Diffuse changes in the liver and pancreas indicate an increase in tissue, but this does not always mean the development of some kind of pathology. A feature of the gastrointestinal tract is that the organs are connected to each other by ducts, which is why when a disease develops in one part of the digestive tract, nearby systems suffer.
With timely contact with a specialist, in ninety percent of cases it is possible to restore the functioning of organs. Diffuse changes in the parenchyma of the liver and pancreas can cause both minor deviations and complex dysfunctions. Pathology can appear at absolutely any age, even in infancy.
In infants, such changes may be associated with congenital anomalies. At older ages, disruption of tissue structure is often associated with hepatitis A and poisoning. Disturbances in the structure of the digestive organs are widespread in our time, but what are the causes of this phenomenon, how does it manifest itself and is it possible to fight it? In this article we will take a closer look at the answers to all these questions.
What are diffuse organ changes?
When undergoing a routine ultrasound examination of the peritoneal organs, a conclusion such as “diffuse changes in the parenchyma of the liver and pancreas” is possible. It turns out that this condition means an increase in the size of the organ parenchyma
– its main functioning part, as well as changes in its echogenicity (type of echo signals). This condition is not a disease in itself, but is considered an ultrasound sign of various pathologies, and therefore serves as important information for making a diagnosis.
Changes in the structure of the digestive organs can be observed at any age. They are often detected even in young children: for example, with a history of acute respiratory viral infection or allergies
the pancreas reacts by compacting the structure. Disturbances in liver tissue are more common in adults and older people, although they are sometimes present in children.
Changes in the parenchyma can be different in degree - moderate, pronounced, insignificant
. They can also be hypertrophic and sclerotic, dystrophic and swelling - the ultrasound doctor will indicate detailed data in the examination report.
Principles of pathology therapy
To eliminate the diffusion process, three significant factors must be taken into account: the origin of the disease, pathogenesis and the degree of damage.
The doctor develops an individual treatment regimen for each patient.
To cure a diffusely heterogeneous process, certain conditions must be met.
These mandatory conditions are:
- follow a special diet;
- avoid drinking alcohol;
- stick to the daily routine;
- treat concomitant gastrointestinal pathologies.
The diet excludes the consumption of salty and spicy foods. Normally, a person should consume at least 5 grams of salt per day. You should also forget about spices, flour products, fatty and fried foods. The diet should be enriched with fresh fruits and vegetables, cereals, liquid meals, low-fat dairy products, lean meat and fish.
There is no talk of drinking alcohol or smoking. These two bad habits only aggravate the diffusely heterogeneous process of damage to the liver and pancreas. A daily routine means that a person with such a diagnosis needs to properly distribute his time for work and rest. Adequate sleep is important.
Drug therapy is aimed at stabilizing the function of the digestive tract. It is very important to normalize the beneficial microflora of the small and large intestines. The doctor prescribes antibacterial and enzyme agents, which the patient takes for 3-4 weeks.
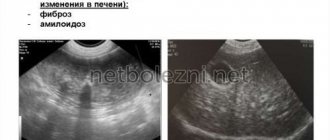
To reduce the muscle tone of the diseased organ, antispasmodics are prescribed to improve the flow of enzyme juice into the intestines. If diffuse changes develop against the background of fibrosis, anti-inflammatory treatment will be relevant.
Causes of changes in the pancreas
A change in the structure of the pancreas may have natural causes - the organ changes echogenicity as the body ages. Disturbances in the structure of the gland can also indicate a variety of phenomena:
- circulatory disorders;
- infectious diseases;
- metabolic problems;
- intoxication;
- chronic diseases.
Echogenicity
allows you to evaluate the density of the organ - normally it is homogeneous. Thus, an increase in the indicator is characteristic of an inflammatory process with edema. Pancreatitis in any form causes an increase in echogenicity, so ultrasound alone can suggest a diagnosis. Below are the main problems of the pancreas, which are expressed by diffuse changes in the parenchyma.
| Disease | Echo signs by ultrasound |
| Diabetes | Lipomatosis (replacement of normal tissue with fat cells), diffuse compaction, reduction in the size of the gland, sclerosis, dystrophy. |
| Chronic pancreatitis | Dilation of the Wirsung duct, tuberosity of the contours of the organ, decreased echogenicity, increased size of the gland. |
| Acute pancreatitis | Increased size, increased echogenicity, unclear contours, the presence of cysts, and sometimes an abscess. |
| Cancer | Identification of a cavity or lesion with heterogeneous density. |
Small changes in the gland can appear due to poor nutrition, alcohol abuse, obesity, smoking, after infections and poisoning, and with cardiovascular diseases.
Causes of changes in the liver
Liver tissue normally has low density
, homogeneous structure. If there are diffuse changes, then the density of blood vessels, tissues and bile ducts increases. This can be due to both serious pathologies and functional, temporary disorders.
In children, reactive changes in the structure of the organ most often occur, for example, due to the use of antibiotics or poisoning. Also, newborns may have problems with the organ due to its underdevelopment, structural abnormalities, or the mother taking toxic drugs in the last stages of pregnancy.
The causes of disturbances in the structure of the organ parenchyma are:
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- chronic hepatitis;
- acute hepatitis (jaundice);
- fatty hepatosis;
- liver tumors;
- cystic formations, organ fibrosis.
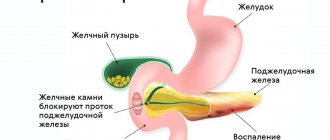
Often diffuse changes accompany hepatomegaly (pathological enlargement of the liver), as well as hepatosplenomegaly (enlargement of the liver and spleen). Such conditions are typical for poisoning, severe intoxication, and also appear in acute cholecystitis and bile duct obstruction.
Uncontrolled drinking of alcohol and consumption of spicy, fatty foods in the future almost always leads to diffuse changes in the structure of the liver.
Diseases not related to the liver can also cause liver changes:
- diabetes;
- viral infections;
- gastritis;
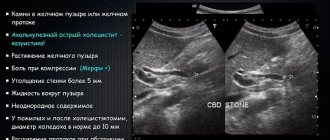
- cholelithiasis.
Liver
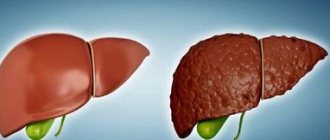
Structural changes in the liver parenchyma are not a disease, but only a symptom indicating the presence of a developing pathology. In order to determine what exactly caused such changes, it is necessary to undergo a thorough examination. People of all ages are susceptible to the pathological process.
Bad habits, poor diet, poor environment - these are not all the reasons that negatively affect the condition of the liver. Changes in the parenchyma can cause autoimmune processes, alcohol abuse, irrational use of medications, sudden changes in weight and much more.
In the initial stages, the patient experiences nausea and mild pain in the area of the right hypochondrium, but usually few people pay attention to this. More often, diffuse changes are already detected during ultrasound. Additionally, a CT scan, x-ray, or blood test may be required.
Fatty hepatosis
Normally, liver tissue has a homogeneous structure. The development of this disease is based on the accumulation of large amounts of lipids and a decrease in functional activity. Dystrophy often develops against the background of diabetes, obesity and metabolic disorders. Fatty hepatosis manifests itself in the form of the following symptoms:
- liver enlargement;
- change in shape;
- the organ has a rough and dense structure;
- distinct vein pattern.
Patients complain of nausea, vomiting and heaviness in the right hypochondrium
Experts distinguish three main stages in the development of fatty degeneration:
- Manifests itself in the form of fluctuations in liver enzymes. This stage is characterized by a sluggish inflammatory process.
- At this stage, clinical symptoms increase. Patients complain of discomfort in the abdomen on the right side; upon examination, there is a noticeable increase in the size of the liver.
- This stage is characterized by constant nausea, bloating and pain in the right side, constipation, flatulence, and impaired digestion of food.
A gastroenterologist deals with the diagnosis and treatment of fatty degeneration. You can reduce the level of fat in the liver by normalizing your lifestyle and correcting your diet. A treatment table with a high protein content and limited animal fats is prescribed.
The diet should increase the consumption of cereals, cottage cheese, and rice. These products help dissolve fats in the liver. Don’t forget about foods that have a choleretic effect: carrots, pumpkin, white cabbage. In order to eliminate the cause of liver cell destruction, it is necessary to approach the problem comprehensively. You can't get by with just medications.
Dietary nutrition will have to be followed for several months. If the patient continues to drink alcohol and abuse fatty and fried foods, the treatment will be unsuccessful. You can restore liver function with the help of hepatoprotectors. Patients are also prescribed dietary supplements. With normalization of blood pressure and timely treatment, the prognosis for hepatosis is favorable.
The first results of treatment can be seen in about a month. The liver will be able to fully recover only after several months.
Echo signs of diffuse liver changes
Cirrhosis
Violation of the tissue structure occurs due to the proliferation of connective tissue. As a result, functional failure of the organ develops. A number of reasons can serve as an impetus for the development of cirrhosis:
How to detect cirrhosis of the liver?
- viral hepatitis;
- alcoholism;
- intoxication;
- long-term use of medications;
- hereditary diseases;
- congestion;
- damage to the bile ducts.
As pathological changes develop, patients begin to complain of weakness, increased fatigue, loss of strength, and loss of appetite. Dyspeptic disorders also appear in the form of bitterness in the mouth, nausea, vomiting, belching, intolerance to fatty foods and alcohol.
With diffuse changes in the liver such as cirrhosis, spider veins appear
Among the signs of cirrhosis, the following symptoms are of diagnostic importance:
- redness of the palms;
- the appearance of vascular networks mainly in the upper half of the body;
- hemorrhages under the skin;
- bleeding of mucous membranes;
- skin itching;
- weakness, irritability;
- sleep disturbance;
- painful sensations in the joints;
- decreased libido;
- baldness in the pubic and armpit areas.
Patients with this diagnosis are strictly limited in mental and physical activity. If the patient feels well, he is allowed to walk and do therapeutic exercises.
Symptoms of disorders in internal organs
Symptoms are not determined by identified abnormalities in the structure of organs, but by the diseases that provoked them. If the changes are moderate, then the clinical picture may be completely absent, and the problem is detected by chance, during an ultrasound examination. Internal organs can “tolerate” unfavorable conditions for a long time, although minor signs are still noticeable.
Enlarged liver
with a dense structure it is easy to detect under the ribs on the right side by palpation.
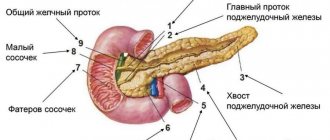
Normally, the organ does not protrude from under the edge of the costal arch and is not painful. The pancreas
is quite difficult to palpate, but it causes pain when palpating the upper abdomen.
Symptoms of organ diseases may be:
- heartburn;
- bad odor in the mouth;
- vomit;
- nausea;
- itchy skin;
- pain in the center of the abdomen, in the right hypochondrium;
- headache;
- fatigue;
- bitterness in the mouth;
- discomfort after fatty foods;
- belching.
If the cause of the pathology is jaundice or cholelithiasis, the sclera of the person’s eyes turn yellow, the skin also becomes yellowish, and the stool becomes discolored.
In severe cases (for example, with cirrhosis of the liver, cancer), fluid accumulates in the peritoneum, and dropsy (ascites) occurs.
Manifestations of pathology
Basically, changes in the structure of the parenchyma do not manifest themselves in any way. In rare cases, the following symptoms may be observed: heaviness in the right side of the abdomen, pain in the liver, yellowness of the sclera. Most often, diffuse changes in the liver occur without visible signs.
Unpleasant sensations may intensify while running, exercising, driving on uneven surfaces, or eating fatty foods. The painful outbreak becomes permanent. As structural changes progress, other signs appear:
- attack of nausea;
- heartburn;
- belching bitter;
- loss of appetite;
- vomiting reflex;
- headache;
- hormonal disorders;
- skin hemorrhages;
- jaundice;
- darkening of urine;
- white color of stool;
- disruptions in the functioning of the sexual sphere;
- weakness and increased fatigue.
When a person is at rest, pain in the right hypochondrium subsides
Depending on the degree of damage, structural changes are divided into three main groups:
- minor. Most often appear with hepatitis and under the influence of negative factors;
- moderate. At this stage, lifestyle correction, a course of vitamin complexes and strengthening procedures are required;
- expressed. The formation of severe swelling is characteristic. Such changes are typical for patients with obesity, diabetes mellitus, cirrhosis, chronic hepatitis, and tumor processes.
Important! The diagnosis is made by a doctor after the results of an ultrasound examination.
Diagnosis of diseases of internal organs
Diagnostic measures after identifying changes in the parenchymal digestive organs by ultrasound do not end
. The fact is that a similar ultrasound picture can correspond to different diseases, as well as their unequal severity. Also, additional examinations will help to identify the function of the organ and discover the cause of the changes that have occurred.
After collecting anamnesis, the therapist, hepatologist or gastroenterologist gives a referral for a number of studies
:
- general blood test
- to determine blood sugar, identify the inflammatory process; - blood biochemistry
- to evaluate lipids, bilirubin, AST, ALT, cholesterol, albumin, amylase, etc.; - coprogram
- for analyzing digestive function; - repeat ultrasound
– to assess the condition of organs over time; - MRI or CT
– to clarify the type, extent and form of the disease; - Liver biopsy
– indicated for cirrhosis, hepatitis, cancer.
Diagnostic measures
To be referred for examination, you must first contact a general practitioner or gastroenterologist. The doctor will ask about signs of concern, conduct an external examination and draw up a clinical picture. Next, he will refer you for tests and hardware examination of the endocrine part of the pancreas.
A laboratory test is usually prescribed to study the concentration of biochemical substances:
- amylase in urine and blood;
- pancreatic enzymes in urine and blood;
- pancreatic elastase No. 1 in feces.
Of the hardware diagnostics, ultrasound and x-rays are primarily used.
The central task of ultrasound examination of the pancreatic organ is to identify echo signs indicating the presence of DI of the parenchyma. Ultra-fine sound waves “probe” the density and structure of the internal organ. Increased echogenic conductivity indicates that the organ is enlarged and its parenchyma is changed (replaced by connective or fatty tissues).
Characteristic echogenic manifestations help not only in determining diffuse changes, but also in diagnosing pancreatitis, diabetes mellitus, tumors, fibrosis and abscesses.
Treatment of pancreatic diseases
The detected diffuse changes in this most important organ cannot be left to chance. It is not the ultrasound signs that need to be treated, but the diagnosed disease. With reactive changes, most often it is enough to follow a healthy lifestyle, proper nutrition, and the gland tissue will return to normal in 1-6 months.
Diabetes mellitus type 2 is treated with a strict diet and taking glucose-lowering medications. If type 1 diabetes mellitus is detected, insulin injections are prescribed. Acute pancreatitis must be treated in a hospital using novocaine blockades, cooling the pancreatic area, and therapeutic fasting. The patient is also prescribed:
- antacids
to reduce gastrointestinal acidity (Almagel, Gaviscon); - proton pump inhibitors
to reduce acid production (Omez, Pantoprazole); - proteolysis inhibitors
to suppress the production of enzymes (Kontrikal, Ingitril); - antibiotics
to relieve inflammation (Amoxicillin, Suprax).
For chronic pancreatitis, the use of enzymes (Pancreatin, Mezim), painkillers, antispasmodics, and medications to relax smooth muscles is indicated.
The operation is indicated in the presence of areas of necrosis, cysts, and abscesses in the pancreas.
Treatment of changes in the liver
Liver pathologies are closely related to problems in the gallbladder, so most often treatment will be joint. Refusal of alcohol, smoking, normalization of nutrition is required
.
Viral hepatitis is treated with special antiviral agents, hepatoprotectors. The latter help restore the functioning of hepatocytes and are indicated for almost any liver pathology. The main hepatoprotectors are Essentiale, Heptral, Phosphogliv, Gepabene
.
Vitamin E, amino acid preparations, B vitamins improve the condition of the liver. Choleretic preparations (Allohol, Chofitol) will eliminate stagnation of bile in the liver, and preparations for diluting bile (Ursosan, Ursofalk) will prevent the formation of stones. The operation is indicated for large liver cysts, portal hypertension, tumors, and metastases.
Diet and folk remedies
As soon as diffuse changes are detected in the digestive organs, you need to urgently start following a diet. Therapeutic nutrition will be quite simple. It is necessary to remove soda, strong tea, any coffee, and alcohol from the menu. Smoked meats, sausages, spicy dishes, with spices, and marinades are prohibited. You also need to avoid fatty foods and salty foods. All dishes should be steamed, boiled, stewed without adding animal fats.
Traditional medicine also recommends a number of recipes to reduce changes in the liver and pancreas:
- Rinse 3 cups of oat grain with peel in water, mix with 3 tablespoons of birch buds, 2 tablespoons of mint. Pour 3 liters of boiling water over everything and leave for a day. Then cook for 20 minutes, add 2 tablespoons of knotweed herb. Cook for 10 minutes, strain. Drink 150 ml three times a day until the decoction is complete.
- Brew 2 tablespoons of rose hips (berries) and 400 ml of boiling water in a thermos, leave overnight. Drink 100 ml four times a day for 10 days.
You cannot carry out treatment on your own; even herbal medicine must be approved by the attending physician, and it must also be combined with conservative treatment.