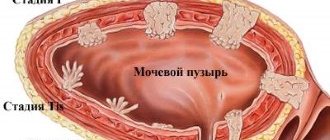
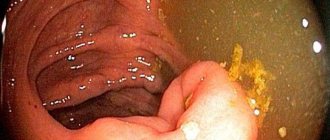
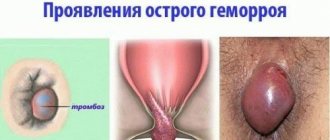
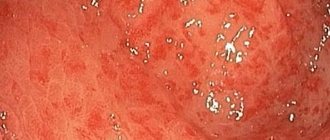
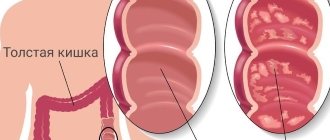
An anal polyp is any neoplasm in the intestinal lumen within the anal canal. This definition is given by the authors of clinical guidelines for coloproctology. This term is descriptive.
Anal canal polyp. Atlas “Coloproctology” 1999
Any neoplasm detected in the rectum when visiting a doctor is subject to careful study. Further treatment tactics are selected depending on the results of clinical and histological examination.
Polyps can vary in shape and structure. Based on the nature of their growth, benign and malignant polyps are distinguished. Benign polyps grow only in the lumen of the rectum, pushing away the surrounding tissue at the site of attachment and not penetrating into them. When malignant polyps develop, they can lead to the destruction of intestinal tissue.
Based on the type of attachment, flat polyps and pedunculated polyps are distinguished. A flat polyp has the same thickness along its entire length. A pedunculated polyp has a clearly visible thickening at the end.
Also, when a polyp is identified, its morphology and structure are assessed. This study is the most valuable from a diagnostic point of view; it allows one to determine the prognosis of the development of the disease and take timely measures to prevent the development of intestinal cancer.
The authors of clinical guidelines and many colorectal surgeons say that most benign polyps in the anal canal are discovered by chance. Most often this happens during examination by a coloproctologist, if the patient presents with symptoms of other intestinal diseases. A polyp can be detected by digital examination, as well as by instrumental examination of the inner wall of the intestine.
Possible symptoms
Small polyps do not manifest themselves in any way. Therefore, sometimes they are discovered during an appointment with a proctologist, when the patient comes to him for another reason. But large APs can cause:
- pain, itching and burning in the anus;
- constant feeling of discomfort;
- the appearance of mucus and blood in the stool.
Large pedunculated polyps often fall out of the anus during bowel movements. After the act is completed, they are drawn inside on their own. Therefore, they are easily confused with hemorrhoids.
Treatment of rectal polyps
Surgery to remove polyps in the rectum
is the only way to eliminate them, since conservative treatment of the disease is not carried out.
Depending on the individual indications of the patient, endoscopy of the polyp
, i.e., its removal during endoscopic examination without surgical intervention. In addition, other methods are available, the features of which can be found in our table below:
| Polyp removal method | Description |
| Transanal excision | It is used to remove polyps located at a distance of no more than ten centimeters from the anus through the anus. The polyp is removed and sutures are applied or electrocoagulation of the vessels is performed. After this, treatment is carried out with an antiseptic. |
| Electrocoagulation | It is optimal for single polyps with a diameter of no more than three centimeters, located at a distance of no more than 30 cm from the anus. Removal is carried out through the anus by capturing the stalk of the tumor with a diathermic loop. A current is applied to it, after which the polyp is pulled out. If it is small, one cauterization will be enough, if larger - several. |
| Transanal endoscopy | It makes it possible to remove polyps in any part of the rectum and is a modern method that involves the use of a surgical endoscope with a video camera, which is inserted into the rectum. If a polyp is detected, it is excised, and the bleeding is stopped through coagulation. It is the key to maximum accuracy and minimal risk of complications. |
| Resection | A radical technique used when a malignant tumor is detected. Requires the use of general anesthesia and an incision in the abdominal cavity and excision of the part of the rectum in which the polyp is located. |
How are polyps diagnosed?
Patients usually come to the proctologist with complaints when the AP has reached a large size, has begun to fall out or cause discomfort. To make an accurate diagnosis, the doctor visually assesses the condition of the anus and probes the anal canal with his fingers. If deviations from the norm are detected, he performs an anoscopy - an instrumental examination of the AV using an endoscope.
Since anal polyposis has similar symptoms to other proctological diseases, the following pathologies should be excluded:
- haemorrhoids;
- Crohn's disease;
- ulcerative colitis;
- anal fissure;
- prolapse of the rectum or its mucosa;
- malignant neoplasm in the lumen of the rectum or AC.
Features of the rehabilitation period
No specific care for the surgical wound is required. But in order for healing to take place as quickly as possible, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- refrain from work for 5-7 days;
- avoid constipation;
- do not sit for a long time;
- follow a gentle diet - soft food, rich in fiber and fibre, drink plenty of fluids;
- do not lift weights for 2-3 weeks;
- move more;
- Maintain careful hygiene of the anal area.
Thanks to minimally invasive intervention technologies, the recovery period is almost painless. In the first 2 days, minor pain may occur, which is quickly relieved with a drug prescribed by your doctor. Complete healing occurs within 2-4 weeks. After a polypectomy, you will need to be regularly monitored by a proctologist to monitor the possible formation of new polyps.
Why do polyps need to be removed?
Polyps are called benign neoplasms. But over time, they can become malignant. Therefore, their removal is a simple method of preventing colorectal cancer.
Less serious consequences include inflammation of the AP. The inflammatory process develops when the body of the polyp is damaged and pathogenic or conditionally pathogenic microbes enter. It causes pain in the anorectal area and is often accompanied by anal bleeding after defecation.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of rectal polyps is carried out by a coloproctologist surgeon. For this purpose he can use:
- finger examination;
- endoscopic methods - sigmoidoscopy, sigmoidoscopy, colonoscopy;
- X-ray methods - irrigoscopy;
- stool examination for occult blood - if the result is positive, it allows one to suspect the presence of bleeding polyps, but a negative result does not mean that there are no polyps.
If at least one polyp is found, a complete examination of the entire large intestine is necessary, since in 30% of cases polyps are multiple.
Methods for removing anal polyps
Depending on the severity of the disease, AP is removed on an outpatient basis, in a day or 24-hour hospital setting. In public clinics, removal is performed surgically using a scalpel. For this:
- The patient is asked to sit in a special chair and given local or general anesthesia.
- A rectal speculum is inserted into the AC to view the AP.
- The upper part of the AP is grabbed with a special tool and pulled outward.
- The growth is cut off with a scalpel to healthy tissue. It is taken to the laboratory for histological analysis and identification of its nature.
- A gas outlet tube is inserted into the anus to reduce the risk of damaging the walls of the anal canal in case of possible gas formation. It is removed only the next day.
The patient is discharged from the hospital after the first successful bowel movement without the use of laxatives. In the postoperative period, the patient is prescribed a diet. It prohibits the consumption of hot, salty and spicy foods, as they cause irritation of the intestinal mucosa. It is not allowed to consume alcoholic beverages, as well as foods that cause constipation, diarrhea or increased gas formation. To normalize stool, the patient is recommended to diversify the diet with vegetables, fruits, cereals and dairy products. To prevent complications, the proctologist prescribes him a course of antibiotics.
If you suspect anal polyps, contact your doctor. We employ qualified doctors with extensive experience. Our proctologists will conduct a thorough diagnosis and identify the cause of the alarming symptoms. If the diagnosis is confirmed (AP), we will remove the polyps using a laser or radio wave method. These methods of removing tumors are more preferable than the traditional use of a scalpel, since they injure tissue less and cause complications less often.
Polyps in the rectum: causes
The exact reasons leading to the development of polyps have not yet been established. Experts put forward the theory that the main initiating factor is chronic inflammatory processes in the intestinal mucosa. It is confirmed by numerous studies that identify polyps in areas that are more often prone to trauma or irritation due to stagnant processes. In addition, there are a number of factors that contribute to the onset of the disease. These include:
- genetic predisposition;
- poor diet and, as a result, regular constipation;
- frequent consumption of foods that irritate the gastrointestinal mucosa;
- pathological condition of the large intestine in a chronic form;
- sedentary lifestyle and the adverse impact of the environmental component;
- infectious diseases such as dysentery, salmonellosis, rotavirus infection.
Polyp classification
Content:
- Polyp classification
- Cause of occurrence
- When should you go to the doctor?
- The right preparatory approach
- Polyp removal
- Complications after surgery
A polyp localized in the rectum is a benign tumor that consists of the mucous membrane of both the rectum and colon. Such a growth likes to “settle” on the wall of a hollow organ, attaching to the surface due to the base or a strong leg. Although it grows from epithelial tissue, it contains other cells inside.
The cost of measures aimed at neutralizing such formations depends on their number, characteristics and severity of the lesion. The cost will also be affected by the specific type of polyp and the method by which it will be removed. Taking into account all of the above, it is difficult to say exactly how much the entire set of procedures costs. Because of this, doctors recommend that you first undergo a preliminary examination and discuss the price directly with your doctor.
It is believed that all benign tumors of this kind have only three main geometric shapes. Most of it falls on the ball. There are options that look like a mushroom with an extensive cap. The least common are branched versions without a clearly defined shape. It is precisely such proposals that surgeons usually have the most difficulty with.
The consistency of the polyp is close to a soft composition, which is pink, burgundy, and dark red in color. The exact shade depends on how well the nutrient supply has been established between the lesion and the blood vessels nearby.
In general, polyps can choose any organ of the digestive tract as their location, not just the rectum. Moreover, they are almost equally common in men and women. According to statistics, representatives of the stronger sex are approximately one and a half times more susceptible to this disease. In rare cases, they make themselves felt even in children.
Before referring a victim for endoscopic removal of an unhealthy area, the doctor must first establish the specific class of the lesion. In addition to division according to the quantitative component, experts use another classification. It relies on differences in structure:
- fibrous;
- adenomatous;
- villous.
Variations of the fibrous polyp are usually created on the basis of connective tissue, choosing for the site of attachment those areas of the mucous membrane that are often inflamed. These kinds of processes often become the cause of an extensive inflammatory process with initially healthy tissue being drawn into it. Also, the fibrous component often becomes an ideal environment for triggering the mechanism of suppuration. However, it quite rarely transforms into a malignant neoplasm that metastasizes throughout the rectum. Doctors advise not to test the theory in practice and treat the original source of the disease with a laser or another method according to medical indications immediately.
The adenomatous class is distinguished by its ability to grow up to 3 cm in diameter, attaching to the wall with its leg. It has glandular tissue inside. Unlike its fibrous counterpart, it much more often becomes the cause of a full-fledged oncological neoplasm. To prevent the development of the worst scenario, it is worth immediately removing the detected growth.
Even in the initial phase of development, an adenomatous polyp is a precancerous condition, so it is worth quickly deciding on the optimal excision technique. But treatment with folk remedies is not worth practicing, since education usually progresses very quickly. In attempts to correct the situation by self-medication, you can only miss the chance for a successful recovery.
The villous category includes processes that are round or slightly elongated. It has a velvety surface, which is made possible by the many fibers. Due to the fact that its structure is very soft, it is quickly injured even with slight pressure.
In the future, it becomes one of the fundamental causes of the development of malignant oncology of the digestive tract. Any medical forum where there is expert advice from experienced doctors will confirm these concerns.
Multiple polyps are considered separately, which are represented by mixed classes, ranging from mucocystic to villous-glandular. If the victim was diagnosed with diffuse polyposis, this indicates the growth of a large group of polyps. They literally stick to the inner surface of the intestine, which makes it much more difficult for processed food to pass through.