Duodenum
The process of intestinal digestion begins in the duodenum.
Before moving on to what diseases a person may develop and what symptoms they will manifest, it is necessary to pay attention to the organ itself, learn about its functions and purpose.
It must be said right away that the name duodenum was given for a reason. Its length is 25-30 centimeters, or as they also consider 12 sizes of a human finger (transverse). The intestine is divided into four sections:
- Upper. This part of the intestine is directed obliquely, and then forms a slight bend and passes into the next part. Its length is approximately 5 or 6 centimeters
- Descending. This section is located immediately after the upper one. And if we talk roughly about its location (to make it more clear), then it is approximately at the level of the lumbar region to the right of the spine. In this part of the intestine there is a very important fold with a papilla from which ducts extend. The length of this part of the intestine is approximately 7 to 12 centimeters
- Lower. This area is located transverse to the spine. Its length is approximately 6-8 centimeters
- Rising. This is the shortest part of the intestine, the length of which ranges from 4 to 5 centimeters (depending on the individual characteristics of the organism). This part is located directly at the level of the lumbar region. But in some people it is not clearly expressed
In addition, the duodenum has one anatomical feature that depends on age and fullness. So, in people who are fuller and younger, it is located much higher than in thin or elderly people. If we talk about the functions of the organ, they are as follows:
- The process of intestinal digestion begins in it, that is, the food bolus is treated with acid and alkali to such a state that its further passage is possible
- Regulates the release of pancreatic enzymes depending on what food is ingested and how much effort is required to digest it
- Maintains feedback between the stomach, that is, it has a direct effect on the normal functioning of all digestive processes
And therefore, if some pathological changes occur in the duodenum and it stops working as the body requires, this will negatively affect all organs of the digestive system, and then the entire human body in general.
Functions
Let us highlight the main functions of the duodenum:
- production of enzymes and duodenal juice necessary for normal digestion;
- motor and evacuation function, that is, responsible for moving food gruel;
- secretory;
- regulation of bile pancreatic enzymes;
- supporting communication with the stomach. She is responsible for opening and closing the gatekeeper.
- adjusting the acid-base balance of food. It makes the food bolus alkaline.
Since the duodenum is the initial section of the entire intestine, it is here that the processes of absorption of nutrients that come with food and drink actively occur. This is where the stage of intestinal digestion begins.
Digestion
After the food bolus enters the initial part of the colon, it mixes with bile, secretions of the intestinal walls, as well as fluid from the pancreatic ducts. The acidic environment of food is then neutralized by bile, thereby protecting the mucous membrane. In addition, bile breaks down fat and breaks it down into small emulsions, which speeds up the digestion process.
Under the influence of bile secretion, fat breakdown products dissolve and are absorbed into the intestinal walls, and complete absorption of vitamins and amino acids occurs. It is also worth noting that bile regulates intestinal motility, stimulating the contraction of its muscles. Thanks to this, the food bolus moves faster through the intestinal lumen and is promptly evacuated from the body.
Pancreatic juice also plays an important role, with the help of which starch is digested, as well as proteins and fats. The duodenal glands produce intestinal juice, which mostly consists of mucus. This secret promotes better breakdown of proteins.
Considering all of the above, we can say that the duodenum plays a huge role in the digestive process. It saturates the food bolus with the necessary enzymes and ensures further digestion.
DPC ensures the normal course of digestive processes
Duodenitis
Duodenitis is inflammation of the duodenum.
One of the most common diseases of this organ is duodenitis, or otherwise inflammation of the duodenum. There are many reasons for the development of the disease, however, doctors note that as an independent disease it is quite rare. It mainly develops due to the influence of the following negative factors:
- Food poisoning. At least once in his life, a person ate foods that caused him food poisoning. For some, it could occur in a weaker form, but for some they had to call an ambulance. And it is precisely this kind of poisoning that can provoke the development of duodenitis
- Poor nutrition, namely abuse of spicy foods. Since the mucous membrane becomes inflamed only because it is damaged in some areas, something must be damaging it. And it’s precisely spicy food that negatively affects the condition of the mucous membrane, contributing to its destruction.
- Abuse of alcoholic beverages, which negatively affect not only the duodenum, destroying it, but also the entire body as a whole
- Damage to the mucous membrane by a foreign object. Such damage can occur if the remains of shellfish, bones, etc. enter the body.
- The presence of foci of infections in the body
- The presence in the body of such a harmful bacterium as Helicobacter, which has a destructive effect on the stomach and duodenum, respectively
- Stress, during which the body’s main forces are aimed at maintaining the emotional state, and this is done at the expense of the well-being of other organs
- Taking certain medications that negatively affect the mucous membrane, destroying it
Depending on what caused the development of the disease, the chosen treatment tactics will depend, because initially doctors fight not only the symptoms, but also the irritants (provocateurs). If we talk about the symptoms of duodenitis, there are a lot of them:
- Digestive problems, which can manifest as heaviness in the stomach, a feeling of overeating, even if not much food was eaten
- Poor appetite due to digestive problems
- Attacks of nausea and sometimes vomiting that occur during an exacerbation
- Painful sensations in the abdominal area, and the pain does not have a specific character of manifestation
- Night hunger pains, which cause a person to get up at night and either eat or take a pill
- Impurities of blood in the stool or vomit, which appear there due to damage to the mucous membrane. And this means that the damage is much more serious than the person himself assumes
- Anemia, which indicates that there is a bleeding site in the body
- Constant weakness due to anemia, poor appetite
Depending on which part of the duodenum the lining of the duodenum is damaged and inflamed, symptoms may vary slightly, especially when it comes to pain after eating. If the upper section is damaged, it will appear much earlier than if the lower section is damaged.
General information
The disease can occur in acute or chronic form. In the first case, drug therapy eliminates the symptoms of the disease and prevents structural changes in the mucous membrane of the duodenum. The chronic type of inflammation is characterized by regular relapses and changes in the structure of the intestinal epithelium. The disease remains the most common pathology of the duodenum. Up to 95% of clinically diagnosed cases of acute duodenitis resulted in the transition of the pathology to the chronic stage. Men suffer from inflammation of the mucous membranes of the duodenum twice as often as women.
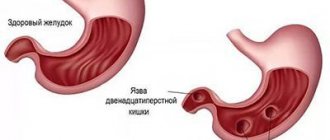
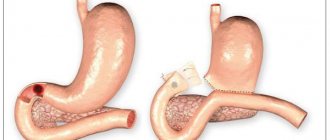
Peptic ulcer
Peptic ulcers can be caused by Helicobacter bacteria.
Almost every person knows that there is such an unpleasant and dangerous bacterium as Helicobacter, which provokes the appearance of ulcers in the gastrointestinal tract, and the duodenum is no exception. Of course, this is not the only reason.
This also includes increased acidity of gastric juice, which enters the upper intestine, weak immunity, genetic predisposition, stress, poor diet, etc. But the cause does not play a special role in the manifestation of symptoms. They will be the same in any case. The main symptoms of duodenal ulcer include:
- Painful sensations, which are one of the most basic symptoms that a person has developed an ulcer. Moreover, duodenal ulcers are characterized by special manifestations of pain. So, it appears mainly on an empty stomach, or after about 2 hours have passed after eating. But that's not all. Patients note that most often they are tormented by pain at night, which occurs due to a strong accumulation of hydrochloric acid in the stomach at night. Sometimes pain occurs in case of poor nutrition, namely the consumption of spicy, fatty, salty, alcohol, etc.
- Heartburn, and some patients note that it begins abruptly and does not go away on its own. You have to take special medications because at some moments the heartburn becomes unbearable. Belching. This is one of those symptoms that causes a person more discomfort, as it appears very suddenly and at inopportune moments.
- Bloating
- Nausea, which can occur at any time of the day or night
- Vomiting, and it brings relief to the patient. And often, in order to somehow improve their well-being, a person specifically calls it
- Constipation. For people with duodenal ulcers, stool retention lasts for several days, and in the most severe cases, for several weeks.
- An admixture of blood in the stool, which appears due to damage to the mucous membrane. But to a greater extent, blood is present in the stool after long-term constipation, when the stool itself can damage the intestinal walls
- Losing weight while the person continues to eat normally and consumes the same amount of calories as always
Doctors note that symptoms may appear once a year, or several times. Yes, and a certain seasonality stands out. Thus, most patients with duodenal ulcers note that there are much more attacks in spring and autumn than in summer and winter.
Classification
According to the localization of the inflammatory process:
- bulbar;
- local;
- diffuse;
- postbulbar.
By origin:
- primary;
- secondary.
According to the results of endoscopic examination:
- Erosive duodenitis. The formation of erosive lesions of varying depths is characteristic. Erosive duodenitis is also known as hypertrophic.
- Atrophic duodenitis. Characteristic is the thinning or death of the cellular layer in the mucous membrane, which leads to disturbances in the secretion of digestive juice.
- Hemorrhagic duodenitis. Identified during a diagnostic search for the causes of duodenal bleeding.
- Erythematous duodenitis. With this form, the mucous membrane becomes swollen with severe redness.
- Nodular duodenitis.
According to the severity of structural lesions:
- interstitial;
- atrophic;
- superficial duodenitis (characterized by slight inflammation in the upper layer; superficial duodenitis is often found in the literature as catarrhal duodenitis).
Among the specific duodenitis it is customary to distinguish:
- immunodeficient;
- duodenitis in Whipple's disease;
- tuberculosis;
- for Crohn's disease ;
- with amyloidosis ;
- fungal.
Standard clinical classification
- duodenitis that developed against the background of duodenostasis ;
- chronically occurring acidopeptic bulbitis , combined with type B gastritis ;
- inflammation of the papilla or peripapillary diverticulitis as a separate local inflammatory process;
- chronic duodenitis, combined with enteritis or various enteropathies.
What is gastric duodenitis? There is no such medical term as “gastric duodenitis”, because The very concept of duodenitis implies inflammation of the mucous wall of the duodenum, and not the stomach. Although the cause of the inflammatory process in the intestines can be precisely the pathology of the stomach.
Duodenal dyskinesia
Another serious disease, the symptoms of which are similar to those listed above, is duodenal dyskinesia. Dyskinesia is a disorder of motor function, due to which chyme is retained in the intestine. Symptoms of the disease will be as follows:
- Pain after eating, which will intensify immediately after eating, and subside a little after a while
- Constipation, which causes many other discomforts. Moreover, the most dangerous thing that can happen as a result of prolonged constipation is intoxication of the body, during which a person’s well-being will sharply deteriorate. And if treated incorrectly, it can be fatal.
- Poor appetite, and after this the patient’s weight will decrease
- Heaviness after eating, which is difficult to relieve with medications
- Nausea and sometimes even vomiting
The symptoms are quite common, and therefore only a specialist can make an accurate diagnosis, who, based on the research carried out, can prescribe the correct treatment.
Dowdenitis complications
What are the complications of duodenitis ? A severe complication of long-term duodenitis is duodenal hormonal insufficiency. Inflammation, destroying the duodenal mucosa, causes death and inhibition of cells that secrete hormones. The appearance of symptoms of duodenal insufficiency is facilitated by congenital weakness of the endocrine apparatus of the duodenum, hypoxia, and concomitant chronic infectious diseases. Insufficiency of the hormonal function of the duodenum causes indigestion, carbohydrate metabolism, significant emaciation or weight gain. Severe neuropsychic and cardiovascular disorders occur.
In young women, duodenal hormonal insufficiency begins to manifest itself in the premenstrual period. Headaches, nausea, vomiting, irritability appear, and performance decreases. Attacks of severe weakness can last from one to four weeks. Weakness is accompanied by palpitations, heart pain, nausea, vomiting, often in the morning on an empty stomach. Patients lose their ability to work, interest in life and family. In a number of patients, attacks of weakness with trembling, pain in the heart, and frequent urination occur immediately after eating or several hours later, less often at night.
Duodenal hormonal insufficiency in acute and chronic duodenitis, duodenostasis is manifested by diencephalic, dumping, Meniere-like, hypoglycemic syndromes, attacks of severe weakness, dizziness, headaches, tachycardia, weight loss, muscle atrophy, depression. There is a dysfunction of other endocrine organs, especially the insular apparatus.
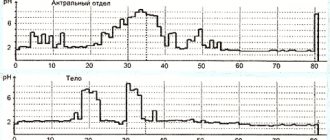
Tests and diagnostics
The disease is diagnosed based on the results of the endoscopic picture obtained during gastroscopic examination. Additional diagnostic methods are:
- X-ray examination of the stomach and duodenum;
- determination of pH of gastric juice and its biochemical study;
- duodenal intubation;
- coprogram;
- blood chemistry.
A biopsy specimen is taken and examined if malignancy of the pathological process is suspected.
Prognosis and prevention
Primary prevention consists of a balanced diet, avoidance of tobacco products and alcohol. Timely diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the digestive tract, as well as rational use of medications, can prevent the development of duodenitis.
The basis of relapse prevention is regular annual examination according to the profile and receiving sanatorium-resort treatment. The prognosis is considered favorable if all the above recommendations are followed.