Having received an ultrasound report with the phrase “diffuse changes in the parenchyma of the pancreas,” adults try to independently find out what kind of disease it is and how it can be treated. It is important to avoid such erroneous actions for several reasons.
Firstly, the doctor’s conclusion from the ultrasound diagnostic room does not mean a diagnosis, but a description of the result of using hardware research. It complements other available tests, clinical symptoms, and is used by the attending physician in combination to assess the state of digestion and search for the cause of disorders.
Secondly, the detected changes are also characteristic of the pathology of other organs. Thirdly, diffuse changes in the pancreas (DIPD) do not always require treatment. Medical terms are difficult for non-professionals to understand. Let's understand the scary concepts.
What is the process of "diffusion" in the pancreas
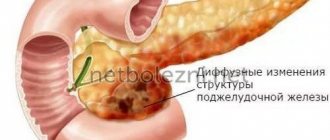
Translated from Latin, the diffusion process is changes spreading from one area to the entire organ or tissue. In this case, the correct structure of the structures collapses, blood vessels and blood flow change, and the functioning of some cells may cease.
From histology it is known that up to 90% of the pancreas tissue is occupied by its exocrine part, consisting of lobules. Inside each lobule there are acini that produce pancreatic juice.
The secretion is collected in small ducts (in the center of the acini), then merges into the main duct and is sent to the duodenum
With the help of ultrasound, the anatomical structure of the parenchyma is structured only when healthy cells are replaced with denser ones. Diagnostics is based on the possibility of reflection or absorption of a sound wave. Each tissue has its own echogenicity. Normally, the pancreas is distinguished as a uniformly dark formation located in the retroperitoneal zone. The density of the parenchyma does not differ from the liver and is considered hypo- and anechoic.
When any changes or compactions appear inside the organ, echo signs of a lighter shade (hyperechogenicity) are visible on the ultrasound machine monitor. Based on them, the specialist doctor identifies the most typical picture of a focal (only in a certain zone) or diffuse nature.
Diagnostics
To identify the causes of detected changes, laboratory and functional diagnostic methods are used. From laboratory tests the following are required:
- general clinical blood test,
- biochemical (blood diastase, bilirubin, transaminases, protein and its fractions).
This method can detect acute inflammation (leukocytosis, high ESR), increased diastasis confirms pancreatitis, changes in bilirubin and transaminases (ALT, AST, GGT) indicate the presence of hepatitis.
If the diagnosis is unclear, CT or MRI of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space (AP and ZP) is recommended, which can significantly increase the likelihood of determining the correct diagnosis.
In complex diagnostic cases, MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is more often used to clarify the pathology of the abdominal organs. If for some reason it is not suitable for the patient, computed tomography is used, which has received good feedback from doctors of all specialties. The method allows you to see layer-by-layer sections of organs in various projections and identify even minor defects in the structure of tissues.
There are contraindications for CT scanning because it uses x-rays. A child cannot be sent for the study; CT is not performed on a woman during pregnancy, on an adult with iodine intolerance (if performed with contrast), as well as on pathologies of the liver and kidneys.
Echosigns
Echo signs occupy a leading place in ultrasound diagnostics. The method is based on the use of ultra-high sound waves that are safe for humans. They penetrate the organ and are reflected, giving an objective picture of the tissue. The main echo signs are:
- heterogeneity of the pancreas structure due to areas of increased echogenicity,
- uneven increase in echogenicity,
- uneven expansion of the ducts,
- change in the size of the pancreas (increase due to edema in the acute phase of the disease or decrease in the final stages of the disease with atrophy and fibrosis),
- additional echo signs (presence of cysts and pseudocysts, changes in ducts).
What types of diffuse changes are detected?
There may be areas of heterogeneous structure. If there is pathology, its size is increased or decreased.
The nonspecific nature of diffuse changes on ultrasound can be different:
- Moderate diffuse changes with reduced echo density and heterogeneous structure are more characteristic of acute pancreatitis, when tissue structures do not change throughout the entire length of the organ. Under the influence of enzymes, self-digestion occurs, which leads to swelling (local or acute) and enlargement of the gland. Acute pancreatitis is characterized by focal, segmental or total changes.
- Reduced echogenicity and echodensity, the structure may be different, but changes evenly, the size of the pancreas remains the same. This is characteristic of chronic pancreatitis: with it, normal tissue is often replaced by fatty tissue, the ducts change their shape and wall thickness.
What types of disorders cause diffuse changes?
Diffuse changes in the pancreas reflect the formation of hyperechoic tissue structures, but do not indicate the variant of the pathological process that caused them. The most common types of violations are related to:
- with dystrophy;
- inflammation and swelling (with pancreatitis);
- replacement of healthy acini with fatty inclusions such as steatosis;
- fibrosis of the parenchyma (proliferation of scar connective tissue).
With the help of echo signs of diffuse changes in the pancreas, it becomes possible to establish the degree of development of the pathology and identify the proportion of remaining undamaged tissue. This is important for choosing the optimal treatment tactics in a particular case.
A lighter duct passes through the parenchyma, the grain pattern is similar to lipomatosis
What are the reasons
Diffuse parenchymal changes may be accompanied by an increase or decrease in the size of the organ. With edema, the tissues swell and contribute to the growth of the gland mass. Dystrophic disorders and fibrosis reduce the size and wrinkle the shape.
The most common echographic signs are:
Pancreatic hyperfunction
- with general metabolic-dystrophic processes in old age;
- impaired blood circulation in the pancreas area;
- endocrine diseases and metabolic syndromes;
- changes in the functioning of the liver and bile ducts.
In elderly people and patients with diabetes, the iron appears normal or reduced in volume on ultrasound. Parenchymal changes in the pancreas are caused by the replacement of healthy tissue with fatty tissue. As a result, echogenicity increases. In such cases, the question of the need for treatment must be decided taking into account the existing disorders.
In acute pancreatitis with severe symptoms of inflammation, diffuse changes in the parenchyma are considered an indicator of a severe course of the disease and a high risk of complications. Swelling and impaired internal circulation in the organ cause an increase in size with increased echogenicity.
Chronic pancreatitis is accompanied by gradual destruction of gland tissue, replacement with scars, and wrinkling of the shape. The appearance of dense echogenic structures indicates the degree of loss of the functional usefulness of the organ. A similar picture is given by diabetes mellitus with disruption of the endocrine activity of the pancreas.
The causes of diffuse disturbances in echogenic properties are those that contribute to the following diseases:
- nutritional deficiencies (excessive consumption of fatty, spicy, fried or canned foods, sweets, confectionery or fasting);
- frequent stressful situations;
- chronic alcoholism, nicotine addiction, drug poisoning;
- disruption of the functioning of the digestive system;
- negative effects of drugs;
- burdened heredity.
Predisposing factors
Often the causes of diffuse liver changes lie in our daily habits. Here are the most common factors predisposing to such changes:
- improper nutrition . Despite frequent reminders from doctors about the benefits of diet for liver health, many people continue to eat unhealthy foods. Semi-finished meat products (sausages, sausages) with fried potatoes, doused with liters of mayonnaise or ketchup - the picture, you see, is quite typical and familiar to everyone. Then you can enjoy a couple of ice cream cones. And while the unlucky gourmet eats his unhealthy dinner, the liver works in emergency mode. And very soon, abuse of alcohol, fatty, fried, spicy, sweet foods, as well as products containing harmful additives and preservatives (the main range of supermarkets) leads to chronic hepatitis, cholecystitis, and other diseases;
- Alcohol abuse is a separate issue. A safe daily dose of alcohol is approximately 50 grams of a strong drink (for example, cognac or vodka). But who will limit themselves to one glass? Liver enzymes break down alcohol, resulting in the formation of many harmful compounds such as acetaldehyde. As a result of regular alcohol consumption, liver cells begin to die, and fat cells appear in their place. Thus, fatty degeneration of the liver occurs. Alcoholic hepatitis, if untreated, has every chance of developing into cirrhosis, in which the death of liver cells is irreversible. According to statistics, about 15% of drinkers suffer from cirrhosis;
- side effects of drugs . Unfortunately, many drugs, in addition to their therapeutic effect, have a number of side effects, including hepatotoxic effects. That is why any medications should be taken in moderation, strictly following the instructions.
- unfavorable environmental conditions . Any toxic substances that affect our body sooner or later enter the liver through the bloodstream, where they are filtered and neutralized. However, the liver's resources have their limits, so regular inhalation of exhaust gases or vapors of chemical compounds can cause liver disease. People living in environmentally unfavorable areas (near factories, plants, industrial complexes or busy highways) are more at risk of chronic hepatitis than residents of villages;
- psychological stress . It doesn’t matter what they are caused by - traffic jams, loud music behind the wall or inappropriate behavior of management at work. The important thing is that stress is accompanied by a release of adrenaline. And this hormone, which the liver has to break down, is very toxic for it. Therefore, regular stress will sooner or later lead to damage to hepatocytes.
To prevent liver and gallbladder diseases, you must be careful when choosing pharmacological drugs, do not abuse alcohol and adhere to a diet.
Living a healthy lifestyle, avoiding stress and eating right may seem like too much of a challenge for many. However, treating diffuse liver changes without following these rules is even more difficult.
Symptoms
The doctor finds out any manifestations of pancreatic pathology by interviewing the patient, examining them, and comparing them with the results of blood, urine, feces, and biochemical tests.
Ultrasound results are a valuable diagnostic tool. However, they are not associated with specific symptoms and complaints of the patient.
In acute pancreatitis, severe pain of a girdling nature with nausea, vomiting, and signs of shock (pallor, tachycardia, drop in blood pressure) comes first. The patient needs intensive therapy to prevent necrosis (death) of the parenchyma and diffuse peritonitis caused by the release of enzymes into the abdominal cavity.
In a chronic course, pain occurs only during exacerbation or violation of the diet. More worrying is loss of appetite, weight loss, frequent diarrhea, bloating. Digestion is disrupted as tissue is replaced by fibrous tissue and requires increasing compensation with medications.
Fibrosis of the parenchyma in a chronic process necessarily affects the endocrine part of the gland and suppresses insulin production. Diabetes mellitus in such a patient is difficult because it depends on an irreversible process. Symptoms include: vomiting, weight loss, thirst, diarrhea.
Diabetes mellitus is accompanied by diffuse changes
The replacement of normal cells with fat cells (lipomatosis) also leads to disruption of the functions of the gland. The severity of the manifestations is related to the degree of damage to the organ, compression of the main duct and endocrine tissue.
With a degenerative process or fatty infiltration, a person may not be aware of the dysfunction of the pancreas for a long time. The pain is intermittent and moderate and is explained by other reasons. Pathology is detected only by ultrasound.
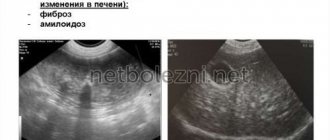
Hereditary liver diseases
Hereditary chronic liver diseases are quite rare, therefore, even with repeated examinations, they are not recognized by doctors and patients are treated for a long time for other diseases.
The main hereditary liver diseases include: Gilbert's syndrome, hemochromatosis, Wilson-Konovalov disease, etc.
Hemochromatosis is a disease of autosomal recessive inheritance, characterized by impaired iron metabolism, excessive absorption in the intestine, increased content in the blood and deposition in various tissues with increased structure and dysfunction of the liver, heart, and pituitary gland. Clinical symptoms in the early stages of the disease are nonspecific: weakness, fatigue, weight loss, joint pain. The examination reveals an increase in ALT and AST.
In the terminal stage, the classic triad manifests itself: skin pigmentation, cirrhosis and diabetes mellitus. For diagnosis, the level of iron in the blood, transferrin, ferritin, total iron-binding capacity, as well as ALT and AST are determined. Genetic analysis for hemochromatosis reveals the presence of hereditary factors - mutations of the HFE gene. Genetic testing is also carried out for close relatives of patients with confirmed hemochromatosis.
The goal of treatment is to remove excess iron from the body. Good results are obtained by bloodletting under the control of a clinical blood test and the patient’s well-being. In addition, drugs are used to help remove iron from the body and prevent the formation of cirrhosis. Timely initiation of therapy prolongs the life of patients by several decades.
Konovalov-Wilson disease is a hereditary disease based on increased absorption of copper in the intestine and decreased synthesis of the copper-binding protein ceruloplasmin in the liver. This leads to excessive accumulation of copper in the blood and its deposition in tissues with primary damage to the liver, central nervous system, kidneys, cornea and other organs. The clinical picture consists of symptoms of liver damage, neurological and mental disorders. In the early stages of the disease, symptoms of hepatitis, hepatomegaly, and splenomegaly (enlarged liver and spleen) appear. Later, signs of functional liver failure, portal hypertension, jaundice, and a slowly progressive form of cirrhosis increase.
Damage to the nervous system is manifested by hand tremors, speech impairment, prolonged muscle spasms, decreased intelligence up to dementia. A typical sign of the disease is the deposition of a greenish-brown pigment containing copper in the cornea - Kayser-Fleischer rings. Treatment is aimed at removing excess copper from the body - a special diet with a limited copper content and drugs that bind and remove copper.
What variations in echogenicity indicate the stage of the disease?
Based on the violation of tissue density for the ultrasonic wave, the connection with other signs, one can be guided by the degree of pathological disorders in the pancreas. Main diagnostic options:
- decrease in parenchyma density (reduced echogenicity) + increase in organ size → the outflow of pancreatic juice is hampered, enzymes enter the blood, characteristic of acute pancreatitis;
- the same if the size remains normal → typical for chronic pancreatitis, tortuosity of the excretory duct;
- a general increase in echogenicity, with normal size of the gland, is a sign of beginning fatty tissue replacement, accompanies diabetes mellitus, obesity, dystrophy in the elderly;
- increased parenchyma density + increased echogenicity, but the size of the organ is reduced or normal → signs of fibrosis during the recovery period after inflammation, with metabolic disorders.
What thyroid diseases are detected by ultrasound examination?
The list of thyroid diseases is quite diverse. Most of them are detected by ultrasound.
There are:
- Diffuse diseases - diffuse hyperplasia, various types of thyroiditis, Graves' disease, etc.
- Focal diseases of the thyroid gland are nodular and cystic formations.
- Mixed (diffuse-focal) diseases.
Autoimmune thyroiditis.
Hypertrophic form Fibrosing thyroiditis
It also happens that ultrasound reveals changes, but the gland functions normally. For example, with some types of nodular goiter, laboratory data - thyroid hormones and their antibodies - may be within normal limits. In this case, it is important to consult with an endocrinologist, examine the node and evaluate its size, which is done with repeated ultrasound examinations.
What is meant by “diffuse changes in the tail of the pancreas”?
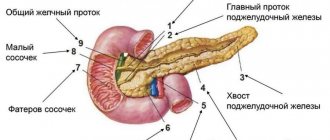
The anatomical parts of the pancreas are divided into body, head and tail. The latter is located on the left, next to the spleen. The excretory duct begins here, collecting secretions from the entire organ and passing through the main part. The tail width is no more than 30 mm.
With a diffuse change in the tail, the zone expands and thickens. In diagnosis, this sign is important for identifying impaired patency of the splenic vein. It is often associated with portal hypertension.
Diffuse changes in the tail are found in ¼ of all studies of the pancreas
Treatment
Treatment of diffuse changes is indicated only in cases where they are pathological. Minor disturbances in the structure of the parenchyma or those caused by a previous disease or the age of the patient do not require specific therapy. In such cases, the patient is prescribed conservative treatment, which consists of following a diet, getting rid of bad habits and stressful situations.
If diffuse changes were provoked by acute or chronic inflammatory processes occurring in parenchymal tissues, then the patient is prescribed a number of additional diagnostic procedures to establish an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the necessary therapy and diet. For diffuse changes caused by diabetes mellitus, the patient is prescribed a special diet and treatment that ensures the maintenance of normal blood glucose levels.
When neoplasms are detected in the tissues of the pancreas, treatment tactics are determined individually for each patient. This may involve diet, medication or surgery.
Causes of diffuse reactive changes
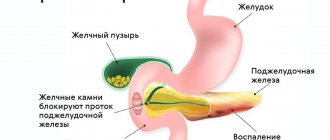
The reaction from the pancreas occurs in response to various diseases of the digestive system. Moreover, on ultrasound they appear diffusely in the parenchyma. Most of all, the secreting function of the gland changes depending on the activity of the liver and the biliary system. In patients with cholecystitis, cholelithiasis, hepatitis, secondary pancreatitis may develop.
A violent reaction develops with symptoms of poisoning with drugs, industrial and household poisons. In the same way, changes in the pancreas occur in a child, with increased sensitivity or negative effects of medications.
In childhood, unexplained enzyme deficiency and abnormalities in the development of the biliary tract play a role. Ultrasound reveals signs similar to acute pancreatitis. A special feature is the more frequent localization of changes in the tail zone of the gland, expansion of the duct.
Ultrasound examination of the pancreas is included in a comprehensive examination of the abdominal organs
What does increased echogenicity mean?
An unusual increase in the recoil force of the waves indicates compaction of the parenchyma and a reduction in the amount of fluid in it. Diffuse hyperechogenicity, the causes of which are external factors, is not considered a pathology. Most often it manifests itself in the hot season, after eating hot and rich food, and during colds.
Echogenicity increases markedly with inflammation. Causes for concern may be: tumors, metastases, calcium deposits and stones, cysts, fibrosis. Such inclusions are the consequences of ignoring the early symptoms of pancreatitis.
A number of parameters indicate acute pancreatitis:
- General increase in organ size.
- Presence of large echogenic areas.
- Heterogeneity of structure.
- Exceeding the width of the gland duct.
- Blurred boundaries.
A more severe form of the disease involves changes in the density and contours of neighboring organs. Possible formation of pseudocysts.
When diagnosing chronic pancreatitis, the following picture is observed:
- Echogenicity increases slightly.
- The width of the duct increases by more than 2 mm.
- The size of the gland itself increases.
- Unclear outline.
- Heterogeneous structure.
- There is fluid in the omental bursa behind the stomach.
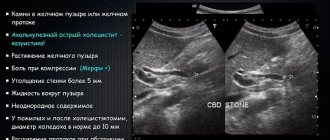
The disease may be accompanied by the formation of stones. In the picture they appear as spots with an echogenic trace. The progressive disease is easy to notice due to the significant discrepancy in the ratio of the size of the gland to the Wirsung duct. The latter is greatly swollen in width.
Parameters such as increased echogenicity and blurred contours suggest that healthy cells in the organ have replaced fat cells, which occurs with lipomatosis. Hyperechogenicity along with a decrease in the pancreas indicate the development of fibrosis. The growth of connective tissue and its replacement of normal cells is accompanied by the appearance of scars.
Ultrasound alone is not enough to accurately diagnose a patient. The patient is sent for auxiliary procedures: magnetic resonance or computed tomography, laparoscopy or biopsy.
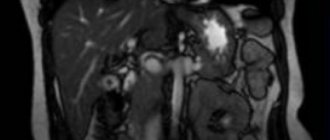
A lighter image of the pancreas indicates increased echogenicity