a small amount of pellet-shaped feces;
- the release of large, even excessive amounts of mucous impurities and gases accumulated in the intestines.
All attempts to calm the pain and finally go to the toilet normally when using laxatives and antispasmodics can result in dangerous consequences for the patient, since the reaction will be potentially exaggerated.
Another reason why mucous colic often develops is an allergic reaction of the colon. In such cases, pain comes unexpectedly and overcomes the body in a cramping manner, after you have experienced any strong emotion. An attack can last for hours or days, but at the end of it the following manifestations occur:
- profuse diarrhea;
- mucus discharge of an unusual shape, in the form of threads, plates or bundles, due to which patients often think that their intestines have rejected part of the mucous membrane, or that worms have come out of it.
Intestinal infections
Intestinal infections of a bacterial or viral nature. These are dysentery, colitis, enteritis, typhoid fever. These pathologies are a fundamental factor predisposing to an extremely active process of mucus secretion in the feces. This occurs due to increased secretion of glands and the removal of dead pathogenic bacteria, viruses and leukocytes from the body during the act of defecation. In addition to mucous discharge, symptoms such as intense abdominal pain, diarrhea, high fever and weakness are observed.
Lack of normal intestinal microflora - dysbiosis causes digestive disorders, as a result of which jelly-like clots and undigested food fragments appear in the stool. Factors such as alcohol abuse, smoking, stress, poor diet, as well as antibiotics and hormonal drugs taken without a doctor’s prescription act as a trigger for dysbiosis. The most noticeable symptoms, besides excessive mucus secretion, are frequent migraines, susceptibility to respiratory diseases and the likelihood of skin rashes.
Neoplasms in the colon
Tumor processes localized in the stomach or intestines lead to the death of epithelial cells. This is accompanied by the release of thick mucus. An expressive sign of a serious illness is sudden weight loss and chronic fatigue.
In the presence of a neoplasm in the intestines in adults, mucus is usually secreted:
- abundantly;
- with admixtures of blood.
In children, the process does not occur so clearly, however, it can still be tracked. If the mucous discharge is accompanied by pain, diarrhea or constipation, blood, or fever, you need to go to the hospital as soon as possible.
Treatment in case of development of oncological processes will consist of:
- in tumor removal;
- undergoing specific chemotherapy;
- radiation therapy.
Diverticulitis
Diverticulitis is an intestinal pathology in which the protruding parts of the desired organ, the so-called diverticula, become inflamed. The desired condition is accompanied by the following manifestations:
- mucus in the stool;
- various dyspeptic stool disorders;
- bleeding;
- increased body temperature;
- weakness;
- painful sensations in the lower abdominal cavity that occur periodically;
- sometimes vomiting also occurs.
Diagnosis of diverticulitis requires the use of various instrumental research methods, such as:
- ultrasonography;
- endoscopy;
- laparoscopy, etc.
In addition, laboratory tests are also performed to clarify the disease.
The disease is always localized in the place where the diverticulum was located - the blind protrusion of the intestine. Not all people have the desired protrusions, but a large number do, and they become inflamed quite rarely. Inflammation can be caused by various reasons, but most often it develops due to constant poor nutrition, for example:
- non-compliance with water regime;
- consuming less than 30 grams of fiber per day.
Due to the factors listed above, the intestinal muscles do not work at full strength, and the feces inside are not sufficiently moistened and hardened, so pathogenic microflora is retained inside the organ and provokes inflammation of the diverticulum.
Irritable bowel syndrome
The term irritable bowel syndrome refers to a condition of the intestine known to many people, in which there is a violation of the contractile activity of its muscles.
Until now, doctors have not been able to accurately explain the cause of increased intestinal sensitivity, since in itself in this case it is not a disease.
Momentary intestinal irritation can occur in this condition under the influence of many different factors, among which there are problems of a psychological nature. Any stress instantly worsens the processes of digestion by the desired organ of food, as a result of which various symptoms appear, such as:
- secretion of mucus in the stool;
- unexpected urge to defecate;
- frequent desire to defecate;
- diarrhea;
- constipation;
- flatulence and similar manifestations.
You can aggravate the situation and provoke additional mucus secretion by eating one of the following foods:
- coffee;
- strong tea, black or green;
- semi-finished products;
- store food, etc.
Individual food intolerance
Sometimes the cause of the appearance of mucous impurities in stool can be intolerance to specific foods that other people can eat at least every day. So, the most common situation in this case is when the human body cannot absorb lactose - milk sugar contained in all products made from cow's milk.
Even a small consumption of dairy products in this case can provoke various disorders, for example:
- vomiting;
- nausea;
- constipation;
- diarrhea;
- bowel movements with a lot of mucus, etc.
If you are intolerant, there is only one treatment - eliminating foods that are contraindicated for you from your diet.
Cystic fibrosis
The disease we are looking for is very severe and, unfortunately, has the nature of a congenital pathology. A person who is unlucky enough to suffer from it from birth experiences constant discomfort associated with:
- damage to tissues and body structures consisting of them;
- disruption of the glands;
- other functional disorders, usually of the respiratory system and gastrointestinal tract.
So, the pathological process can affect:
- liver;
- intestines;
- pancreas;
- salivary glands;
- bronchial and pulmonary system;
- sweat glands.
The disease in question is inherited from parents who have a mutant component in their genome. All associated disorders begin to develop directly within the mother’s womb, and after birth and as a person grows older, they only become more pronounced. The sooner the consequences of the disease make themselves felt, the more likely its course will be more severe, and the increase in various side effects will be faster. In cystic fibrosis, the secretory function of intestinal goblet cells is also affected, various putrefactive processes begin in it, which provokes the production of excessive amounts of mucus, which is clearly visualized in the stool during bowel movements.
Helminthiasis
Unfortunately, if simple hygiene rules are not followed, the human body can be colonized by parasites - helminths, better known as worms. Such worms can live inside our organs for years, undermining the health of the body.
The danger of intestinal parasites is as follows: during their life activities, they damage the walls of organs, inflaming them through mechanical action.
An irritable intestine activates a protective function that provokes copious mucus secretion, which will be easily noticeable in the stool that leaves the intestine. In addition, the desired disease is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- vomiting;
- sudden weight loss;
- nausea, etc.
Find more information about the symptoms and treatment of helminthiasis here.
Poor nutrition
We have already mentioned many times that a huge number of different factors that form a person’s quality of life, including his physical health, really depend on nutrition. Mucus in the stool can, not surprisingly, also be caused by poor nutrition, that is, the desired impurity will not characterize any health problems. So, a large amount of mucus is caused by the following nutrition-related reasons.
We are talking about an incorrect diet that exhausts you:
- psychologically;
- and physically.
Thus, suffering from insufficient food intake, not only your sides are depleted, but also the intestinal mucosa, which is forced to secrete a large amount of mucus in order to somehow maintain its performance and protect itself.
In addition, eating the following foods can also cause mucus to appear in the stool, which will pose absolutely no danger:
- oatmeal porridge;
- rice porridge;
- bananas;
- cottage cheese;
- watermelon
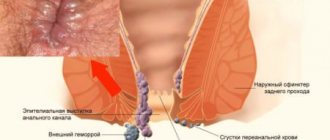
Haemorrhoids
Inflammation of the hemorrhoids can provoke the secretion of mucus by the goblet cells of the intestine and its appearance from the butt along with the feces. The discharge of mucus is a symptom of rupture of the nodes and can turn pink and have an unpleasant odor when smearing.
Weeping hemorrhoids have symptoms specific to it. Skin irritation due to constant humidity leads to the appearance of:
Discomfort in the anorectal area
- itching;
- burning;
- prickly heat.
The progression of the disease is manifested by intense mucus secretion and the development of an abscess. The appearance of pus indicates the addition of a bacterial infection. Such discharge (whitish with an admixture of pus) is characteristic of grade 3 - 4 hemorrhoids.
Crohn's disease
Irritable bowel syndrome is classified as an autoimmune inflammatory disease that has a specific course. Mucus released from the anus in Crohn's disease with impurities of blood and pus during inflammatory processes. The proximity of the prostate gland to the rectum during discharge from the anus provokes an exacerbation of prostatitis in men.
Crohn's disease affects the entire gastrointestinal tract, and its clinical picture has the following symptoms:
Blood from the anus
- false urge with mucus secretion;
- sudden weight loss;
- intoxication;
- abdominal pain;
- anal ulcers;
- defecation up to 8 times a day;
- blood in stool;
- skin rashes (erythema, pyoderma);
- eye diseases (iridocyclitis, uveitis);
- stomatitis;
- rectal fistulas.
The localization of the inflammatory process upon examination has the form of an infiltrate, which is found in the iliac region or in the projection of the rectum. The disease occurs with alternating exacerbations and periods of remission.
Dysbacteriosis
Violations of the barrier function of the digestive system and intestinal microbiota lead to the development of dysbiosis. The clinical picture of dysbacteriosis depends on the microflora that caused it.
Such pathogenic microorganisms are:
Intestinal infections
- staphylococcus;
- fungi;
- proteas;
- enterococci;
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa;
- coli;
- salmonellosis.
Discharge from the anus due to dysbacteriosis has a liquid consistency with mucus impurities and a foul odor.
Symptoms of dysbiosis appear:
- intoxication;
- loose stools;
- abdominal pain;
- weakness;
- fever.
Mucous discharge that appears from the anus is a product of the vital activity of microorganisms that have infested the intestines. Mucus, as a product of their vital activity, causes disruption of intestinal motility and poisons the body. An abundance of mucus can cause false tenesmus and be excreted in scanty quantities in the form of feces.
Prevention
If the appearance of white streaks in the stool is due to the presence of a disease that was subsequently cured, then you should take care of your body to prevent this from happening again.
The following can be done as preventive measures:
- carefully monitor food, avoiding eating expired food;
- it is recommended to adhere to a healthy diet and refuse (or at least limit) the consumption of any foods that are “heavy” for the digestive system, that is, anything fatty, spicy or smoked;
- Maintain personal hygiene - wash your hands thoroughly, keep the room clean;
- prevent hypothermia and immediately begin treatment of any infectious diseases;
- try to prevent the occurrence of such unpleasant conditions as diarrhea or constipation, bloating or irritation of the mucous membranes;
- Periodically visit a doctor and undergo routine examinations. A timely diagnosed disease is much easier to cure than its advanced form.
The main thing to remember during treatment is that only under the guidance of a specialist can you completely get rid of the problem and minimize possible consequences.
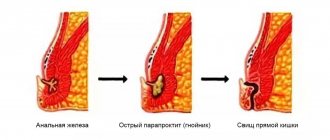
Proctitis
Inflammation of the intestinal mucosa that develops in its end section is called proctitis.
Causes of mucus discharge from the anus during proctitis:
Proctitis
- sexually transmitted infections (anal sex);
- intestinal infections;
- colitis;
- Crohn's disease.
The disease occurs in waves, alternating exacerbations and remissions. During the period of asymptomatic remission, the main natural manifestations are an admixture of mucus.
An acute period of proctitis develops within a few hours. Main symptoms:
- tenesmus;
- nagging pain;
- pain in the perineum;
- discharge mixed with pus and blood;
- heaviness and burning in the rectum.
Mucous discharge is pink or yellow in color and its intensity depends on the development of the inflammatory process. Pathological impurities in the stool cause irritation of the anus, and when liquid stool wets the anus, irritation and secondary infection appear. The spread of infection along the ascending path in the rectum leads to the development of complications.
What is anal itching - main signs and symptoms
It is very simple to distinguish pathological itching in the anal area from short-term irritation of the perianal area. Pathological is considered a symptom that occurs, if not constantly, then regularly. The majority of patients who sought medical help complaining of daily discomfort associated with certain situations:
- eating;
- eating certain foods;
- going to the toilet;
- body position;
- human activity.
Anal itching can occur for no apparent reason. However, it causes significant inconvenience and reduces the patient’s quality of life. An attack of severe itching can last from several minutes to several hours.
Pathological itching does not go away on its own, becomes longer and more intense, and in most cases is complicated by inflammation of the skin around the anus. In this case, itching and burning, tingling and swelling of the anal folds become a constant companion for the patient.
Additional symptoms that accompany itching in the anus indicate pathological processes:
- discharge of mucus from the anus;
- anal bleeding (traces of blood visible on stool and/or paper);
- sensation of a foreign object in the anus;
- intestinal disorders (diarrhea, flatulence, constipation);
- rashes in the perineum;
- acute pain during bowel movements;
- discharge from the genital tract.
All of these conditions require proper treatment. However, before you start, you need to find out what exactly caused the itching.
Without knowing the reasons why the anus itches and burns, it is impossible to select effective treatment methods. If you pay attention only to eliminating this symptom, the disease will progress.
Neoplasms
Neoplasm in the intestine
Oncological diseases are asymptomatic and at the stage when treatment of neoplasms does not bring results, symptoms of inflammatory processes appear. The breakdown of tumor tissue leads to the appearance of pus, mucus, and foam in the stool, released from the anus. Oncological diseases have a complex treatment process and can cause disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract in its early stages.
Such disorders are dyspeptic disorders, manifested by nausea, vomiting, and loose stools. Mucus and food impurities may be released from the anus, which are not a pathology, but are a protective mechanism in response to chemotherapy.
Where can I get tested?
If such signs appear, you should immediately visit a clinic that offers proctologist services. For patients for whom this is quite difficult, for example, elderly people, many private medical institutions provide a call to the proctologist at home
for conducting an initial examination, as well as taking some types of tests.
You can find out more about the services provided using the “Your Doctor” website. This universal service for collecting information about various private clinics also makes it possible to make an appointment at any of them.
This article is posted for educational purposes only and does not constitute scientific material or professional medical advice.
Author:
Isaeva Nadezhda Anatolyevna
Back to section
Oily discharge
The consumption of fatty, fried foods in the diet of some people leads to the development of inflammation of the gallbladder and pancreas. Normally, in a person’s diet, the amount of fat per 70 kg of weight should be 80-90 grams. This amount is the daily norm. Oily mucus released from the anus has causes related not only to diet, but also to the use of certain medications and intestinal inflammation.
Enzyme preparations for the breakdown of fats serve as a provoking factor for the appearance of oily discharge. The appearance of such discharge from the anus is an indicator of pancreatic dysfunction. Taking drugs that break down fats disrupts the basic physiological mechanisms in its work, and when they are discontinued, it can no longer cope with the breakdown of fats.
Another cause of oily discharge is gallstone disease. Violation of the outflow of bile, which emulsifies fats and breaks them down, causes such discharge. Such discharge does not have a distinct odor. The stool is viscous and sticky and leaves marks.
How to treat pathology?
Treatment will depend on the diagnosis made by the doctor. But even if an infection, helminthic infestation or cancer is detected, treatment should be comprehensive and include:
- Drug treatment.
- Compliance with diet and proper nutrition.
- Maintaining a daily routine.
If worms are detected in a patient, tablets are prescribed to eliminate parasites; for fungal infections, it is more appropriate to use antibiotics or antifungal suppositories. When the cause of mucus in the stool is a viral infection, a complex of antiviral drugs is prescribed, as well as symptomatic treatment. For pancreatitis, medications are prescribed to normalize the functioning of the pancreas.
If a patient is diagnosed with cancer or other neoplasms of the gastrointestinal tract, chemotherapy and radiation therapy are prescribed. If the appearance of mucus in the stool of an adult is associated with excessive consumption of alcohol or inappropriate foods, as well as taking medications, then it is enough to eliminate the provoking factor and the problem will go away. An important stage of not only recovery, but prevention is maintaining proper nutrition and daily routine.
Products such as rolled oats or cottage cheese cause excessive formation of white, dense mucus, but bananas or persimmons will better bind it to a normal state. So before treating a symptom, consult a doctor. Perhaps in your case there is no reason to worry, but unjustified use of medications can only do harm.
What to do
Impurities in stool, discomfort and pain become the main reasons for visiting a doctor.
Consultation and treatment of problems with weeping hemorrhoids, fissures in the rectum, and irritable bowel syndrome are provided by:
Coloproctologist
- proctologist;
- coloproctologist;
- gastroenterologist;
- oncologist;
- infectious disease specialist;
- therapist;
- surgeon;
- dermovenereologist.
Treatment of the disease that provokes the secretion of mucus is the main way to solve the problem. The nature of the discharge, quantity, color are the main indicators for determining diagnostic and therapeutic procedures.
Diagnostics
When visiting a doctor, the main procedures that are performed are:
Examination using a sigmoidoscope
- Blood analysis. Biochemical, general, serological (syphilis, hepatitis), PCR. The parameters allow the doctor to make an interpretation - inflammatory processes, metabolic disorders and others.
- Stool analysis. Feces are checked for helminthic infestations and bacteriological (intestinal microbiota).
- Instrumental studies – FGDS, colonoscopy, abdominal x-ray, ultrasound, irrigoscopy.
- Digital rectal examination.
- Biopsy of intestinal tissue.
Characteristic symptoms that cause discomfort during discharge are:
- orange oily discharge from the anus;
- irritation in the anal area;
- the appearance of blood, stains on clothes and underwear;
- impurities in feces (white plaque, flakes, blood, pus);
- skin rashes;
- burning, itching of the anus;
- discomfort in the anal area.
Research results determine the choice of therapy.
Symptoms
Usually people detect mucus in their stool not by chance, but in cases where something bothers them. That is, a large amount of mucus is one of the symptoms that signal the development of the disease.
In addition, patients usually feel:
- severe abdominal pain, cramps;
- bloating and excessive gas formation;
- abdominal tightness, constipation or diarrhea;
- in severe cases, vomiting or other signs of intoxication;
- pain during defecation;
- blood or pus in the stool, possibly undigested food debris;
- change in the shape and consistency of feces, its nonspecific smell;
- mucus or bloody substance may remain on the patient's toilet paper or underwear;
- for respiratory diseases, characteristic symptoms of cough, nasal congestion, rhinitis and more;
- headaches and fatigue.
If you find these symptoms, as well as ichor or white discharge with feces, you should immediately consult a doctor and get tested to determine the cause of this phenomenon.
Treatment
The treatment method depends on the etiological factors and the main methods are:
- medicinal;
- surgical;
- conservative;
- invasive.
Each disease is treated using an integrated approach.
| Treatment method | Techniques and remedies |
| Medication | Antispasmodics. Their mechanism of action is aimed at relieving muscle spasms, abdominal pain, inflammatory processes, and improving intestinal motility. Medicines in this group:
Gastroprotectors. Protects the mucous membrane of the gastroduodenal part, reduces the effects of acids and alkalis on the mucous membrane. Funds from this group:
Laxatives. Prescribed for a tendency to constipation, it softens stool, facilitating its passage and evacuation. These include:
Adsorbents. Medicines have absorptive capacity and absorb substances regardless of their harm or benefit. These include:
Rectal suppositories. They relieve inflammatory processes, heal mucous membranes, and have an antibacterial and antimicrobial effect. Dissolving in the intestines, they are like an ointment that moisturizes the skin of the perianal area from wet calluses. These include:
Antibacterial agents. This is a group of drugs that reduce the activity of pathogenic flora. These include:
Medicines have a complementary, preparatory and anti-inflammatory effect during treatment. |
| Invasive | Colonoscopy. An endoscopic examination of the lower intestine will allow you to assess the condition of its mucous membrane and take histological material. X-ray with contrast. Examination of the walls, lumen and shape of the intestine allows you to assess its condition and detect a neoplasm. |
| Conservative | The use of distracting procedures (baths, massage) is common in the absence of inflammatory processes, in the treatment of children and the acute period in the development of a chronic disease. |
| Surgical | Surgical treatment is indicated for neoplasms and complications of hemorrhoids and is carried out under anesthesia. |
Diseases for which drugs are used:
- Crohn's disease;
- dysbacteriosis;
- proctitis;
- haemorrhoids.
Treatment of weeping, purulent hemorrhoids with complex therapy using antibacterial, rectal suppositories and examination of the condition of the rectum. When complications develop, surgical treatment methods are used.
Treatment of mucus in the anus
Treatment is prescribed by a proctologist and carried out on the premises of the clinic, under the full supervision of the attending physician. No surgery or hospitalization!
Our methods:
- Proxon - treatment of hemorrhoids in one visit. Alan Clinic is the only medical center in Kazan that uses this method.
- Latex ligation;
- Infrared photocoagulation (INFRARED device);
- Radio wave treatment method (SURGITRON device);
- Sclerotherapy;
- Drug treatment;
- Physiotherapy;
- Treatment with active oxygen (ozone therapy);
- Hirudotherapy (treatment with leeches).