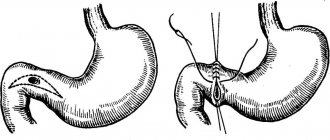
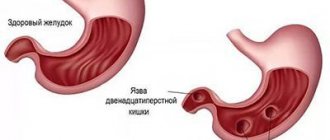
Cicatricial deformation of the duodenal bulb is formed in the initial section of the intestine. The disease develops after an ulcer in the place where the wounds were. The disease is characterized by the formation of scars, which can change shape and disrupt the functioning of the bulb.
- Etiology
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Complications
- Forecast
- Prevention
Most often, an ulcer forms on the bulb, which is located on the border of the upper and lower gastrointestinal tract. Scars form during the healing process of wounds. The principle is very similar to the healing of a wound on the human body when a scar is formed. If duodenal ulcers are poorly treated, the patient may develop scars. Soon, deformation of the duodenal bulb can lead to the formation of a lumen, and food can leave the stomach. In this case, surgical intervention cannot be avoided.
Symptoms
The fact that scarring of the ulcer has begun is indicated by a small number of symptoms. The disease is an asymptomatic illness. It can develop over many years and not show any significant signs.
It is almost impossible to find out that the duodenal bulb has begun to deform. During research and identification of repeated attacks of peptic ulcer, in which new scars are formed, a narrowing of the lumen between the intestines and the stomach becomes noticeable.
However, the disease has some significant symptoms that are a bit similar to those of an ulcer:
- nausea before meals, in the morning and on an empty stomach;
- colic;
- flatulence;
- heartburn;
- constant feeling of hunger;
- there may be bleeding.
Protrusion and deformation of the duodenal bulb
Symptoms of scar deformation of the duodenum
The symptoms of scar deformation of the duodenum are not specific and depend on the severity of scarring and its type, the presence of secondary provoking circumstances that form the prerequisites for exacerbation of the process.
In general, during the remission stage, the problem practically does not manifest itself, especially if the scarring is minor.
In this context, during instrumental examination, asymmetry of the bulb is observed, caused by partial shortening of one of its contours, but the lumens of the organ are open, and the evacuation of the contents proceeds normally.
Primary, externally diagnosed signs are characteristic of moderate and severe deformities with the formation of diverticulum-like protrusions, “trefoils” within the framework of cicatricial convergence with a narrowing of the lumen up to 50% or more, a parallel slowdown in the function of evacuation of biological contents up to 1 day or more.
In this context, the following manifestations are possible:
- Pain in the upper abdomen radiating to the back and neighboring organs. The pain syndrome intensifies with prolonged fasting and at night,
- The appearance of belching , nausea, increased gas formation and intestinal discomfort, and other broad-spectrum dyspeptic disorders,
- Staining of vomit and feces with bloody inclusions, indicating the start of internal bleeding - such a symptom directly threatens the patient’s life and requires his immediate hospitalization in a hospital and intensive care unit.
In addition, a relapse of the ulcerative pathological process against the background of organ structures weakened by cicatricial deformations sometimes leads to partial or complete blocking of the passage to the pylorus, where hydrochloric acid for the stomach is located.
Ultimately, this causes the substance to enter the intestine with subsequent migration of pancreatic bile fluids through various parts of the gastrointestinal tract, contributing to the development of a complex pathological acute process.
Diagnostics
To identify the disease, the doctor prescribes the same examination methods to the patient as for a stomach ulcer. Instrumental methods can help identify affected areas:
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy;
- X-ray of the stomach and duodenum;
- Ultrasound of the stomach.
Additionally, ultrasound of the digestive organs and gallbladder, endoscopic and X-ray examination of the intestines can be performed.
The doctor also resorts to laboratory diagnostic methods. To do this, the patient needs to undergo the following tests:
- blood;
- feces;
- study of hydrochloric acid levels.
Symptoms and diagnosis
The symptoms of bulbitis are very similar to the symptoms of gastritis
As mentioned above, the signs of bulbitis are very similar to gastritis. Therefore, without examination and further diagnostics, it can be difficult to make a diagnosis. But the following symptoms may indicate it:
- Abdominal pain. Pain with bulbitis can be different: both acute and severe, and girdling paroxysmal. It hurts either in the stomach area or a little lower - in the navel area. In case of very severe pain, when painkillers do not help, you must call an ambulance. Usually the pain begins when food reaches this part of the intestine, that is, an hour and a half after eating.
- Heartburn. With bulbitis, food cannot be digested normally, so heartburn occurs after eating. If heartburn has become a constant phenomenon, it can cause a lot of inconvenience.
- Vomit. Vomiting with bulbitis is rare; it usually ends in nausea. But with serious violations, vomiting is also possible. In this case, traces of bile can be seen in the vomit.
- Constipation. Due to impaired intestinal function, food is retained in the body, causing constipation. If not treated promptly, constipation can develop into hemorrhoids.
- Headache, weakness. These are common symptoms of bulbitis. These may also include decreased appetite and dizziness.
Diagnostic methods include external examination. The doctor palpates the abdomen for pain. The specialist may also prescribe an x-ray examination, which will reveal disturbances in peristalsis and spasms.
The most informative method of examination for this disease remains duodenoscopy.
The duodenoscope is inserted through the mouth and reaches the duodenum. Using a small camera at the end, you can carefully examine the entire mucous membrane and identify pathologies, foci of inflammation, ulcers, erosions and other disorders. During the examination, the mucous membrane is not injured, since the duodenoscope has a small diameter. To reduce pain and the gag reflex, the doctor will treat the larynx with an anesthetic.
Diagnostic methods can also include electrogastroenterography. This examination method can be compared to a cardiogram. Electrodes are attached to the patient's body, which catch and display on the monitor screen impulses transmitted by the gastrointestinal tract. In this way, the stability of peristalsis can be checked.
Treatment
A peptic ulcer must be treated, especially if it has begun to heal. The disease can affect all organs, the symptoms will become stronger and malignant tumors may form. Doctors prohibit treating duodenal ulcers with any folk remedies. Therapy can only be prescribed by a doctor, which should consist of medications and diet.
Drug therapy is aimed at protecting the duodenal bulb from hydrochloric acid.
During treatment, the patient needs to adhere to the correct diet. The diet excludes the consumption of spicy, fried and fatty foods, ham, smoked meats, yeast products, and canned food. Doctors advise patients to eat:
- White bread;
- vegetables;
- soups without cabbage;
- cooked meat and fish;
- slimy porridge.
Nutrition for duodenal ulcer
In order for the duodenal ulcer to heal, it is also recommended to consume dairy products - natural cream, cottage cheese, cheese. You can cook an omelet. In case of pathology, you can eat sweet fruits without rough peels.
Bulbit: cause of the disease, diagnosis and treatment
Bulbit is a type of duodenitis (inflammatory lesion of the duodenum).
The disease is a chronic or acute inflammation of the mucous membrane of the duodenum - the so-called bulb, which is adjacent to the stomach. Most often, bulbitis is accompanied by other gastrointestinal diseases - duodenogastric reflux, gastritis, as well as pathology of the hepatobiliary system. Rarely does bulbitis have an isolated character. If you do not consult a doctor in a timely manner, do not have a gastroscopy, do not undergo a course of treatment and do not pay attention to the symptoms, there is a high probability of developing duodenal ulcers.
4 types of bulbit
With the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, food after primary processing passes from the stomach to the duodenum. The ducts of the pancreas and gallbladder open in its bulb. As a result, the environment changes properties and becomes alkaline. The digestive process continues under the influence of pancreatic enzymes. If there are disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract, one of four types of bulbitis occurs:
- Acute bulbitis involves exposure of the mucous membrane to various aggressive environments - medications, alcohol, toxic substances, etc.
- The cause of the development of the chronic form of bulbitis is gastritis caused by the presence of Helicobacter pylori infection. Less commonly, its appearance is associated with giardiasis, helminthic infestation, and autoimmune lesions, such as Crohn's disease. Food allergies are not the cause of chronic bulbitis, as many people think.
- Catarrhal bulbitis occurs with irregular nutrition, constant stress, excessive alcohol intake, and the presence of Helicobacter pylori infection. All this leads to an imbalance in the acid balance and constant irritation of the duodenal mucosa.
- Erosive bulbitis occurs as a consequence of catarrhal disease. If exposure to irritating factors continues for a long time, erosions occur - a superficial defect of the mucous membrane.
Symptoms and diagnosis of bulbitis
With bulbitis, pain occurs in the peri-umbilical and epigastric areas. The pain is aching in nature and occurs approximately an hour and a half after eating, accompanied by nausea, heaviness in the stomach, and loss of appetite.
To confirm the diagnosis of bulbitis, you can do a gastroscopy, perform a urease breath test, and also take a biopsy material to determine the presence of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori.
Treatment of bulbitis in the Clinic of Professor Gorbakov
Complex treatment and an individual approach are the main principles that guide the doctors of the Gorbakov Clinic when choosing treatment methods for each patient. Specialists develop a diet and prescribe drug therapy. The patient is prescribed drugs that reduce acidity, regulate gastrointestinal motility, as well as those that have an enveloping effect. If necessary, treatment for Helicobacter and parasitic infections is prescribed. In some cases, the patient is examined by an immunologist who prescribes additional strengthening drugs.
Bulbit is an inflammatory disease of the duodenum. In the vast majority of cases, it is associated with other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Without proper treatment, an ulcer may form at the site of inflammation. If you are suffering from any symptoms of dysfunction of the digestive system, then immediately contact a gastroenterologist and undergo the recommended examination.
Bulbit is a type of duodenitis (inflammatory lesion of the duodenum). The disease is a chronic or acute inflammation of the duodenal mucosa - the so-called bulb. Most often, bulbitis is accompanied by other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract - duodenogastric reflux, gastritis, as well as pathology of the hepatobiliary system. Rarely does bulbitis have an isolated character.
If you do not consult a doctor in a timely manner, do not have a gastroscopy, do not undergo a course of treatment and do not pay attention to the symptoms, there is a high probability of developing duodenal ulcers.
Types of bulbite
With the normal functioning of the digestive organs, food after primary processing passes from the stomach to the duodenum. The ducts of the pancreas and gallbladder open in its bulb. As a result, the environment changes properties and becomes alkaline. The digestive process continues under the influence of pancreatic enzymes. When there are disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract, one of the types of bulbitis occurs:
- Acute bulbitis involves exposure of the mucous membrane to various aggressive environments - medications, alcohol, toxic substances and others.
- The cause of the development of the chronic form of bulbitis is gastritis caused by the presence of Helicobacter pylori infection. Less commonly, its appearance is associated with giardiasis, helminthic infestation, and autoimmune lesions, such as Crohn's disease. Food allergies are not the cause of chronic bulbitis, as many people think.
- Catarrhal bulbitis occurs with irregular nutrition, constant stress, excessive alcohol intake, and the presence of Helicobacter pylori infection. All this leads to an imbalance in the acid balance and constant irritation of the duodenal mucosa.
- Erosive bulbitis occurs as a consequence of catarrhal disease. If exposure to irritating factors continues for a long time, erosions occur - a superficial defect of the mucous membrane.
Forecast
If the treatment of a peptic ulcer is successful and correct, then the bulb will not be deformed, and a small scar may form on the organ. Large ulcers can cause tightening of the intestinal walls, which leads to obstruction.
With proper therapy, the healed section of the intestine can return to its original position for several months or a year. If the patient is faced with a severe form of duodenal ulcer, then quick and complete restoration of the organ is impossible.
Treatment and diet
You can't do without a diet!
The first thing to do is to eliminate the cause of the bulbitis. If it is gastritis, then they treat it; if it is worms, then they remove the parasites. And only then can you begin to restore the functioning of the bulb and the entire duodenum. If you have an infection, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics. Antacids are also often prescribed, which reduce acidity, which helps restore the intestinal mucosa. For pain, it is also recommended to take painkillers. All treatment methods must be prescribed by a doctor. Self-medication is dangerous and can harm your health.
Traditional methods can be added to the main course of treatment. Before using them, be sure to consult your doctor. You can drink decoctions of chamomile, cloves or St. John's wort. They will help relieve inflammation. A decoction of tansy is useful for intestinal parasites. It is often recommended to take a paste of plantain and honey. Don't overdo the herbs. This is medicine, not tea, compliance with the dosage is mandatory. If you notice signs of an allergic reaction, stop treatment immediately and take antihistamines. Remember that not every bulbitis can be treated with folk remedies. If there is a suspicion of ulcers (erosive form), taking herbs is strictly prohibited, since these drugs can provoke breakthrough of the ulcers.
Preventive actions
As part of basic preventive measures aimed at preventing the development of scar-ulcerative deformation of the duodenal bulb or the progression of the pathological process after healing of the ulcer, it is recommended to perform the following actions:
- Full completion of the rehabilitation period. It includes drug therapy, physiotherapy, a special regime,
- Dieting. The adaptive nutrition system must be adhered to on an ongoing basis, until the final disappearance of all signs of pathology, including those confirmed by diagnostic measures,
- Rejection of bad habits. First of all, we are talking about alcohol consumption and smoking,
- Moderate physical activity. If there is deformation of the duodenal bulb, active physical activity is contraindicated, however, light cardio training is acceptable and recommended,
- Regular preventive examinations. Includes a visit to a gastroenterologist, laboratory tests, ultrasound, fluoroscopy, and other procedures as necessary.
Possible complications
Cicatricial deformation of the duodenal bulb often causes complications, especially in the presence of predisposing circumstances. The most common problems:
- Relapse of the ulcerative process. Observed on average in a quarter of patients, even when they undergo full-fledged treatment 3-6 months after therapy,
- Blockage of the duodenum. It is formed in the case of advanced forms of scar deformities, with the development of an extreme pathological process. Leads to systemic spillage of bile/hydrochloric acid throughout the gastrointestinal tract, requiring hospitalization,
- Bleeding. Caused by a violation of the integrity of the mucous membranes and epithelial structures in the localization of scars. Requires first aid and qualified treatment in a hospital with hospitalization of the patient.
- Secondary manifestations. Dyspeptic disorders that do not disappear for weeks and months, induction of the development of irritable bowel syndrome, and so on.