Chronic diffuse liver diseases often occur in women of childbearing age. The most common form of liver damage is chronic hepatitis of viral etiology, more rare are autoimmune and drug-induced hepatitis, cholestatic forms of damage (primary biliary cirrhosis, primary sclerosing cholangitis), alcoholic liver damage, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (due to obesity, diabetes mellitus), Wilson's disease - Konovalova and others.
Recent decades have been marked by an increase in the number of people infected and suffering from viral chronic liver diseases (CLD), especially among young people, as well as the emergence of a number of new drugs that allow successful etiopathogenetic treatment of some forms of liver damage. This leads to an increase in the number of pregnant women and postpartum women suffering from CKD. Features of the course of CKD in pregnant women, management tactics for such patients, in particular, indications for drug treatment and issues of its safety have not been sufficiently studied.
Causes of chronic liver diseases
Chronic liver diseases - hepatitis - can be caused by a variety of reasons, the main ones:
- hepatitis viruses (hepatitis B virus, hepatitis C virus) are the most common cause of chronic hepatitis;
- a violation of fat metabolism, which leads to fat deposition in the liver (steatohepatitis);
- alcohol abuse (alcoholic liver disease);
- autoimmune disorders (autoimmune hepatitis, primary biliary cirrhosis, primary sclerosing cholangitis);
- long-term use of medications;
- genetic defects - hereditary liver diseases.
Possible manifestations
Diffuse changes in the structure of the pancreas can manifest themselves in different ways. If we talk about primary manifestations, we can distinguish the following symptoms:
- decreased appetite and, as a result, decreased body weight;
- nausea, belching, heartburn;
- intestinal disorders (manifested by constipation, diarrhea, bloating, etc.);
- feeling of heaviness in the epigastric region.
Unpleasant sensations in the epigastric region are the main sign of impaired pancreatic functionality
If the patient has pronounced diffuse changes, then the clinical picture is acute. That is, a person experiences constant nausea, diarrhea, pain, aversion to food, etc. In this case, the patient must be immediately hospitalized and provided with comprehensive treatment.
Hereditary liver diseases
Hereditary chronic liver diseases are quite rare, therefore, even with repeated examinations, they are not recognized by doctors and patients are treated for a long time for other diseases.
The main hereditary liver diseases include: Gilbert's syndrome, hemochromatosis, Wilson-Konovalov disease, etc.
Hemochromatosis is a disease of autosomal recessive inheritance, characterized by impaired iron metabolism, excessive absorption in the intestine, increased content in the blood and deposition in various tissues with increased structure and dysfunction of the liver, heart, and pituitary gland. Clinical symptoms in the early stages of the disease are nonspecific: weakness, fatigue, weight loss, joint pain. The examination reveals an increase in ALT and AST.
In the terminal stage, the classic triad manifests itself: skin pigmentation, cirrhosis and diabetes mellitus. For diagnosis, the level of iron in the blood, transferrin, ferritin, total iron-binding capacity, as well as ALT and AST are determined. Genetic analysis for hemochromatosis reveals the presence of hereditary factors - mutations of the HFE gene. Genetic testing is also carried out for close relatives of patients with confirmed hemochromatosis.
The goal of treatment is to remove excess iron from the body. Good results are obtained by bloodletting under the control of a clinical blood test and the patient’s well-being. In addition, drugs are used to help remove iron from the body and prevent the formation of cirrhosis. Timely initiation of therapy prolongs the life of patients by several decades.
Konovalov-Wilson disease is a hereditary disease based on increased absorption of copper in the intestine and decreased synthesis of the copper-binding protein ceruloplasmin in the liver. This leads to excessive accumulation of copper in the blood and its deposition in tissues with primary damage to the liver, central nervous system, kidneys, cornea and other organs. The clinical picture consists of symptoms of liver damage, neurological and mental disorders. In the early stages of the disease, symptoms of hepatitis, hepatomegaly, and splenomegaly (enlarged liver and spleen) appear. Later, signs of functional liver failure, portal hypertension, jaundice, and a slowly progressive form of cirrhosis increase.
Damage to the nervous system is manifested by hand tremors, speech impairment, prolonged muscle spasms, decreased intelligence up to dementia. A typical sign of the disease is the deposition of a greenish-brown pigment containing copper in the cornea - Kayser-Fleischer rings. Treatment is aimed at removing excess copper from the body - a special diet with a limited copper content and drugs that bind and remove copper.
General information
Diffuse changes in the pancreas are not a pathology, but a condition indicating abnormalities that can “develop” into various diseases. In this case, deviations are observed in the tissues of the gland. They may or may not be significant. Sometimes such changes are a consequence of pathologies that a person already has, for example, internal hemorrhages, tumors or stone deposits.
Diffuse changes in the pancreas are recorded against the background of compaction of its tissues or, conversely, their degeneration. In other words, when such deviations are identified, a person requires a more detailed examination in order to promptly begin treatment of existing pathologies or carry out a number of measures that will help him prevent their development.
Symptoms of liver disease
Symptoms of liver disease include frequent nausea, heartburn, a very unpleasant, pungent odor of sweat, yellowish skin color, dark yellow urine, diarrhea, discoloration of feces to dark brown or light yellow, sometimes green. Also, liver disorders can lead to acne in adulthood, frequent feelings of hunger or strong and frequent thirst, itching of some thin areas of the skin, and blurred vision. For example, a person may begin to confuse white with yellow, suddenly feel either cold or hot, and cannot sleep at night, experiencing fever and rapid heartbeat. Hair and eyebrows may begin to fall out. Convulsions occur, papillomas form, and the development of atherosclerosis of the brain, heart, intestines, and blood vessels of the legs begins.
Typical cases of organic and functional liver problems are easily recognized by their characteristic symptoms. But some situations make it difficult for even experienced hepatologists (specialists who deal with liver diseases) to make a correct diagnosis. It all depends on the specific type of disease, the individual characteristics of the body, the presence or absence of concomitant pathology.
- Discomfort and pain in the projection of the liver;
- Enlargement of the liver;
- General weakness and malaise;
- Headache;
- Impaired mental and thinking abilities;
- Increased skin sweating and swelling;
- Yellowness of the skin and sclera;
- Skin rash;
- Increased fragility of blood vessels and tendency to bleeding;
- Signs of hypovitaminosis;
- Stool instability, changes in the nature and color of stool;
- Increase in abdominal size;
- Increased venous pattern on the skin of the abdomen;
- Unmotivated weight loss;
- Bitterness in the mouth;
- Cracks on the surface of the tongue and its coating with a white or brown coating;
- Temperature reaction of varying severity.
Pain due to liver damage can be of a different nature. They can be interpreted like this:
- Minor pain in the right hypochondrium in the form of aching pain, bloating and heaviness. Characterize a sluggish pathological process of inflammatory toxic or other origin. This type of pain in the liver is most likely caused by an increase in the size of the organ and overstretching of the liver capsule. Patients cannot clearly identify one pain point;
- Intense widespread pain in the right hypochondrium. They are rare and speak of either a pronounced inflammatory, purulent, traumatic pathological process, or damage to the bile ducts by stones;
- Severe local point pain in the projection of the liver. It is not typical for liver damage and in most cases is associated with pathology of the gallbladder and extrahepatic bile ducts;
- Complete absence of pain in the liver. It is very common in indolent liver diseases, which remain undetected for a long time and are detected only at the stage of liver failure or cirrhosis.
Based on the characteristics of the skin, one can determine the functioning of various organs, including the liver.
With such diseases, the skin may be:
- Pale or dark-skinned with severe sweating and swelling of the subcutaneous tissue, especially in the face and limbs;
- Dry, flaky with multiple scratch marks and cracks;
- Jaundice. By the nature of this type of skin changes, one can determine the origin of jaundice. In case of liver problems, jaundice is of moderate intensity and is represented by an orange tint. When carrying out the differential diagnosis of jaundice, this criterion allows us to exclude mechanical types (brown skin tone) and hemolytic types, accompanied by a lemon-yellow skin tone;
- With the presence of striae. Striae are stretch marks of the skin, mostly of the abdomen, in the form of bluish stripes of thinning. The reason for their appearance is a hormonal imbalance, both in the male and female body, when the liver is not able to neutralize excess steroid hormones.
In most patients with liver pathology, along with changes in skin color, various rashes appear.
- Pustular elements, tendency to folliculitis and furunculosis. They are based on an immune imbalance that occurs against the background of a decrease in the liver’s ability to synthesize immunoglobulins;
- Allergic rash of the type of spots and papules. It is caused by a violation of the detoxification function of the liver, which underlies the occurrence of allergic reactions to environmental conditions familiar to the body;
- Hemorrhagic rash. Small hemorrhages over the entire surface of the skin, which are called petechial rashes, are typical manifestations of a decrease in the synthetic function of the liver. First of all, the proteins that make up the blood coagulation system are affected. Such patients have an increased tendency to form hematomas at the slightest injury.
It is characteristic that any type of skin rash in liver diseases is accompanied by severe itching. It becomes especially persistent when yellowing of the skin is combined with rashes. This symptom is explained by the fact that bilirubin, which is not neutralized by the liver, is deposited in the skin, causing irritation. In addition, other toxic metabolic products are concentrated in the wide microcirculatory network of the skin, which additionally causes irritation and itching. In this regard, when examining patients with liver pathology, you can notice scratch marks, especially on the lateral surfaces of the abdomen and forearms.
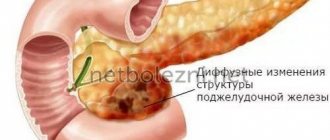
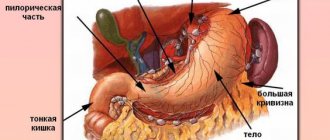
What are diffuse changes?
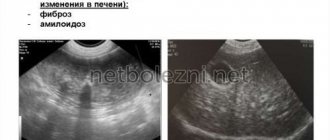
The term “diffuse changes in liver tissue” is usually used by medical professionals when describing the results of ultrasound examination (ultrasound). Most often the phrase “echographic signs of diffuse changes in the liver” appears in the conclusion. Let's talk more about what this means.
Meaning of the term
What are diffuse liver changes? To understand this, it is first necessary to clarify the term “parenchyma” itself.
Parenchyma is a complex of functional elements of one organ, which is enclosed in a fibrous membrane. Parenchymal organs include the liver, kidneys, and lungs.
Normally, the liver parenchyma is homogeneous and has a weak density. Any change in structure - the appearance of compactions, loosening, ducts, etc. - may be a sign of pathological processes occurring in this organ.
In this case, what does diffuse liver change mean? Let's try to understand the etiology of these terms. Diffusion literally means dispersion, and in this case, the spread of pathology throughout the entire organ.
Thus, the concept of “diffuse changes in the liver parenchyma” is rather vague - diffuse changes in the parenchyma can be called any pathological changes in the tissue of the organ.
Types of diffuse changes
Speaking about diffuse changes in the liver, we can distinguish several types of pathological changes in the structure of this organ:
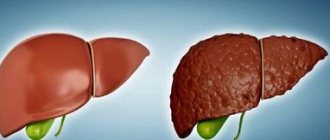
- hypertrophy - diffuse enlargement of the organ occurs (usually with hepatitis). Due to the death of liver tissue, fibrous tissue grows, which leads to an increase in the size of the organ (hepatomegaly). This condition is also dangerous because fibrous tissue, when extensively grown, can press on the hepatic veins, which can lead to swelling of the entire parenchyma;
- with hemosiderosis or galactosemia, moderate diffuse changes in the parenchyma occur, which manifest themselves in an increase in the granularity of the liver tissue;
- liver tissue becomes heterogeneous. If in the initial stage the contours of an organ are indicated by ultrasound or computed tomography as smooth, then at the stage when hepatitis imperceptibly flows into cirrhosis, the evenness of the tissue contours changes;
- structural changes such as dystrophy - the organ decreases in size. If an increase occurs with hepatitis, then with cirrhosis the liver may shrink (this is especially noticeable on the right lobe), and the contours will be uneven. Toxic dystrophy leads to necrosis of hepatocytes, which is fraught with liver failure;
- the presence of a cyst or tumor is also considered a diffuse change in the parenchyma;
- fatty degeneration of the parenchyma . This condition is characterized by excessive fat content in the liver tissue. The reasons may be different, but usually the development of this pathology is based on a violation of lipid metabolism. Heredity plays an important role in this aspect;
- moderate diffuse changes in the liver can occur under the influence of parasitic infestations. Parasites can enter the liver ducts and block them. In some cases, parasitic infestations lead to cirrhosis.
This list makes it possible to understand, at least in general terms, what a diffuse change in the liver is. In some cases, diffuse changes in the liver are minor; in others, the structure of the liver is disrupted quite significantly, which affects its functioning and causes many manifestations. Let's talk about how to recognize signs of diffuse changes in the liver.