A person’s complaints of severe pain in the left hypochondrium often indicate inflammation of the pancreas. The examination of the patient begins with an ultrasound of the abdominal organs. A diagnostic method based on measuring the intensity of reflection of sound waves from the surface of organ tissues makes it possible to identify the smallest deviations in the functioning of the digestive system.
When assessing an echogram and morphological parameters of tissues, it is difficult for a doctor to make a mistake. The images that the sonographer creates during the examination are different in color. Light colors indicate the presence of seals in the organ, dark and black colors indicate liquid formations. A healthy pancreas, due to its homogeneous watery structure, is displayed in dark colors. The opposite picture indicates pathological changes and organ disease.
If you have been diagnosed with increased echogenicity of the pancreas, then carefully study the information below.
What is echogenicity
Echogenicity is a sign system used by uzologists, which allows one to establish the correspondence of the anatomy of organs to the level of reflection and absorption of high-frequency waves. Liquid tissue of the pancreas is characterized by an average echogenicity. The echo density of the liver parenchyma is used as a standard sample.
Echogenicity scale for assessing study results
Using ultrasound, you can not only determine the degree to which internal organs perceive high-frequency waves, but also obtain information about other equally important parameters. During the examination of the gland, the following parameters are carefully studied:
- Size.
- Form.
- Structure.
- Circuit.
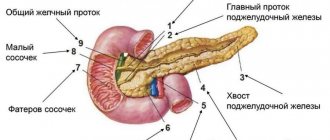
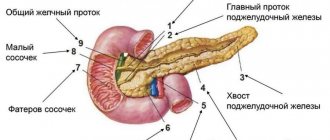
When determining the volume of the pancreas, the length of the head, body and tail is calculated. Ideally, they should not exceed 30, 24 and 25 mm, respectively.
An increase in the latter indicates local or general inflammation in the organ. Abnormally large sizes are a typical sign of pancreatitis. Causes of increased size can also be: abdominal trauma, cystic fibrosis, biliary dyskinesia, hepatitis, infectious diseases. Local changes are associated with malignant tumors and cysts.
In appearance, the digestive gland resembles a comma and has an oblong shape. Sometimes there is a thickening in the head area. Ring-shaped, additional, split forms are deviations from the norm. Improper development of the organs of the digestive system is associated with disturbances in the processes of embryogenesis.
Healthy pancreas. The dark longitudinal stripe is the hypoechoic shadow of the duct.
As for the external contours, they must be clearly defined in the longitudinal and cross sections. Blurring of any part of the gland may indicate the development of an inflammatory process. Blurred outlines and swelling also cause diseases of the organs adjacent to the pancreas (stomach and duodenal ulcers). Uneven borders are created by tumors, cysts, and stones. The contours of malignant formations are lumpy and blurry.
The structure of the digestive gland should be homogeneous and fine-grained.
Having discovered single fatty inclusions or numerous calcifications and pseudocysts in the organ, the doctor has every reason to suspect fibrolipomatosis and chronic pancreatitis in the patient.
Insufficient preparation of the person himself can lead to errors in research results. Three days before the procedure, the patient must adhere to a diet that eliminates the possibility of increased gas formation. For prevention, patients are recommended to take adsorbents. On the day of the procedure, it is advisable to empty your bowels and limit your food intake.
How is an ultrasound of the pancreas performed?
Before ultrasound diagnostics, the patient will be asked to remove clothing from the abdominal area and lie down on his back on a medical couch. The diagnostician will apply a medical gel to the area under study, which will ensure tight contact between the ultrasound scanner sensor and the surface of the skin, eliminating air inclusions. This approach allows for better visualization.
During the examination, the doctor moves the sensor along the abdomen in the area of the projection of the pancreas, turning it at different angles. From time to time he asks the patient to hold his breath after a deep breath or to flex his stomach.
Sometimes, in order to visualize certain parts of the organ, the diagnostician makes rotational movements with the sensor. This allows him to determine the size of the gland, detail its structure and the structure of surrounding tissues. On average, the procedure lasts no more than ten minutes. It does not require the use of painkillers as it is painless.
What does increased echogenicity mean?
An unusual increase in the recoil force of the waves indicates compaction of the parenchyma and a reduction in the amount of fluid in it. Diffuse hyperechogenicity, the causes of which are external factors, is not considered a pathology. Most often it manifests itself in the hot season, after eating hot and rich food, and during colds.
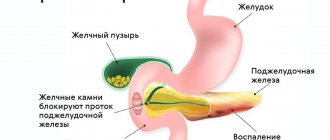
Echogenicity increases markedly with inflammation. Causes for concern may be: tumors, metastases, calcium deposits and stones, cysts, fibrosis. Such inclusions are the consequences of ignoring the early symptoms of pancreatitis.
A number of parameters indicate acute pancreatitis:
- General increase in organ size.
- Presence of large echogenic areas.
- Heterogeneity of structure.
- Exceeding the width of the gland duct.
- Blurred boundaries.
A more severe form of the disease involves changes in the density and contours of neighboring organs. Possible formation of pseudocysts.
When diagnosing chronic pancreatitis, the following picture is observed:
- Echogenicity increases slightly.
- The width of the duct increases by more than 2 mm.
- The size of the gland itself increases.
- Unclear outline.
- Heterogeneous structure.
- There is fluid in the omental bursa behind the stomach.
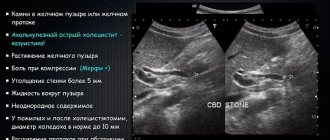
The disease may be accompanied by the formation of stones. In the picture they appear as spots with an echogenic trace. The progressive disease is easy to notice due to the significant discrepancy in the ratio of the size of the gland to the Wirsung duct. The latter is greatly swollen in width.
Parameters such as increased echogenicity and blurred contours suggest that healthy cells in the organ have replaced fat cells, which occurs with lipomatosis. Hyperechogenicity along with a decrease in the pancreas indicate the development of fibrosis. The growth of connective tissue and its replacement of normal cells is accompanied by the appearance of scars.
Ultrasound alone is not enough to accurately diagnose a patient. The patient is sent for auxiliary procedures: magnetic resonance or computed tomography, laparoscopy or biopsy.
A lighter image of the pancreas indicates increased echogenicity
Interpretation of pancreatic ultrasound results
In order to determine whether the patient has deviations, the doctor conducts a comparative analysis of the results obtained and the average parameters of the norm according to a number of criteria that allow obtaining an objective assessment. The following is considered the norm:
- Location: intraperitoneal, behind the stomach on the posterior abdominal wall in the epigastric region;
- The contours of the organ are smooth, clear, delimited from the surrounding tissues;
- Homogeneous coarse- or fine-grained echostructure;
- The diameter of the pancreatic duct is from one and a half to two and a half millimeters.
The normal sizes of the pancreas are presented in our table below:
| Parameter | Adults | Children |
| Head of the gland | from 18 to 28 mm | from 10 to 21 mm |
| Body | from 8 to 18 mm | from 6 to 13 mm |
| Tail | from 22 to 29 mm | from 10 to 24 mm |
Violations of the above parameters allow the attending physician to make a diagnosis or refer the patient for additional research. Ultrasound diagnostics allows us to identify the following diseases:
- Various forms of pancreatitis;
- Pathological enlargement of nearby lymph nodes;
- Cysts and neoplasms of various nature;
- Congenital anomalies of anatomical structure;
- Tissue death;
- Diffuse changes in functionally active epithelial cells;
- Stones in the ducts.
Heterogeneity of structure
In a healthy person, pancreatic tissue is homogeneous, fine-grained, and homogeneous. The echostructure suspiciously increases in subacute and chronic pancreatitis, cysts and tumors.
Acute interstitial pancreatitis is often diagnosed in people who abuse alcoholic beverages and high-fat foods. On palpation they feel sharp pain. Unpleasant symptoms are associated with swelling of the gland. A person complains of cramps in the upper abdomen may contact a doctor.
The heterogeneity of the structure is indicated by arrows (white and dark areas).
Severe pain in the left or right hypochondrium occurs with chronic pancreatitis. During periods of exacerbation of the disease, the patient experiences an increase in temperature, abnormal blood pressure, changes in the color of the skin and sclera (jaundice). The patient is worried about constant nausea, vomiting, and lack of appetite. In addition to poor nutrition, the following diseases can affect the development of pancreatitis:
- Cholecystolithiasis.
- Ulcer penetration.
- Viral hepatitis.
- Parasites (worms).
- Typhoid and typhus.
- Alcohol abuse.
There are many lovers of alcoholic beverages among men, so the likelihood of chronic pancreatitis in the stronger half of humanity is much higher than in women.
Heterogeneity of structure in children
Changes in the homogeneity of the structure of the pancreas often occur in childhood. They manifest themselves as disruptions in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Disturbances occur due to spasms of the gland ducts and increased enzyme activity. The obstructed outflow of the latter causes swelling of the pancreas in the child.
Preparatory stage for ultrasound of the pancreas
In order for diffuse changes in the pancreas and any other abnormalities to be clearly visible on ultrasound, the patient needs to prepare accordingly. The fact is that gaseous environments seriously complicate visualization and negatively affect its quality, so preparation should be aimed at minimizing gas formation. To do this, a few days before the procedure, the patient needs to exclude foods that promote gas formation from the diet. Since the manipulations are carried out on an empty stomach, the last meal should take place no later than eight hours before them. At the same time, if the purpose of the study is the pancreatic duct, then it is carried out after breakfast.
Why deviations are dangerous
Negligence towards pancreatitis can increase the risk of new foci of inflammation. The combination of diseases affects the overall health of a person. A critical manifestation of complications is disability.
If treatment of the disease is not started at its early stage, pancreatic enzymes enter the blood and create conditions for infection of other organs. Several diseases find a corresponding response:
- Liver and kidney failure.
- Bleeding in the stomach and intestines, erosions, ulcers.
- DIC syndrome (blood clotting disorder).
- Purulent-necrotic parapancreatitis.
- Mechanical jaundice.
- Liver hepatosis.
- Cholangitis, cholecystitis.
- Abdominal abscess.
Necrosis of the gland parenchyma develops tumors and cysts. Malignant tumors often appear in older men. Unusual thinness, loss of appetite, abdominal pain are the main symptoms of the disease. Only adequate timely therapy can reduce the chances of such complications occurring.
Video: Complication of chronic pancreatitis
Indications for ultrasound examination of the pancreas:
Recent abdominal trauma and symptoms indicating a high risk of pancreatic injury;- Painful symptoms of unknown etiology, localized in the upper abdominal cavity;
- Suspicion of complications of acute pancreatitis;
- Frequent vomiting for unknown reasons;
- Jaundice discoloration of the skin;
- Chronic inflammation of the pancreas with frequent exacerbations;
- Diagnosed neoplasm in the upper abdominal cavity, accompanied by an increase in abdominal volume;
- Suspicion of a neoplasm of a malignant nature.
Why is ultrasound better than other methods?
Obtaining high information content. Thanks to modern ultrasound equipment, the size of the pancreas is determined as accurately as possible, and the picture displayed on the monitor is recorded. The doctor uses the information obtained to plan a puncture or as a preparatory stage for surgery. Using this diagnostic method, it is possible to identify pancreatitis, organ sclerosis, salt, fat and calcium deposits, cysts, tumors and other pathologies. With early diagnosis of a particular disease, it is possible to begin treatment measures in a timely manner, resulting in a reduced risk of complications.
There are no absolute contraindications. Ultrasound examination is the safest diagnostic method of the pancreas. This procedure does not expose the patient to harmful radiation. The study consists of using an ultrasonic wave. This method is allowed not only for adults, but also for children, pregnant women, nursing mothers, and those who have a pacemaker. The only obstacle to performing an ultrasound of the pancreas is the presence of an abrasion, wound or scratch on the abdomen. Such damage prevents normal contact between the sensor and the skin. In such a situation, you need to wait until the wound heals. The procedure is then carried out as usual.
No pain. An ultrasound examination of the pancreas is not capable of causing pain or discomfort in the patient.