The first option may occur as a result of a gunshot, stab or cut injury. The second type of injury is the result of severe damage affecting the liver directly. But this can also be facilitated by an indirect impact, for example, a fall from a significant height on one’s feet. With pathological disorders such as syphilis or fatty degeneration, even mild trauma can lead to liver rupture.
Clinical manifestations
A two-stage rupture of the liver is often observed, in which first there is a rupture of the organ parenchyma and accumulation of blood in the capsule. Subsequently, slight physical activity leads to rupture of the capsule and blood enters the abdominal cavity.
When the liver ruptures, the victim is in extremely serious condition. Especially if the cause of injury is gunshot damage. First of all, shock manifestations develop, then signs of peritonitis. In very rare situations, immediately after liver damage, the victim can stand up and make any movements, but then symptoms of intra-abdominal hemorrhage occur. Liver injuries of a closed nature are often manifested only by anemization of the skin; there are no traces of damage.
Symptoms of liver rupture also appear:
- frequent, weak pulse, but in the abdominal cavity due to rupture of the bile ducts, bile can accumulate and be absorbed, which contributes to the development of bradycardia;
- shallow, disturbed breathing;
- nausea, vomiting;
- the occurrence of pain upon palpation of the abdomen, and in the lateral areas of the abdominal cavity the presence of fluid (blood, bile) is easily determined.
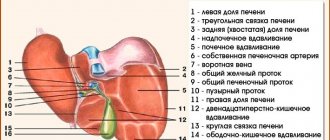
Liver injuries
The characteristics of the injury depend on the mechanism of injury. With a direct impact, ruptures of the lower surface or both the lower and upper surfaces more often occur. When compression and counter-impact occur, the upper surface of the organ often suffers. At the same time, compression is characterized not only by multiple linear breaks, but also by crush spots.
With fractures of the ribs on the lower right, a part of the liver may be destroyed by a fragment embedded in it. A fall from a great height can cause an organ to sever from its ligamentous apparatus. Central and subcapsular hematomas are formed mainly when there is a sharp bend or sharp turn of the body.
The patient's condition is serious and rapidly deteriorating. Symptoms of traumatic shock and internal bleeding are observed. Chest breathing, pale skin, lethargy, cold sweat, decreased blood pressure and tachycardia. In this case, a rapid increase in tachycardia is a prognostically unfavorable sign.
The patient complains of increasing pain in the right hypochondrium. Irradiation to the right supraclavicular region is often noted. A sharply expressed pain syndrome in the first hours after injury is not typical for isolated liver injuries - its presence may indicate a simultaneous violation of the integrity of the hollow organ.
Palpation of the right hypochondrium is painful, moderate muscle tension and dullness upon percussion are detected. A positive Shchetkin-Blumberg symptom is determined. Blood tests show increasing anemia with a rapid increase in the number of leukocytes.
Without emergency medical care, the patient usually dies from bleeding in the first hours or days after liver injury. With minor injuries, the patient can survive, but on the 2-3rd day in such cases peritonitis develops, caused by the outpouring of bile or blood into the abdominal cavity.
Central and subcapsular hematomas at the initial stage proceed more favorably. However, on days 1-3 the hematoma may rupture, which entails profuse hemorrhage into the abdominal cavity. Such liver injuries are called biphasic ruptures.
Diagnosis of closed liver injuries is quite difficult, especially with combined and multiple injuries, when there are other, more noticeable injuries that cause bleeding and the development of traumatic shock. Another factor that complicates the diagnosis is disturbances of consciousness caused by severe shock, massive blood loss, traumatic brain injury, or alcohol intoxication.
The diagnosis is made based on examination of the patient, blood tests and additional studies. Ultrasound, computed tomography, and angiography can be used to identify damage. The most informative research method is laparoscopy. During this procedure, an endoscope is inserted into the abdominal cavity through a small incision, through which you can directly examine various organs, establish the fact of bleeding and identify its source, and also approximately estimate the amount of blood loss.
Treatment of closed liver injuries is surgical and carried out on an emergency basis. Watchful waiting is used only in those rare cases when the damage cannot be clearly diagnosed and blood loss is insignificant and does not increase.
During the operation, an inspection of the liver is performed. Small tears and cracks are sutured. In case of deep ruptures and heavy bleeding, the damaged vessels are first ligated. In case of crush injury, liver resection is performed. In case of difficult to stop bleeding, tamponade is performed using the patient's muscle or omentum or a hemostatic sponge. The abdominal cavity is washed and the wound is sutured.
Surgical intervention is performed against the background of blood transfusion and blood substitutes. If the internal organs are not damaged, a transfusion of blood collected in the abdominal cavity and pre-filtered is possible.
Therapeutic measures
Damage of this kind leads to severe bleeding, which cannot stop on its own. Therefore, if an organ rupture is suspected, urgent surgical intervention is necessary. It is extremely important to normalize the blood volume in the body. The liver wound is sutured during the operation using a Kuznetsov-Pensky suture; if there are deep injuries, tamponade of the wound area is performed with an omentum on the leg.
Using Vivocol, a hemostatic sponge and hemostatic gauze, stop bleeding from small vessels.
Hepatoprotective therapy
Considering all the risks to the liver, patients with severe Corona are necessarily prescribed hepatoprotectors. These are medications that increase the organ’s resistance to pathological influences and toxins, promote its speedy recovery, and enhance its neutralizing functions by increasing the activity of the liver system.
Hepatoprotectors can be of chemical, synthetic and natural origin. Depending on the composition, they can dilute and remove bile, exhibit antioxidant activity, and relieve inflammation.
Is a cyst in the liver a tumor or not?
A liver cyst is a benign tumor that is completely treatable. The main thing is not to miss the moment of its appearance and control the condition and size of the tumor in order to prevent serious consequences.
The team of doctors at the Yusupov Hospital, based on the latest advances in medicine, will draw up a plan for adequate and effective therapy, or prescribe a method of surgical intervention that is suitable for a particular patient in accordance with his clinical picture and general health.
Asymptomatic liver cysts require dynamic monitoring by a gastroenterologist or hepatologist. As a rule, surgical intervention is required only in case of complications or gigantic cyst size.
Diet for liver cysts
The diet for liver cysts excludes the following dishes and products:
- fatty, sour, fried, smoked and spicy;
- pickles, preserves, foods high in salt;
- yolks;
- fresh yeast bread;
- broths;
- fatty meat and fish;
- legumes;
- mushrooms;
- sweets made from refined or cane sugar;
- alcohol.
Preference should be given to foods high in fiber, vegetable fats, and foods with a high content of vitamins B and A. You should definitely include dairy and fermented milk products in your diet. Despite the fact that when a liver cyst is diagnosed, treatment with folk remedies and the use of all kinds of drugs should be discussed with a doctor, it is absolutely safe for patients to drink a decoction or tea of chamomile, mint or rose hips.
Liver recovery after coronavirus infection
The organ is unique. It has the ability to self-heal. Even after a serious defeat, he can normalize his work if a person helps him with this. Basic requirements for the speedy restoration of liver structures:
- Eat a balanced diet. Refractory fats, spices, herbs, alcohol, offal, ice cream, and carbonated drinks are prohibited. A person who is recovering should eat porridge, vegetables, fruits, steamed and boiled meat, cottage cheese, vegetable soups, savory cookies, and a protein omelet. It is also important to drink plenty of clean water.
- Take hepatoprotectors prescribed by your doctor. It is unacceptable to use medications purchased at a pharmacy without medical advice or recommended by friends. This approach to treatment is ineffective and dangerous. The pharmaceutical market offers a wide range of geratoprotective medications. They all have their own side effects, dosages and indications. Only an experienced doctor can determine whether a particular patient needs a particular drug composition.
- Move more. If you no longer need to stay in bed, you should take walks in the fresh air more often. Activity contributes to the stable functioning of hepatobiliary structures.
- Don't overeat. This is the sin of many people who are forced to stay in a hospital for a long time. In order for all internal organs to function normally, it is important to eat four to five times a day in small portions.
- Follow doctor's orders. This is the main condition for a speedy recovery. If the doctor told you to take laboratory tests and undergo ultrasound diagnostics, then that’s what you need to do. By ignoring the doctor's recommendations, a person makes things worse for himself.
If you are sick with coronavirus, be sure to take care of your liver health. Don't ignore the symptoms of inflammation. Then, after discharge from the hospital, you will not have to take hepatoprotectors for a long time.
Symptoms
Some gland injuries are not accompanied by severe symptoms. The first signs appear when the patient's condition worsens due to light physical activity. This is because the injury worsens and the subcapsular hematomas rupture, causing bleeding.
You can detect that the liver is ruptured by the following signs:
- increased heart rate and pulse;
- sometimes the heartbeat slows down due to the accumulation of bile;
- breathing depth is below normal;
- nausea, vomiting.
Attention! Intense pain in the right hypochondrium, which intensifies during movement, is a clear sign of liver problems.
- paleness of the skin and visible internal membranes;
- cold sweat;
- severe decrease in pressure;
- vertigo (dizzy).
Negative consequences and prognosis
The most likely complications are hemobilia, massive blood loss, formation of an abscess in the gland, neoplasms (cysts, fistulas). In 8% of cases, the patient dies during surgery when the patient has combined injuries (for example, there is a rupture of the gland, a damaged spleen), the risk is 23%.
The prognosis is different, since it all depends on the patient’s age, the amount of blood loss, the timeliness of medical assistance, and the degree of rupture. The body of elderly people and children often cannot cope with the injuries they receive, which causes death.
Treatment methods
A person with symptoms of a ruptured gland should be given first aid. First of all, you need to call an ambulance.
Carefully! The victim is prohibited from moving, as the risk of increased hemorrhage increases.
A cold compress is applied to the area of the right hypochondrium. In addition, you should pay attention to your heart rate and breathing. It is important to constantly talk to the patient so that he does not lose consciousness.
Upon arrival, emergency doctors apply ice to the damaged area and inject the victim with adrenaline (no more than 1 ml). Painkillers are not recommended, as they can “lubricate” the symptoms.
Typically, the patient is given immediate medical attention. Watchful waiting is appropriate only if hemodynamics (blood movement) are stable and the free blood volume is up to 150 ml. In this case, the gap should be of a blunt, closed nature.
Reference. The victim is prescribed hemostatic drugs: Etamzilat, Vikasol, aminocaproic acid. Infusion treatment allows you to restore and maintain the volume and quality of blood.
If hemodynamic parameters are unstable, doctors prescribe laparotomy. The operation is performed under general anesthesia after intubation (insertion of a tube into the larynx and trachea) and administration of muscle relaxants (drugs that reduce muscle tension). Doctors insert venous catheters through which saline, Ringer-Locke solution, Reopoliglucin, and glucose are injected.
Transfusions of platelet concentrates, plasma, and cryoprecipitate (precipitate from fresh frozen blood plasma) are also performed.
Upper midline laparotomy is used if the operation is not urgent or doctors have not yet established an accurate diagnosis. After examining the abdominal organs and establishing the degree of damage, access is expanded. Then the damaged gland tissue and vessels are sutured. If part of the liver needs to be removed, then thoracofrenolaparotomy is prescribed.
To stop bleeding, surgeons find the damaged vessel, grab its ends, fix it with a clip or stitch it. Dead areas are removed using an ultrasonic scalpel. A special fibrin insulator will help to completely stop the bleeding.
When suturing the vessel, a special self-absorbable material is used. A blunt, curved needle is used to apply sutures.
Liver cyst: causes
The reasons for the formation of cysts directly depend on their type. For example, a true cyst forms during intrauterine development, however, what causes this has not yet been determined. An acquired cyst can occur against the background of an infectious or inflammatory disease (especially due to inflammatory hyperplasia of the biliary tract), tumor necrosis or mechanical trauma to the liver.
The choice of therapy or surgical intervention depends entirely on the cause of the tumor or its causative agent. A liver cyst can occur due to:
- hormonal imbalance. Taking hormonal contraceptives and hormone replacement therapy have a positive effect on the development of liver cysts. This occurs due to an increase in the level of estrogen, a female sex hormone that affects the growth and development of liver tumors;
- failure of the formation of internal organs during embryonic development. This reason can be attributed to a genetic predisposition, since very often a liver cyst is a disease transmitted through the genes of the parents. The cyst in this case is called true;
- parasite infestation. Parasitic cysts occur due to infection with echinococci or alveococci. In such cases, the cyst serves as a habitat for the tapeworm until it moves into the small intestine and continues to live in the human body at the expense of its resources;
- inflammatory diseases of the liver or biliary tract;
- traumatic liver injuries;
- necrosis of liver tumors;
- amoebic abscess.
In order to find out the causes of the disease, it is necessary to conduct a series of laboratory tests, since only by knowing the root of the disease can you completely get rid of it.