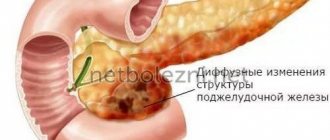
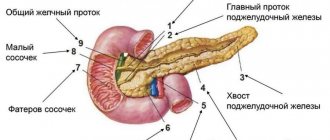
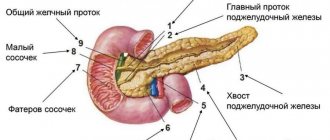
The pancreas is considered healthy if its echogenicity is comparable to this indicator for sound diagnostics of the spleen and liver. The doctor can see the head, body and tail of the pancreas on the monitor screen; all its sections have optimal sizes.
But, unfortunately, doctors rarely see such rosy pictures on the monitors of their diagnostic machines, because healthy people do not come to the hospital. An inflamed or other pathological pancreas is characterized by so-called diffuse tissue changes. What is diffuse change in the pancreas?
General information
Often, when examining the gastrointestinal tract in patients, diffuse changes in the pancreatic parenchyma . Receiving such a conclusion, a person often does not understand what such a diagnosis means and whether it is necessary to take any measures to treat it. According to experts, diffuse changes in the pancreatic parenchyma indicate that the body already has prerequisites for the development of pancreatitis .
Therefore, already at the stage of receiving such a diagnosis, the patient should reconsider his lifestyle in general and his diet in particular. Most often, such changes are diagnosed in elderly people, as well as in those who suffer from pancreatitis , diabetes , liver dysfunction, and digestive tract organs. Pathology can develop as a consequence of infectious and inflammatory diseases of internal organs, in which there is a violation of metabolic processes in the body.
This article will discuss what such a diagnosis means, how this pathology manifests itself, and what treatment methods should be practiced.
Why do DI occur in pancreatic tissues?
The following reasons lead to DIP:
- nutritional imbalance. The predominance of fatty, floury, salty, sweet and spicy foods.
- genetic predisposition
- nervous tension
- alcohol and nicotine addiction
- diseases of the digestive tract
- unsystematic use of medications.
Lack of insulin in the blood and glucose in the urine also provokes DIP. Pancreatitis is also a provoking factor, requiring treatment and attention from the patient.
Pathogenesis
Diffuse changes in the pancreas are not an independent diagnosis, but evidence of the development of a pathological condition and its separate symptom. This symptom is not always accompanied by an underlying disease.
The pancreas is the largest endocrine and exocrine gland. It produces pancreatic juice, performing an exocrine function. The pancreatic tissues also contain endocrine glands that produce insulin . Parenchyma is the main component in the structure of the gland. If the biochemical balance is disturbed, destruction and replacement of its tissues can occur. Consequently, when parenchyma cells are replaced, the process of normal pancreatic functioning may gradually be disrupted.
With certain disorders in the gland, along with tissue density, the echo structure , that is, the ability to reflect sounds during an ultrasound examination. Consequently, this condition is interpreted not as a disease, but as a fact that is observed on ultrasound.
What variations in echogenicity indicate the stage of the disease?
Based on the violation of tissue density for the ultrasonic wave, the connection with other signs, one can be guided by the degree of pathological disorders in the pancreas. Main diagnostic options:
- decrease in parenchyma density (reduced echogenicity) + increase in organ size → the outflow of pancreatic juice is hampered, enzymes enter the blood, characteristic of acute pancreatitis;
- the same if the size remains normal → typical for chronic pancreatitis, tortuosity of the excretory duct;
- a general increase in echogenicity, with normal size of the gland, is a sign of beginning fatty tissue replacement, accompanies diabetes mellitus, obesity, dystrophy in the elderly;
- increased parenchyma density + increased echogenicity, but the size of the organ is reduced or normal → signs of fibrosis during the recovery period after inflammation, with metabolic disorders.
Classification
According to the characteristics of the changes, the following forms of pathology are distinguished:
- Moderate diffuse changes in the pancreatic parenchyma - as a rule, this form does not lead to the appearance of unpleasant symptoms. Moderate changes are observed throughout the parenchyma and are distributed evenly.
- Diffuse changes in the pancreas like lipomatosis - with this form, the parenchyma is gradually replaced by fat cells. As long as no more than 30% of the tissue is replaced, a person does not feel any unpleasant symptoms. Replacement of the lipomatosis type occurs due to toxic lesions, chronic inflammatory processes, and injuries. Most often observed in older people with diabetes . If the pathological process progresses, then the functions of the organ are disrupted.
- Diffusely heterogeneous changes in the structure of the pancreas - such changes may be associated with the development of a number of diseases, in particular diabetes mellitus, pancreatitis. In addition, diffusely heterogeneous changes can be a consequence of edema, the formation of pseudocysts, and inflammatory processes.
Depending on the severity, the following forms of pathology are distinguished:
- Minor changes - appear as a consequence of a recent inflammatory disease, frequent stressful situations, constant errors in the diet. Such disorders may be associated with the influence of the central nervous system, since due to frequent stress, pancreatic juice is very actively secreted, and with depression its secretion is inhibited. To prevent further development of the pathology, it is necessary to adjust your lifestyle.
- Moderate changes are observed in the first stages of gastrointestinal diseases and inflammatory processes. A similar pathology can be observed in chronic pancreatitis, diseases of the gallbladder, and duodenum.
- Unexpressed changes are determined if pathological processes occur in the organ that do not affect its functions. Their appearance may be associated with elevated blood sugar levels, liver and gallbladder diseases. They may also be associated with hereditary disposition, infectious diseases, etc.
- Pronounced changes are a consequence of the pathological process. Sometimes they may be accompanied by pain and discomfort in the gastrointestinal tract.
What are diffuse changes in the pancreas?
A pathogenic change in tissue can be chronic and not manifest itself for a long time.
In older people, especially with pathologies of the cardiovascular system, blood circulation, and those suffering from diabetes, healthy pancreatic tissues often die under the influence of pathogenic circumstances, and in their place connective or adipose tissue is formed.
This condition is not recognized as a disease and therefore cannot be treated. But ultrasound shows increased echogenicity with normal organ sizes. Such transformations are observed in the following violations:
- blood supply to the enzyme-forming organ
- functioning of the biliary tract
- liver function
- metabolic and endocrine processes.
Similar symptoms are characteristic of pancreatitis and dystrophic metabolic disorders. If the diagnosis of pancreatitis is not confirmed, then DIP is not recognized as a disease and treatment is not prescribed. The object of spreading changes, as a rule, is the pancreatic parenchyma, that is, the glandular tissue that performs the main functions of the organ. A pathogenic change in tissue can be chronic and not manifest itself for a long time.
Causes
Diffuse changes can occur due to various reasons. The reasons that provoke the development of such a pathology may be:
- Metabolic-dystrophic processes.
- Circulatory disorders.
- Metabolic disorders.
- Endocrine diseases ( diabetes , etc.).
- Functional disorders of the biliary tract and liver.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
The development of such changes can be provoked by the following factors:
- Poor nutrition – excessive amounts of spicy, sweet, starchy, salty, fatty foods in the diet.
- Constant stress.
- Hereditary disposition.
- Alcohol abuse, smoking.
- Irrational use of medicines.
Causes of changes in the liver
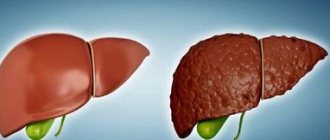
Liver tissue normally has low density
, homogeneous structure. If there are diffuse changes, then the density of blood vessels, tissues and bile ducts increases. This can be due to both serious pathologies and functional, temporary disorders.
In children, reactive changes in the structure of the organ most often occur, for example, due to the use of antibiotics or poisoning. Also, newborns may have problems with the organ due to its underdevelopment, structural abnormalities, or the mother taking toxic drugs in the last stages of pregnancy.
The causes of disturbances in the structure of the organ parenchyma are:
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- chronic hepatitis;
- acute hepatitis (jaundice);
- fatty hepatosis;
- liver tumors;
- cystic formations, organ fibrosis.
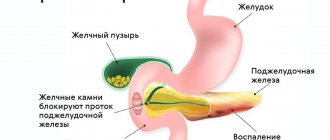
Often diffuse changes accompany hepatomegaly (pathological enlargement of the liver), as well as hepatosplenomegaly (enlargement of the liver and spleen). Such conditions are typical for poisoning, severe intoxication, and also appear in acute cholecystitis and bile duct obstruction.
Uncontrolled drinking of alcohol and consumption of spicy, fatty foods in the future almost always leads to diffuse changes in the structure of the liver.
Diseases not related to the liver can also cause liver changes:
- diabetes;
- viral infections;
- gastritis;
- cholelithiasis.
Symptoms
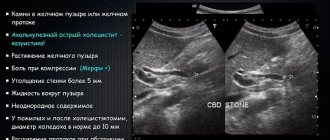
As a rule, signs of diffuse changes in the pancreas depend on the underlying disease, which provoked the development of such signs. However, most often with such changes their signs are detected on ultrasound. The following echographic signs of diffuse changes in the gland are distinguished:
- Heterogeneous texture of the pancreas due to changes in echogenicity in some areas.
- Bile ducts are unevenly enlarged.
- Unevenly increased echogenicity.
- The volume of the gland has changed.
- Additional echo signs may also be detected - cysts, pseudocysts.
With such pathological changes, the following symptoms may appear:
- Feeling of heaviness under the right rib.
- Pain in the hypochondrium.
- Constant feeling of nausea, feeling of heaviness in the stomach.
- Decreased appetite.
- Heartburn , bitter belching.
- Constipation or diarrhea.
- Feeling of weakness, decreased ability to work.
- Headache.
Depending on the diseases in which this pathology develops, other symptoms may be observed. Thus, in acute pancreatitis, intoxication of the body tachycardia develops blood pressure decreases . There is severe pain in the hypochondrium. With chronic pancreatitis, the symptoms are less pronounced.
However, very often diffuse changes in the pancreas do not cause concern, and symptoms of the condition do not appear.
Increased echogenicity of the pancreatic parenchyma
When performing ultrasound diagnostics, you can find out the density of internal organs. If decreased or increased echogenicity of the pancreas is detected, then this is a serious reason to undergo an extensive examination, providing an accurate diagnosis and determining methods for eliminating problems.
Increased echogenicity of the pancreatic parenchyma is detected during inflammation with the formation of fibrosis, which develops against the background of metabolic disorders, when healthy parenchyma tissue is replaced by fat, during acute pancreatitis and relapse of chronic inflammation that changes the density of the parenchyma.
The absorption coefficient of ultrasonic radiation depends on the increased echogenicity of the parenchyma. Malignant tumors that form in the parenchyma have a higher absorption coefficient of ultrasonic energy than benign tumors.
Tests and diagnostics
Diffuse changes in the pancreatic parenchyma are determined during ultrasound examination. However, to establish the reason why diffuse changes appear, it is necessary to conduct the following additional studies:
- Laboratory tests - general and biochemical blood tests.
- Endoscopic examination - allows you to determine the condition of the excretory duct of the gland.
- X-ray – can be performed as an additional study.
- CT or MRI.
Other studies may also be performed, which are prescribed depending on the disease and condition of the patient.
Diagnosis of diffuse changes
DIPVs are determined using an ultrasound machine. Ultrasound shows an increase or decrease in tissue density, changes in structure, and foci of inflammation. But this is not enough. And therefore, to confirm the presence of DI, a biochemical blood test and endoscopy of the gland are performed. An important role in diagnosis is played by anamnesis, that is, questioning the patient about the presence of complaints, instrumental examination and palpation. Additionally, a general blood test, stool urine analysis, and gastrointestinal endoscopy are performed. The purpose of the research is:
- the amount of pancreatic enzymes and glucose in the blood
- ratio of inhibitor to trypsin.
Ultrasound allows you to determine the size of the gland, the condition of the duct, the presence of tumors and seals. Additionally, computed tomography and ERCP are performed, which help identify the true causes of changes in the tissues of the enzyme-forming organ.
Treatment with folk remedies
If a patient experiences unpleasant symptoms, some traditional methods of treatment can be practiced to improve the condition. However, you must first coordinate the use of such methods with your doctor.
- Honey with pumpkin . Carefully remove seeds from a small pumpkin and fill with honey. Leave in a dark place for 20 days. Drink liquid from pumpkin three times a day, 1 tbsp. spoon.
- Oat infusion . Pour 500 g of oats into 1 liter of boiling water and leave for an hour. Strain and drink half a glass of the product three times a day.
- Lemon remedy . Grind 1 kg of lemons with peel in a meat grinder (remove the seeds first), 300 g of garlic and 300 g of parsley. Mix everything and place in a glass jar. Store in the refrigerator and consume 3 tsp. in a day.
- Herbal mixture . Mix lingonberry, blueberry, strawberry leaves, as well as corn silk and bean pods in equal proportions. 2 tbsp. l. Place the mixture in a thermos and pour 300 ml of boiling water. Leave for 1 hour, drink throughout the day.
- Potato juice . Grate two medium potatoes and squeeze out the juice. Drink half a glass twice a day.
- Kefir and buckwheat . Grind the buckwheat in a coffee grinder and pour in 1 tbsp in the evening. such flour with 1 glass of kefir. Drink in the morning on an empty stomach.
- Lingonberry tincture . Pour 500 ml of water over lingonberry leaves (2 tablespoons of raw material) and boil for 20 minutes. Drink 250 ml of the product twice a day.
Diagnosis of diseases of internal organs
Diagnostic measures after identifying changes in the parenchymal digestive organs by ultrasound do not end
. The fact is that a similar ultrasound picture can correspond to different diseases, as well as their unequal severity. Also, additional examinations will help to identify the function of the organ and discover the cause of the changes that have occurred.
After collecting anamnesis, the therapist, hepatologist or gastroenterologist gives a referral for a number of studies
:
- general blood test
- to determine blood sugar, identify the inflammatory process; - blood biochemistry
- to evaluate lipids, bilirubin, AST, ALT, cholesterol, albumin, amylase, etc.; - coprogram
- for analyzing digestive function; - repeat ultrasound
– to assess the condition of organs over time; - MRI or CT
– to clarify the type, extent and form of the disease; - Liver biopsy
– indicated for cirrhosis, hepatitis, cancer.
Prevention
To prevent the development of diffuse changes in the pancreas, it is necessary to follow the following rules of prevention:
- Get rid of bad habits - do not abuse alcohol, do not smoke.
- Drink herbal teas instead of regular teas. A specialist will help you choose the right herbs. You can also buy special preventive teas at the pharmacy.
- Eat rationally and properly, removing all harmful foods from the menu. Maintain moderation in food. You need to eat often and in small portions.
- If you experience unpleasant symptoms indicating problems with the gastrointestinal tract, immediately visit a doctor and undergo the prescribed examinations.
- Sleep at least 8 hours a day.
- Avoid stressful situations.
Heterogeneous structure of the pancreatic parenchyma
The pancreas of a healthy person has a homogeneous structure, equal echogenicity, clearly visible contours, an uncinate process, correct position and normal dimensions of the head and tail. Deviation from the norm is determined by an increase in the size of individual parts of the pancreas and the heterogeneity of the structure of its tissues.
Heterogeneity of the pancreas is evidence of the presence of various diseases, including pancreatitis and diabetes mellitus. This pathology can be found in any part of this organ. Diffuse heterogeneous changes can be caused by edema, inflammation and the formation of pseudocysts.
Diet
Diet for diffuse changes in the pancreas
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after 14-21 days
- Terms: 1-6 months/permanently
- Cost of products: 1600-1700 rubles. in Week
Diet 5th table
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after 14 days
- Duration: from 3 months or more
- Cost of products: 1200 - 1350 rubles per week
If you have problems with the pancreas, it is recommended to follow the Table No. 5 . In addition, nutrition may vary depending on the disease that caused problems with the pancreas.
The following products must be entered into the menu:
- lean fish and meat;
- dairy and fermented milk products;
- porridges from various cereals;
- vegetable dishes;
- fruits;
- grain products.
The diet should be low-calorie, meals should be fractional. It is also important to give up processed foods and sausages. Products need to be boiled, baked, steamed.
You should strictly avoid eating fried and smoked foods, canned food, sour and spicy foods. It is necessary to completely give up alcohol. It is also important to give up sweets and sweet fruits. The amount of salt in seasonings should be kept to a minimum.
Symptoms of disorders in internal organs
Symptoms are not determined by identified abnormalities in the structure of organs, but by the diseases that provoked them. If the changes are moderate, then the clinical picture may be completely absent, and the problem is detected by chance, during an ultrasound examination. Internal organs can “tolerate” unfavorable conditions for a long time, although minor signs are still noticeable.
Enlarged liver
with a dense structure it is easy to detect under the ribs on the right side by palpation.
Normally, the organ does not protrude from under the edge of the costal arch and is not painful. The pancreas
is quite difficult to palpate, but it causes pain when palpating the upper abdomen.
Symptoms of organ diseases may be:
- heartburn;
- bad odor in the mouth;
- vomit;
- nausea;
- itchy skin;
- pain in the center of the abdomen, in the right hypochondrium;
- headache;
- fatigue;
- bitterness in the mouth;
- discomfort after fatty foods;
- belching.
If the cause of the pathology is jaundice or cholelithiasis, the sclera of the person’s eyes turn yellow, the skin also becomes yellowish, and the stool becomes discolored.
In severe cases (for example, with cirrhosis of the liver, cancer), fluid accumulates in the peritoneum, and dropsy (ascites) occurs.
List of sources
- Gubergrits N. B., Linevskaya K. Yu., Belyaeva N. V. Differential diagnosis in gastroenterology. From symptom and syndrome to diagnosis and treatment: practical work. hands - Kyiv: Trush E. N. [ed.], 2022. - 623 p.
- Danilov M.V., Fedorov V.D. Pancreatic surgery. Guide for doctors. M.:b Medicine, 1995. 312 p.
- Zakharova O.P., Egorov V.I., Karmazanovsky G.G. Surgical treatment of pancreatic tumors: computed tomographic criteria for resectability. Annals of surgical hepatology. 2011. 16. No. 1. pp. 84-91.
- Zimmerman Ya.S. Chronic pancreatitis // Bulletin of the Pancreatology Club. - 2009. No. 1. - P. 38-47.
Treatment of changes in the liver
Liver pathologies are closely related to problems in the gallbladder, so most often treatment will be joint. Refusal of alcohol, smoking, normalization of nutrition is required
.
Viral hepatitis is treated with special antiviral agents, hepatoprotectors. The latter help restore the functioning of hepatocytes and are indicated for almost any liver pathology. The main hepatoprotectors are Essentiale, Heptral, Phosphogliv, Gepabene
.
Vitamin E, amino acid preparations, B vitamins improve the condition of the liver. Choleretic preparations (Allohol, Chofitol) will eliminate stagnation of bile in the liver, and preparations for diluting bile (Ursosan, Ursofalk) will prevent the formation of stones. The operation is indicated for large liver cysts, portal hypertension, tumors, and metastases.
Diet and folk remedies
As soon as diffuse changes are detected in the digestive organs, you need to urgently start following a diet. Therapeutic nutrition will be quite simple. It is necessary to remove soda, strong tea, any coffee, and alcohol from the menu. Smoked meats, sausages, spicy dishes, with spices, and marinades are prohibited. You also need to avoid fatty foods and salty foods. All dishes should be steamed, boiled, stewed without adding animal fats.
Traditional medicine also recommends a number of recipes to reduce changes in the liver and pancreas:
- Rinse 3 cups of oat grain with peel in water, mix with 3 tablespoons of birch buds, 2 tablespoons of mint. Pour 3 liters of boiling water over everything and leave for a day. Then cook for 20 minutes, add 2 tablespoons of knotweed herb. Cook for 10 minutes, strain. Drink 150 ml three times a day until the decoction is complete.
- Brew 2 tablespoons of rose hips (berries) and 400 ml of boiling water in a thermos, leave overnight. Drink 100 ml four times a day for 10 days.
You cannot carry out treatment on your own; even herbal medicine must be approved by the attending physician, and it must also be combined with conservative treatment.
Causes of pancreatic diseases
According to WHO, pancreatitis is considered the most common pancreatic disease. This is an aseptic inflammation of the organ, which provokes tissue breakdown. It occurs due to the accumulation of enzymes produced in the gland and their negative impact on the organ itself.
Experts identify many reasons that provoke the appearance of pancreatic diseases. The main ones:
- Poor nutrition – abuse of fatty, spicy foods and fast food.
- Failure to maintain water balance - a person should consume at least 2 liters of water daily.
- Having bad habits – drinking alcohol and smoking.
- Excessive stress and nervous overload.
Main symptoms of pancreatic diseases
There are a number of signs of pancreatic diseases. They differ depending on the type of disease and the form of its course. However, experts identify several main clinical manifestations that indicate the development of lesions in this organ.
The main symptoms of pancreatic diseases in women and men:
- The presence of unbearable acute pain in the left hypochondrium. The pain syndrome can spread to the shoulder blade, back and sternum. The duration of pain varies from several hours to several days. When the gallbladder is involved in the inflammatory process, the pain spreads to the epigastric region. Painful sensations intensify with palpation, as well as when the affected area is exposed to heat.
- Metabolic disorders are also the main symptom of pancreatic diseases. It develops due to the death of healthy organ cells. This reduces the production of digestive enzymes. Because of this, diabetes and other hormonal diseases may begin to develop in the patient’s body.
- Nausea, vomiting and acute diarrhea often accompany patients with pancreatic disorders. It all starts with bloating, frequent belching, after which flatulence appears. An increase in body temperature is also possible.
- The appearance of rashes in the chest, back and abdomen. The rash appears as a cluster of small red spots. They arise as a result of rupture of capillaries.
- Increased pain in the abdomen and hypochondrium after eating. Typically, patients change their diet to relieve pain - eat less often. As a result, weight loss occurs and the body begins to lose its protective functions. Against this background, a severe form of hypovitaminosis may develop, which can lead to deterioration of the condition of hair, nails and skin.
When the first symptoms of the disease appear, you should consult a specialist. The doctor will conduct a survey, examination and diagnosis. After which a treatment strategy will be prescribed. It is better not to delay going to the doctor. Then the disease can provoke serious complications. Timely recognition of the disease and effectively selected treatment, as well as a balanced diet, can eliminate the inflammatory process in the pancreas, normalize its functioning, and also prevent surgery - one of the radical methods of surgical treatment.
Fully or partially limited products
The diet for diffuse changes in the pancreas excludes:
- Soups with concentrated meat/mushroom/fish broth, okroshka, borscht, beetroot soup, cabbage soup.
- Legumes, vegetables with coarse fiber (turnips, eggplants, rutabaga, bell peppers, white cabbage, radishes, radishes, onions, garlic), mushrooms.
- Fatty fish/meat, domestic waterfowl meat (goose and duck), smoked meats, all fried foods, fish caviar, salted fish, sausages, stewed meat/fish, canned food, offal.
- Fresh wheat (rye) bread, puff pastry, muffins, pastries with cream, baked goods (yeast/butter), cakes, cheesecakes and pancakes, fried pies, pancakes.
- Porridge (barley, pearl barley, corn, millet).
- Fried/hard-boiled chicken eggs, high-fat high-acid cottage cheese, cream, full-fat milk, salty spicy cheese.
- Fermented/salted/pickled foods.
- Chocolate, black strong coffee, condensed milk, jam, honey, grape juice, ice cream, cocoa, carbonated/alcoholic drinks.
- Cooking/animal fats, spices and seasonings (herbs, horseradish, mayonnaise, ketchup, mustard, pepper).
- Fruits (bananas, grapes, dates) containing simple carbohydrates. Sour fruits/berries (cranberries, sour apples, cherries).
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| canned vegetables | 1,5 | 0,2 | 5,5 | 30 |
| eggplant | 1,2 | 0,1 | 4,5 | 24 |
| swede | 1,2 | 0,1 | 7,7 | 37 |
| peas | 6,0 | 0,0 | 9,0 | 60 |
| cabbage | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,7 | 27 |
| bulb onions | 1,4 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 41 |
| chickpeas | 19,0 | 6,0 | 61,0 | 364 |
| salad pepper | 1,3 | 0,0 | 5,3 | 27 |
| parsley | 3,7 | 0,4 | 7,6 | 47 |
| radish | 1,2 | 0,1 | 3,4 | 19 |
| white radish | 1,4 | 0,0 | 4,1 | 21 |
| dill | 2,5 | 0,5 | 6,3 | 38 |
| beans | 7,8 | 0,5 | 21,5 | 123 |
| horseradish | 3,2 | 0,4 | 10,5 | 56 |
| spinach | 2,9 | 0,3 | 2,0 | 22 |
| sorrel | 1,5 | 0,3 | 2,9 | 19 |
Fruits | ||||
| bananas | 1,5 | 0,2 | 21,8 | 95 |
Berries | ||||
| grape | 0,6 | 0,2 | 16,8 | 65 |
Mushrooms | ||||
| mushrooms | 3,5 | 2,0 | 2,5 | 30 |
| marinated mushrooms | 2,2 | 0,4 | 0,0 | 20 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| nuts | 15,0 | 40,0 | 20,0 | 500 |
| raisin | 2,9 | 0,6 | 66,0 | 264 |
| seeds | 22,6 | 49,4 | 4,1 | 567 |
| dates | 2,5 | 0,5 | 69,2 | 274 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| corn grits | 8,3 | 1,2 | 75,0 | 337 |
| millet cereal | 11,5 | 3,3 | 69,3 | 348 |
| barley grits | 10,4 | 1,3 | 66,3 | 324 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| pasta | 10,4 | 1,1 | 69,7 | 337 |
| dumplings | 11,9 | 12,4 | 29,0 | 275 |
Bakery products | ||||
| buns | 7,9 | 9,4 | 55,5 | 339 |
| Rye bread | 6,6 | 1,2 | 34,2 | 165 |
Confectionery | ||||
| pastry cream | 0,2 | 26,0 | 16,5 | 300 |
| shortbread dough | 6,5 | 21,6 | 49,9 | 403 |
Ice cream | ||||
| ice cream | 3,7 | 6,9 | 22,1 | 189 |
Chocolate | ||||
| chocolate | 5,4 | 35,3 | 56,5 | 544 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| mustard | 5,7 | 6,4 | 22,0 | 162 |
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
Dairy | ||||
| milk 4.5% | 3,1 | 4,5 | 4,7 | 72 |
| cream 35% (fat) | 2,5 | 35,0 | 3,0 | 337 |
| whipped cream | 3,2 | 22,2 | 12,5 | 257 |
| sour cream 30% | 2,4 | 30,0 | 3,1 | 294 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| parmesan cheese | 33,0 | 28,0 | 0,0 | 392 |
Meat products | ||||
| fatty pork | 11,4 | 49,3 | 0,0 | 489 |
| salo | 2,4 | 89,0 | 0,0 | 797 |
| bacon | 23,0 | 45,0 | 0,0 | 500 |
Sausages | ||||
| smoked sausage | 9,9 | 63,2 | 0,3 | 608 |
Bird | ||||
| smoked chicken | 27,5 | 8,2 | 0,0 | 184 |
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| smoked duck | 19,0 | 28,4 | 0,0 | 337 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
| black caviar | 28,0 | 9,7 | 0,0 | 203 |
| salmon caviar granular | 32,0 | 15,0 | 0,0 | 263 |
| salmon | 19,8 | 6,3 | 0,0 | 142 |
| canned fish | 17,5 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 88 |
| salmon | 21,6 | 6,0 | — | 140 |
| trout | 19,2 | 2,1 | — | 97 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| animal fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
Alcoholic drinks | ||||
| dry red wine | 0,2 | 0,0 | 0,3 | 68 |
| vodka | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,1 | 235 |
| beer | 0,3 | 0,0 | 4,6 | 42 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| soda water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| cola | 0,0 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 42 |
| instant coffee dry | 15,0 | 3,5 | 0,0 | 94 |
| sprite | 0,1 | 0,0 | 7,0 | 29 |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| grape juice | 0,3 | 0,0 | 14,0 | 54 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Pancreatitis is a disease of the pancreas: symptoms of the disease in women and men
Pancreatitis is inflammation of the pancreas tissue. The disease is characterized by a violation of the outflow of organ secretion. The damage occurs due to increased activity of enzyme systems. In this case, the secreted juices do not have time to escape into the lumen of the duodenum, but accumulate and begin to digest the gland’s own tissues.
According to WHO, the prevalence of the disease has increased several times. The main factors influencing the occurrence of pancreatitis are poor diet and abuse of alcoholic beverages.
Experts divide pancreatitis into two forms - acute and chronic. The first requires urgent hospitalization and hospital treatment under the supervision of specialists.
The main symptoms of acute pancreatitis in men and women:
- Changes in skin color – the skin becomes duller and takes on an earthy color. Brown or blue spots appear in the lumbar region and above the navel. Some patients report the appearance of obstructive jaundice.
- A feeling of acute pain in the hypochondrium - the syndrome can be encircling or localized only in the left or right side of the body.
- Impaired functioning of the digestive tract - the appearance of hiccups, belching with an unpleasant odor, nausea and continuous bouts of vomiting, diarrhea and constipation.
- General deterioration of the body - dehydration, dry mouth, severe weakness, apathy. Changes in blood pressure - increase or decrease, increased sweating, shortness of breath, increased body temperature.
Signs of chronic pancreatitis
They are less pronounced. Experts identify the following series of symptoms for this disease:
- There are changes in the color of the skin - yellowness.
- In advanced forms, sudden weight loss is observed.
- Serious illnesses and digestive disorders such as anemia, diabetes, constipation or diarrhea may occur.
- Feeling pain after eating. Most often, pain occurs after eating fatty or fried foods, as well as large amounts of alcoholic beverages. The pain is localized in the hypochondrium.
- Disorders of the gastrointestinal tract - constipation, flatulence, belching, belching with an unpleasant odor.
In the early stages, it is almost impossible to detect the disease without the intervention of a specialist, since the chronic form occurs without pronounced symptoms.
Pancreatitis of the pancreas rarely manifests itself as an independent disease. Typically, the pathological process combines several digestive organs, involving the hepatobiliary system - liver, gall bladder and ducts, duodenum, stomach. This fact requires diagnosing the entire human digestive system.
Factors influencing the development of diseases
In most cases, pancreatic pathologies develop as a result of chronic pancreatitis. The disease is characterized by a progressive inflammatory process and includes several varieties, which are classified according to the causes of their occurrence.
| View | Cause |
| biliary | violation of the outflow of bile due to inflammatory diseases (cholangitis, cholecystitis), cholelithiasis |
| alcoholic | chronic alcoholism |
| destructive | structural destruction of gland cells |
| medicinal or medicinal | incorrect therapy with diuretics, cardiovascular drugs, antiviral drugs, antibiotics, statins, hormones, psychomotor and psychotropic drugs |
| parenchymal | inflammation of the parenchyma caused by impaired enzyme production |
| pseudotumorous | proliferation of connective tissue, formation of cysts and calcifications |
One of the reasons for the development of dysfunction and the formation of a diffusely heterogeneous structure of the pancreas is considered to be eating behavior: the predominance of fatty foods, smoked foods in the diet, an unhealthy addiction to confectionery, hot spices and seasonings, and abuse of alcoholic beverages. An unhealthy diet provokes a failure of metabolic processes; alcohol and its breakdown products poison the tissues and cells of the gland.
Another factor in reducing functional abilities and changing the morphological characteristics of the gland is prolonged neuropsychological stress (distress) and depressive states. Psycho-emotional instability causes hormonal disruptions that negatively affect the functioning of the entire body, including the hormone-producing pancreas.