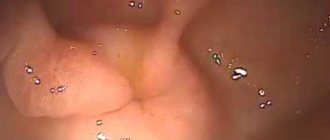
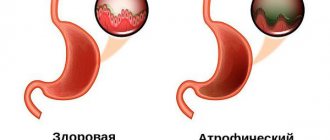
Polyps are growths of the glandular epithelium and the underlying connective tissue. They are small papillae or round formations that rise above the mucous membrane. Hyperplastic polyp of the colon mucosa is a precancerous disease. Doctors at the proctology department conduct a comprehensive examination of patients who are suspected of having a hyperplastic type colon polyp, using modern equipment from the world's leading manufacturers.
If a hyperplastic colon polyp is identified, does it need to be removed? Proctologists at the Yusupov Hospital are guided by the following axiom: all identified colon polyps must be removed. The incidence of colorectal cancer developing from hyperplastic polyps more than 2 cm in diameter is 35-53%. For polyps with a diameter of more than 3 cm, the probability of their transformation into a cancerous tumor is 100%.
The risk of transforming a benign neoplasm into a malignant tumor is too high to neglect the recommendations of proctologists and waste precious time. An exception to the rule is the detected single polyps up to 0.5 cm in diameter. In this case, doctors take a wait-and-see approach with repeat endoscopy. The treatment of choice for patients with solitary hyperplastic colon polyps is endoscopic polypectomy. If the neoplasms are located no higher than 5-7 cm from the edge of the anus, doctors at the proctology department perform transanal resection.
What is lymphoid hyperplasia
The mucous membrane of the digestive tract, including the ileum, is susceptible to the development of a number of diseases. Lymphoid hyperplasia manifests itself in the form of rapid proliferation of mucosal cells.
As a result of the spread of the pathological process, follicular tissue begins to form. In medicine, local and diffuse forms are distinguished. In the first case, the growth has a benign course.
The diffuse form is characterized by the appearance of small follicles. They are malignant.
Pathology is established in adults and children. Experts have not established a connection between ileal disease and gender or age category. There was also no relationship with the disease and eating habits.
Scientists believe that the main cause of lymphoid hyperplasia of the ileum is endocrine disorders.
Treatment methods for hyperplasia
An increase in tissue volume or proliferation is called hyperplasia or metaplasia. Metaplasia is a tumor growth of cells with signs of malignancy.
Hyperplasia is the same cell growth, but it is distinguished by the benign nature of the process: the overgrown tissues have the correct intracellular structure and chromosomal composition. Only if hyperplasia is started will the process become malignant.
Treatment of hyperplasia can be medication or surgery. The method is selected depending on the type of hyperplasia, its location, and stage.
The article will discuss treatment methods for the most common types of disease, such as endometrial hyperplasia, benign prostatic hyperplasia, thyroid hyperplasia, and lymphoid hyperplasia.
Types and methods of treatment of endometrial hyperplasia
The endometrium in a healthy state consists of a base (stroma) and a gland. Therefore, depending on which endometrial tissue grows, the following types of disease are distinguished:
- glandular hyperplasia;
- cystic hyperplasia;
- glandular cystic hyperplasia;
In addition, a new classification of the disease was recently adopted: simple hyperplasia and atypical. Atypical, in turn, is divided into two forms: diffuse hyperplasia and focal hyperplasia.
The standard treatment regimen for endometrial hyperplasia is a combination of surgery and hormonal therapy. But since we are talking about a disease of the most important reproductive organ, the woman’s age is also taken into account. If the stage and type of hyperplasia make it possible to stop cell growth and reduce the volume of overgrown tissues only with the help of hormonal drugs, surgical intervention is avoided.
First, let's look at the standard approach to treating this type of disease as glandular hyperplasia. Treatment in most cases involves curettage of the uterine cavity, which is both a diagnostic and therapeutic procedure. Hormonal therapy for the disease glandular hyperplasia consists of prescribing combined contraceptive drugs (medicine Regulon) or gestagens. It has been established that glandular hyperplasia responds well to the gestagenic drug Duphaston. Treatment is often limited to the prescription of this drug alone, and it lasts at least three months. Contraceptives are prescribed in courses of 21 days, with control examinations carried out in between.
Cystic hyperplasia and glandular cystic hyperplasia are treated in the same way. Often, in the absence of obvious abnormalities, cystic hyperplasia and glandular cystic hyperplasia are considered to be the same disease.
Simple hyperplasia is a proliferation of tissues in which atypical cells are not found in them. Simple hyperplasia is a benign process with a positive prognosis. Simple hyperplasia, when treated promptly, is often successfully treated with hormones.
Atypical diffuse hyperplasia is a uniform proliferation of endometrial cells. Atypical focal hyperplasia is the proliferation of cells in a limited area of the uterine cavity.
Both diffuse hyperplasia and focal hyperplasia of an atypical nature are considered precancerous conditions; in most cases they require surgical intervention - either the entire uterine cavity is curetted if diffuse hyperplasia is diagnosed, or a separate altered area if focal endometrial hyperplasia is observed. Read more about drug treatment for endometrial hyperplasia. Regulon is usually prescribed to women of childbearing age - up to 35 years of age and to teenage girls with complaints of irregular or heavy menstruation. As already mentioned, the drug is taken in the standard course - 21 days. To stop uterine bleeding, the patient is prescribed to take 2-3 Regulon tablets per day. If the bleeding does not stop, curettage of the uterus is performed.
Duphaston for such a disease as benign endometrial hyperplasia is prescribed to women both during childbearing age and during menopause. The drug is taken in courses of 3-6 months, from days 16 to 25 of the menstrual cycle.
Women during premenopause can be prescribed the drug Buserelin. The medicine inhibits ovarian function. This process is reversible (the ovaries return to normal after 2-3 weeks), but side effects such as menopausal symptoms are usually poorly tolerated by patients from a psychological point of view, so they try not to prescribe Buserelin to younger women.
In addition to hormonal therapy, a woman with endometrial hyperplasia must undergo restorative treatment. Vitamins, iron supplements, medications with a sedative effect are usually prescribed, acupuncture and physiotherapy are practiced.
If hyperplasia does not respond to surgical and hormonal treatment, and after a while it appears again, the woman is advised to have the uterus removed.
In order to prevent such serious consequences, it is necessary to undergo regular examinations by a gynecologist and be sure to seek medical help if the following signs of endometrial hyperplasia are detected:
- menstrual irregularities;
- heavy and/or painful menstruation;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- infertility;
- intermenstrual bleeding or spotting.
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)
To begin with, it should be noted that prostatic hyperplasia is always a benign process. With timely detection of the disease and prescribing adequate treatment, it is possible to prevent the degeneration of adenoma (the second common name for BPH) into a malignant neoplasm.
Therefore, a man should pay attention to the following signs of hyperplasia:
- frequent urge to urinate, incl. at night time;
- the stream of urine becomes intermittent or weaker than usual;
- urination begins with difficulty;
- urine drips for a long time at the end of urination;
- after urination there is a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder.
Benign prostatic hyperplasia in the initial stage is amenable to drug treatment. There are two types of medications used to treat BPH:
- such that they reduce the size of an enlarged prostate;
- such that they relax the smooth muscles of the prostate, urethra and bladder neck.
Surgery on the prostate is resorted to if the following signs of hyperplasia are detected:
- serious urinary retention - when even catheterization does not help, or there is no way to use it;
- renal failure secondary to BPH;
- recurrent urinary tract infection developing against the background of BPH.
In addition, resection of the prostate gland is indicated for patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia if they have kidney stones, scar processes in the pelvis, neurogenic disorders, acute inflammation of the lower urinary tract, as well as hypersensitivity to drugs.
Hyperplasia of the thyroid gland
The functioning of the thyroid gland is regulated by the endocrine system. Hyperplasia of this organ begins when its function deteriorates, when the gland stops producing thyroid hormones. This often occurs due to iodine deficiency in food and water.
The growth of thyroid tissue can be different, but most often patients are treated about the appearance of nodules in the gland.
Nodular hyperplasia of the thyroid gland is dangerous because the resulting nodules often degenerate into tumors. The most dangerous is considered to be nodular hyperplasia of the gland, in which solitary (single) nodes are formed.
Signs of thyroid hyperplasia are an increase in size of the organ (which is first felt upon palpation, and some time later is easily determined visually), pain, difficulty swallowing and breathing, and hoarseness. All these symptoms are explained by the fact that the gland, increasing, compresses the nerves, blood vessels, and respiratory organs.
As we have already said, nodular hyperplasia is a fairly serious disease, therefore, the sooner the endocrinologist makes a diagnosis, the better the prognosis for hyperplasia. First, nodular hyperplasia is determined by ultrasound - thanks to this examination method, nodules in the gland can be seen. The malignancy of the process can be excluded only after a biopsy - the gland is pierced with a thin needle, the contents of the node(s) are taken and sent for laboratory histological examination.
In addition, a person who is diagnosed with nodular hyperplasia must undergo a gland scanning procedure with radioactive iodine. Such an examination makes it possible to identify “cold” nodules that are prone to degeneration into cancerous tumors.
With timely contact with an endocrinologist and the absence of “cold” nodes, nodular hyperplasia can be successfully treated with drugs containing thyroid hormones.
Nodular hyperplasia of the thyroid gland, which provokes the appearance of “cold” nodes, is subject to surgical treatment. The operation is also indicated if, as a result of histological examination of the contents of the nodes, poor or questionable results are obtained.
If we are talking about surgery, a patient diagnosed with nodular hyperplasia is first prescribed only removal of the nodes. During the operation, an additional histological examination of the gland tissue is performed, and if cancerous (atypical) cells are found in them, it is completely removed, along with the nearby lymph nodes.
Prevention of a disease such as nodular hyperplasia of the thyroid gland is the daily use of iodine. The daily iodine intake for adults is 200 mcg, for children – 100 mcg, for pregnant and lactating women – 250 mcg.
Lymphoid hyperplasia
Lymphoid hyperplasia is a pathological proliferation of lymphocytes in the lymph nodes. Lymph nodes perform a protective function - they suppress the growth of viruses, bacteria, and the spread of malignant processes. Most often, the enlargement of nodes is a response to inflammation, but in some cases the lymph nodes themselves are involved in the inflammatory process - this is lymphoid hyperplasia.
The location of enlarged lymph nodes can often indicate the presence of serious diseases. For example, hyperplasia of the lymph nodes in the groin can be caused by cancerous tumors in the legs or cancerous metastases in the external genitalia. Pathologically enlarged nodes in the neck appear due to tumors on the face or in the jaw bones.
Lymphoid hyperplasia is treated comprehensively. First, a full examination is carried out to identify the cause of such severe inflammation of the nodes. Based on the results, conservative or surgical treatment may be prescribed. Conservative treatment of the disease lymphoid hyperplasia is selected depending on the location of the inflamed nodes. If the stomach is affected, I can prescribe probiotics, hepatoprotectors; if the adenoids are inflamed, desensitizing drugs, antiseptics, as well as laser therapy, vibroacoustic therapy, and ultraviolet irradiation are prescribed. If lymphoid hyperplasia is caused by intestinal disease, corticosteroids may be prescribed. Thus, we can conclude that conservative treatment of lymphoid hyperplasia is aimed at relieving inflammation. If this does not produce results and the growth of lymph node tissue does not stop, surgery is prescribed to trim or remove nodes and other affected tissues or organs.
First of all, it should be remembered that lymphoid hyperplasia is still a benign process, and symptoms such as enlarged nodes, their pain, and persistent high temperature require medical attention. Surgery and complications in the form of degeneration of overgrown tissue into cancerous tumors can be avoided if you undergo a timely examination.
The same can be said about all types of hyperplasia that are described here. In most cases, you can get by with taking medications and stopping pathological processes that occur in the body under the influence of external factors, due to poor nutrition, increased trauma, etc.
Hyperplasia, treatment
Stages
Pathology has several stages of progression, each of which has its own characteristics. The degree of spread of hyperplasia is determined based on the diagnostic results.
Stage 0
Foci of hyperplasia are small in size and are not accompanied by symptoms. In some cases, epithelial proliferation is completely absent, but an inflammatory process is detected.
Stage 1
There are no clinical manifestations. Hyperplasia has a diffuse form. The pathological process does not affect large areas of tissue.
Stage 2
Foci of hyperplasia increase in size, but have clear contours. There is no merger between them.
The occurrence of mild symptoms that resemble symptoms of other gastrointestinal diseases is determined.
Stage 3
Symptoms of lymphofollicular hyperplasia are increasing. The foci of the pathological process begin to merge, uniting into conglomerates.
Stage 4
Hyperplasia is accompanied by ulcerative and necrotic lesions. Lack of therapy causes complications to develop. The development of metastases is observed when the process has a malignant course.
When carrying out diagnostic measures, a change in the shade of the mucous membranes is determined. A vascular pattern is revealed on the surface of the membrane. The changes are irreversible.
Causes
Based on research results, it has been established that predominantly lymphofollicular hyperplasia of the ileum occurs against the background of incomplete treatment of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Experts also identify such provoking factors as hormonal imbalance, hereditary predisposition, and long-term use of certain groups of medications.
The cause of the development of hyperplasia can be constant and prolonged exposure to carcinogens. They irritate the gastrointestinal mucosa.
Low immunity becomes a provocateur for the development of pathology. When the body's defenses are unable to cope with certain processes in the body, inflammation occurs.
Prevention of duodenal cancer
The basis for the prevention of tumor processes in the intestines is a healthy diet, giving up bad habits, regular examinations with a doctor, and timely treatment of any digestive disorders.
Sources:
- Barnhill M. Tripartite differentiation in a carcinoma of the duodenum / M. Barnhill // Cancer. - 1994. - Vol. 73. - P. 266-272. Nielsen M. Duodenal carcinoma in MUTYH-associated polyposis / M. Nielsen // J. Clin. Pathol. - 2006. - Vol. 11. - No. 59. - P. 1212-1215.
- Ershov V.V. Two-stage treatment of complicated duodenal cancer / V.V. Ershov [et al.] // Modern technologies in medicine. - 2012. - No. 2. - P. 146-147.
- Kovalenko V.L. Observation of primary duodenal cancer complicated by severe anemia / V.L. Kovalenko [and others] // Bulletin of surgery named after I.I. Grekova. - 2011. - T. 170. - No. 1. - P. 78-81.
- Encyclopedia of Clinical Oncology: a guide for practicing physicians / ed. M.I. Davydova, G.L. Vyshkovsky. - M.: RLS, 2005. - 1536 p.
Information verified by an expert
Mikhailov Alexey Gennadievich operating oncologist, doctor of the highest qualification category, Ph.D. experience: 21 years
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
Diseases as causes of hyperplasia
The disease can also occur as a result of violations of the integrity of the ileal mucosa. This can be either pathological or mechanical damage.
Lymphofollicular hyperplasia, in which the pathological process affects the ileal mucosa, occurs against the background of gastritis. The causes of the development of pathology are inflammatory diseases of the mucous membranes. Such processes are considered the main provocateurs of hyperplasia.
Ulcerative lesions can also provoke uncontrolled division of cells in the ileal mucosa.
Among the causes are infectious and viral diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Pathological microorganisms have a negative effect on the mucous membrane. Hyperplasia can also occur against the background of autoimmune diseases.
Clinical picture
The symptoms of the disease are varied, but do not appear in the first stages. The intensity of manifestations depends on the extent of spread of the pathological process.
First signs
Hyperplasia, like many diseases of this type, does not show specific symptoms in the early stages of its development. During this period, signs appear that the patient often does not pay attention to.
Why can our articles be trusted?
We make health information clear, accessible and relevant.
- All articles are checked by practicing doctors.
- We take scientific literature and the latest research as a basis.
- We publish detailed articles that answer all questions.
As a result of the development of inflammation and excessive uncontrolled cell division, weakness is observed.
Patients may complain of increased bowel movements, increased body temperature, and fatigue. Patients do not always pay attention to such symptoms or mistake them for simple fatigue or indigestion.
Further development
As the pathological process spreads, ileal hyperplasia is characterized by severe symptoms.
First of all, there is a violation of the stool. The urge to defecate occurs up to 7 or more times a day. The stool contains various impurities in the form of blood and mucus.
When the process affects a large area of the mucosa, painful sensations occur. They are abdominal in nature.
At stage 2, they occur after eating or physical activity. As the process spreads, it becomes permanent.
Patients note a deterioration in appetite, against the background of which weight begins to rapidly decrease. Discomfort occurs in the stomach area, bloating appears, and gas formation increases.
Patients experience apathy and depression, and weakness increases. Over time, the condition worsens.
Duodenal cancer: main symptoms and signs
Typical symptoms of duodenal cancer are practically not detected in the early stages. The disease can be asymptomatic for quite a long time. For this reason, from the first signs of the disease to surgical intervention, it takes from 6 to 12 months Source: Kovalenko V.L. Observation of primary duodenal cancer complicated by severe anemia / V.L. Kovalenko [and others] // Bulletin of surgery named after I.I. Grekova. - 2011. - T. 170. - No. 1. - P. 78-81.. A tumor can be identified at this time by chance, during examinations for other diseases. In a later stage, pain may occur with duodenal cancer. But they do not always alert the patient, as they can be mistaken for signs of indigestion or overeating. The pain is dull and diffuse, usually localized in the upper abdomen, under the ribs or epigastric region. Painful sensations may occur at night or after prolonged fasting. As the disease progresses, intoxication with tumor decay products may occur. This is manifested by weight loss, severe pallor, and constant weakness.
Manifestations of cancer largely depend on the stage of cancer, the size of the lesion and additional pathologies that complicate the condition. In later stages, cancer may manifest itself with the following symptoms:
- apathy, depression, weakness with fatigue, lethargy;
- sleep disturbances with drowsiness or insomnia;
- dizziness and headache;
- a sharp decrease in appetite, which leads to sudden weight loss, loss of up to 10% of weight or more;
- pale skin with a waxy or bluish tint, yellowness of the sclera;
- dryness of the mucous membranes of the mouth, eyes and nose;
- constant low-grade fever;
- sweating at night;
- persistent anemia;
- nausea, vomiting, abdominal discomfort;
- frequent colds, decreased immunity.
If the tumor tissue disintegrates, blood vessels are damaged and bleeding begins, black stool may appear.
Diagnostics
It is impossible to establish an accurate diagnosis based on the results of the examination, since the symptoms of ileal hyperplasia are similar to other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
After studying the medical history, determining the symptoms and the time of their occurrence, the specialist prescribes a number of instrumental and laboratory diagnostic methods.
Endoscopy
If there is a suspicion of pathologies of the digestive system, endoscopy is the main and most informative method of research.
The procedure is carried out not only for the purpose of surgical intervention, but also for diagnostic purposes. The technique involves the use of a special endoscope, which is inserted into the intestine.
A camera and a lighting device are attached to the end of the apparatus. The image is transferred to the monitor. Thanks to this, the doctor can conduct a visual examination of the intestinal mucosa in real time.
Endoscopy allows you to determine the extent of hyperplasia, the depth of the lesion and the stage of development of the disease.
After the procedure, discomfort occurs, which goes away on its own after some time. Complications include bleeding and perforation of the intestinal walls. But consequences after endoscopy occur in rare cases.
Biopsy
The specialist prescribes a biopsy of the affected tissue to determine the presence of cancer cells.
The sample collection procedure is carried out during endoscopy. The obtained samples are sent for histological examination.
MRI or CT
Computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging is prescribed to confirm a previously established diagnosis.
The procedure can be performed with or without contrast material. It allows you to determine the exact location of the pathological process. The substance is administered before the study.
MRI and CT allow for layer-by-layer scanning of tissues and determine the depth of damage to the pathological process.
Radiography
An X-ray examination is prescribed to determine the extent of the process and identify other changes.
X-ray is completely safe for health and allows you to obtain reliable data.
Ultrasound
The use of ultrasound makes it possible to determine the cause of hyperplasia of the ileal mucosa.
The study is completely painless and allows you to quickly obtain reliable information. Based on ultrasound, a specialist can identify the root cause of the process of excessive growth of the mucous membrane.
Laboratory research
The patient is prescribed blood, urine and stool tests. Studies can determine the presence of inflammation and infectious diseases.
Changes are observed in the composition of the blood in certain pathologies that can cause the development of the disease.
Urine contains more calcium, protein compounds and other substances. With the help of laboratory tests, a specialist can determine the cause of hyperplasia and determine the course of therapy.
Types of colon polyps
Hyperplastic polyp of the colon - what does it mean? Hyperplastic polyps account for 28 to 42% of all colon polyps. Most often they are localized in the left half of the colon, mainly in the lower sections, are multiple in nature and have no clinical manifestations. During an endoscopic examination, proctologists in most cases identify flattened “sessile” formations measuring 0.1–0.5 cm, rarely 1.0 cm, with a pearl-colored surface.
There are three histological variants of hyperplastic polyps:
- Rich in goblet cells;
- Microvesicular;
- Poor mucin.
Most hyperplastic polyps show no signs of cellular atypia. The diameter of small hyperplastic polyps of the large intestine does not exceed 0.5 cm. They are of normal color, slightly rise above the level of the mucous membrane, and have a soft consistency. These formations are characterized by elongation and cystic expansion of the crypts.
In such polyps, the epithelium is saw-toothed and the number of goblet cells is reduced. Morphologically, not being true adenomas, miliary hyperplastic polyps during histological examination often reveal a picture of atypia and proliferation of the epithelium with an increase in the amount of chromatin in the nuclei and an abundance of cell division (mitoses).
Benign glandular polyps, or tubular adenomas, are pedunculated or sessile hyperplasia of the mucosa. These are true adenomatous polyps. Upon examination, they are close in structure to the surrounding mucous membrane of the large intestine, but have a denser consistency, move along with the mucous membrane, and rarely ulcerate or bleed.
Adenomatous polyps are represented by glands that are lined with homogeneous glandular epithelium. Their cystic expansion is often noted. According to the degree of morphological differentiation of the epithelium, three groups of tubular adenomas are distinguished: with mild, moderate and significant dysplasia. With electron microscopy, morphologists often detect changes in them that are typical of cancer cells.
Juvenile polyps are not hyperplastic neoplasms. They lack enlargement of glands and changes in the glandular epithelium. These formations are quite large, sometimes hanging into the intestinal lumen on a long stalk, smooth, bright red or cherry color.
Treatment
If lymphofollicular hyperplasia of the ileal mucosa is detected, the specialist prescribes a course of therapy in accordance with the degree of development of the pathology.
Self-medication is dangerous with complications!
Attention
Despite the fact that our articles are based on trusted sources and have been tested by practicing doctors, the same symptoms can be signs of different diseases, and the disease may not proceed according to the textbook.
Pros of seeing a doctor:
- Only a specialist will prescribe suitable medications.
- Recovery will be easier and faster.
- The doctor will monitor the course of the disease and help avoid complications.
find a doctor
Do not try to treat yourself - consult a specialist.
Treatment may be through the use of medications or surgical removal. Patients are also prescribed a special diet.
Drug therapy
Medicines are prescribed according to the underlying cause of the disease.
If the causative agent is bacteria, the use of antibiotics is indicated. They will suppress the growth of microorganisms and stop the process of tissue proliferation.
Restorative and enveloping agents are also used to protect the mucous membrane.
Surgical intervention
In severe cases, surgical removal of the affected area or part of the ileum is prescribed.
The operation can be performed endoscopically or laparoscopically. If there are contraindications to the use of techniques or the impossibility of their use, the specialist uses classic removal using a scalpel.
The advantages of laparoscopy or endoscopy are a short recovery period and the absence of large scars. After the operation, 3-5 days later the patient can go home. Complications occur in rare cases.
Classic resection is carried out by making an incision in the abdominal cavity, leaving scars and scars on the body.
Chemotherapy or radiation therapy
The methods are aimed at destroying cancer cells and reducing the size of the focus of the pathological process.
Chemotherapy drugs and radioactive treatment also have a negative effect on healthy tissue. As a result, complications and side effects occur.
The duration of courses and their number are determined by the attending physician based on the results of instrumental and laboratory diagnostic methods. The techniques are used only when a malignant process is detected.
Treatment of rectal polyps
Doctors at the proctology department of the Yusupov Hospital use the following methods of endoscopic treatment of rectal polyps: endoscopic loop polypectomy and endoscopic loop resection of the mucous membrane. During endoscopic loop polypectomy, the doctor places a diathermic loop at the base of the formation, tightens it and cuts it off, alternating coagulation and cutting modes.
During endoscopic loop resection of the mucous membrane, after marking the boundaries of the formation, the proctologist creates a hydraulic cushion to reduce the risk and excise the formation as radically as possible. The doctor injects a solution of glycerol, which is tinted with methylene blue, under the mucous membrane. After infiltration of the submucosal layer, it lifts the neoplasm and cuts it off using a diathermic loop. In the first case, there is a high risk of bleeding during surgery, and in the second case, there is a high risk of perforation of the rectal wall.
The method of choice for pedunculated tubular neoplasms is simultaneous electroexcision of polyps, which doctors perform during sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy. Radical methods of treating villous tumors of the rectum include transanal muco-submucosal or full-thickness resection of the intestinal wall. Taking into account the extensive experience of the doctors of the proctology department, they perform this operation using transanal endoscopic microsurgery.
Diet
Diet is important in the treatment of hyperplasia. The goal of changing your diet is to reduce the load on your intestines.
Patients should avoid heavy and unhealthy foods. During the treatment period, it is forbidden to eat fatty and fried foods. Vegetables and fruits should be consumed daily.
It is necessary to avoid fatty meats and fish. It is recommended to steam, boil, and stew dishes.
The number of meals per day should be at least 6 times. At the same time, portions should be small so as not to overload the intestines.
Duodenal cancer: prognosis
With annual medical examinations and preventive examinations, cancer can be detected at an early stage. In the first stage, up to 98% of patients survive after full treatment. They can be completely cured and have favorable prognoses for life and health.
In the second stage of cancer, survival rate over 5 years reaches 70-90%, by the third stage it decreases to 40-70%, but the prognosis is unfavorable, disability is possible. At the fourth stage, no more than 30% of patients survive for 5 years. The disease is extremely difficult to treat.
Possible complications
Benign lymphoid hyperplasia is rarely accompanied by complications. But a malignant process, if left untreated, can cause certain consequences.
In patients in the last stages, there is a disruption in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. The pathological process extends beyond the ileum and affects neighboring organs.
The most dangerous consequence of the disease is metastasis. Cancer cells enter the blood and spread throughout the body. They often form in the liver, lungs, and brain.
Metastases cause dysfunction of the affected organs, which leads to the development of cardiac, renal, liver and pulmonary failure. Over time, death occurs.
Classification of duodenal cancer
Approximately 80% of all tumors are exocrine cancers
. Its main form is adenocarcinoma. Less commonly, an undifferentiated form of exocrine cancer occurs. Most often, this type affects the peripapillary part of the intestine; the tumor grows circularly into the wall, narrowing its lumen, which leads to intestinal obstruction. Less commonly, exophytic growth occurs with the development of bleeding. The development of both single and multiple primary formations is possible.
About 5% are endocrine tumors (apudomas)
. They can be in the form of carcinoid, insulinoma, VIPoma, gastrinoma, glucagonoma. They are usually detected in the middle third of the intestine. They grow slowly and infiltrate tissues.
Non-epithelial tumors may also develop
. The most common of them is leiomyosarcoma, reaching a size of 8 cm or more. Less common is fibrosarcoma, reaching 3 cm, which can have low and high differentiation. Malignant neuromas, ganglioneuroblastomas or neurofibrosarcomas are also possible, and are especially common in children.
From vascular tumors
Lymphosarcoma is the most frequently recorded tumor, ranking second after exocrine cancer.
Forecast
Further prognosis depends on the nature of the pathology. Benign hyperplasia does not pose a threat to the patient's life.
But with a malignant process, life expectancy is determined depending on the degree of development of the disease. Timely therapy allows for a more favorable prognosis. But with severe damage, it is impossible to achieve complete recovery. The five-year survival rate is no more than 5%.
Lymphoid hyperplasia of the ileum is a serious disease when the process is malignant. The pathology requires immediate treatment, since in the absence of it serious complications and consequences arise.
Therapy is carried out comprehensively. Therapeutic measures include not only the use of drugs or surgery, but also following a diet. This allows you to get a more favorable prognosis. If signs of hyperplasia appear, it is important to consult a specialist promptly.
Treatment of duodenal cancer
Typically, treatment for duodenal cancer involves a combination of surgery, chemotherapy and radiation. This allows you to remove the primary tumor focus as completely as possible and prevent the spread of metastases to neighboring organs, preventing relapse of oncology.
Chemotherapy
carried out using carefully selected cytostatic drugs used before surgery to reduce the size of the tumor, and after it to completely suppress the remaining cells. The use of this method is associated with many side effects, so doctors carefully monitor the patient’s condition.
During surgery
the affected part of the intestine is completely removed within healthy tissue. The operation is prescribed for persons under 75 years of age, in the initial stages of the disease. For terminal stages of cancer, surgery is not prescribed.
During radiation therapy
ionizing radiation is used aimed at the tumor focus. The rays suppress tumor growth and lead to cell death. This helps prevent the spread of metastases as well as the regrowth of cancer. Radiation therapy is carried out at any stage of the process.