Intestinal proctitis: symptoms and treatment in adults
Proctitis is an inflammatory process that occurs in the lower part of the rectum. In most cases, the disease occurs in combination with infectious infection of the sigmoid colon.
In the absence of proper treatment, proctitis can also affect the area of adipose tissue. In this case, the disease will be local in nature, called paraproctitis. Experts do not have accurate information about the extent and prevalence of the disease. It is known that most often it affects patients of different age categories and gender.
Causes of the disease
The main group of reasons leading to the development of proctitis:
- intestinal infections;
- presence of syphilis;
- the appearance of parasitic diseases;
- the appearance of nonspecific inflammation;
- the presence of various disorders in the rectum;
- eating foods that are low in nutrients;
- gonorrheal proctitis - during this disease in women, bacterial cells penetrate the rectum from the vagina;
- the appearance of tuberculosis - bacterial cells enter the rectum along with the bloodstream, as well as through wounds, and a person develops ulcers and fistulas.
In addition, the development of proctitis is provoked by some diseases:
- the presence of cancerous tumors in the rectum;
- long-term radiation exposure and the effects of toxic substances;
- presence of autoimmune diseases;
- diseases localized in the gastrointestinal tract are hepatitis, as well as cirrhosis, cholecystitis, pancreatitis, the development of gastritis, peptic ulcers, dysbacteriosis;
- diseases of the circulatory system - the development of hemorrhoids, varicose veins, as well as thrombophlebitis, cardiac and venous insufficiency.
Causes of proctitis in adults
There are many causes of proctitis. Usually the disease is caused by a whole complex of reasons, and not by any specific one.
Often, intestinal inflammation is caused by dietary disturbances: lack of a routine, excess of unhealthy, spicy, salty and fatty foods, excess of alcohol. This can also lead to constipation, which can provoke proctitis.
Classification
A disease such as proctitis can be diagnosed in various forms. The differences between the species lie in the reason for their formation. In form, this pathological process can be acute or chronic. Let's consider what subtypes acute proctitis has:
- Stagnant - people who have constant constipation and stagnation of blood in the pelvic organs fall into the risk zone.
- Nutritional – formation is associated with poor nutrition and consumption of alcoholic beverages.
- Superficial is a pathological process that damages only the superficial layer of the mucosa.
- Catarrhal - characterized by the presence of hemorrhages affecting the intestinal mucosa.
- Erosive - erosions are formed that affect the intestinal walls. Hemorrhagic – the cause of formation is hemorrhoids.
- Radiation is the result of radiation treatment used to eliminate tumors in the pelvic organs.
- Infectious – its formation is influenced by bacteria that have entered the body. Taking into account the type of these viruses, the attending physician can diagnose an illness of gonorrheal, gonococcal, chlamydial and herpetic origin. As a rule, the presence of viruses in the body is a direct threat to the development of purulent processes. As a result, the patient is diagnosed with purulent proctitis, which is characterized by the formation of purulent plaque deposited on the walls of the rectum.
Chronic proctitis may have the following classification:
- Atrophic - the result of thinning of the rectal mucosa.
- Post-radiation is a radiation type of proctitis, only its course occurs in a chronic form.
- Hypertrophic – characterized by thickening of the intestinal wall, so it is loose.
What is proctitis
Proctitis is one of the inflammatory bowel diseases.
In terms of prevalence, they are inferior to other diseases of the digestive system. But in terms of the number of complications and mortality, they occupy one of the first places in the world among all diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Inflammation of the rectum is called proctitis. But this process may not be limited only to this area.
If there is also inflammation of the sigmoid colon - the part of the colon that passes into the rectum - the disease will be called proctosigmoiditis. Anusitis - if the inflammatory process affects only the anus. If the inflammation spreads to the adipose tissue around the rectum, this is paraproctitis.
The disease can occur both acutely and chronically. There are no statistics on the prevalence of proctitis. It can occur at any age, with women and men getting sick equally often.
The rectum is the final section of the intestine. It is located in the pelvis and is surrounded by adipose tissue. The rectum is a small section, it starts from the sigmoid colon, soon ending at the anus. It is through the rectum that undigested food is eliminated.
This is the reason for the structure of the rectum – mucous membrane and muscles. They push through feces, and the mucous membrane secretes mucus, which serves as a kind of “lubricant.” To ensure that the process of bowel movements is controlled, there are two sphincters. These muscle rings hold feces when they contract and relax during bowel movements.
Under the influence of various factors, the outer layer of the intestine can become inflamed. Inflammation of the rectum is painful, since there are many nerve endings in the mucous membrane. There are also many veins under the mucous layer, so a small injury quickly leads to bleeding.
Symptoms of acute proctitis
As a rule, signs of the acute form appear immediately or several hours after the action of the damaging factor (with the exception of tumors).
Adult patients are concerned about two main symptoms of proctitis:
- Violation of the act of defecation - the patient constantly “pulls to go to the toilet” (false urge). Due to the frequency of defecation, the stool becomes mucous in nature; only mucus (a small amount) mixed with blood can be released. Constipation may develop due to a psychological block - the patient is afraid to go to the toilet, as this provokes increased pain.
- The pain is low to medium intensity, nagging in nature, which can intensify at the time of defecation. Quite often, the patient cannot indicate the exact location of the pain syndrome, since the pain may radiate to the lower back or lower abdomen. But upon active questioning, it turns out that the exact localization of pain is the area of the anus or sacrum. Unpleasant sensations do not go away throughout the day and begin to disturb the patient, leading him to a state of increased irritability. The pain syndrome can be slightly relieved by taking combination drugs (Spazmalgon, Baralgin) or anti-inflammatory drugs (Nimesulide, Ibuprofen, Ketorolac).
- Signs of acute proctitis can be supplemented by a decrease in appetite, a short-term increase in temperature (no more than 37.6 ° C), and discomfort in the abdominal area (due to impaired motor skills).
Symptoms of chronic proctitis alternate with periods of remission. The main criterion for diagnosis is the course of the disease for more than 6 months. The clinical picture of the pathology outside the period of exacerbation in most cases is limited to a periodic feeling of discomfort in the rectal area. Since the cause of the development of chronic proctitis is most often the presence of another pathology, the symptoms primarily reflect the disease that caused the problem.
Diagnostics
In order to correctly diagnose proctitis, you need to undergo a comprehensive examination. The procedure should begin with a routine examination of the perinatal and anal area.
In the presence of acute proctitis or at the time of exacerbation of the chronic form of the pathology, the following changes are present:
- the wall of the anal canal is painted a rich red color. In some cases, cracks are determined visually with the naked eye;
- fistulous openings may be present. They are small protrusions of the skin that are painful on palpation and secrete blood or pus;
- redness of the skin in the perinatal area (around the anus).
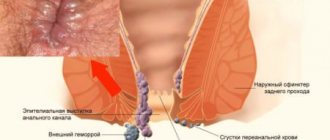
Bleeding damage to the anus allows one to suspect the presence of acute proctitis. With a long course of proctitis in adult patients, the appearance of hemorrhoidal nodules, which are dark in color, is quite often observed. Upon examination, they may be located within the rectum or protrude from the organ cavity.
How to treat proctitis?
Typically, proctitis treatment is carried out at home. But in severe forms of inflammation, the patient is recommended to be treated in a hospital: firstly, this allows the patient to follow a diet, secondly, it helps to give up bad habits and lead a healthy lifestyle, and thirdly, it provides effective treatment under the supervision of specialists.
When treating proctitis, adults may be prescribed the following medications:
- Antiallergic drugs - relax the walls of the rectum.
- Antispasmodics (No-spa) - to relieve pain, eliminate spasms, and facilitate bowel movements.
- Antibacterial and antiviral, depending on the results of bacteriological studies (metronidazole, chloramphenicol, penicillins, macrolides, etc.)
- Hormonal drugs (dexamethasone, hydrocortisone) are prescribed for some types of proctitis.
- Products that improve tissue regeneration (suppositories with methyluracil, sea buckthorn oil) help restore the mucous membrane, improve metabolic processes, and relieve symptoms of inflammation.
As additional measures, cleansing enemas (to ensure bowel movements), enemas with medicinal solutions, herbs (chamomile, calendula, collargol) are recommended. Sitz baths with potassium permanganate have a local antiseptic effect.
Prevention of proctitis in adults at home
Everything we eat passes through the intestines, so the best prevention is proper nutrition. Avoid fatty, salty, pickled foods, do not get carried away with spices and alcohol.
It is important to maintain hygiene and use barrier contraception in intimate relationships. Otherwise, there is a risk of bacteria moving from the genital area to the anus, where they will cause inflammation. Also avoid damaging the rectum.
You cannot prescribe enemas for yourself and do them too often. Also avoid sitting and lying for long periods of time, and do a minimum of exercise even if your condition is severe.
Treatment of the chronic form
Since chronic proctitis is a disease caused by pathological processes in the body, in its treatment all efforts are directed towards treating the underlying disease. During the period of remission, a number of activities are carried out to support the immune system and relieve inflammation.
- Mud therapy.
- Balneotherapy.
- Massage.
- Physiotherapy.
- Radon baths.
- Spa treatment.
If the cause is an autoimmune disease, treatment involves hormonal therapy. For sexually transmitted infections, antibiotic therapy is carried out in combination with anti-inflammatory drugs. For parasitic diseases, antiparasitic drugs are prescribed, and in the presence of complications, surgical intervention is performed.
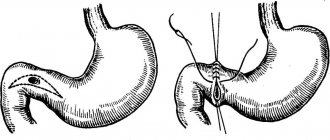
Surgery
In some cases, surgery is indicated. It is resorted to in case of complications: in cases where proctitis turns into paraproctitis, that is, the inflammatory process spreads to fatty tissue.
Surgical intervention is performed when the lumen of the rectum narrows, the appearance of neoplasms, or nonspecific ulcerative colitis. Surgical methods are also used if the inflammation cannot be eliminated with medication for a long time.
Is it true that pregnancy can cause hemorrhoids?
Unfortunately, hemorrhoids during pregnancy are a really common problem. The fact is that in pregnant women, the growing uterus puts pressure on the lower abdomen. It is the compression of the veins, combined with low physical activity, that leads to the development of hemorrhoids during pregnancy. Very often, the disease makes itself felt in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy, but in the presence of a hereditary predisposition, it manifests itself earlier - already from 10-15 weeks.
If you have problems with the intestines, we recommend treating them in advance, at the stage of
pregnancy planning .
You should not worry about hemorrhoids during pregnancy - they can be treated conservatively (without surgery). We recommend that you consult an experienced doctor: he will give recommendations on adjusting your diet, exercise, and prescribe safe medications.
Folk remedies
For inflammation of the rectum, remedies from the arsenal of traditional medicine have proven themselves to be effective:
- Sitz baths - pour half a glass of horsetail herb into a liter of boiling water, leave for ten minutes, strain and pour into the bath. Take for thirty minutes.
- Microclysters from a tablespoon of a three percent solution of boric acid and a tablespoon of calendula infusion. The procedure is performed before bed every day.
- Use calendula decoction two tablespoons three times a day. To prepare it, pour two tablespoons of flowers with boiled water and heat for fifteen minutes in a water bath. You can perform microenemas with this product by diluting a teaspoon of infusion in a quarter glass of water.
Popular questions and answers
Many patients miss proctitis at an early stage, when it responds well to treatment. We will find out what to do to prevent the disease from developing further from a surgeon of the highest category, proctologist, Ph.D. Vasily Gavrilov.
What complications can there be with proctitis?
In general, proctitis is an inflammation of the rectum.
This is a fairly general condition, which can be a manifestation of a large number of proctological, as well as gastroenterological, urological diseases. Complications of proctitis are very diverse due to the various causes of proctitis. They are divided into local and general. In both cases, this occurs when inflammation of the rectum extends beyond the rectum itself. Local ones include quite painful and unpleasant: ● anal itching; ● suppuration; ● formation of fistulas between the vagina and rectum; ● bleeding, etc.
All of them require attention, an individual approach and a detailed search for the reasons for each specific patient.
When to call a doctor at home for proctitis?
If we are talking about a local general practitioner, then there is no indication for calling him.
Only if proctitis, for example, as a result of radiation therapy for cancer in a bedridden, elderly and seriously ill patient. In this and similar cases, a therapist is more likely to be needed for symptomatic treatment. In all other cases, diagnosis requires an examination in a proctology office with special equipment by a proctologist. Consulting a proctologist at home is difficult, again due to the need for equipment to examine the rectum, and sometimes a biopsy of the mucous membrane. Therefore, it is worth seeing a doctor in a hospital rather than calling him to your home.
Is it possible to treat proctitis with folk remedies?
Under no circumstances should you self-medicate, including folk remedies. Since, I repeat, there are many reasons for the development of inflammation of the rectum. And only after establishing the causes can comprehensive, adequate treatment be prescribed.
Is it true that one of the methods of treating proctitis is physical therapy?
I would say that one of the mandatory components of the treatment of proctitis, and most other proctological diseases, is the normalization of stool.
It is soft and regular stool that significantly alleviates symptoms and is an important condition for healing. One of the components of normalizing stool is physical activity and work of the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall, as well as blood supply to the pelvic organs. Given this, physical therapy is certainly part of the recovery program for patients with proctitis, but should not be considered as the only method.
Diet for proctitis
During the period of exacerbation of proctitis, the patient is given gentle food in terms of chemical and mechanical indicators: low-fat weak fish and meat broths, minced fish and steamed meat, white crackers, jelly, low-fat pureed cottage cheese, pureed porridge. Whole milk and those foods that are poorly tolerated by patients are completely excluded. As your health improves, the doctor expands the diet, although even during the period of remission, products that irritate the intestinal mucosa - marinades, spices, alcoholic drinks - continue to be excluded from the daily diet.
It is recommended to eat fractional meals (6-7 times a day), in small portions, without overloading the intestines with large amounts of food. It’s good to drink before breakfast (on an empty stomach) a glass of warm boiled water with two tsp added. natural honey and squeezed lemon juice. This will clear the intestines and stomach of toxins and mucus accumulated overnight, improve the blood supply to the stomach and intestines, and activate digestion. The basis of the diet for proctitis is mucous soups made with oatmeal or rice broth, which have an enveloping property and protect the mucous membrane from irritation and the effects of pathogenic microflora.
It is better to use vegetable fats (corn and olive oils). In case of protracted proctitis, patients are prescribed a course of mineral waters - Arzni, Druskininkai, Truskavets, Borjomi, Essentuki.
How is radiation proctitis diagnosed?
Diagnosing diseases is not difficult. The key point here is the presence of a history of radiation therapy and its effect on the pelvic organs, increased frequency of stool, and the presence of pathological impurities in it.
If the course is prolonged, it is recommended to examine the rectum using a rectoscope or endoscope. This will allow you to detect multiple erosions, scar deformation, atrophic changes and telangiectasias and decide on the need for endoscopic or surgical treatment.
Prevention
Primary prevention of proctitis includes following a healthy, balanced diet. It is strongly recommended not to abuse alcohol, as well as fried and spicy foods, various spices and herbs. It is equally important to strictly observe the hygiene of the genitals and anal area. When having sexual intercourse, it is mandatory to use barrier contraception. At the first signs of inflammatory diseases in the pelvic area, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
If competent therapy has been carried out and remission has been achieved, proper personal hygiene and a healthy lifestyle in general will also help to avoid further exacerbations. Persons with an increased risk of developing the disease in question need to monitor bowel function and stool, as well as the condition of the genitourinary system.
Treatment and prevention of proctitis
To treat proctitis, a special diet is used.
Based on symptoms and special examinations, the proctologist can determine the correct cause of the disease. Depending on the severity of the pathology, treatment can be carried out in a hospital setting or at home.
In some cases, it is rational to use a special diet to increase the effectiveness of therapy. The diet completely excludes fatty, fried, spicy foods, as well as alcohol, from the patient’s diet.
You need to eat in small portions - 5-6 meals a day. It is recommended to eat omelettes, vegetable soups, jelly, boiled fish and meat. If proctitis is caused by infection, then the basis of conservative treatment is antibiotics and sulfonamide derivatives.
In the radiation form, an alternative form of therapy is used and drugs such as prednisolone and hydrocortisone are used. The treatment itself is often supplemented with traditional medicine.
With proper treatment of the disease, remission may occur and exacerbations will not occur. The basis for the prevention of proctitis is following a healthy lifestyle, as well as maintaining hygiene. It is important to ensure that your diet is healthy and that foods do not cause stomach upset or constipation.
Constipation is a serious cause that can cause the development of proctitis. In order to avoid them, you should eat plant foods containing fiber more often. Healthy foods, together with a proper diet, can guarantee excellent bowel function and regular bowel movements.
Treatment of proctitis is carried out only after its exact cause is established. Depending on the cause, the doctor prescribes therapy, consisting of medications, diet and general recommendations.