Frequent flatulence, bloating and gas formation, combined with pain in the upper or lower abdomen, are the most common complaints when visiting a gastroenterologist. Not being an independent disease, but only a symptom, this condition may indicate various health problems. It is important to identify the causes of bloating in a timely manner and carry out the correct treatment.
Signs of bloating
Rumbling in the stomach, gas formation, pulling sensations in the left and/or right side after eating or regardless of this, may be accompanied by other symptoms. They indicate possible causes of severe flatulence and require consultation with a doctor:
- colic (cramping pain);
- dyspepsia (belching with air or stomach contents, nausea, feeling of heaviness after eating, rapid satiety);
- constipation, diarrhea or alternation of these conditions;
- feces with particles of undigested food, traces of mucus or blood;
- general weakness, decreased tone, increased fatigue.
Such symptoms in combination with flatulence can indicate many diseases (colitis, pancreatitis, dysbiosis, celiac disease) and require determining why bloating occurs and providing treatment.
“The First Family Clinic of St. Petersburg” invites you to undergo a comprehensive examination and treatment, which is carried out by the best specialists and using the latest equipment and methods. We provide consultations in multidisciplinary centers in the Primorsky and Petrogradsky districts of St. Petersburg.
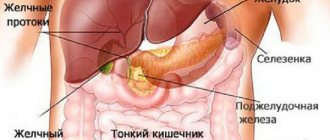
Causes of pain in the right hypochondrium
Biliary dyskinesia
With the hyperkinetic variant of gastric dyskinesia, colicky pain in the right hypochondrium predominates, developing 20-30 minutes after finishing a meal.
A painful attack can be provoked by physical activity and stress. Cramping pain is accompanied by nausea and then vomiting. Unpleasant sensations go away on their own or are relieved with antispasmodics. Between attacks, general health is good, there is no pain under the ribs on the right. Hypokinetic dyskinesia is characterized by constant aching pain, a feeling of heaviness and fullness in the hypochondrium. Eating fatty foods increases pain. When palpating the right upper abdomen, a person feels a dull pain. With this form of dyskinesia, pronounced dyspeptic disorders occur. Patients complain of bitterness in the mouth, belching, and loss of appetite.
Hepatitis
Pain in the right hypochondrium is a typical symptom found in all types of hepatitis. There is a dull soreness and a feeling of pressure in the specified area, usually not associated with food intake or stress. Acute hepatitis is characterized by sharp pain, which is aggravated by palpation of the abdomen in the hypochondrium area. The pain syndrome is supplemented by dyspeptic disorders, signs of intoxication, and jaundice.
Chronic cholecystitis
When the gallbladder is inflamed, moderate pain is felt in the hypochondrium, which persists for several days and even weeks. Irradiation of the pain syndrome to the scapula, lower back, right shoulder girdle or shoulder is typical. Eating fatty and spicy foods and carbonated drinks contributes to increased pain. The disease occurs with periods of remission, during which the pain disappears, and patients are only bothered by discomfort or heaviness under the right costal arch.
With acalculous cholecystitis, the symptoms are less pronounced, the general condition remains satisfactory. As a rule, dyspeptic disorders come to the fore. In chronic calculous cholecystitis, in addition to dull pain, severe painful attacks may occur. In this case, the pain becomes cramping and sharp. In addition, severe nausea, vomiting with bile, and low-grade fever are noted.
Hepatic colic
Symptoms are due to exacerbation of cholelithiasis. A person experiences excruciating pain, which can be cramping, cutting, tearing or burning in nature. At the time of an attack, the patient lies on his side, tucking his legs to his stomach, or rushes around the bed to find a comfortable position. Pathognomonic irradiation of painful sensations into the right shoulder and scapula. The clinical picture is complemented by nausea, vomiting bile, and flatulence.
Pain in the right hypochondrium
Biliary peritonitis
Initially, sharp pain appears in the right hypochondrium with irradiation to the corresponding scapula and shoulder. The patient lies motionless on his side, with his knees pulled towards the abdominal wall. When palpating the right abdomen, the pain intensifies. At the second stage of bile peritonitis, the pain syndrome persists, repeated vomiting occurs, and intoxication increases. If a person does not seek medical help, a terminal phase begins when the pain subsides due to the death of nerve endings.
Parasitic infestations
With echinococcosis of the liver, the pain syndrome gradually increases. At first, the patient is worried about heaviness and discomfort, especially after eating large amounts of food. An increase in the size of the hydatid cyst is accompanied by increased pain. The development of symptoms after physical activity is typical. Pain in the right hypochondrium also occurs with other infections: amebiasis, opisthorchiasis, ascariasis.
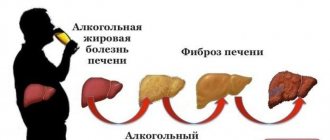
Cirrhosis of the liver
It is asymptomatic for a long time. Patients experience periodic dull pain in the right abdomen, provoked by diet disorders or alcohol consumption. There is rapid satiety and heaviness under the ribs after finishing a meal. When cirrhosis is complicated by portal hypertension, pain spreads to the epigastric and periumbilical areas.
Liver cancer
Painful sensations in the right hypochondrium are caused by an increase in the size of the tumor and stretching of the liver capsule. They bother a person constantly and are not associated with external provoking factors. Typical for oncological pathology is a dull pain, a feeling of fullness and heaviness in the right side. With malignant degeneration of the liver tissue, progressive weight loss, symptoms of dyspepsia, anemia and hemorrhagic syndrome are observed.
Hemolytic anemia
Constant dull pain on the right under the ribs is characteristic of toxic anemia caused by the action of toxic substances or medications. Less commonly, abdominal pain under the costal arch on the right is a sign of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria, autoimmune damage to red blood cells. Severe pain in the liver area is possible with exacerbations of hereditary anemia - membranopathies, fermentopathy, hemoglobinopathies.
Heart failure
Discomfort and pain in the right hypochondrium are typical for dysfunction of the right ventricle of the heart, when blood stagnates in the venous bed. Patients complain of distension in the abdomen, which worsens with active movements, after eating. In addition to pain, swelling of the lower extremities, shortness of breath and fatigue during physical activity, and swelling of the neck veins are determined.
Referred pain
Often, when the pathological process is localized in the right iliac region, irradiation of pain in the hypochondrium is observed, which is due to the peculiarities of innervation. The pain is sharp, stabbing, dull or squeezing in nature. If the symptom is caused by surgical pathology, unbearable painful sensations develop, sharply intensifying when pressing on the abdominal wall. The most common causes of radiating pain:
- Appendicitis.
This localization of pain is typical for the retrocecal location of the appendix. Intense pain is felt in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen, nausea with vomiting, and stool disturbances. - Gynecological diseases.
In women, pain on the right side of the hypochondrium can be a sign of exacerbation of endometritis or right-sided adnexitis. Often the pain syndrome is caused by surgical pathologies: disrupted ectopic pregnancy, apoplexy of the right ovary. - Colon damage.
Pain in the right hypochondrium sometimes occurs with colitis and Crohn's disease. They indicate an exacerbation. Pain may radiate to the right into the hypochondrium in patients with polyposis and colon cancer.
Rare causes
- Gallbladder diseases
: cholesterosis, polyps, malignant tumor. - Vascular pathologies
: Budd-Chiari syndrome, veno-occlusive disease, liver infarction (ischemic hepatitis). - Rare liver diseases
: hepatoptosis, perihepatitis. - Damage to the gastroduodenal zone
: acute and chronic gastritis, gastroduodenitis, peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum. - Complications of pregnancy
: gestosis, cholestasis of pregnant women.
Diagnosis of bloating and gas formation
The causes and treatment of gas and bloating are closely related concepts. Therefore, first of all, it is necessary to conduct an examination, the purpose of which is to evaluate the functions of the gastrointestinal tract and hepatobiliary system, and to detect the source of the problem. The list of diagnostic measures may include:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs, liver with determination of the functions of the gallbladder;
- gastrofibroduodenoscopy;
- X-ray examination with contrast;
- intestinal endoscopy (sigmoidoscopy, colonoscopy);
- laboratory tests of blood, urine and feces.
Special attention is paid to collecting anamnesis - the patient’s diet and daily habits can provide answers to many questions regarding the causes of bloating and gas formation and the elimination of this condition.
Although flatulence is not a disease, but a manifestation of dysfunction of the digestive system, it may indicate diseases of other systems and organs. A decrease in the quality of food digestion and absorption of nutrients due to pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract has a direct impact on overall health. Therefore, a connection is often identified between prolonged flatulence and, for example, headaches, hyperhidrosis or sexual dysfunction in men. This requires examination by specialized specialists (urologist-andrologist, endocinologist, cardiologist).
What to do if pain, spasm, bloating and flatulence interfere with normal life?
Sources of information *Excluding anaphylaxis 1A.R. Babaeva, O.N. Rodionova. Functional diseases of the gastrointestinal tract: current state of the problem // Bulletin of the Volgograd Medical University, 2006, No. 2, p. 3-12. 2 Ivashkin V.T., Shelygin Yu.A., Baranskaya E.K., Belousova E.A., Beniashvili A.G., Vasiliev S.V., Golovenko A.O., Golovenko O.V., Grigoriev E.G., Kostenko N.V., Lapina T.L., Loranskaya I.D., Lyashenko O.S., Maev I.V., Poluektova E.A., Rumyantsev V.G., Timerbulatov V. M., Trukhmanov A.S., Fomenko O.Yu., Khalif I.L., Chashkova E.Yu., Sheptulin A.A., Shifrin O.S., Yanovoy V.V. Clinical recommendations of the Russian Gastroenterological Association and the Association of Coloproctologists of Russia for the diagnosis and treatment of irritable bowel syndrome. Ros journal gastroenterol hepatol coloproctol, 2017; 27(5): 76-93. 3World Gastroenterology Organization (WGO). World Gastroenterology Organization Global Guideline: Irritable bowel syndrome: a global perspective. Munich (Germany): World Gastroenterology Organization (WGO); 2009. Available at https://guideline.gov/content.aspx id=15232&search=irritable+bowel+syndrome. Accessed July 15, 2020. 4 Yu.V. Vasiliev. Irritable bowel syndrome: modern aspects of diagnosis and therapy // Medical Council, 2014, No. 4, pp. 72-77. 5 Instructions for medical use of the drug Duspatalin® (Mebeverine 135 mg), film-coated tablets, dated 07/13/2021. 6 UK National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. Irritable bowel syndrome in adults: diagnosis and treatment of irritable bowel syndrome in primary healthcare. Clinical guidelines, March 2022. 7E.P. Yakovenko et al. Abdominal pain: mechanisms of formation, rational approach to the choice of therapy. RMJ supplement “Diseases of the Digestive Organs” No. 2 dated 01.09.2009. P.48. 8Ivashkin V.T., Maev I.V., Baranskaya E.K. et al. Recommendations of the Russian Gastroenterological Association for the diagnosis and treatment of cholelithiasis RZHGGK 2016; 3:64-80 2.
RUS2208248 (v1.0) Registration number: LP-001454. The material was developed with the support of Abbott Laboratories LLC in order to inform patients about the disease. The information in the material does not replace the advice of a healthcare professional. Contact your doctor.
Treatment methods
What to do with bloating and stomach pain is determined by the results of the examination, medical history and individual health characteristics of the patient.
When treating diseases with bloating and gas, the doctor selects an individual therapy program that is aimed at:
- to eliminate symptoms of the disease;
- to eliminate the underlying pathology that led to flatulence;
- to restore the functions of the gastrointestinal tract and prevent relapses of the disease.
Considering that intestinal health is directly related to the health of the body as a whole, therapy may also include treatment of other systems and organs if the underlying disease has managed to affect their condition. Thus, in case of disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, treatment of anemia, metabolic disorders and other conditions caused by disorders of digestion and absorption of nutrients by the intestinal walls is often required.