Intestinal obstruction - symptoms and treatment
Correct diagnosis and physician tactics play a big role in the treatment of intestinal obstruction. Treatment involves:
- timeliness of infusion therapy;
- identifying the cause of the pathological process;
- choosing a compression relief method;
- determining the scope of surgical intervention;
- prevention of postoperative complications and patient rehabilitation.
Objectives and content of surgical intervention
Intestinal decompression (surgical removal of its compression) is divided into closed and open methods.
The closed method consists of inserting an 80-100 cm nasogastric tube with many side holes with a diameter of 0.3-0.4 cm - intestinal intubation. The duration of intestinal drainage is 2-5 days.
Open decompression methods include enterotomy, jejunostomy, and colonostomy.
Less effective methods of decompression are:
- intestinal intubation (70-80 cm below the Treitz ligament) through a microgastrostomy;
- end ileostomy - should be performed at a distance of 25-30 cm from the cecum;
- hanging enterostomy;
- cecostoma;
- transcecal retrograde intubation of the small intestine;
- contranatural anus.
If there is colonic obstruction of the left intestine, then Hartmann's operation . If the site of occlusion is located in the rectum, then the tactics change: extirpation of the rectum is performed and, if the intestine is long enough, a coloanal anastomosis is performed.
To correct fecal incontinence, anal ring plastic surgery is performed using the adductor magnus muscle of the thigh or a magnetic sphincter.
Performing surgical intervention in patients with acute insufficiency at a late stage and in conditions of developed peritonitis has its own characteristics. They are associated, first of all, with the need for thorough sanitation of the abdominal cavity during surgery.[16]
Treatment and observation of patients in the postoperative period is of great importance.[3][5] For this purpose the following is carried out:
- correction of hypohydration - introduction of polyionic solutions;
- restoration of water-electrolyte and colloid-osmotic functions;
- restoration of acid-base relationships.
An important aspect in the treatment of acute infusion is infusion therapy . A patient with OKN is prescribed crystalloids, protein, glycosylated and colloidal drugs. Antibiotic therapy should also be carried out .
In the treatment of acute insufficiency, broad-spectrum antibiotics are used - third generation cephalosporins, fluoroquinolones, carbapinems and metronidazole. The duration of antibacterial treatment is 7-9 days.
All postoperative treatment tactics should be aimed at eliminating intoxication, restoring water-electrolyte balance and maintaining gastrointestinal motility. Patients are prescribed:
- sodium bicarbonate solution;
- 5% glucose solution;
- Ringer's solution.
In the absence of contraction of the intestinal walls, proserine derivatives or neuromidin are added. As an analgesic measure, a paraumbilical blockade is performed (if the initial cause was pancreatic pathology).[15]
In the postoperative period, a mandatory measure is to rinse the intestines with antiseptic solutions through a probe, which remains until intestinal motility is restored, gases begin to escape and the amount of discharge through the intestinal tube decreases.
Is it possible to cure intestinal obstruction without surgery?
Therapeutic methods for treating intestinal obstruction are usually ineffective and are not used, since lost time can lead to complications and death.
If a patient sees a doctor with intestinal obstruction that is just developing, and its cause is constipation or decreased intestinal tone, then cleansing siphon enemas (a solution of magnesium sulfate and magnesium sulfate) and laxatives are used. These methods are effective in treating constipation and developing intestinal obstruction.
It is important to understand that only a doctor can judge whether intestinal obstruction has formed after diagnosis. It is impossible to treat yourself, since the patient can suffer serious complications if intestinal obstruction has already formed and caused a persistent block of the intestinal lumen.
Physical exercise
In case of intestinal obstruction, physical exercise is strictly prohibited . The basic rule: “cold, hunger and peace” and contact a specialist.
Can I use a laxative?
Laxatives can be used only in case of developing intestinal obstruction and under the supervision of a doctor, since it is impossible to independently determine the stage of the disease.
Can I use an enema?
Enemas are effective if you consult a doctor before intestinal obstruction has formed, and this is confirmed by diagnostic methods. When the disease has developed, the use of enemas is dangerous and can lead to serious complications.
Causes of small intestine cancer
Small intestine cancer is a malignant neoplasm of the small intestine: duodenum, jejunum or ileum. In most cases, small intestinal cancer develops against the background of chronic enzymatic or inflammatory diseases of the digestive system:
- Peptic ulcer;
- Celiac disease;
- Duodenitis;
- Enterita;
- Diverticulitis;
- Nonspecific ulcerative colitis;
- Crohn's disease.
Benign epithelial neoplasms of the intestine can transform into a cancerous tumor. Doctors explain the predominant damage to the duodenum by the irritating effect of bile and pancreatic juice on the initial part of the small intestine, its active contact with carcinogens that enter the digestive tract with food.
Increased risk factors for developing small intestinal cancer are sporadic or familial adenomatous polyposis. The likelihood of developing small intestinal cancer is higher for people exposed to radiation or suffering from alcohol addiction, smokers, people whose diet is dominated by canned foods, animal fats, and fried foods. There is a relationship between colon cancer and malignant neoplasms of the small intestine.
What is the problem
Malabsorption, or malabsorption in the intestine, is a malfunction in the functioning of this organ, which is manifested by a number of symptoms resulting from a violation of the digestive and transport functions of the small intestine. This definitely affects metabolism. Malabsorption syndrome is often congenital and manifests itself in children in the first 10 years of life. But there are also cases of acquired disease.
Article on the topic The intestines have neurosis. How to properly treat irritation?
Diagnosis directly depends on symptoms. So, for example, if the clinical manifestations of the congenital variant and the moderate and severe form of the acquired variant can actively manifest themselves, then the latent forms of the syndrome do not have clear manifestations and require a different diagnostic approach.
Treatment of the problem
First of all, the efforts of doctors will be aimed at the pathology that leads to the development of problems with the absorption of nutrients in the intestines. However, the situation also needs to be corrected, so at the same time a special diet will be prescribed (usually they mean one that excludes lactose and gluten), a program for replenishing vitamins and microelements will be prescribed (this can be dietary supplements, special droppers, etc.), and an option will be proposed to restore the microbiota by connecting pro- and prebiotics.
How to diagnose
The examination in this situation should begin with a blood test. It will reflect anemia, an increase in leukocytes in the blood and ESR. You should also pass biochemistry. Here you should pay attention to such parameters as total protein, albumin, glucose, triglycerides, cholesterol, calcium, zinc, magnesium, all enzymes, electrolytes, ferritin, vitamins B9, B12, D in the first place. You should also take a blood test for clotting.
A mandatory part of the examination is submitting stool for analysis. This is necessary to determine muscle fibers and starch in it, changes in acidity, appearance and smell.
If we talk about specific tests, then procedures such as the D-acid test and the Schilling test should be performed. In parallel, doctors can prescribe FGDS, colonoscopy and microbiota analysis. This will allow you to assess the manifestations of dysbiosis in the intestines and select optimal treatment options.
Captured by advertising. Which drugs help digestion and which ones harm Read more
3.Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnosis of intestinal necessity is carried out by studying general symptoms and analyzing the medical history. The doctor may ask you about any digestive problems or previous surgeries or procedures in this area. A general examination is needed to check for tenderness and distension of the abdomen.
In addition, X-rays
which may show a blockage in the small or large intestine.
A computed tomography scan
of the abdominal area will help determine whether the blockage is complete or partial.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Risk factors
Cases of sporadic or familial adenomatous polyposis are increased risk factors for developing small intestinal cancer. The risk of developing small intestinal cancer is higher in:
- Smokers;
- Persons exposed to radiation;
- Suffering from alcohol addiction;
- People whose diet is dominated by animal fats, canned foods, and fried foods.
Based on the nature of the growth of tumor tissue, exophytic and endophytic cancer of the small intestine are distinguished.
- Exophytic tumors grow into the intestinal lumen, causing its narrowing and the development of intestinal obstruction; macroscopically may resemble a polyp or cauliflower;
- Endophytic forms of cancer infiltrate the wall of the small intestine in depth, accompanied by intestinal bleeding, perforation and peritonitis.
According to the histological structure, malignant tumors of the small intestine are more often represented by adenocarcinoma; sarcomas, carcinoids, and intestinal lymphoma are less common in oncological practice.
Diagnosis of small intestine cancer
For a malignant tumor of the duodenum, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital perform fibrogastroduodenoscopy and contrast fluoroscopy. Colonoscopy and irrigoscopy are informative for diagnosing cancer of the terminal ileum.
Barium passage X-ray allows you to identify obstacles to the advancement of the contrast agent, areas of narrowing and suprastenotic expansion of the intestine. During an endoscopic examination, the doctor performs a biopsy for subsequent morphological verification of the diagnosis. In cases that are difficult to diagnose, selective angiography of the abdominal cavity is performed.
In order to identify metastases and germination of small intestinal cancer into the abdominal organs, a comprehensive examination of patients is carried out at the Yusupov Hospital:
- Ultrasound examination of the liver, pancreas, kidneys, adrenal glands;
- Multislice computed tomography of the abdominal organs;
- Chest X-ray;
- Bone scintigraphy.
Small intestinal cancer is differentiated from benign tumors, intestinal tuberculosis, occlusion of mesenteric vessels, and Crohn's disease. In women, differential diagnosis is carried out with neoplasms of the uterus and appendages.
Symptoms
If the form of the disease is mild, it may not be recognized. However, as the situation worsens, symptoms can become quite pronounced. You should contact your doctor for a more detailed examination if even one of the following symptoms is observed:
- Discomfort in the intestines of varying severity
- Anemia according to blood tests
- Deficiency of vitamins B12, B9, C and others
- Increased dryness of skin and hair, brittle nails and other signs of vitamin deficiency, especially if you are taking special medications
- Deficiency of fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, K
- Hypocalcemia
- Weakness
- Increased excitability or, conversely, apathy
- Losing weight for no apparent reason
Article on the topicFor gastritis, contagious and inherited. Debunking myths about stomach ulcers
You should also pay attention to pain. In this case, the pain may radiate to the lower back, be cramping in nature, or be girdling (it is often compared to intestinal colic). It starts to hurt after eating, and at the same time you can notice bloating and rumbling. The stool changes, becomes more frequent and has an unpleasant odor. The syndrome also leads to a feeling of nausea and affects appetite.
2. Symptoms of the disease
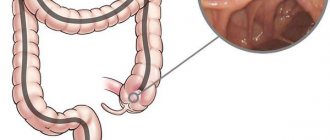
Symptoms of intestinal obstruction may include:
- Cramps and pain in the abdomen that comes and goes. The pain is usually located around or below the navel;
- Vomit;
- Abdominal bloating, rigidity;
- Constipation and lack of gas formation if the intestines are completely blocked;
- Diarrhea if the intestines are partially blocked.
You should see a doctor immediately if these symptoms cause abdominal pain that becomes too severe or persistent
. This may indicate internal ruptures in the intestines or a disruption in the blood supply to the intestines. Both cases are emergencies requiring emergency hospitalization.
Visit our Gastroenterology page