Doctors Cost
Price list Doctors clinic
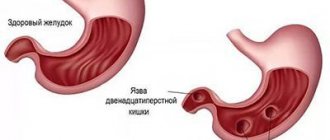
Duodenitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the duodenal wall. There are acute and chronic forms of the disease, they differ in the severity of symptoms. Timely treatment of acute duodenitis allows one to avoid structural changes in tissue, while in chronic cases frequent exacerbations can be observed, and emerging foci of inflammation lead to restructuring of the mucosal structure. Therefore, timely consultation with a doctor in case of severe severe symptoms often helps to avoid unwanted changes.
Factors provoking the disease
Medical statistics show that duodenal ulcers are diagnosed in middle-aged and young people, with the male population accounting for a larger percentage.
This phenomenon is associated with excessive alcohol consumption and smoking. Also, duodenal ulcers are provoked by the modern rhythm of life with great psycho-emotional stress, nervousness, and persistent stressful situations. As a result, vasospasm occurs and the normal nutrition of the body’s cells is disrupted. Under the influence of acids, foci of ulcers appear in the duodenum area. The leading place in the list of factors provoking duodenal ulcers is occupied by Helicobacter bacteria. This microorganism is found in seven out of ten people, but it does not always cause health problems. The bacterium is transmitted through shared objects, medical instruments, saliva and other close contacts. You can also get a duodenal ulcer if you do not follow the rules of personal hygiene.
Duodenal ulcers also develop against the background of other factors. These include:
- genetic predisposition;
- abuse of coffee and foods with high acidity;
- long breaks between meals;
- using medications without a doctor’s prescription;
- accompanying illnesses.
According to some data, night work doubles the risk of ulcers.
Perforation of the ulcer
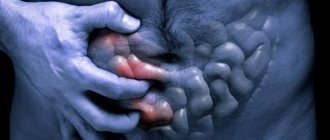
The most serious complication of gastric and duodenal ulcers is perforation. This is an acute surgical disease that occurs as a result of through destruction of the wall of the stomach or duodenum in the area of the ulcer. When the stomach or duodenum is perforated, highly acidic contents enter the free abdominal cavity, causing irritation of the peritoneum.
The main symptom of perforation: sharp, sudden pain (“as if hit with a dagger in the stomach”) pain in the epigastric region (in the upper abdomen).
May also be noted:
- nausea,
- vomit,
- drop in blood pressure,
- cardiopalmus,
- increased sweating.
In obese, immunocompromised patients taking steroid drugs, as well as in patients with a reduced level of consciousness, the elderly and children, the clinical picture may be less pronounced.
An objective examination reveals pain on palpation of the abdomen. The pain intensifies with movement, the abdominal muscles are “board-shaped” tense. The patient's position is forced - he lies on his side or on his back, his knees are pulled up to his stomach, his face is pained, his skin is pale, his lips are cyanotic (blue), his limbs are cold, his facial features are pointed, a rare pulse and low blood pressure are recorded.
When percussing the abdomen, sharp pain is noted. Symptoms of peritoneal irritation are positive. With the development of peritonitis, muscle tension in the anterior abdominal wall increases, and fever and chills may appear.
Symptoms of the disease
The main symptom of a duodenal ulcer is pain. During periods of remission, it may not make itself felt; the person feels comfortable and calm. But as the seasons change, painful symptoms and signs return with a vengeance. Painful symptoms are especially intense after eating and at night. Localization of discomfort is observed in the sternum, but can spread to the upper abdomen. The severity depends on the stage of the ulcer and ranges from almost indistinguishable to acute.
When a person has duodenal ulcers, the following symptoms are observed: heartburn, belching, bloating, stool disturbance, feces mixed with blood. Signs of ulcers include loss of appetite and sudden weight loss. Symptoms such as nausea and vomiting are reported by a minority of people, but they do occur after eating. If you notice these symptoms, you should make an appointment with a doctor. Do not treat yourself!
Gastroduodenitis - inflammation of the duodenum
09.10.2021
Inflammation of the duodenum and stomach , otherwise called gastroduodenitis, is one of the most common pathologies of the digestive system. The symptoms are similar to those of gastritis , but gastroduodenitis very often accompanies other diseases of the digestive system, so it is not so easy to diagnose.
Manifestations of gastroduodenitis
accompany an inflamed duodenum and stomach :
- pain in the epigastric region
- nausea
- heartburn (if acidity level is elevated)
- sensation of expansion in the epigastric region
- belching accompanied by a bitter taste
- vomiting, occasionally with bile
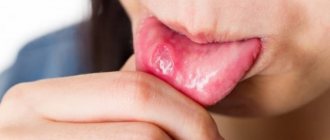
Pain due to gastroduodenitis occurs a couple of hours after eating, radiating to the navel and under the right rib. They weaken immediately after a meal or consumption of antacids. The patient in such cases is thin, with pale skin. Its tongue has a yellow-white coating with teeth . When palpating the right rib and the right part of the epigastric region, pain occurs.
In children with gastroduodenitis, in addition to the above symptoms, the following are observed:
- recurring headaches
- regular overwork
- sleep disturbance
- my head is spinning
The cause of such symptoms is endocrine diseases due to the fact that the functioning of the duodenum is impaired.
Causes of gastroduodenitis
Factors that cause inflammation of the duodenum are:
- unbalanced diet - consumption of very spicy, hot and fatty foods or a poor diet
- no power mode
- constant stress
- various bacteria (especially Helicobacter Pylori)
- infection of the mouth and throat
- heredity
Course of gastroduodenitis
Inflammatory processes in the duodenum may appear unexpectedly (acute gastroduodenitis), but often the disease is chronic with pronounced symptoms. Often, chronic gastroduodenitis worsens in the fall/spring, and the exacerbation is followed by a weakening phase. The degree of severity in the exacerbation phase is determined by the strength of pain, its duration, and the general condition of the patient. After a few months, the disease enters a phase of partial (when symptoms of the disease are identified using endoscopy ) or complete weakening (in the absence of critical manifestations).
Treatment of chronic gastroduodenitis
Therapy for an inflamed duodenum is carried out in the same way as for gastritis . The patient is prescribed bed rest (in the initial 7 days of exacerbation), as well as diet No. 1 with a further transition to diet No. 5. During the weakening process, a complete and balanced diet is required. Diet is very important. If acidity is increased, then the pathology is cured through H2 receptor blockers, histamines and medications that suppress the development of Helicobacter Pylori bacteria. If necessary, the patient is prescribed medications to normalize the motor functions of the organs. After the crisis, therapeutic exercises, treatment in sanatoriums, and physiotherapeutic procedures will also be useful.
Treatment of gastroduodenitis with folk remedies
It is recommended for inflamed duodenum and stomach to drink fresh juices from:
- aloe - three times a day, half an hour before meals, a dessert spoon (two-month course)
- black currants - a quarter of a glass every day
- cabbage - heated three times a day before meals
- potatoes - a quarter of a glass on an empty stomach early in the morning
Cabbage and black currants provide an effect on inflammation with a reduced level of acidity, and potatoes are suitable for patients who have increased secretion.
Inflammation is also effectively treated with herbal infusions:
- a spoonful of dry plantain leaves is poured into a glass of boiling water, infused like tea; consume in small sips throughout the day.
- spoons of dry or fresh mint leaves are poured with boiling water (0.4 l) and infused; consume before each meal.
- 0.02 kg of yarrow is poured with boiling water (0.4 l), boiled for a quarter of an hour, and then infused for 40 minutes; consume before each meal in case of decreased secretion (1 tablespoon).
Published in Gastroentorology Premium Clinic
Diagnosis and treatment of the disease
Before starting treatment for a duodenal ulcer, you will need to undergo an examination and laboratory tests. The initial visit includes collecting anamnesis and clarifying data on hereditary diseases. Further actions are aimed at detecting ulcers in the duodenum, determining their size and location.
Diagnosis of duodenal ulcers will be incomplete without determining the acidity of gastric juices, x-rays and other methods of establishing health status. Based on the information received, a treatment regimen for duodenal ulcers is selected that is suitable for each individual case.
A wide range of medications are used in the treatment of duodenal ulcers. Treatment of duodenal ulcers includes:
- antibacterial therapy;
- taking antibiotics;
- relief of pain syndromes;
- decrease in acidity.
If the body is severely damaged, treatment of duodenal ulcers requires surgery. In this case, treatment consists of excision of part of the intestines with severe damage to the mucous membranes.
Complications of the disease
Treatment of duodenal ulcers combines a complex of different manipulations and is carried out under the supervision of the attending physician. Self-treatment and taking medications is unacceptable! Such treatment of ulcers leads to attenuation of symptoms and transfers the disease to a latent, sluggish form, threatening serious complications and death.
In the absence of timely treatment, the problem can progress, causing complications. These include:
- bleeding;
- intestinal perforation;
- narrowing of the intestine;
- pyloric stenosis.
The listed complications are fatal to humans, so it is necessary to urgently begin treatment for ulcers as soon as the diagnosis is confirmed.
Dietary table and prevention
A prerequisite for the treatment of the duodenum is a dietary table. First of all, you should avoid alcohol and stressful situations. Remove spicy, salty, and spicy foods from your diet, replacing them with stewed, boiled or steamed foods, and eat small portions. Table waters, such as Essentuki, are recommended as an additional treatment method.
Authorized products:
- low-fat dairy products;
- porridge;
- crackers and dried bread;
- light soups;
- vegetable oils;
- lean varieties of fish and meat.
The treatment regimen must include taking medications prescribed by a specialist. For a speedy recovery, it is recommended to follow all the doctor’s instructions and remember to alternate between rest and work. Treatment regimens and dietary patterns may differ in some cases, so it is worth discussing food intake with a specialist.
Any disease is easier to prevent than to treat. We recommend that everyone watch their diet and not eat dry food. Lead an active lifestyle and avoid stressful situations. Give up alcohol and cigarettes, toughen up and regularly undergo a full medical examination.
Treatment of duodenal ulcer
Treatment of perforated gastric and duodenal ulcers is only surgical and consists of suturing the perforated hole, sanitation, revision and drainage of the abdominal cavity.
The main measure for the prevention of all these complications, early detection of stomach and duodenal cancer is a timely visit to a specialist and an endoscopic examination with a biopsy. This is especially important in the presence of complaints, risk factors, and heredity for cancer.
The main goal of treating peptic ulcers is to reduce the secretion of hydrochloric acid and eliminate the main causes leading to ulcer formation.
Nutrition for ulcers 12
The basis of treatment for gastric and duodenal ulcers is proper balanced nutrition, as well as lifestyle correction. Reducing emotional stress is mandatory.
To avoid exacerbations of peptic ulcer disease, try to eat regularly, 3 to 4 times a day, with a mandatory small meal in the evening. Do not overuse spices, hot sauces, fried foods, or strong meat broths. If you have a peptic ulcer in the off-season, you should especially carefully monitor your health. After all, it is often combined with inflammation of the gallbladder, cholelithiasis, and intestinal diseases. Exacerbation of these concomitant diseases can cause exacerbation of the ulcer itself.
Currently, the pharmacy chain has a large number of drugs that reduce the secretion of hydrochloric acid, envelop and others. But only a specialist can correctly select the necessary therapy and make a diagnosis, and, therefore, determine the correct treatment tactics.
If you have symptoms of a peptic ulcer, you should immediately contact a specialist for examination and treatment. DO NOT SELF-medicate!