- home
- general surgery
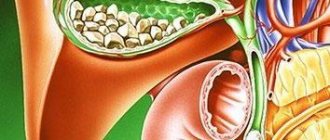
- Polyps in the gallbladder
Among the pathologies of internal organs, gallbladder diseases are quite common. But some of them may remain undetected for a long time, despite the fact that the patient regularly attends preventive examinations. One of these pathologies is polyps in the gallbladder, which are not so easy to diagnose.
Puchkov K.V. in the TV show “Health” with Elena Malysheva"
Unlike other ailments, for example, a kink in the gallbladder, the presence of polyps does not cause specific symptoms. The symptoms of this pathology are vague; the signs accompanying this disease are often found in other diseases. Therefore, diagnosis is sometimes carried out by the method of exclusion. In this case, the patient is usually prescribed an ultrasound examination of the internal organs, if their functioning is disrupted, similar signs arise. For example, intestinal dysfunction occurs in most diseases of the digestive system. In addition, the reason for the low detection of polyps in the gallbladder can be attributed to the ineffectiveness of conventional examinations. Only a targeted examination, measured for gallbladder diseases, can be successful. However, for this the patient should undergo the necessary studies.
There are several types of polyps in the gallbladder:
- Inflammatory polyps appear as a result of an acute reaction of the organ mucosa to the proliferation of granulation tissue.
- Cholesterol - the mucous membrane of the bladder changes due to cholesterol deposits and accumulations; This type is the most common. Despite the fact that the presence of such plaques does not pose a danger, the need for urgent surgical treatment causes debate among doctors.
- Papilloma is a benign tumor, which is characterized by the presence of papillae on the mucosa.
- Gallbladder adenoma is a benign formation that appears as a result of the growth of glandular tissue.
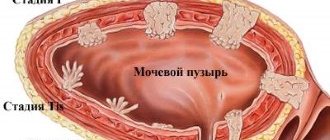
Gallbladder polyp.
Diagnosis of duodenal polyps
At different stages of identifying a polyp, an examination is indicated, including:
- complete blood count (exclude anemia),
- blood biochemistry (exclude diseases of the liver and biliary tract),
- stool test for occult blood (exclude bleeding),
- blood test for antibodies to Helicobacter pylori JgG and JgA,M,
- Ultrasound of the liver, gallbladder and pancreas,
- Ultrasound of the duodenum is carried out in 3 stages: examination of the duodenum on an empty stomach, after a choleretic breakfast, after emptying the duodenum. This study determines the growth of the polyp and its size,
- X-ray examination of the stomach and duodenum with contrast (barium). This study does not detect duodenal polyps less than 10 mm and the degree of malignancy,
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy (endoscopy of the stomach and duodenum) with biopsy. Given the often benign nature of the polyp, it is discovered by chance during an endoscopic examination. If detected, observation is carried out over time 6 and 12 months after removal of the polyp,
- A CT scan of the abdominal cavity shows an image of the polyp and its size. This study is not performed very often due to the complexity of the structure of the intestinal wall. Small polyps may be detected, but inflammation cannot be seen with this method.
Causes of polyps
- Heredity and predisposition more often than other reasons lead to the formation of polyps. This may be due to the structure of the bladder mucosa - most often this is the so-called “launching pad” for the appearance of polyposis.
- Irregular and irrational nutrition, abuse of food containing cholesterol is also one of the unfavorable factors.
- Chronic cholecystitis, in which the flow of bile into the duodenum is impaired.
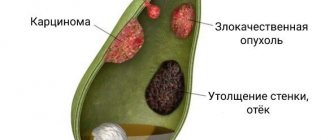
Despite the fact that adenoma and papilloma are benign formations, there is a possibility of their degeneration into malignant tumors. In addition, tumor particles entering outside the gallbladder can lead to the spread of polyps to other organs.
Possible consequences and complications
Cysts, or polyps as they are also called, are neoplasms that can cause the following complications:
- opening of internal bleeding;
- exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis;
- peritonitis;
- cholestasis;
- abscess;
- formation of fistulas;
- cyst suppuration;
- splenic rupture.
Peritonitis, abscess, cyst suppuration and splenic rupture - these conditions require emergency surgery, as they can be fatal in a matter of hours
All these conditions are very dangerous to human health and life. Therefore, when polyps are detected in the pancreas, it is necessary to immediately begin their treatment. It is pointless to carry out therapy with folk remedies, since they will not give a positive result. To get rid of tumors once and for all, surgery will be required.
Symptoms of the disease
Often the disease is asymptomatic. Half of the patients experience only a feeling of discomfort in the right hypochondrium. Some patients experience heartburn and belching, and sometimes pain may occur. Soreness is a common symptom in cases where the polyp is localized in the narrowest place of the gallbladder - in the neck. If large in size, it can lead to blockage of the duct, which will cause stagnation of bile. As a result, the digestion process is disrupted, leading to belching, pain in the right hypochondrium, constipation, etc.
Preventive measures
No one is immune from pancreatic polyps and cysts. Therefore, each person needs to constantly carry out preventive measures that will allow him to maintain the functionality of his pancreas and prevent the formation of neoplasms in it.
Preventive measures are simple and include:
- quitting smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages;
- introduction of an active lifestyle;
- proper nutrition;
- adherence to daily routine;
- do not exceed the dosage and duration of taking medications that were prescribed by a doctor for the treatment of other diseases;
- undergo preventive examinations in a timely manner (at least once a year).
Summarizing all of the above, it should be noted that polyps cannot form in the pancreas. And even if the doctor talks about their presence in this organ, then most likely he means a cyst by his words. Its presence in the pancreas is dangerous and can lead to serious health problems. Therefore, there is no need to delay the operation. The smaller the cyst and the sooner it is removed, the lower the risk of consequences.
Treatment of polyposis
First of all, nutritional correction is necessary. As a result of the disease, the amount of incoming bile is insufficient for digestion. But with the help of diet you can ease the work of the gastrointestinal tract. Fractional balanced nutrition in small portions, easily digestible foods will help prevent the occurrence of digestive system dysfunction.
As a rule, the most effective way to get rid of polyps is surgery. However, the question of the advisability of surgical treatment is decided only individually. Therapeutic tactics are based on observation of the patient, taking into account the structure and number of polyps, the presence of a pedicle, etc. If there is a formation with a pedicle, it is recommended to conduct an ultrasound every six months; in the absence of a pedicle, control studies should be done more often.
Treatment of intraductal formations of the pancreas
If doctors at the Yusupov Hospital identify a formation inside the pancreatic ducts that is shaped like a polyp, they collectively determine treatment tactics. Active surveillance using non-invasive diagnostic methods is carried out only in a limited group of patients with an intraductal papillary mucinous tumor less than 3 cm in size without clinical manifestations and no signs of malignant transformation. At the slightest suspicion of malignancy of the tumor, patients are offered surgical intervention.
Depending on the location and nature of the papillary mucinous tumor, various types of pancreatic resection are performed, up to pancreatectomy (removal of the entire organ). When a benign intraductal papillary mucinous tumor is detected, limited resections of the pancreas are performed depending on the location of the tumor:
- Excision of the head of the pancreas while preserving the duodenum;
- Distal resection of the pancreas with preservation of the spleen;
- Median resection of the gland.
At the slightest suspicion of a malignant process during surgery, surgeons refuse to perform organ-preserving operations and proceed to standard organ resections. During the operation, an urgent histological examination of the edges of the organ resection is carried out. If necessary, the scope of surgical intervention is expanded to pancreatectomy. The indication for removal of the pancreas is total damage to the ductal system of the organ.
Long-term results of surgical treatment of patients with benign and borderline forms of intraductal papillary mucinous tumor are good. The results of treatment of patients with malignant forms of the disease are worse. In this regard, early diagnosis and timely surgical treatment will improve treatment results. When the first signs of damage to the pancreas appear, make an appointment with a gastroenterologist by phone.
Surgical treatment of polyposis
Report on the master class by Prof. Puchkova K.V.
The absolute indication for surgery is the large size of the formation and the pain experienced by the patient. In addition, you should know that polyps that do not have a stalk tend to degenerate into malignant carcinomas. They are characterized by rapid growth and progression, which poses a threat to the patient's health. In this case, immediate surgery is the only solution.
The scope of surgical intervention is discussed in each specific case individually. Indications for surgical intervention are polyps measuring 7 mm and above, as well as any size of polyp located in the neck of the gallbladder due to a sharp disruption of the function of the organ and the development of chronic cholecystitis.
Symptoms and diagnosis of the disease
Symptoms of a polyp-type tumor in the pancreas are observed in 81% of patients. Clinical symptoms are scanty and nonspecific. In 27% of cases, intraductal papillary mucinous tumor is detected by chance.
The main clinical symptoms are:
- Abdominal and back pain;
- Weight loss;
- Obstructive jaundice;
- Nausea and vomiting.
13% of patients develop acute pancreatitis, 12% develop diabetes mellitus. The appearance of obstructive jaundice, diabetes mellitus or worsening of its severity speaks in favor of the malignant nature of the polyp-like formation. 29% of patients with malignant intraductal neoplasms have no clinical symptoms.
Diagnosis of intraductal papillary mucinous tumor, which patients call pancreatic polyp, is very difficult. Routine laboratory tests have no diagnostic value. At the Yusupov Hospital, formations are identified using modern instrumental non-invasive methods:
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
- Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography;
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography.
Intraductal papillary mucinous tumor of the main pancreatic duct on MRI is manifested by segmental or diffuse dilation of the Wirsung duct with filling defects, which is caused by accumulations of mucin. Inside the duct is visible in the shape of a “bunch of grapes”, which is more common in the area of the uncinate process of the pancreas and has a direct connection with the ductal system of the gland. Diagnostic signs of a malignant intraductal papillary mucinous tumor are the presence of parietal nodes and diffuse dilation of the main duct of the gland more than 15 mm.
An alternative method for diagnosing intraductal papillary mucinous tumor is endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. Using this diagnostic method, doctors determine segmental or diffuse dilation of the main pancreatic duct and collect pancreatic juice. Laboratory assistants perform biochemical and molecular analysis of it for the content of pro-oncogenes of the K-ras family. During the study, a targeted biopsy of the epithelium of the gland duct is performed, followed by a cytological examination.
An important role in the differential diagnosis of benign and malignant forms of intraductal papillary mucinous tumor belongs to endoscopic ultrasound examination with fine-needle puncture of the cystic tumor, followed by cytological and biochemical examination of the obtained material.
Surgical methods for treating gallbladder polyps
Watch a video of operations performed by Professor K.V. Puchkov. You can visit the website “Video of operations of the best surgeons in the world.”
Today there are two main methods of surgical treatment of polyposis:
Puchkov K.V., Khubezov D.A., Puchkov D.K., Rodimov S.V. Minimally invasive laparoscopic methods for treating gallbladder diseases: a textbook for surgeons // Ryazan State Medical University of the Ministry of Health of Russia. - Ryazan: RIO RyazGMU, 2015. - 115 p.
Puchkov K.V., Puchkov D.K. SURGERY FOR GALLSTONES: laparoscopy, minilaparoscopy, single port, transanal access, simultaneous operations. - M.: ID "MEPRACTIKA-M", 2022, 312 p.
Patent. A method for temporary fixation of abdominal and pelvic organs during laparoscopic operations.
Laparoscopic gallbladder removal - single-port cholecystectomy
- Laparoscopic cholecystectomy - with this method, the intervention is performed using laparoscopic equipment through small incisions on the anterior wall of the peritoneum, through a puncture in the umbilical area or transvaginally. Today, laparoscopy is recognized as the “gold” standard in abdominal surgery. Among the advantages of this method, it is worth noting the excellent cosmetic result: only small incisions remain on the skin. The rehabilitation period is much shorter than with traditional surgical treatment. The patient begins to walk on the first day, and on the second day he is allowed to take liquid food. The operated patient usually leaves the clinic on the 2nd or 3rd day after the operation. A person can usually start work within 10-14 days.
- traditional cholecystectomy
is an open operation, performed manually, with a 15-20 cm long incision made on the anterior abdominal wall. Currently, surgical intervention by this method is performed only for complications of gallbladder polyps - degeneration into cancer with metastases to regional lymph nodes.
These operations are performed under general anesthesia, and the gallbladder is removed along with the polyps. Unfortunately, there are currently no methods for removing polyps from the gallbladder.
Treatment
Pancreatic polyps and cysts can only be treated surgically. This is due to the fact that these tumors do not have the property of self-resorption under the influence of certain medications. However, before the operation, patients are still prescribed a course of drug therapy, the purpose of which is to prevent the occurrence of postoperative complications.
As a rule, such therapy includes a five-day course of antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs. In parallel with them, a diet is prescribed that helps relieve the load on the pancreas. A day before the operation, a hunger strike is prescribed, during which it is forbidden to even drink water.
Removal of pancreatic polyps and cysts is carried out in two ways: laparotomy and laparoscopic. The latter is used if the tumor is small in size. During surgery, not only the polyp is removed, but also nearby gland tissue.
Surgery is the only way to treat pancreatic polyps and cysts. How exactly it will be carried out is decided by the doctor after a complete examination of the patient.
Since this leads to dysfunction of the gland, after the operation the patient is prescribed lifelong therapy, which includes taking enzyme preparations. If during the operation the pancreatic cells responsible for the production of insulin were damaged, sugar-lowering agents are used along with enzyme preparations, since in this case the body loses the ability to independently control blood sugar levels. Otherwise, postoperative treatment depends on the exact size of the polyps and their location.
Why is it better to seek treatment from us?
The Kuntsevo Multidisciplinary Center has an individual approach to each patient. Here, in the absence of queues, you will be examined for polyps and neoplasms in the gastrointestinal tract. Our gastroenterologists are true professionals of the highest category. Among the doctors there are candidates and doctors of medical sciences. Experts are constantly researching gastrointestinal diseases.
Why us:
- friendly staff;
- the best prices;
- innovative equipment and devices;
- modern technologies of endoscopic methods;
- personal approach.
Make an appointment with our clinic by calling the phone number listed on the website or request a call back!
The contents of this article have been checked and confirmed for compliance with medical standards by gastroenterologist-nutritionist Tatyana Vladimirovna Lucheninova
Treatment of duodenal polyps
Polyp of the duodenum, its location, size, shape of the polyp, the result of the biopsy allow us to determine whether it is a hyperplastic or true polyp of the duodenum, and decide on treatment tactics.
The main method of treating a polyp is a minimally invasive method of endoscopic removal of the polyp without opening the abdominal cavity.
Polyps smaller than 5 mm are subject to dynamic endoscopic monitoring after 6 months. When taking a biopsy of such a polyp, it can be completely removed, i.e. diagnostic and therapeutic endoscopy is combined.
It is more convenient for endoscopists to remove a pedunculated polyp. A wide-based polyp leaves significant damage to the mucosa, and after removal of the polyp, conservative treatment is carried out for 2-4 weeks.
For large polyps larger than 4 cm and endoscopic removal of the polyp is impossible, the patient is subject to surgical treatment.
What kind of disease is this
Polyps and neoplasms of the gastrointestinal tract are growths on the mucous membrane of the digestive system, which appear from the pharynx to the rectum. The sizes of the tumor are very different - from a few millimeters to 2-3 cm. New growths grow alone and in groups, resembling a bunch of grapes and cauliflower. If polyps do not bother a person, then he can live with them all his life. But in 5% of cases the pathology takes a malignant form, so it is better to get rid of it.
The etiology of the disease is not completely known. But studies have shown that tumor formation occurs for a number of reasons:
bad ecology;- wrong lifestyle;
- alcohol and drug abuse;
- entry of toxic substances into the body;
- chronic diseases and infections of the digestive system;
- genetic predisposition;
- excess weight;
- age after 50 years.
It is believed that the main factor is heredity. But this is just a guess. Among all types of polyps, the greatest attention should be paid to adenomatous neoplasms. Adenomas account for 10% of the total number of tumors and pose a threat of developing into cancer.
Adenomatous polyps are divided into several types:
- Villous - large in size. They grow on the rectum and other parts of the gastrointestinal tract. Reminds me of a cauliflower inflorescence. The risk of cancer is quite high.
- Tubular - small growths that appear mainly in the large intestine. A small percentage of cancers until adenomas reach large sizes and form fleecy elements.
- Tubular-hairy - neoplasms associated with a high risk of developing cancer. They grow throughout the digestive system and throughout the body.
- The more villous elements a polyp contains, the higher the likelihood of the neoplasm degenerating into a malignant one. There are also juvenile, hyperplastic, hamartomatous, inflammatory growths. But these tumors do not pose a threat to humans.
Diagnostics
It is difficult to accurately make a diagnosis confirming the presence of polyps in the pancreas. Therefore, doctors insist on simultaneous research using three methods:
- clinical;
- laboratory;
- instrumental.
Only after assessing all the data can you confidently differentiate the disease and decide on the actions necessary to eliminate the problem.
Clinical diagnostic method
Clinical examination of the patient includes:
- studying the hereditary background to identify the prerequisites for pathology;
- a detailed survey of the patient about all suspicious symptoms and discomfort, the frequency of their occurrence, intensity and duration;
- external examination and study of the epigastric region of the abdomen by palpation.
Abnormal formations can be suspected at this stage of diagnosis, but only if they are significant in size. In any case, the diagnosis is confirmed by laboratory tests.
Laboratory diagnostic method
Any damage to the pancreas is accompanied by characteristic changes in the biochemical composition of blood, urine and feces. Their traditional general analysis is mandatory.
If polypous formations are suspected, the following additional studies are preferred:
- measuring the amount of insulin production;
- determination of cancer markers;
- detection of fats and proteins that are not broken down during the digestion of food;
- assessment of fecal elastase.
Studies of pancreatic juice and enzymatic disorders are also important in clarifying the picture as a whole.
Instrumental diagnostic method
Instrumental methods are widely used in modern medicine. This is the most reliable way to informatively describe all the nuances of a polyp:
- its exact localization in the pancreas duct;
- its size;
- the degree of proliferation in a quantitative aspect (new emerging polyps);
- the nature of the inflammatory process in the surrounding tissues;
- the degree of destruction of the mucosa to which the polyp is attached.
Such detailed information is obtained from one method or in a cumulative study in several instrumental ways:
- ultrasound examination;
- computed tomography;
- magnetic resonance;
- endoultrasonographic;
- fluoroscopic;
- retrograde endoscopic;
- cholangiopancreatographic.
The most common method is ultrasound. With sufficiently large polyps, this type of hardware research can reveal both the exact localization of formations and the size of their growths.
Endoultrasonography is informative and convenient in the study of the upper gastrointestinal tract. This is a method that uses a special endoscope with an ultrasound scanner at the tip. The method gives a visual picture of the condition of the tissues and walls of internal organs. When prescribing such a procedure, the patient is prepared for it for at least 10 hours. The main preparation is to refuse to eat.