Constipation is a condition characterized by excessive straining during bowel movements, a feeling of incomplete bowel movement, difficult and painful passage of hard stool in small portions.
The definition of constipation as a decrease in stool frequency (less than three times a week) is not considered correct today. This is primarily due to individual characteristics: if a person is generally healthy, both daily bowel movements and bowel movements with a frequency of no more than 3 times a week are considered normal. Thus, the American College of Gastroenterology defines constipation based on symptoms, including poor bowel movements, difficult and infrequent passage of stool, and changes in stool consistency (stool that is hard and dry).
Constipation may be accompanied by abdominal cramps and pain, bloating, nausea, fever, and bleeding from the rectum.
What is constipation
Constipation is said to occur when a person has infrequent or difficult bowel movements.
On average, it is believed that the number of bowel movements should not be less than 3 times a week, although in fact there are no required minimums or maximums. Also, defecation should occur without tension, frequent and prolonged straining. And after defecation, a person should not have the feeling of incomplete bowel movement. Constipation is defined as slow or difficult bowel movements. In the medical literature, this condition is also called constipation or obstipation. Moreover, the term “constipation” itself is not just colloquial and appears in the International Classification of Diseases ICD-10.
Important! According to statistics, up to half of the population of developed countries experience difficulties with defecation. At the same time, constipation is not only a problem for adults. Constipation also occurs in 5-20% of children. With age, the likelihood of constipation (as well as other gastrointestinal disorders) increases. Thus, in older people over 65 years of age, constipation occurs 4-5 times more often than in young people.
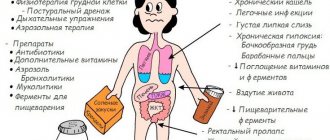
People of all ages experience constipation for various reasons. According to the etiological factor, constipation is divided into organic and functional.
Organic constipation
Constipation is considered organic if it is caused by congenital developmental abnormalities, inflammatory or tumor diseases of the intestine. For example, constipation occurs with congenital intussusception, volvulus, inflammatory damage to the omentum and a number of other pathologies. In other words, such constipation develops against the background of organic intestinal lesions.
Functional constipation
Functional constipation develops against the background of impairment of certain functions. For example, secretory or suction. Constipation often occurs due to disruption of the nervous system, including under severe stress.
With functional constipation (FC), there are no organic intestinal lesions. In children and adolescents, FZ is determined by criteria including: infrequent and hard stools, fecal incontinence, painful bowel movements - provided that these symptoms are not explained by another medical condition, according to the Rome IV criteria (functional gastrointestinal diseases). In adults, the criteria are slightly different, including a feeling of straining or obstruction, a feeling of not completely emptying the bowels, and infrequent (less than 3 times a week) hard stools in at least a quarter of all bowel movements. However, sometimes patients may have bloating or abdominal pain - but these are not the predominant symptoms of FZ.
According to the nature of the course, constipation is divided into acute and chronic. Let's take a closer look at the features of acute and chronic constipation.
Acute constipation
This is episodic constipation that occurs suddenly and lasts no more than 12 weeks. Most often, acute constipation occurs due to poor nutrition and organic intestinal lesions, and less often due to functional disorders.
Acute constipation can occur with intestinal obstruction, inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, disorders of the nervous system, endocrine pathologies, physical inactivity and other diseases and circumstances. Sometimes severe constipation occurs as a side effect of taking certain medications.
Chronic constipation
With chronic constipation, difficult or infrequent bowel movements occur for 12 weeks or more. People suffering from chronic constipation have bowel movements less than 3 times a week for a long period of time. This condition significantly reduces the quality of life and is also fraught with the development of a number of complications. In particular, chronic constipation can lead to anal fissure, hemorrhoids, rectal prolapse and other complications.
How to reduce pain
There are several ways you can help yourself at home.
- Lumbar massage. It is necessary to gently and gently rub the lumbar area. Do this yourself or with the help of another person. Massage only if the pain is not associated with muscle inflammation or a herniated lumbar spine.
- Physical training. No earlier than an hour after eating, you can do the usual 15-minute exercises: squats, bends, exercise “bicycle”.
- Correct body position. You need to lie with your back on a semi-hard surface, bend your knees, place them on a support at an angle of 90 degrees. Another option is to lie on your side with your legs bent and a small pillow between your knees.
There is no need to relieve lower back pain after constipation with antispasmodics. Experts do not recommend taking analgesics: these drugs will blur the real picture of the disease, and if you need urgent medical help, the doctor will not be able to immediately make an accurate diagnosis. Contact your physician, make sure there is no serious pathology, and get advice on which drug should be taken in such cases.
Get rid of intestinal problems
The natural British drug is not addictive and works immediately
Find Phytomucil with benefits
Causes of constipation
Constipation develops against the background of congenital or acquired organic changes in the intestine. As a rule, these are anatomical abnormalities of the intestines that slow down the movement of feces. Such pathologies include:
- Dolichocolon is an abnormal elongation of one of the sections or the entire colon. Thus, the movement of feces through the large intestine slows down. Dolichocolon can be congenital or acquired. If the congenital pathology is not treated, then in adulthood the colon will be elongated. Acquired dolichocolon in adults develops against the background of frequent use of enemas and abuse of laxatives. Lengthening of the colon is also possible if metabolic processes in the large intestine are disrupted.
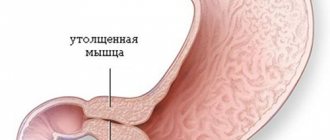
- Megacolon is a pathological enlargement of the large intestine that occurs due to congenital disorders of the innervation (supplying the organ with nerves - provides communication with the central nervous system) of the colon. Like dolichocolon, megacolon can be congenital or acquired. With congenital megacolon, already from the first years of life, the child experiences constipation due to slow passage of feces. Sometimes constipation also bothers newborns who are diagnosed with Hirschsprung's disease.
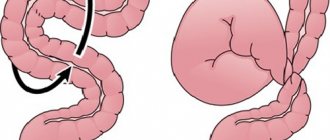
- Dolichosigma is an increase in the size of the sigmoid colon. This pathology is also congenital or acquired. Congenital dolichosigma is a consequence of a violation of intrauterine development of the fetus. In adults, the sigmoid intestine lengthens with a sedentary lifestyle against the background of fermentation and/or putrefaction processes in the large intestine. With dolichosigma, the frequency of bowel movements is approximately once every 3 days. In severe cases, stool retention reaches up to 8-10 days. In this state of affairs, there is a risk of intestinal obstruction and even peritonitis, which can develop with intestinal perforations due to constipation.
Slow passage of feces in the sigmoid colon is also possible in the presence of additional loops and kinks in this section of the intestine.
- Colonoptosis is a prolapse of the colon associated with weakness of the mesenteric ligaments (thanks to it, the intestines are attached to the posterior wall of the abdomen). It is not uncommon for the colon to prolapse in women after childbirth. Against the background of colonoptosis, intestinal motility worsens, which is why constipation occurs. One of the variants of colonoptosis is transversoptosis, in which prolapse of the transverse colon occurs. Transvertoptosis often develops against the background of spinal diseases - scoliosis or lordosis.
- Ileocecal valve dysfunction. The ileocecal valve (bauginian valve) is located at the border between the small and large intestines. This valve prevents the contents of the large intestine from refluxing into the small intestine. If the functioning of the bauhinium valve is disrupted, then the movement of feces through the colon slows down, which leads to constipation and/or diarrhea. Often with this pathology, a person alternates between periods of constipation and diarrhea.
- Diverticulosis is a protrusion of one of the sections of the large intestine. The most common protrusion is the sigmoid colon. As a rule, diverticulosis is acquired and most often occurs in older people. The appearance of such diverticula leads to slower stool passage, pain, bloating and intestinal bleeding.
Figure 1. Main causes of constipation. Source: MedPortal
Causes of acute constipation
Now let’s take a closer look at the reasons for the development of acute constipation in adults and children. Acute constipation most often develops with intestinal obstruction, an acute condition that is caused by fecal impaction, hernia, adhesions, volvulus, or tumors in the intestine.
Separately, there is a dynamic intestinal obstruction (caused by impaired peristalsis), which, for example, occurs with peritonitis, severe injuries to the brain and spinal cord, as well as with prolonged physical inactivity (for example, bed rest).
Acute constipation due to medication use
Some medications have side effects that include disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, in particular constipation. These medications include, for example, drugs with anticholinergic effects. These are allergy medications (antihistamines), antispasmodics and antipsychotics. Constipation can also be caused by taking medications containing bismuth, iron, barium, calcium and aluminum.
Taking antibiotics also leads to changes in the functioning of the large intestine. The exact reasons for the development of constipation while taking antibiotics are still unknown. According to most researchers and doctors, constipation occurs due to dysbiosis, which develops with long-term use of systemic antibacterial drugs. Obviously, with dysbacteriosis, the physiological activity of the large intestine decreases, which causes peristalsis to worsen and the movement of feces through the intestine to slow down.
Constipation due to a sedentary lifestyle
Almost all bedridden patients, as well as most people leading a sedentary lifestyle, sooner or later experience constipation. This is due to the fact that the lower part of the rectum is most sensitive to the pressure exerted by the rectum filled with feces. Therefore, the urge to defecate increases in an upright position.
Constipation after surgery
Temporary constipation often occurs in patients who have had gallbladder removal or intestinal surgery. When the gallbladder is removed, the leading cause of constipation is postcholecystectomy syndrome, which reduces intestinal tone. Partial removal of the intestine, anastomosis, suturing of the intestinal wound and other surgical interventions on the intestine are also fraught with stool problems - constipation or diarrhea.
Causes of chronic constipation
As for chronic constipation, they are most often caused by the following diseases and circumstances:
- Tumors of the colon, most often parts of the sigmoid colon.
- Endocrine diseases - diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism (lack of thyroid hormones), hypo- and hypercalcemia (lack or excess of calcium in the body). Constipation also occurs due to hormonal changes during pregnancy.
- Diseases of the nervous system. These are various pathologies of the central and peripheral nervous system. Most often, constipation is accompanied by Parkinson's disease, circulatory disorders, spinal cord pathologies, multiple sclerosis, neuropathies, neurofibromatosis, Hirschsprung's disease and others.
- Functional disorders. Most often these are diseases combined into irritable bowel syndrome.
- Nutritional features. Depending on your eating habits, constipation can be episodic or long-lasting. Insufficient consumption of dietary fiber (fiber), as well as lack of fluid, are the main reasons contributing to the retention of feces in the intestines. Foods that slow down the movement of feces: rice, potatoes, meat and meat products, as well as pasta and bread.
Why is constipation dangerous?
Source: ru.freepik.com
The danger of constipation depends on the stage - compensated, subcompensated and decompensated.
- Compensated constipation is most often observed in people under 45-50 years of age. This form of constipation does not pose a serious danger to the body. As a rule, dietary adjustments and physical activity are sufficient to eliminate such constipation.
- Subcompensated constipation is a more serious form of constipation, in which some pathological changes in the gastrointestinal tract are already noted. At this stage, people experience liver damage, abdominal pain, as well as damage to other organs and systems.
- Decompensated constipation is observed against the background of serious pathological changes in the body. With decompensated constipation, bowel movements may not occur for up to 7 days or more. Undesirable consequences of constipation include inflammatory bowel disease, bleeding during bowel movements, hemorrhoids, and the risk of tumors.
Constipation in pregnant women
During pregnancy, constipation often occurs due to hormonal changes. The situation is aggravated by dietary violations and taking iron and calcium supplements. Already in late pregnancy, constipation occurs due to decreased physical activity, increased size and changes in the position of the fetus (when the baby's head puts strong pressure on the intestines), as well as emotional experiences.
Common consequences of constipation in pregnant women include:
- disturbances of intestinal microflora;
- inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs;
- intoxication of the body due to putrefactive processes in the intestines;
- premature birth (due to strong straining during bowel movements).
Constipation in a child
Constipation in children is a fairly common problem. However, the causes of constipation in children are not the same as in adults. Most often, the causes of constipation in children are allergies, improper feeding of the child, as well as congenital abnormalities of intestinal development.
Early potty training and inadequate sanitary conditions in the place of residence or study also contribute to the appearance of constipation in a child.
As in adults, frequent and prolonged constipation in children can trigger the development of inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. In addition, constipation weakens the child’s immunity and contributes to frequent colds and other infectious diseases.
X-ray of constipation in a young child. Photo: James Heilman, MD / (CC BY 3.0)
When to see a doctor
Occasional constipation happens to everyone. Most likely, the cause is poor nutrition or stress. Such cases do not require medical intervention and go away on their own with normalization of nutrition. You should consult a doctor if constipation bothers you often and for a long time. The fact that laxatives are needed for normal bowel movements already suggests that it’s time to see a doctor.
When to see a doctor
If you have pain of any intensity or origin, you should definitely consult a doctor. But there are cases when medical assistance must be provided immediately. Urgent contact with a specialist is necessary in cases where constipation radiates to the lower back and/or lower abdomen and the following symptoms are observed:
- high body temperature;
- bloody discharge from the rectum, urethra;
- vomit;
- severe dizziness.
Any signs atypical for constipation require immediate diagnosis.
Treatment
Treatment of constipation involves correction of diet and lifestyle, as well as the use of folk remedies and medications. If constipation develops against the background of another disease, then treatment should be aimed at eliminating the causative pathology. In severe cases, treatment of constipation includes surgery (for example, in case of acute intestinal obstruction).
What to do if you are constipated
Photo: pvproductions / freepik.com
If you have constipation, your doctor usually recommends reconsidering your eating habits. Here are some tips to follow when treating constipation:
- Eat more dietary fiber (fiber). They are found in vegetables, fruits, legumes and whole grain bread.
- Move more. Try to spend more time on physical activity. Regular walking at a medium or fast pace will be helpful. This speeds up intestinal motility and promotes freer movement of feces.
- Drink more fluids.
- Don't be patient. If you feel the urge to defecate, go to the toilet immediately. If you often ignore the urge to defecate, over time these signals weaken, which leads to bowel dysfunction.
- Less stress. It is better to avoid stress, since constipation often occurs against the background of emotional experiences.
Medicines
If correction of diet and lifestyle is not enough to get rid of constipation, then in this case the person is prescribed medications that accelerate the evacuation of feces and relieve the unpleasant symptoms that accompany constipation. These medications include:
- Secretory laxatives - have an irritating effect on intestinal receptors.
- Bulk laxatives – increase the volume of stool by absorbing water, thereby speeding up the passage of stool.
- Osmotic laxatives are drugs that increase the osmotic pressure in the intestines, which promotes the flow of water.
- Emollients – soften stool, speeding up its elimination from the intestines. Unlike stimulants, emollients act more slowly.
- Probiotics are preparations containing live cultures of beneficial bacteria. These medications can help with dysbiosis.
Photo: modesto3 / Depositphotos
Home Remedies
The following home remedies can help relieve constipation:
- A glass of water on an empty stomach has a stimulating effect on the intestines.
- Dried fruits have a laxative effect. Prepare a puree from pre-soaked dried fruits (dried apricots, prunes, raisins, figs and dates) and honey. Take morning and evening instead of dessert.
- Cucumbers, plums and beets – eat more of these vegetables and fruits as they have a laxative effect.
- Morning coffee has a stimulating effect on the intestinal mucosa, stimulating peristalsis.
ethnoscience
Humanity encountered constipation long before the advent of pharmacological agents. There are several more or less effective remedies, but before using them it is best to consult a doctor. There are four such means:
- Herbs with a laxative and stimulating effect - senna leaves, dill seeds, plantain seeds, cumin.
- Vegetable oils - flaxseed, olive, castor, pumpkin, sea buckthorn and sesame.
- Bran – wheat, buckwheat, oat and others.
- Freshly prepared vegetable juices - potato, cucumber, beet, carrot and celery juice.
How to quickly get rid of constipation
It all depends on the cause and stage of constipation. If this is episodic constipation, then quick relief occurs with correction of nutrition and physical activity. In more complex cases, it is necessary to follow all the doctor’s recommendations. And remember that when taking medications for constipation, adjustments to your diet and lifestyle are necessary. Only an integrated approach will allow you to effectively cope with the problem.
Nutritional Features
If constipation causes lower back pain, it is important to follow a special diet. This will help cope with the main problem and reduce pain.
You won’t have to adjust your diet for a few days; you need to stick to the diet for a long time. Fortunately, you don't have to give up most foods. There are several principles that should be followed:
- Eat less and more often. Divide the daily amount of food into 5-6 meals. The interval between meals is about 2 hours.
- Chew your food more thoroughly and longer and try not to snack on the run.
- Include foods rich in dietary fiber in your diet, as well as fermented milk products and sauerkraut - they contain bifidobacteria and lactobacilli.
Avoid crackers, rice, baked goods, and foods with a lot of preservatives. It is better to limit the consumption of peppery and spicy foods. Give preference to steamed or boiled foods.