People often experience a lump in the throat. Everyone has experienced this feeling at least once in their life. The feeling of a lump in the throat most often occurs without physical reasons, after experiencing stress. At some point, you notice that something is bothering your throat or starting to feel sore.
For some people, this feeling remains for a long time and even begins to cause discomfort when swallowing. In this case, other accompanying symptoms may occur, for example, sleep disturbances, increased levels of anxiety, decreased mood, etc. But there is no need to rush to conclusions and think about the presence of some complex, incurable disease or physical damage.
In the vast majority of cases, this feeling has psychological roots, and treating a lump in the throat is not difficult and responds well to therapy. However, in advanced cases, when it is not treated correctly or the process is prolonged or untreated for a long time, complications develop. Therefore, in order to undergo high-quality therapy and get rid of a lump in the throat, it is necessary to undergo a psychological differential diagnosis.
We carry out full differential diagnosis and treatment, which is completely successful in more than 90% of cases. There are many different options for disruption of higher nervous activity and the formation of sensations of a lump in the throat.
Our slogan is from quality diagnosis to complete recovery!
Find out what may be causing that lump in your throat! When is a complex disorder likely to occur? What to do when you feel a lump in your throat?
How does a lump in the esophagus manifest itself?
A lump in the esophagus is a very unpleasant sensation
A description of this symptom is found in the works of the great ancient physician Hippocrates. He considered a lump in the esophagus to be a manifestation of hysterical natures. Since then, the idea of a coma in the esophagus has changed somewhat. It is characterized by the following signs:
- Difficulty swallowing and breathing.
- Sensation of a foreign body in the area of the esophagus.
- Constant desire to cough, to swallow obstruction.
- Feeling of lack of air, suffocation.
- Fear of suffocation, choking (especially in sleep).
- Hoarseness, pain when talking or eating.
Such sensations are not always permanent; they can manifest themselves after taking a certain body position, or after eating, mental stress, or the appearance of strong emotions.
The influence of nervous tension on the appearance of unpleasant symptoms in the esophagus
If such a symptom appears infrequently and is not associated with food intake, it can be assumed that the lump in the throat is caused by mental characteristics, in particular, a tendency to hysteria. With nervous tension associated with anxiety, excitement, or stress, a sensation of a lump appears closer to the pharynx in the area of the esophagus, which is usually called “hysterical”.
After a short period of time, everything usually goes away without any drug intervention or complications. Subsequently, in such cases, you can do several breathing exercises, massage the collar area, and take a mild sedative. Even a simple change of environment will help get rid of this symptom.
A lump in the esophagus may also be psychogenic in nature
From a physiological point of view, this reaction of the body is explained by the fact that during stress the body needs a large amount of oxygen. In this case, the glottis becomes so wide that it cannot be completely covered by the epiglottis. As a result, it is impossible to utter a word, swallow tears, or take a breath.
If the feeling of a coma in the esophagus is accompanied by panic attacks and mood swings, it is necessary to take sedatives, antidepressants, and consult a psychotherapist. The prerogative of a neurologist will be to treat a lump in the throat if it is accompanied by:
- Dizziness
- Nausea
- Apathy
- Increased sensitivity to weather fluctuations.
In this case, we are talking about vegetative-vascular dystonia, which has recently become the scourge of the modern city dweller. Dysfunction of the nervous system manifests itself in this way. If someone in the esophagus experiences pain between the ribs, which intensifies with exercise, as well as with inhalation and exhalation, we may be talking about intercostal neuralgia - inflammation of the nerve responsible for the innervation of the chest.
Symptomatic therapy
Episodic heartburn in the throat is often associated with dietary errors, so to relieve it, it is important to properly adjust the diet. To reduce discomfort, it is recommended to radically limit the intake of salty and spicy foods, smoked foods, strong tea and coffee. You need to eat 4-5 times a day in small portions, chewing food thoroughly. In many patients, symptoms completely disappear after quitting smoking and reducing the amount of alcohol consumed.
To reduce the frequency and duration of heartburn episodes, it is advisable to avoid wearing tight belts, corsets and fanny packs. Sleeping on a high pillow can help reduce the likelihood of attacks at night. If a burning sensation in the throat is observed constantly and does not disappear after correcting food habits, this indicates a gastrointestinal disease. Before a clinical diagnosis is established, antacids, proton pump inhibitors, and prokinetics can be used to relieve symptoms.
Thyroid problems and esophageal conditions
Pathologies of the thyroid gland associated with its increased or decreased function (hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism) can cause a feeling of a lump in the esophagus. If, at the same time as this symptom, you experience irritability, a feeling of chilliness, or, conversely, constant sweating, dry and brittle nails, hair, and memory impairment, you may need to consult an endocrinologist. Causes of thyroid dysfunction:
- Hormonal changes in the body.
- Iodine deficiency in food and drinking water.
- Metabolic disorders.
To clarify the diagnosis, you will have to do an ultrasound of the thyroid gland and donate blood for the presence of its hormones.
Diagnostics
There is considerable controversy regarding the appropriate way to diagnose LPR.
Most patients are diagnosed clinically, based on symptoms associated with LPR.
During laryngoscopy (examination of the larynx), swelling and hyperemia (redness) of varying degrees are noted. However, the relatively weak correlation between symptoms and endoscopic findings argues against the use of endoscopic diagnostic methods.
The Reflux Symptom Score and Reflux Symptom Index are well suited for both diagnosis and monitoring response to therapy.
Daily Ph-metry with a dual sensor probe, despite its excellent sensitivity and specificity, is questioned, since the results of this diagnostic method often do not correlate with the severity of symptoms.
Another diagnostic option may be empirical PPI therapy.
Lump in the esophagus as a symptom of digestive system disease
Most often, a lump in the esophagus is a gastrointestinal problem
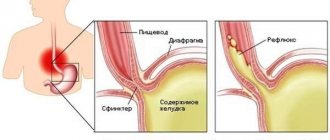
This reason for the appearance of a coma in the esophagus is the most common among other pathological conditions. Problems with the muscle sphincter that separates the esophagus from the stomach can cause stomach contents to back up into the esophagus. The acidic environment of gastric juice, which contains half-digested food, is irritating to the walls of the esophagus, which is not adapted to such contents.
This pathology is called a symptom of reflux exophagitis, it is accompanied by heartburn, and if repeated frequently, it can lead to the development of a malignant tumor of the esophagus. To clarify the diagnosis, a gastroscopy and consultation with a gastroenterologist will be required. If the treatment prescribed to them does not lead to positive results, it is possible to perform surgery on the muscle sphincter.
A hiatal hernia can cause a lump in the esophagus. It is accompanied by heartburn, chest pain and frequent, uncontrollable hiccups. The physiological reason for this condition is displacement of the diaphragm muscles due to prolonged coughing, frequent constipation, excess weight, hereditary predisposition, and mental stress.
The hernia must be distinguished from disorders of the cardiovascular system and qualified treatment must be carried out. An untreated hernia can cause reflux esophagitis.
Survey
The diagnostic search for the appearance of sour belching is aimed at establishing the root cause of the symptom. Patients undergo a comprehensive laboratory and instrumental examination of the digestive system, which is necessary to study the morphological state and functionality of the gastrointestinal tract. The most informative diagnostic methods are the following:
- Endoscopic examination
. To assess the condition of the upper gastrointestinal tract, gastroscopy (EGD) is performed. The study examines the mucous membrane of the esophagus and stomach in order to look for signs of inflammatory diseases or ulcerative destructive lesions. If suspicious formations are detected, endoscopic tissue biopsy and histological examination of the material can be performed. - Intragastric pH-metry
. The study is carried out to study in detail the acid-producing function of the organ. pH measurements during the day are carried out to study all phases of gastric secretion and assess the condition of the exocrine cells of the organ. If reflux esophagitis is suspected, intraesophageal pH measurement is prescribed. Additionally, a blood test for gastrin levels is indicated. - X-ray methods
. Contrast radiography allows you to assess the condition of all parts of the digestive tract. A series of x-rays are taken at regular intervals to study the rate of gastric emptying and the function of the esophageal sphincters. The method is highly informative in diagnosing diaphragmatic hernia. - Ultrasonography
. Ultrasound is used as a screening examination, which makes it possible to quickly identify gastroenterological pathology without the use of invasive procedures. The method helps to detect inflammatory changes, space-occupying formations, and deformation of the walls of the gastrointestinal tract. Sonography does not require preparation and is prescribed for express diagnostics.
Manometry is performed to assess cardiac sphincter contractility and upper gastrointestinal motor function. Laboratory research methods are used to diagnose Helicobacter pylori infection. Diseases that cause acid belching are often accompanied by changes in stool, so it is advisable to perform a coprogram and bacteriological analysis of stool. The patient is examined by a gastroenterologist; if organic prerequisites for erection are excluded, consultations with other specialists are necessary.
The diet for sour belching is based on the exclusion of hot, spicy, salty foods
Osteochondrosis and discomfort in the esophagus
Lump in the esophagus due to a problem with the thyroid gland
The not entirely clear connection between a spinal pathology such as cervical osteochondrosis and a lump in the esophagus can be explained by the fact that compression of the nerve roots by overgrown osteophytes on the vertebrae can occur throughout the entire periphery of the human body. The cervical spine bears a considerable load; it is one of the most vulnerable due to the constant mobility of its vertebrae.
Lack of physical activity with a sedentary lifestyle, spending a long time in static positions, exceeding the optimal body weight can lead to the fact that osteochondrosis manifests itself even in adolescence. The nerve endings of the cervical spine, damaged by osteochondrosis, cannot fully innervate the chest area, which leads to the sensation of a lump in the esophagus.
This pathology is accompanied by headaches, limitation of movements and pain when turning the head, moving the arms, or bending the neck. A neurologist or vertebrologist will help establish the correct diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Chest trauma and esophagus
When a coma appears in the esophagus, a cause such as chest injury cannot be ruled out. This could be a bruised sternum, fracture or cracked rib. Soft tissues suffer during a fracture, their trophism is disrupted, and swelling appears, which is positioned as a lump in the esophagus. In case of a chest contusion, a dangerous complication may initially be unnoticed internal bleeding.
If the feeling of a coma in the esophagus is accompanied by a symptom such as the appearance of bruises under the skin or a deterioration in the general condition, it is necessary to urgently consult a traumatologist and call an emergency ambulance.
A lump in the esophagus can be a symptom of a variety of diseases and conditions, both dangerous and those that do not require significant medical care. Only a doctor can correctly assess the condition, prescribe examination and treatment, and you should contact him if these sensations appear.