the whole list
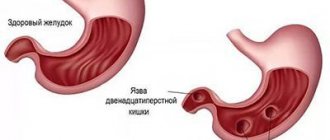
Peptic ulcer disease is a chronic disease that occurs with alternating periods of exacerbation and remission, the main symptom of which is the formation of a defect (ulcer) in the wall of the stomach and/or duodenum.
An ulcer is a defect in the mucous membrane that has a clear boundary. A superficial ulcer is called erosion. Peptic ulcer disease is detected in 5–10% of the adult population.
Depending on the location, ulcers are divided into gastric and duodenal (duodenum - duodenum).
The ratio of gastric and duodenal ulcers is approximately 1: 4. Young people have a lower incidence of gastric ulcers compared to duodenal ulcers (1: 13). Conversely, in middle-aged and elderly patients the frequency of gastric ulcers increases.
Along with peptic ulcer disease as an independent disease, it is now customary to distinguish secondary symptomatic ulcers of the stomach and duodenum that occur under the influence of stress, circulatory disorders, taking antipyretics, painkillers (acetylsalicylic acid, indomethacin, diclofenac, ibuprofen) and others.
Depending on the cause, there are:
- stress ulcers (for example, with myocardial infarction, widespread burns, after neurosurgery, etc.);
- drug-induced ulcers (taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, hormones and other medications);
- endocrine ulcers (with Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, hyperparathyroidism);
- ulcers in certain diseases of internal organs (Crohn's disease, atherosclerosis of the branches of the abdominal aorta, etc.).
Duodenal ulcer, its types and stages
Peptic ulcer is a chronic disease with periodic relapses, in which a defect forms on the mucous membrane and submucosal layer - an ulcer.
The sizes of the ulcers are:
- small - up to 0.5 cm in diameter;
- medium - 0.6–1.9 cm in diameter;
- large - 2.0–3.0 cm in diameter;
- gigantic - more than 3.0 cm in diameter.
There are also diseases associated with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori (hereinafter referred to as HP) and those not associated with HP.
A duodenal ulcer can be localized on the bulb and in the postbulbar region.
The division into stages is accepted:
- exacerbation - characterized by the formation of a fresh ulcer;
- scarring - epithelization with subsequent scar formation;
- remission - healing of the ulcer.
Separately, cicatricial and ulcerative deformation of the duodenum is distinguished.
Histamine blockers – control the production of hydrochloric acid
The ability to maintain an optimal level of acid-base balance directly contributes to the scarring of defects in the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines. It is desirable that this balance be maintained for a month for 18-20 hours a day, this significantly reduces the number of complications from peptic ulcer disease.
The most commonly prescribed drugs are Ranitidine or Quamatel (Famotidine). Ranitidine is prescribed for peptic ulcers at 300 mg daily for a month. To prevent relapses, this amount is halved (150 mg). Kvamatel is taken in the same way, that is, to obtain a therapeutic effect you need 40 mg, to prevent complications - 20 mg per day.
These drugs help stop bleeding of mucosal defects (Kvamatel). In addition to the above, Roxatidine, Cimetidine, Famotidine have the same effect. Their antisecretory effect extends for a period of 10-12 hours, for Cimetidine - 5 hours.
Main causes
The main causes of the disease include an imbalance between the aggressive acid-peptic effect of gastric juice and the protective properties of the duodenal mucosa. This refers to hypersecretion - excessive production of hydrochloric acid, impaired intestinal motility.
The decrease in protective properties comes down to a decrease in mucus production, deterioration of blood flow and regeneration - restoration of intestinal cells. Hormonal factors can also influence the occurrence of ulcers.
Predisposing factors include:
- abuse of sour, spicy foods and coffee;
- eating disorder;
- genetic predisposition;
- depression and stress;
- taking certain medications;
- work on the night shift;
- smoking and alcohol abuse;
- concomitant inflammatory diseases.
In 1983, the critical role of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori in reducing the protective properties of the intestinal mucosa was established. In studies conducted, it was detected in 93% of patients with duodenal ulcers. Helicobacter is resistant to drugs and acidic environments. When multiplying, the microorganism secretes enzymes that cause inflammation of the mucous membrane, leading to intestinal ulcers.
Methods for diagnosing duodenitis
Diagnostics plays an important role. An incorrect or inaccurate diagnosis will affect the entire treatment. Therefore, you should not be afraid and refuse diagnostic procedures prescribed by your doctor.
Gastroscopy
- Cost: 3,000 rub.
More details
- EGDS (esophagogastroduodenoscopy) - using a flexible probe equipped with a video camera, the doctor examines the esophagus, stomach and duodenum. Using this method, you can see redness and swelling of the mucous membrane, erosion, and with a decrease in tone, smoothing of folds, the presence of nodules, hemorrhages and other signs that can be used to diagnose duodenitis.
- X-ray using a contrast agent (barium sulfate), which allows you to identify anatomical disorders, signs of inflammation, obstruction, the presence of an ulcer or tumor, signs of impaired intestinal tone and motility.
- Ultrasound diagnostics allows you to evaluate nearby organs, diseases of which can lead to duodenitis.
- A laboratory examination is prescribed (general blood test, biochemical analysis, examination for the presence of Helicobacter pylori infection, and others).
- Fecal occult blood test to ensure there are no bleeding ulcers or erosions.
- General analysis of stool (coprogram), which helps to identify signs of disturbances in duodenal digestion.
Symptoms of the disease
The leading symptom of the disease is severe pain that occurs on the right side just above the navel or slightly below the sternum. Typically, such painful sensations occur on an empty stomach, 3 hours after eating. After eating, the pain subsides. Patients may experience heartburn, nausea, and vomiting after eating, which provides temporary relief. Also characterized by loss of appetite and rapid weight loss. In such patients, irritability increases, lethargy and decreased vitality occur.
Peptic ulcer disease is typically seasonal, with exacerbation of symptoms observed in spring and autumn. Sometimes the pathology is asymptomatic. This occurs when the ulcer is small.
Etiology
A focus of inflammation in the duodenum is formed due to damage to epithelial cells by hyperacid juice coming from the stomach. The increased acidity of this compound irritates the intestinal mucous membranes. In the absence of pronounced symptoms, the pathology proceeds unnoticed by the patient and quickly progresses to the chronic stage. Degenerative processes develop in the intestinal wall (leading to the formation of foci of atrophic duodenitis).
Pathology of the secondary type occurs due to functional digestive disorders provoked by the primary disease. Chronic damage to the liver, gallbladder and pancreas leads to changes in the enzyme balance. As a result of these changes, the protective properties of the epithelium of the duodenum are weakened - a focus of inflammation is formed.
Treatment of the disease
Methods of treatment and a set of medications are determined by the attending physician based on the diagnostic results.
Drug treatment
The presence of many factors that cause duodenal ulcers has led to the emergence of drugs that act selectively on different pathogenetic mechanisms of the disease. All drugs can be divided into etiological, affecting the cause of the disease, and symptomatic, alleviating the patient’s condition.
Antibacterial drugs
Since helicobacteriosis is detected in 93% of patients, complex treatment includes medications that destroy these bacteria. Typically, several antibacterial agents are used in pharmacotherapy, so a complex of antibiotics effectively suppresses the growth and reproduction of Helicobacter pylori.
For duodenal ulcers, antiprotozoal drugs with antibacterial properties show good results. Macrolides and antibiotics of the penicillin and tetracycline series have proven themselves well. They are prescribed in a course of 10–14 days.
Bismuth preparations
Medicines containing bismuth tripotassium dicitrate have a triple effect:
- relieve inflammation;
- have antibacterial activity;
- have astringent properties that give an anesthetic effect.
Such drugs form an insoluble colloid and combine with a protein that creates a protective film on the surface of the mucous membrane.
Antacids
Drugs with dual effects:
- reduce the acidity of gastric juice, thereby eliminating the main irritant;
- envelop the mucous membrane, relieving pain and creating a protective barrier.
Medicines of this type are symptomatic remedies with immediate results.
Antiulcer proton pump inhibitors
Reduce gastric secretions, including the production of pepsin and the secretion of hydrochloric acid. They belong to prodrugs that exhibit activity when they form compounds under the influence of acid. They do not give an immediate effect, but have a prolonged effect, promoting the healing of the mucous membrane.
Since these drugs suppress calcium ions, preparations of this mineral are prescribed in combination with them.
In addition to etiological treatment, medications may be prescribed that eliminate the root cause of the ulcer, for example, drugs that normalize hormonal levels, eliminate anxiety disorders and other medications.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy can be used in the complex treatment of duodenal ulcers, taking into account the localization of the pathology and intestinal dysfunction.
In case of duodenal localization, a good result is achieved by a physical effect that affects the mechanisms of self-regulation and adaptation:
- laser puncture;
- EHF therapy;
- magnetotherapy.
Intestinal motility can be improved using low-frequency ultrasound therapy, which also helps relieve inflammation, improve blood supply to the organ and reduce the number of pathogenic microflora.
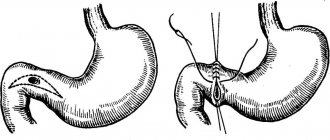
Surgery
Indications for surgical intervention of ulcerative pathology may include complicated forms of the disease and non-healing ulcers. In case of perforation, emergency surgery is performed if the bleeding cannot be stopped by conservative methods.
Surgical intervention is also indicated for malignancy, when the ulcer becomes malignant. Such an operation can be performed endoscopically or laparoscopically in the early stages, and in the later stages - in the traditional way.
specialist
Our doctors will answer any questions you may have
Tumasova Anna Valerievna Gastroenterologist
Anatomy
Most people have a variety of shapes. Even in the same person, the shape and location of the organ can change over time. First, let's talk about the structure of the duodenum.
Structure
The organ has several layers:
- outer shell;
- muscle layer with longitudinal and circular layers;
- submucosa, thanks to which the mucous membrane can be collected in layers;
- mucous layer covered with villi.
Location
The organ has four main parts:
- Upper, or initial. It is located approximately at the level of the first lumbar vertebra or even the last thoracic vertebra.
- Descending. It is located to the right of the lumbar region and touches the kidney.
- Bottom, or horizontal. It goes from right to left, and then passes next to the spine and bends upward.
- Rising. Forms a bend and is located at the level of the second lumbar vertebra.
Where is the duodenum located? Most often it is located at the level of the second or third lumbar vertebrae. The location may differ for each person and is influenced by a large number of factors, such as age and weight. For example, in elderly and thin people the organ is located slightly lower than in young and well-fed subjects.
The photo clearly shows where the duodenum is located in humans
The intestine is in contact with other abdominal organs on all sides:
- liver;
- bile ducts;
- pancreas;
- right kidney;
- ureter;
- ascending colon.
The length of the duodenum is 25-30 cm.
Nutrition and bad habits during illness
Diet is an essential part of complex therapy for duodenal ulcers. During the period of exacerbation, food should be as gentle as possible, therefore, at this time, mucous soups with rice water without meat and vegetables, sweet warm tea with crackers or dried bread, and jelly are recommended. All products should be easily digestible and not irritate the intestinal mucosa. In the future, you need to follow several rules.
Authorized Products
General nutrition rules:
- meals should be fractional, up to 6 times a day;
- the interval between doses is no more than 2.5 hours;
- you need to eat in small portions;
- spices are excluded;
- vegetables must be ground to a pulpy state;
- Use boiling, baking, stewing as heat treatment; food should not be fried.
For duodenal ulcers, the following products are allowed:
- cereals, potatoes, pasta;
- rabbit, turkey, veal meat;
- low-fat fish;
- eggs in the form of an omelet;
- dried bread (crackers);
- fermented milk products: fresh kefir, fermented baked milk, unsalted cheeses;
- milk porridge;
- grated boiled vegetables;
- fruits, baked or pureed;
- drinks: jelly, weak tea, dried fruit compotes.
Prohibited Products
Food products that irritate the mucous membrane of the duodenum and stimulate the secretion of gastric juice are excluded from the diet. Does not include salads made from vegetables with coarse fiber, including radishes, radishes, daikon, tomatoes, cabbage, turnips, and mushrooms.
Baked goods, fatty meats, canned products, any smoked products, confectionery with cream, preserves, dishes with spices and vinegar, and garlic are excluded.
You should not eat foods that stimulate fermentation: sweet fruits (kiwi, pear, melon, grapes, etc.), legumes, sour and sweet juices, as well as foamy and carbonated drinks.
If a duodenal ulcer is detected, you must permanently stop drinking alcohol and not smoke, since ethyl alcohol and tobacco irritate the mucous membrane.
Preventive measures
The basis for the prevention of gastrointestinal diseases is a balanced diet. Doctors recommend that patients stop smoking and drinking alcohol. Reducing the risk of developing inflammatory processes in the duodenum is facilitated by timely treatment of pathologies of the digestive system.
In the chronic course of the disease, a child or adult will need to regularly undergo clinical examinations and take medications that help eliminate the cause of inflammation of the intestinal epithelium. In this case, a favorable prognosis is formed - the patient’s quality of life remains at a consistently high level.
Prevention of peptic ulcers
To prevent the onset of the disease or its relapse, it is necessary to follow a diet. The interval between meals should not exceed 4 hours. You can't eat it dry. Giving up bad habits is part of prevention.
If you are predisposed to peptic ulcers, do not work at night. Shift work should be changed to regular five-day work. Try to avoid traumatic situations and visit a gastroenterologist at least once every six months. It is necessary to promptly treat concomitant diseases.