Gastroenterologist
Belousov
Evgeniy Leonidovich
20 years of experience
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Member of the Russian Gastroenterological Association.
Make an appointment Many patients experiencing problems with the gastrointestinal tract are interested in what a stomach ulcer is, what are the first signs of a stomach ulcer, and what triggers the onset of the disease. A gastric ulcer should be understood as a pathology of the gastrointestinal tract; ulcers appear on the walls of the stomach due to various reasons.
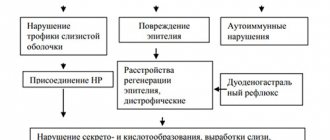
This pathological process is characterized by complex changes and painful sensations in the patient’s body, which are provoked by a local ulcer. Such processes occur in the stomach and duodenum due to reasons that we will analyze further, consider the development of stomach ulcers and methods of treating the disease.
General information about stomach ulcers
Almost every person has experienced stomach pain due to irregular nutrition.
But with frequent painful sensations in the human stomach, patients are recommended to undergo examinations and tests, because such signals may be the first indicators of the development of a stomach ulcer. You should pay attention to the manifestations of signs of gastrointestinal diseases, because failure to consult a doctor in a timely manner can cause irreversible changes, which will require surgical intervention. If you suspect a stomach ulcer, it is recommended to immediately undergo diagnostics and examination by an experienced doctor, who will identify the causes and manifestations and prescribe appropriate effective treatment depending on the stage and specifics of the stomach ulcer.
In the first stages, the symptoms and manifestations are not too pronounced; it is for this reason that the transition of the disease to an acute advanced form can be missed. The danger of stomach ulcers lies in the fact that the mucous membrane, muscles, and the entire depth of the stomach wall are affected, which is why ulcers require timely detection and treatment. The signs become clear starting from the second stage of the disease.
Risk factors include neglecting hygiene rules before eating, eating from dirty dishes, and eating stale food. It is recommended to take full responsibility for the freshness of products and personal hygiene in order to avoid pathological processes in the gastrointestinal tract.
Symptoms of stomach ulcer
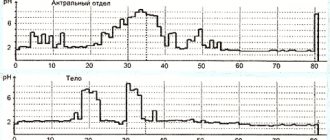
The clinical course of gastric ulcer is characterized by periods of remission and exacerbation. Exacerbation of peptic ulcer is characterized by the appearance and increase of pain in the epigastric region and under the xiphoid process of the sternum. With an ulcer of the body of the stomach, the pain is localized to the left of the center line of the body; in the presence of ulceration of the pyloric region - on the right. Pain may radiate to the left half of the chest, shoulder blade, lower back, and spine. Gastric ulcer is characterized by the onset of pain immediately after eating with increasing intensity within 30-60 minutes after eating; pylorus ulcer can lead to the development of night, hunger and late pain (3-4 hours after eating). The pain syndrome is relieved by applying a heating pad to the stomach area, taking antacids, antispasmodics, proton pump inhibitors, and H2-histamine receptor blockers.
In addition to the pain syndrome, ulcerative gastrointestinal tract is characterized by a coated tongue, bad breath, and dyspeptic symptoms - nausea, vomiting, heartburn, increased flatulence, and stool instability. Vomiting mainly occurs at the height of stomach pain and brings relief. Some patients tend to induce vomiting to improve their condition, which leads to progression of the disease and complications.
Atypical forms of gastric ulcer can manifest as pain in the right iliac region (appendicular type), in the heart (cardiac type), and in the lower back (radiculitis pain). In exceptional cases, pain syndrome with gastric ulcer may be completely absent, then the first sign of the disease is bleeding, perforation or cicatricial stenosis of the stomach, for which reason the patient seeks medical help.
Symptoms and causes of the disease
The main causes of the development of stomach ulcers can be:
- pathological inflammatory processes in the gastrointestinal tract;
- Among the common causes of the disease is an increased level of gastric acidity;
- the cause is constant alcoholism and drinking alcoholic beverages of different strengths;
- the reason may be chronic stress and depression;
- decreased immunity;
- Causes of ulcers can also occur under the influence of the pathogenic microorganism Helicobacter. Helicobacter multiplies in the acidic substance of the stomach, possessing some protective factors;
- Negative factors also include heredity, improper and irregular nutrition;
- the disease occurs as a result of consuming low-quality products, smoking, and taking certain medications with significant side effects for the gastrointestinal tract.
To establish the cause of stomach ulcers, it is also necessary to check the patient for concomitant diseases, such as diabetes, syphilis, pancreatitis, gastritis, tuberculosis, Crohn's disease, and cirrhosis of the liver.
Clinical manifestations of diseases of the stomach and duodenum are usually pronounced. The severity of symptoms is determined by the stage - remission or exacerbation. The symptoms manifest themselves most clearly during the period of exacerbation of ulcerative pathology, which is characterized by pronounced manifestations of signs of a stomach ulcer; they can be determined by a doctor during examination and during diagnosis using modern methods.
The main symptoms are:
- painful sensations in the epigastric zone of varying intensity - periodic or worsening. If you experience regular pain, you should check with a qualified doctor;
- a common symptom is hunger pain, which decreases after eating;
- The nature of the pain is different - from aching to sharp cutting. Depending on this symptom, drug treatment is prescribed to reduce pain and spasms;
- heartburn or rotten belching, which depends on the level of stomach acidity. Such symptoms are more often observed with increased acidity;
- Frequent symptoms include stool disorders - constipation with high acidity or diarrhea with low acidity;
- signs of an ulcer also include nausea, bloating;
- rumbling in the stomach, since the underlying parts of the gastrointestinal tract are susceptible to pathology.
Having noticed these signs in a timely manner, you must immediately consult a doctor at the hospital to make a diagnosis and prescribe an appropriate treatment regimen. If there is no response to the signs, the disease occurs with certain complications:
- perforation of the stomach, that is, the occurrence of a through defect connecting the lumen of the stomach with the peritoneal area;
- penetration or defect in the gastric mucosa, which is closed by a nearby organ (omentum or pancreas);
- bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract - special attention must be paid to this sign, it requires immediate hospitalization and, without taking action, leads to death;
- malignant oncological formation in the area of the ulcer.
Are you experiencing symptoms of a stomach ulcer?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
Prognosis and prevention
The prognosis for gastric ulcer largely depends on the timeliness of seeking medical help and the effectiveness of anti-Helicobacter therapy. Peptic ulcer is complicated by gastric bleeding in every fifth patient, from 5 to 15% of patients suffer perforation or penetration of the ulcer, and 2% develop cicatricial stenosis of the stomach. In children, the incidence of complications of gastric ulcer is lower - no more than 4%. The likelihood of developing stomach cancer in patients with peptic ulcer is 3-6 times higher than among people who do not suffer from this pathology.
Primary prevention of gastric ulcer includes preventing infection with Helicobacter pylori infection, eliminating risk factors for the development of this pathology (smoking, cramped living conditions, low standard of living). Secondary prevention is aimed at preventing relapses and includes following a diet, avoiding stress, and prescribing an anti-Helicobacter drug regimen when the first symptoms of peptic ulcer appear. Patients with gastric ulcer require lifelong monitoring, endoscopic examination with mandatory testing for H. pylori once every six months. Source: https://www.krasotaimedicina.ru/diseases/zabolevanija_gastroenterologia/stomach-ulcer
Diagnosis of ulcers: features and procedures
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out by an experienced gastroenterologist, who can determine an accurate diagnosis after examination, history taking and diagnostics using hardware methods.
The gastroenterologist analyzes the patient’s medical history and complaints, family history, and also carries out a number of diagnostic measures. An ulcer is diagnosed using a general blood and urine test, the acidity of gastric juice is examined, and diagnostics is carried out using esophagogastroduodenoscopy. If internal bleeding is suspected and for an accurate diagnosis, a stool test for occult blood is collected. The main goal of the doctor in diagnosis is to confirm the ulcerative defect in the stomach wall and the presence of Helicobacter in the patient. The disease is diagnosed in the following ways:
- X-ray method using barium suspension;
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy visualization of the gastric mucosa using a special magnifying device;
- urease method - based on the detection of urease in exhaled air, which occurs as a result of the proliferation of Helicobacter in the stomach;
- PCR diagnostics – determines the nucleic acid complexes that characterize Helicobacter;
- serological methods for diagnosing the disease, involving the determination of immunoglobulins to Helicobacter;
- specialized tests performed during fibrogastroduodenoscopy.
At the same time, examinations are performed to ensure the possibility of excluding the development of pathological complications. Ultrasound examinations of the peritoneal organs and X-ray contrast examination using barium are performed, which makes it possible to determine the size of the ulcer.
Methods for examining a perforated ulcer
The method for diagnosing a perforated ulcer is endoscopy.
A distinctive feature of perforation is attacks of sharp, unexpected pain. Only when diagnosing a history of peptic ulcer, gastritis, etc., does the task become easier.
Basically, when studying ulcers, the differential method is used. Its essence is an examination of the body with future consideration of the presence/absence of such deviations:
- Acute appendix;
- Acute form of cholecystitis;
- Perforation of various tumors;
- Colic in the liver;
- Developing pancreatitis;
- Forms of thrombosis;
- Abdominal aortic aneurysm that dissects;
- Myocardial infarction;
- Lower lobe pneumonia.
In parallel, the following research methods are used:
- X-ray. The effectiveness of the study of abdominal air filling is at least 80%. However, a similar situation is observed with airiness of the intestinal cavity or tubal atony;
- Electrogastroenterographic. This is a method that provides the highest quality diagnosis of the evacuation capacity of the stomach;
- Endoscopy. Used in case of negative results of X-ray diagnostics and small perforation characteristics. Determines the presence of an ulcer and the location of the source. The analysis is carried out by pumping air, which makes it possible to see the true pathological picture;
- A general blood test indicates only quantitative indicators of leukocyte content;
- Laparoscopy. Improves the quality of analysis of abdominal effusion. Has contraindications for use.
Doctors treating the disease
A stomach ulcer requires a qualified, comprehensive approach, so treatment must be carried out in a specialized clinic, where, using modern equipment, research is carried out and a clear diagnosis is established.
For patients who are interested in the question of which doctor treats gastric dysfunction, the answer is clear - this is a gastroenterologist. A specialist conducts examinations and, based on them, prescribes effective treatment methods and surgical intervention for advanced stages of the ulcer. Patients who are disillusioned with general practitioners should contact a gastroenterologist with such a disease, who treats the immediate cause of the disease and helps to overcome the disease without serious consequences for the whole body. A qualified gastroenterologist, based on medical history, causes and symptoms, will determine the nature of the pathology and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Among the many clinics in Moscow where ulcers are diagnosed, one of the leaders is JSC Meditsina. To undergo examination, diagnosis and take appropriate tests, you need to register with a clinic, where you can choose an experienced doctor who will help you effectively and quickly cure the ulcer.
The clinic offers research using modern equipment that allows for color mapping, 3D modeling of tissues and blood vessels, which can be used to examine ulcers and changes in the stomach and gastrointestinal tract in detail, make an accurate diagnosis, and prescribe an effective treatment method. Thanks to high-precision color images, the doctor gets a clear picture of the ulcer.
Doctors at Dr. Roitberg's clinic with many years of experience help overcome the underlying causes, symptoms and manifestations of ulcers, and completely get rid of painful sensations, regardless of how painful the gastrointestinal tract organs are and how the disease progresses.
Complications
Peptic ulcers and symptomatic ulcers of the stomach or duodenum carry a hidden danger due to the tendency to develop complications, which are often life-threatening for the patient. Among them are the following conditions:
- bleeding;
- perforation (formation of a through defect) of the organ wall;
- penetration of the ulcer (its spread to nearby organs);
- malignant degeneration of cells of the mucous membrane and underlying tissues of the stomach;
- cicatricial stenosis with narrowing or closing of the lumen of part of the organ.
Treatment methods
Therapy for the disease should include comprehensive measures.
For the most effective treatment, after diagnosis, the doctor uses antibacterial medications, antispasmodics, prokinetics, medications to stabilize stomach acidity, and the patient is prescribed dietary nutrition if there are problems with the gastrointestinal tract. During the medical treatment of peptic ulcers, antibacterial drugs are used - Metronidazole, Furazolidone; medications that regulate acidity - Kvamatel, Omeprazole. In the absence of complications, treatment of ulcerative pathology is carried out conservatively. Surgical treatment methods and gastroscopy are indicated for certain complications, for example, perforation, bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract and other irreversible pathological or inflammatory processes. Also, medications and treatment methods are prescribed based on the stage of scarring of the walls.
Conservative therapy to combat ulcers takes a leading place and has two main goals:
- cause the death of Helicobacter;
- reduce the acidity of gastric juice to a stable level.
Three-component or four-component regimens can be used, depending on the severity of the inflammatory process.
In parallel, physiotherapy can be carried out (electrophoresis of drugs on the epigastric zone). Therapy mainly includes medication and proper nutrition. Surgery is indicated only for complications. Drug therapy for ulcers involves the prescription of antibacterial agents that help remove bacteria from the body. Treatment is carried out in stages:
- stage one - inhibitors or agents to normalize acidity and reduce the release of hydrochloric acid, are used together with antibacterial drugs based on clarithromycin, from the category of semi-synthetic penicillins. Taking medications lasts an average of a week. The dose and type of medications are prescribed by the doctor solely on the basis of an in-depth examination. If the patient is unresponsive to inhibitors, similar histamine H2 receptor blockers are prescribed. Already at this stage, 90% of patients experience complete elimination of bacteria;
- stage two is required if standard treatment does not bring results. Similar inhibitors are used with antibacterial agents from the group of nitroimidazoles and tetracyclines, and gastroprotectors are introduced. The drugs create a film on the walls of the stomach, which reduces pain, relieves inflammation, increases the resistance of the mucous membrane to negative influences, and restores the protection of the stomach. The duration of the treatment phase is a week or more.
During treatment, the doctor also prescribes concomitant medications aimed at alleviating symptoms: vitamins and medications that protect the mucous membrane from the effects of gastric juice, sedative medications (valerian), antispasmodics to reduce pain, probiotics that help stabilize the normal microflora of the gastrointestinal tract, since it suffers due to taking antibiotics.
An important element of the treatment regimen is the correct diet. You need to eat little and often, 5-6 times a day, without overeating. It is necessary that foods do not require prolonged chewing, since this activates the production of juice in the stomach. For stomach ulcers, it is better to eat purees, soufflés, omelettes, porridges and jelly, cutlets and meatballs, and casseroles.
Based on the stage and characteristics of the disease, the following diets are used:
- Table 1A – for exacerbations of pathology. The diet includes soups in the form of pureed cereals, steam soufflé, soft-boiled eggs, milk porridge, jelly, steamed fish;
- Table 1 – prescribed after exacerbations. Meals include white bread and crackers, vegetable and cereal puree soups, boiled lean meat, steamed fish, cottage cheese casseroles, ground porridge, omelettes, boiled vegetables, and lightly brewed tea. Prohibited are rye bread, meat with fat and streaks, rich broths, spicy and fried foods, marinades, fermented milk products, coffee;
- table 5 – used for remission. Allowed are milk, cottage cheese and low-fat sour cream, steamed cutlets, omelettes and soufflés, boiled and stewed fish, steamed cutlets, crackers and bran bread, and individual vegetables. You should not consume coffee and strong tea, sauces and spices, fatty and fried foods, sour fruits, fresh bread and confectionery, and smoked foods.
Indications for stomach ulcers
Timely treatment ensures effective relief from the disease. Main indications for the treatment of ulcers:
- stop drinking alcohol, eat regularly and properly, exclude fried, fatty, spicy and salty foods;
- prevention of Helicobacter infection - for this it is recommended to follow standard recommendations;
- follow hygiene rules (wash hands before eating);
- wash food before eating;
- use fresh food and throw away spoiled food;
- Wash the dishes well, rinse off any remaining detergent.
Lifestyle in the presence of an ulcer is mainly determined by proper dietary nutrition, which is based on the following provisions:
- frequent and small meals (up to 5-6 times a day), while overeating must be avoided;
- eat enveloping foods, such as oatmeal;
- limit the use of extractive substances;
- give up animal fats;
- eat the portion of foods prescribed by your doctor or nutritionist that contain polyunsaturated fatty acids, which promote rapid healing of ulcers in the stomach and duodenum.
Cost of initial appointment, research, treatment
Prices for medical treatment are shown on the website for patients’ information.
To clarify the current cost of treatment, you need to make an initial consultation with a gastroenterologist, at which the doctor will conduct diagnostic measures and examination, identify the features of the pathology, and prescribe treatment with modern techniques and medications. The price of treatment directly depends on diagnostic measures and therapy, but in each specific case of gastric ulcer the most effective drugs are prescribed depending on the symptoms and stage of the disease. In advanced stages, it is necessary to treat the ulcer with the help of surgical interventions, followed by a hospital stay in the clinic to resolve the worsened manifestations and complications. The clinic offers innovative technologies, detailed analysis and comfortable living conditions.
Classification
Until today, scientists and clinicians around the world have not been able to reach agreement on the classification of gastric ulcers. Domestic experts systematize this pathology according to the following criteria:
- causative factor
– ulcers associated or not associated with H. pylori, symptomatic ulcers; - localization
- ulcer of the cardia, antrum or body of the stomach, pylorus; greater or lesser curvature, anterior, posterior wall of the stomach; - number of defects
- single ulcer or multiple ulcers; - size of the defect
– small ulcer (up to 5 mm), medium (up to 20 mm), large (up to 30 mm), giant (more than 30 mm); - stage of the disease
- exacerbation, remission, scarring (red or white scar), cicatricial deformation of the stomach; - course of the disease
- acute (the diagnosis of gastric ulcer is established for the first time), chronic (periodic exacerbations and remissions are noted); - complications
- gastric bleeding, perforated gastric ulcer, penetration, cicatricial ulcerative gastric stenosis.
Advantages of treatment at the clinic of JSC "Medicine"
JSC "Medicine" (clinic of academician Roitberg) is a multidisciplinary medical center that provides a range of services, including surgery and hospital stays.
Treatment at the clinic of JSC "Medicine" has the following advantages:
- license to carry out medical activities, receive patients, perform operations;
- each doctor has appropriate qualifications and significant experience in domestic and foreign clinics, and their achievements are posted on the medical center’s website;
- high-tech innovative equipment for conducting tests and examinations to establish the true causes of pathological conditions of the gastrointestinal tract;
- cooperation with insurance companies, profitable loyalty programs for corporate clients.
Doctors conduct a thorough and in-depth analysis of the patient’s health status, identify the underlying causes that led to the occurrence of stomach ulcers, and prescribe effective therapy on an outpatient or inpatient basis.
Systematization of perforated ulcers
Stomach ulcers can progress quickly.
Regarding the clinical course of the disease:
- Typical form. It is characterized by the leakage of stomach contents into the abdominal cavity;
- Atypical shape. Contents from the abdominal cavity are directed into the omentum or omental “bag”. Even the process of leakage into the retroperitoneal tissue and adhesive zone is possible;
- Perforation that bleeds into the gastrointestinal tract.
Regarding the stages of development of peritonitis:
- Phase of normal pain shock;
- The stage at which bacterial peritonitis develops. This is the phase of contamination of microorganisms;
- The onset of inflammation, accompanied by mild pain and imaginary relief;
- The most severe phase of the disease is the development of purulent peritonitis.
For pathological signs: