27.01.2021 24891 0
- Constipation - what is it?
- Causes
- Consequences
- Symptoms of anxiety - see a doctor immediately
- Help and prevention. Nutrition, lifestyle
Constipation –
This is a violation of bowel movement. Its common symptoms:
- irregular, infrequent bowel movements
- difficulty in defecation
- systematically insufficient bowel movement
- changes in the shape and nature of stool
It turns out that it is important not only, and not so much, the absence of stool for a certain time, but also the feelings of the person himself (a feeling of incomplete emptying, discomfort), as well as the nature of the feces.
What are the causes of constipation in children?
There are a great many of them:
- nutritional pattern
- drinking regime
- Lifestyle
- harmful environmental factors
- psychological and behavioral aspects
- hereditary predisposition
- diseases of the body and intestines
Most often there is not one reason, but several. Which factor is the leading one must be understood in each specific case.
Features of stool in children under one year old
There are average statistical data on the frequency of stool in children under one year of age.
Stool frequency in young children
| Age | Bowel movements per week | Bowel movements per day |
| 0-3 months breastfeeding bottle feeding | 5 — 40 5 — 20 | 2,9 2,0 |
| 6 – 12 months | 5 — 28 | 1,8 |
| 1 – 3 years | 4 — 21 | 1,4 |
| 4 years and older | 3 — 14 | 1,0 |
However, everything is not so simple.
Breast milk
– this is a unique product of nature, which is as gentle as possible on the child’s digestive system. It contains nutrients and enzymes for their absorption. That is, the baby needs to spend a minimum of his own resources to assimilate it. Thus, mother's milk can be completely absorbed, and in this case the baby may not have stool for up to 5, and sometimes up to 7 days. Important! If this does not cause any disturbance in the baby's behavior or hardening of the stool with a difficult process of emptying, then there is no reason to worry. If there is anxiety, behavioral disturbances and hardening of the stool with painful emptying, then this is a picture of constipation and the child needs help.
At the same time, when breastfeeding, even daily bowel movements can be considered constipation, but with a difficult bowel movement, when the child has to strain a lot, worry and even cry during this process. And in this case, it is better to contact a specialist.
If the baby is on mixed or artificial feeding, or has begun to receive complementary foods, bowel movements should be regular and preferably daily.
Why does a baby get constipated when bottle-fed?
Unlike breast milk, the formula molecule takes longer to break down and digest - this is one of the factors that affects the frequency of bowel movements. In addition, if a baby in the first month of life has stool less than twice a week, analyze whether he is receiving enough formula, because underfeeding is also often the cause of constipation in a newborn with artificial feeding.
Quite often, parents experience constipation when switching to artificial feeding too quickly or too early. The baby's intestines, accustomed to breast milk, need time to adapt to the new type of nutrition. And very often at this moment, parents, worried that stool retention is caused by the fact that “the formula is not suitable,” rush to transfer their baby to a new one. This can lead to a vicious circle when another mixture introduced into the diet too quickly (in less than three days) will only aggravate the symptoms.
It should also be taken into account that changes in the frequency and nature of stools can be influenced by conditions such as allergy to cow's milk protein and lactase deficiency. Therefore, a thorough analysis of the situation together with the pediatrician will rule out or confirm the assumption that constipation in a bottle-fed baby is associated precisely with these reasons.
And, of course, constipation during artificial feeding in an infant can occur during the introduction of complementary foods. The child begins to receive food that is completely new to him, the digestion of which requires different enzymes and more time, so the stool becomes rarer and has a completely different consistency.
About the nature of a newborn's stool
To assess this parameter, there is the Amsterdam Stool Rating Scale (Bekkali scale) and the Bristol Stool Shape Scale. Using them, you can evaluate the nature of the stool and even the speed of passage of the food bolus through the gastrointestinal tract.
Thus, the dense nature of the stool, consisting of separate pieces and wide in diameter, indicates a prolonged passage of food through the gastrointestinal tract and indicates the presence of constipation.
What to pay attention to
- late passage of meconium (more than 48 hours after birth in a full-term newborn)
- early onset of constipation (in the first 28 days of life)
- family history of Hirschsprung's disease
Tummy massage for newborns for constipation
Abdominal massage is effective for preventing and treating constipation. For prevention, it is enough to carry it out at least once a day and place the baby on his tummy more often. If constipation has already occurred, then massage sessions should be performed 2-3 times a day.
You can't massage a full belly. After eating, 2 hours should pass, and before the next meal there should be an hour or at least 30 minutes left. Before performing a massage, calm your baby down and play with him so that the baby is in a good mood. If the child cries and screams, and therefore strains the tummy, massage will not help. In order for massage movements to stimulate bowel movements, they must coincide with intestinal movements during food digestion, the so-called peristaltic waves.
How to do a tummy massage:
- Place your baby on his back on a flat surface, such as a changing table. Make sure your hands are warm.
- Do 5-6 circular strokes of the tummy in a clockwise direction.
- Proceed to counter stroking. To do this, place your right palm on top of the left side of the baby's abdomen, and the back of your left hand on the bottom of the right side. Then simultaneously stroke the baby’s belly in different directions: move your right palm down, and lift the back of your left palm up. Repeat 5-6 times.
- To work the oblique muscles, you need to stroke the sides of the abdomen. Place both palms under the child's lower back, and then, with a grasping stroking motion, move your hands up and forward towards each other, connecting them above the navel. Do 5-6 reps.
- We complete the massage again by circularly stroking the abdomen clockwise with the same number of repetitions - 5-6 times.
How to help a child?
Firstly , review your diet and frequency of meals
.
Breast milk contains oligosaccharides (more than 130 types) that promote the formation of regular stool. The mother's diet also affects the baby's stool. Strong tea, blueberries, and starchy foods slow down intestinal motor function. It is better to exclude them.
Infant formula for constipation
An example of a formula that promotes regular soft stools is Nuutrilak Premium COMFORT.
Oligosaccharides are also added to infant formula. They also use gum for this. It is a natural source of polysaccharides (dietary fiber), which regulate intestinal motility. In addition, it has a beneficial effect on the colon microbiota and its diversity. All this contributes to regular soft stools in the child. An example of such a mixture would be Nutrilak Premium Antireflux.
In complementary feeding dishes, preference should be given to vegetables and vegetable purees. Dietary fiber and vegetable fiber should be present in the child’s menu.
Fruits and fruit purees are not main dishes. They can be used as a dessert or as an addition to porridge.
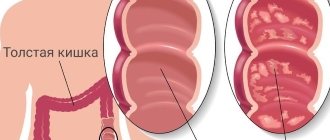
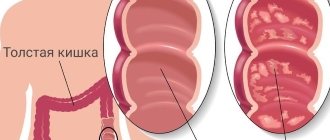
Types of constipation
Peristaltic disturbances can occur 1, 3, 6 due to a variety of factors.
Organic or primary constipation
In childhood, they are associated with congenital diseases and disorders of the intestinal structure1, 3. These include Hirschsprung's disease, dolichosigma, megacolon, fusion of the rectum, stenosis of the large intestine and rectum, impaired development of the anal sphincter1, 3, 4. Stool retention with them - a symptom, a sign that the intestines are not working correctly, their normal physiology is disrupted.
Primary stool retention also occurs due to an acquired violation of the structure and shape of the intestine, a decrease in its lumen1, 2. This may be due to polyps, tumors, hemorrhoids, adhesions3, 6.
Stool retention in these cases goes away after cure (if possible) or selection of a method for correcting the disease.
Up to contents
Functional constipation5
This is the most common type of defecation disorder in children5; it occurs from exposure to a provoking cause that disrupts intestinal tone.
- Intestinal immaturity in young children1. Peristalsis is just getting better, the intestines do not immediately respond to the arrival of food. Feces are retained and thickened.
- Nutritional disorders (nutritional) 1, 3, 5. If the daily menu does not contain enough water, a lot of flour, cereals, and sweets, then the intestines receive little dietary fiber needed to stimulate peristalsis. As a result, the progress of the bolus of feces slows down. In infants, nutritional disorders arise as a consequence4, 5 of improper feeding, the introduction of supplementary feeding, and complementary feeding.
- Hereditary tendency. Research has shown5 that if a baby's mom or dad suffered from constipation, then their child is likely to have this problem too.
- Various acute and chronic diseases not related to the digestive system 4, 5.
- Hormonal diseases1, 5 - congenital hypothyroidism, pheochromocytoma.
- Iron deficiency (anemia), rickets, helminthic infestations5.
- Retention of stool due to atopy, for example, with food allergies1, 5.
- Dehydration. As a rule, it is associated with a painful state of the body - fever, heat stroke. Due to lack of water, feces become dry, move through the intestines with difficulty, and are retained in the rectum1, 2, 5.
- Inactivity. When moving or walking, the abdominal muscles actively work and, as it were, massage the intestines and stimulate peristalsis1, 2, 5.
- Abuse of enemas, gas tubes5. The enema interferes with the natural mechanism of defecation, the nerve endings of the intestine “get unaccustomed” to respond to irritation, urges disappear, and the baby loses the skill of recognizing them1, 5.
- Taking 5 certain medications that reduce intestinal motility.
Up to contents
Psychological constipation in children
This is a functional disorder 5, but due to its formation and prevalence it deserves to be classified as a separate group. For many parents, the absence of stool in a child for psychological reasons comes as a big surprise 2, 3, 5.
Psychological constipation is called if there are no organic causes, there are no other painful conditions that could cause stool retention2, 3, 5. The source of problems with stool are psychological factors, the peculiarities of the nervous system in children.
The nervous system has an autonomic department that regulates the functioning of all internal organs. If a person experiences some difficult situation or stress, then the reaction of the autonomic system can cause intestinal dysfunction5. An example of such a situation is a pet’s illness, moving to a new place of residence, or the loss of a favorite toy. The child forgets to go to the toilet for several days, the stool becomes thicker, defecation becomes painful and difficult, and the baby begins to consciously avoid it2, 3, 5.
Examples of other situations that cause psychogenic constipation:
- The baby consciously suppresses the desire to go to the toilet for a variety of reasons2, 5, “forgets” to go to the toilet, he is not in the mood for it because of games or reluctance to go home. A few days of such conscious retention of stool - and now the stool has become compacted, and going to the potty is painful. The child is not yet able to establish a connection between cause and effect; he begins to avoid what caused the pain, that is, defecation.
- Rejection of the potty2, 5 due to unpleasant sensations when planting or rude, persistent attempts to teach “doing things” without fail to go to the potty with punishment for a mistake.
Another psychological reason that causes difficulty in defecation is prolonged exposure to difficult, mentally difficult circumstances2, 3, 5. Conflicts in the family, difficulties in relationships in a team or with teachers in kindergarten or at school, embarrassment to go to the toilet in front of strangers, uncomfortable bathroom outside the home, memory of past failures (didn’t have time; didn’t understand that the process is not finished yet; doesn’t know how to carry out intimate toileting after bowel movement, etc.) - all this and much more can cause psychological fear of defecation2, 4, 5 .
Up to contents
Transient constipation
Stool retention is not always associated with serious problems. Sometimes this is a transient or one-time retention of feces. Happens infrequently, less than once every 2 or 3 months1, 4, 6, and is usually associated with nutritional reasons or an acute illness: the child has not drunk much for several days, sweats a lot in the heat or temperature, has eaten a lot of fixative food - blueberries or bird cherries. After resuming fluid intake and correcting the diet, motility and stool are restored on their own1, 4, 5.
Up to contents