Dysphagia refers to pathologies of the esophagus and larynx. With this condition, swallowing liquids and food is difficult or impossible. The causes may include both disturbances in the functioning of various organs and diseases of a neuralgic nature. To make a diagnosis, a thorough examination is necessary, and therapeutic measures are selected individually for each patient.
Pathology cannot be left without attention, since it is impossible to do without the help of doctors. Doctors at the 24-hour Yusupov Hospital specialize in this pathology and successfully cope with dysphagia of any severity.
Causes of dysphagia
The disease can occur against the background of both genetic and acquired pathologies. The most common cause of dysphagia is pathological processes in the esophagus, oropharyngeal cavity, heart and brain. Experts include the following common factors that cause the disease:
- Malignant or benign neoplasms in the oropharynx (tumors);
- Inflammatory diseases of the esophagus and its mucous membrane;
- Cancer of the esophagus or stomach;
- Purulent-inflammatory processes in the oropharynx (sore throat, abscess, etc.);
- Diverticula of the esophagus (protrusion of its walls);
- Complete or incomplete paralysis of the pharyngeal muscles;
- Various injuries of the esophagus (knife and bullet wounds);
- Injuries due to sharp foreign objects entering the esophagus;
- Quincke's edema due to severe allergies;
- Enlarged heart after coronary artery disease, heart attack, heart failure;
- A chronic disease accompanied by the reflux of acidic stomach contents into the esophagus;
- Atherosclerotic lesion of the vascular system of the brain;
- Narrowing of the esophagus of various etiologies;
- Multiple system atrophy (death of certain groups of nerve cells);
- Aortic aneurysm (protrusion of the wall of a certain area of the aorta);
- Acute renal or liver failure;
- Severe diseases of the muscles, vascular system and skin (dermatomyositis);
- Injuries to the brain or cervical spine;
- Hiatal hernia;
- Severe hypertension (with damage to target organs);
- Cerebrovascular accidents;
- Systemic lupus erythematosus, affecting the kidneys, musculoskeletal system and other organs;
- Varicose veins in the esophagus;
- Chemical burns of the esophagus (acid, alkali);
- Systemic scleroderma (autoimmune connective tissue disease).
Dysphagia is often caused by a severe toxic infectious disease (botulism), Parkinson's disease (shaking paralysis), encephalitis and neuromuscular diseases (polymyositis, myasthenia gravis and others). In childhood, dysphagia most often occurs with cerebral palsy (cerebral palsy).
Each disease is assigned a code according to ICD 10 (International Classification of Diseases). Dysphagia is coded R13 and refers to pathologies associated with difficulty swallowing.
A high risk group includes children with paralysis of four limbs, athetosis (convulsions), congenital pathologies of the brain, esophagus and pharynx, as well as elderly people with severe chronic diseases.
Classification
Pathology varies depending on the location of the lesions, type and severity. In medical practice, the classification of dysphagia is as follows:
By location
- Oropharyngeal (oropharyngeal) - divided into oral, pharyngeal and cricopharyngeal dysphagia. The lesions are localized in the oropharynx area. The bolus of food moves from the pharynx to the esophagus with difficulty. When trying to swallow, the patient may choke, and the contents may enter the nasal cavity or trachea. Oropharyngeal dysphagia occurs due to a disorder of the neuromuscular connection.
- Esophageal - affects the distal (lower) zone of the esophagus, and difficulty swallowing occurs in the cervical region. Symptoms are similar to the oropharyngeal form. Therefore, an accurate diagnosis can only be determined by a doctor during an examination of the patient.
- Cricopharyngeal incoordination - with this disease, the contraction of certain fibers is impaired, which leads to problems with relaxation of the cricopharyngeal muscle. This often causes protrusion of the walls of the esophagus and the development of pathological processes in the lungs.
By appearance
- Paradoxical - characterized by difficulty swallowing, while solid food passes better than liquid food. Most often occurs against the background of diseases of the esophagus. With tumor neoplasms, patients first refuse solid food, then cereals and soups, and then drinks. Sometimes paradoxical dysphagia weakens or even disappears, but the stage of false remission is short-lived. After some time, the disease makes itself felt again.
- Sideropenic is a dystrophic change in the mucous membranes of the esophagus. Most often this is a consequence of iron and nutrient deficiency in the human body. Is genetic or acquired. Lack of iron causes a disruption in the production of oxidative elements, which leads to pathologies of the muscles responsible for swallowing.
- Neurogenic - caused by a disorder of the nervous system and is characterized by difficult formation of a food bolus in the oral cavity or obstruction of food through the esophagus. The most common factors causing neurogenic dysphagia are major ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke and serious traumatic brain injury.
- Psychogenic - when pathology occurs while eating, the patient feels a “lump” in the throat or pain in the chest area. In addition to impaired swallowing functions, severe heartburn is noted. The cause of the pathological condition is frequent stress and nervous strain.
Due to the occurrence
- Functional - also called nervous dysphagia. Frequent causes of occurrence are a disorder of the esophagus, which was the result of a severe disorder of the nervous system. With pathology, the patient has difficulty swallowing food, and breathing is often impaired. In childhood, the disease is accompanied by loss of appetite, sleep disturbances and vomiting.
- Organic - a consequence of various diseases that contribute to damage to the oropharynx or esophagus.
In addition, dysphagia is also divided according to the form of its course - progressive and chronic. In the second case, the symptoms weaken from time to time and occur during an exacerbation of the pathological process. The chronic form is diagnosed due to complications of the progressive one.
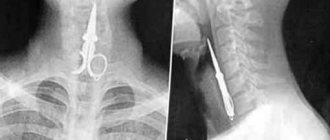
Foreign bodies of the pharynx
Causes.
They are usually localized in the oropharynx and laryngopharynx, where they enter with food, sometimes during manipulations in the mouth (pin, needle, toothpick). The most common foreign body in the pharynx is a fish bone, which penetrates into the loose tissue of the palatine, lingual tonsils, and into the vallecula of the root of the tongue. Less often, foreign bodies (coin, meat bone) are fixed in pear-shaped pockets. Foreign bodies enter the nasopharynx from the nasal cavity (needle), or from the lower parts of the pharynx during vomiting. This occurs more often in children and the elderly.
Symptoms.
Pain in the throat when swallowing with irradiation into the ear (stabbing with a fish bone), discomfort in the projection of a foreign body, sometimes hypersalivation, vomiting, difficulty swallowing.
Complications.
Bleeding, acute pharyngitis, lateropharyngeal abscess, mediastinitis, phlegmon of the pharynx, neck, sepsis, laryngeal stenosis.
First medical aid.
During pharyngoscopy, you should carefully examine the palatine tonsils, moving away the palatine arches; with indirect laryngoscopy, you should carefully examine the root of the tongue, the vallecula of the tongue, and pear-shaped pouches. Finger examination is allowed.
The foreign body is removed with a forceps or tweezers under visual control, after which it is recommended to rinse the oropharynx with an antiseptic solution and adhere to a gentle diet. If the foreign bodies are located in a different location in the pharynx, the patient should be urgently hospitalized in the otorhinolaryngology department.
Specialized assistance.
Foreign bodies of the lingual tonsil, vallecula of the tongue root and pyriform pouches are removed during indirect laryngoscopy in adults and direct hypopharyngoscopy in children using a laryngeal forceps or forceps. Anti-inflammatory therapy is prescribed. If a foreign body is not detected in the pharynx, and the pain syndrome persists, it is necessary to exclude a foreign body of the esophagus. For this purpose, fibrohypopharyngoscopy and esophagoscopy are performed.
Degrees
Depending on the symptoms present, dysphagia is divided into 4 degrees of severity:
- The first is the inability to swallow certain types of solid food.
- Second, the patient eats only soft food; swallowing any hard food is impossible.
- Third, at this stage it is possible to swallow only liquid food.
- The fourth is a severe form with the inability to swallow any food.
Any degree of dysphagia is accompanied by characteristic symptoms and pain in the pharynx or chest. The last severe stage is characteristic, as a rule, of risk grade 4 cancer.
Any type of dysphagia is life-threatening for the patient, so a doctor should be consulted when the first symptoms occur. If your health suddenly worsens at night, you should not postpone your visit to the hospital until the morning. In this case, you can contact the 24-hour Yusupov Hospital, where the necessary medical care will be provided.
Thyroid diseases
Iodine deficiency in the body and hormonal imbalances cause hyper- or, conversely, dysfunction of thyroid cells. In this case, hyperplasia of the thyroid tissue occurs, which can be both diffuse and focal in nature.
The increased size of the gland leads to compression of the esophagus and a feeling of a coma.
Thyrotoxic goiter is characterized by an increase in heart rate, bulging eyes, a sharp decrease in body weight, and nervous system disorders (nervousness, tearfulness). As a rule, the impetus for the development of the disease is given by a severe stressful situation, a nervous shock.
Symptoms of dysphagia
The disease is always accompanied by characteristic symptoms that are difficult to miss. Depending on the location of the pathological process, the manifestations of the disease may vary:
Oropharyngeal dysphagia
This species is characterized by severe cough syndrome, increased salivation and reflux of food into the nasopharynx cavity. When the disease occurs, the patient cannot swallow completely. It takes effort to move food through the esophagus.
The process of eating food is quite painful and causes pain in the oropharynx, as well as in the chest area. Due to the pathological process, appetite is lost, which often leads to exhaustion. Many patients complain of hoarseness and hoarseness.
The symptoms are almost identical to cricopharyngeal incoordination. The only difference is that the second type of disease is more dangerous due to the risk of pathological processes occurring in the lungs.
Esophageal dysphagia
Unlike the oropharyngeal type, the symptoms of food dysphagia are different, since the process of swallowing food is not impaired. The peculiarity of this pathology is that the passage of liquid and solid food through the esophagus is difficult. Among the symptoms, patients experience severe heartburn, pain behind the sternum and in the upper abdomen.
Also, the esophageal type is characterized by frequent belching, after which an unpleasant sour taste occurs in the mouth. In this case, the contents of the stomach are often thrown into the oral cavity and pharynx. Increased regurgitation (movement of gastric contents) occurs when the body bends forward or during sleep. Especially if the last meal was taken less than 1-2 hours before bedtime.
Pain during eating is reduced if the patient drinks water with his food. At the same time, the process of passing the food bolus is facilitated. Both pathologies have identical manifestations - disruption of the gastrointestinal tract, loss of appetite and weight, as well as depression due to the inability to eat properly.
Foreign bodies of the larynx
Symptoms.
When foreign bodies cover more than half of the glottis (live fish, a piece of food, adenoid tissue), fulminant stenosis develops: suffocation occurs, the voice disappears, and consciousness is lost.
Sharp and thin metal foreign bodies (pins, sewing needles, fish bones) initially do not cause severe breathing problems. A convulsive cough occurs, accompanied by sudden difficulty breathing, voice disorder, vomiting, and pain in the larynx are possible. During laryngoscopy, a foreign body can be detected that has stuck into the area of the arytenoid cartilage and aryepiglottic fold. The addition of mucosal edema causes an increase in inspiratory dyspnea.
Complications.
A foreign body obstructing the lumen of the larynx causes fulminant stenosis, and without proper assistance in the next few minutes leads to death. If the larynx is not completely obstructed by a foreign object, acute laryngeal stenosis develops in the coming hours.
First medical aid.
At the IV (terminal) stage of laryngeal stenosis, a conicotomy or cricoconicotomy is performed; at the III (decompensated) stage of stenosis, an urgent tracheostomy is performed. Dehydrating, diuretic, antihistamine, and corticosteroid drugs are administered. The victim is immediately evacuated to the ENT department.
Specialized assistance
consists of immediate removal of the foreign body during indirect (in children) or direct fibrolaryngoscopy with the participation of an endoscopist and an anesthesiologist, carrying out anti-edematous, anti-inflammatory, symptomatic therapy.
Diagnosis of dysphagia
To make an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo a series of clinical examinations. Pathology cannot be detected by visual inspection and palpation. To determine the type of disease and severity, the doctor collects complete information - when the pathology occurred, what symptoms are present, whether there are any chronic diseases, etc. After this, the specialist carefully examines the patient and then prescribes:
- General and biochemical blood test to detect inflammatory processes. FGDS (fibrogastroduodenoscopy) for a detailed study of the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Fecal analysis (coprogram), which allows to identify the remains of undigested food fibers and determine the level of functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Laryngoscopy - instrumental examination of the larynx and vocal cords;
- The examination is carried out for all patients who have complaints of disorders of the ENT organs;
- Ultrasound (ultrasound examination) - examination of the pancreas, biliary tract and other abdominal organs. This is necessary in order to identify or exclude structural changes leading to the formation of dysphagia;
- Irrigoscopy is an X-ray examination of the esophagus with the introduction of a special contrast liquid. The diagnostic method helps determine the degree of narrowing of the esophagus;
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is a study of the brain for the presence of pathologies that may influence the development of dysphagia. It is prescribed if no mechanical obstacles to the passage of food were identified during previous activities.
Diagnostic measures are very important, since the correctness of further treatment and its effectiveness depend on the accuracy of the diagnosis. To eliminate the possibility of an incorrect diagnosis and incorrect prescription of therapeutic measures, you can contact highly qualified specialists at the 24-hour Yusupov Hospital. Many years of experience allows us to accurately determine the type of pathology and eliminate it in the shortest possible time.
Osteochondrosis
Lack of physical activity, prolonged stay in a static position, the presence of excess body weight - all these are predisposing factors in the development of a disease such as osteochondrosis. Damage to the cervical area occurs quite often even at a young age.
It would seem, what is the connection between the condition of the spine and the appearance of a feeling of a lump in the esophagus? And everything is explained by the fact that due to the growth of osteophytes on the vertebrae, compression of the nerve endings occurs. Disorders of the innervation of the thoracic region manifest themselves with characteristic symptoms. Also, this disease is accompanied by severe headaches and stiffness of the cervical spine. To clarify the diagnosis, you need to contact a neurologist.
It is important to note: the sensation of a lump in the esophagus is a sign, a consequence of an underlying disease, which may not be directly related to the organs of the digestive system. What exactly is the cause of these symptoms is determined by the doctor. That is why, in order to avoid complications, you should not self-medicate, but seek specialized medical care as soon as possible.
Treatment of dysphagia
Therapy is prescribed after diagnostic measures have been carried out. Depending on the type of pathology, treatment can be medication or surgical interventions.
Medications
- If the cause of the pathology is increased acidity of the gastric juice, medications are prescribed that reduce its levels - Almagel, Phosphalugel, Zantac.
- In case of pathology caused by bacterial infections, antibiotics are prescribed, the group of which is determined by the doctor. This could be Ceftriaxone, Levobax, Levoximed.
In addition, anti-inflammatory drugs and medications that eliminate the present symptoms - antiemetics, painkillers and other pharmacological groups - can be prescribed.
Operation
Surgery is used if there is no therapeutic effect from drug therapy. Most often, manipulations are performed for dysphagia caused by cancerous tumors, chemical burns of the esophagus, or severe inflammatory lesions. After surgery, the patient requires bed rest in a hospital setting.
Diet therapy
Diet therapy is also important for dysphagia. It involves eating frequent meals in small portions. During the rehabilitation period it is necessary to exclude:
- Alcohol products;
- Fatty, fried, spicy foods;
- Fast food products;
- Smoked meats, saltiness, spices and herbs.
While eating, food must be chewed thoroughly, avoiding swallowing large pieces.
The disease is quite dangerous and requires a competent approach from a certified specialist. In this case, it is important to choose the right doctor, because the final result and prognosis depend on this. With incorrect manipulations, there is a risk of developing aggravating consequences and the pathology becoming severe.
By turning to the Yusupov Hospital, the patient provides himself with safe and effective treatment without complications, which is guaranteed to lead to quick relief from severe pathology. In addition, in the clinic you can undergo a rehabilitation course under the close supervision of a doctor and prevent the recurrence of dysphagia.
Medicines are taken only in consultation with a doctor. Self-medication in all cases aggravates the situation and leads to dangerous complications.
Tracheal foreign bodies
Symptoms.
Foreign bodies (nuts, beans, peas, watermelon seeds), carried away by the inhaled air, can pass through the glottis and become fixed on the mucous membrane of the trachea. This leads to paroxysmal convulsive dry cough, difficulty breathing, chest pain, vomiting during coughing attacks. Symptoms of “balloting” or “popping” of a foreign object in the trachea are detected. The addition of mucosal edema leads to inspiratory dyspnea.
Complications.
Foreign bodies capable of swelling (bean seeds), in combination with reactive edema of the tracheal mucosa, can lead to its stenosis, especially in young children, and the development of tracheitis.
First medical aid.
Prescribe sedatives, dehydrating, antihistamines, corticosteroids, antibiotics, oxygen inhalations. For decompensated stenosis, tracheostomy is performed.
Specialized assistance
consists of urgent removal of a foreign body during upper tracheoscopy under anesthesia using muscle relaxants. If it is impossible to remove a swollen foreign body through the glottis, a tracheostomy is performed on a bronchoscopic tube and removed through an incision in the trachea. Prescribe anti-inflammatory, decongestant, symptomatic therapy.
Treatment of dysphagia in Moscow
Treatment for dysphagia in Moscow is not difficult to find, but when choosing a clinic, it is important to take into account the experience of specialists in this area, since the prognosis directly depends on this. For many years, the Yusupov Hospital has been specializing in pathologies associated with the esophagus and difficulty swallowing.
The clinic is equipped with the latest equipment, offers comfortable conditions, as well as the most favorable atmosphere for patients. The cost of treatment depends on the complexity of the disease and methods of therapeutic measures. Despite the high level of professionalism of specialists and expensive equipment, the Yusupov Hospital offers its patients the most competitive prices in Moscow.
In addition to treating dysphagia of any degree, the clinic offers the following services:
- Treatment of pathologies of a neuralgic nature - stroke, dementia, epilepsy, parkinsonism, myasthenia gravis and other complex diseases.
- Help for patients with cancer - chemotherapy, immunotherapy, rehabilitation, as well as effective pain-relieving procedures.
- Services of highly specialized specialists - cardiologist, pulmonologist, urologist, gastroenterologist, rheumatologist and others.
- Diagnostic examination using the latest devices from leading global manufacturers.
Changes in diet and lifestyle
If you have problems with swallowing, it is necessary to adjust the menu and add soft, easily digestible foods to the diet. It is recommended to use boiled vegetables, lean poultry or fish, and low-fat dairy products. It is necessary to exclude from the diet fatty, salty and hot dishes, fast foods that can cause irritation of the mucous membranes.
It is necessary to exclude carbonated and alcoholic drinks from the diet of patients. You should eat in small portions, several times a day in small portions. You need to swallow food after chewing thoroughly, wash down the food with one or two glasses of clean water.
After eating, it is advised to take a vertical position and ensure complete rest for the body.
Food getting stuck in the throat or dysphagia is a serious disease that can be caused by various factors. Timely treatment of chronic illnesses, proper nutrition and stability of the nervous system will help prevent the occurrence of a pathological condition.