Causes of sigmoiditis
The anatomical shape of the intestine is often the cause of the development of sigmoiditis
Sigmoiditis as an independent disease develops due to the anatomical and physiological characteristics of the sigmoid colon. If we take into account that the sigmoid colon is the place where feces are finally formed, then it becomes clear why the disease occurs.
Feces can irritate this area of the intestine, which allows microdamage to develop and promotes inflammation.
Another cause of the disease is the curved shape characteristic of the sigmoid colon, which contributes to the long-term presence of intestinal contents in it and, as a result, irritation with feces for a longer period of time. This factor also significantly increases the risk of inflammation.
Also, the following factors are often attributed to the causes of inflammation:
- intestinal dysbiosis. Dysbacteriosis is a change in the composition of the intestinal microflora, resulting in the growth of aggressive bacteria that are not typical for this part of the body and a decrease in the protective function of the intestine.
- intestinal circulatory disorders or so-called ischemia. Most often, the cause of this is atherosclerosis, in which plaques appear in the vessels, clogging their lumens. Thus, the amount of blood passing through is reduced and the supply of nutrients to organs and tissues is disrupted. Places of necrosis (necrosis) appear in the intestines, which become foci of inflammation.
- intestinal infections. Due to the action of bacteria that provoke infections, toxic substances are produced that have a destructive effect on intestinal cells, causing ulcers or erosions to form. The sigmoid colon, due to its characteristics, most often undergoes this process.
- influence of ionizing radiation. Radiation contributes to the destruction of certain structures of the body's cells, which causes the formation of free radicals - toxic substances that have a negative effect on healthy cells.
- nonspecific intestinal ulcers, such as ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease. The occurrence of this kind of disease is associated with the action of allergic factors and can cause intestinal damage akin to what happens with intestinal infections.
What fruits and vegetables are good for colitis? What to eat for colitis with diarrhea
Disorder of the functions of the colon imposes significant restrictions on the list of foods consumed. The diet for intestinal colitis with diarrhea allows meat without fat, veins. Steamed minced meat products, pureed puree, and soufflé are prepared from veal tenderloin, chicken or turkey breast, and young rabbit. It is especially good to prepare fresh chicken soup with an egg diluted in broth for lunch.
Lean fish without skin is boiled and chopped. It is better to steam white fish - cod, pike perch, pollock, hake, carp, pollock. It is recommended to eat 100 g of fish fillet for dinner at least 3 times a week. Boiled cod contains 18% protein, its meat is tender and nutritious. The high mineral content of fish restores the balance of electrolytes in colitis with diarrhea.
First courses are prepared using diluted meat and fish broth. Instead of vegetables and pasta, put in cereals. Use semolina, rice, oatmeal. Rice puree soup will help stop diarrhea and form proper stool. Porridge is boiled in water and blended with a blender. Boiled and whipped oatmeal for breakfast gently envelops and protects the intestines.
Vegetables and fruits are allowed only in a boiled and grated state. Vegetable decoctions serve as the basis for the first courses of a diet for colitis. To prepare them take:
- one carrot;
- one zucchini;
- three tablespoons of rice;
- 100 g chicken breast fillet;
- a pinch of salt, 5 g butter;
- 1 liter of water.
Place chopped carrots and zucchini into boiling water and cook for 10 minutes. Remove the boiled vegetables and set aside for the second course. Salt the broth, add washed rice and fillet pieces. Cook for 15 minutes, add butter. Blend the soup with a blender until pureed.
For colitis with diarrhea, you can only eat pureed apples and pears raw. The fruits of fixing berries - quince, blueberry, dogwood, bird cherry - are consumed in processed form. They cook jelly, jelly, compotes. Blueberry jelly envelops, adsorbs toxins, and strengthens due to tannins.
Drinks for colitis with diarrhea have a strengthening focus. They drink rosehip decoction, black and green tea, compotes from blueberries, bird cherry, black currants. You can drink cocoa with water and black coffee for colitis with loose stools.
Bread is allowed no more than 200 g per day, only in the form of dried white crackers. Eggs are eaten soft-boiled or in a steamed omelet for breakfast. On the weekly menu for colitis, plan on 1-2 eggs every other day.
Milk does not go well with diarrhea. Calcium is obtained from unleavened cottage cheese; people with acute inflammation of the large intestine do not eat cheese. A teaspoon of premium butter is added to mashed porridge with water.
Honey for colitis, just like sugar, jam, marmalade, pastille, is eaten in strictly limited portions, no more than 2-3 teaspoons per day or 2-3 ready-made pieces.
Types of sigmoiditis
Sigmoiditis can also become chronic
The course of sigmoiditis can be acute or chronic. Also, depending on the nature of the intestinal damage, the following types of this disease are distinguished:
- catarrhal. This is the mildest form of sigmoiditis, which is characterized by damage to only the upper layer of epithelial tissue.
- erosive. It occurs as a consequence of untreated catarrhal disease and has pronounced erosions - unprotected places on the intestinal mucosa, which appeared due to the destruction of the epithelium.
- ulcerative Prolonged irritation of erosions leads to the occurrence of deeper lesions of the mucous membrane - ulcers.
- perisigmoiditis. The most severe and dangerous form of sigmoiditis. The deeper layers of the intestinal walls become affected. The intestine loses its former mobility and an adhesive process occurs, as a result of which the intestinal loops are connected to each other.
Treatment of proctosigmoiditis in adults
This disease is treated by a proctologist and gastroenterologist. Severe forms of proctosigmoiditis require hospitalization.
First, the cause of the disease is determined, and the main treatment depends on this. After it, all patients with proctosigmoiditis are prescribed complex therapy. It is aimed at reducing inflammation and improving the healing process of the intestinal mucosa.
Regardless of the cause, all patients adhere to a strict diet. The food is prepared soft, using steam and water, and they eat small portions. Puree dishes work well. All foods that irritate the mucous membranes and cause gas formation are excluded: fried, spicy, smoked, fresh fruit, etc.
Microenemas with special medicinal solutions, as well as warm sea buckthorn oil, also help well. They reduce inflammation and help mucosal cells regenerate. Sometimes they use sitz baths with a weak solution of potassium permanganate, which has an antiseptic effect. There are many rectal suppositories that the doctor prescribes depending on the cause of proctosigmoiditis. They fight pathogenic flora, soften the mucous membrane, and relieve inflammation.
Diagnostics
The proctologist collects anamnesis: interviews the patient, finds out when the problem arose and how it manifests itself. It is important to remember these details and tell your doctor.
Next, the doctor palpates the abdomen - usually there is pain on the left side, rumbling in the sigmoid colon.
An important but unpleasant point in diagnosis is digital examination of the rectum. Up to 80% of all rectal tumors are diagnosed using this method; it is extremely effective. The doctor feels the affected area. The sphincter spasms, so the examination is unpleasant. A rectal speculum helps in examination - you can assess the condition of the mucous membrane over a distance of 10 cm.
To examine a larger area, sigmoidoscopy and fibrocolonoscopy are used. A special tube with a camera is inserted to determine the extent of the lesion. Tumors are excluded, and suspicious areas are taken for biopsy.
Stool tests are prescribed: it contains a lot of leukocytes, inflammatory cells, and helminths or bacteria can be detected, if they are the cause of the disease. It also turns out which antibiotics the bacteria are sensitive to.
To make a diagnosis, your doctor may order stool and blood tests. They will show whether there is inflammation and what is causing it. Photo: Globallookpress
Additionally, a blood test may be required. It shows all the signs of inflammation - increased white blood cells, increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate, etc.
Modern methods of treatment
Antibiotics and antiparasitic drugs are effective if proctosigmoiditis is caused by infection or helminths. Antibiotic therapy is adjusted when test results are received and it is known which drugs the bacteria respond to most.
Antispasmodics and carminatives help reduce pain. They reduce cramps and reduce bloating. The intestinal wall stretches less and the pain also decreases.
If digestive problems are detected, enzymes are prescribed. Sometimes their own enzymes are not enough for normal digestion of food; they are replaced with artificial ones. Probiotics help restore damaged beneficial microflora.
In severe cases, hormones - corticosteroids - are prescribed. They suppress the immune system if it is more active than necessary and “hits” its own cells. This helps relieve inflammation.
Characteristic symptoms of sigmoiditis
Symptoms of sigmoiditis can be varied and vary greatly with different types of this disease. But still, there are three main manifestations of it:
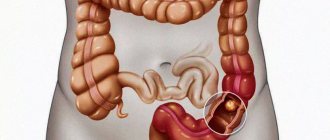
- pain in the left iliac region. The pain intensity is high, often radiating to the lower back or leg. It is important to remember that the sigmoid colon is very mobile. Therefore, pain can be localized not only in the lower left corner of the abdomen, but also move closer to its center or even the diaphragm.
- the occurrence of stool disorders. Diarrhea occurs most often, constipation occurs less frequently. The urge to defecate becomes more frequent, which is simply explained by intestinal irritation and is also characteristic of this disease. In this case, the feces have a liquid consistency, often with admixtures of blood, mucus, pus, and an unpleasant, pungent odor.
- deterioration of the patient's general well-being. Due to the depletion of the body by a long-term disease, weight loss, sleep disturbances, deterioration and decreased performance may occur.
Prevention of proctosigmoiditis in adults at home
Following a diet and diet is the most effective way to avoid such problems. It is also important to maintain a drinking regime and avoid constipation.
It is necessary to exercise and prevent blood stagnation in the pelvic area, especially if you sit a lot.
To avoid infections, you need to maintain hygiene and avoid anal sex. If you experience unpleasant symptoms, do not be shy, consult a doctor - delay can cost you your health.
To the point
How to treat hemorrhoids in men: pills, diet or surgery
Diagnosis of sigmoiditis
Diagnosis and treatment of sigmoiditis are the responsibility of doctors such as a gastroenterologist, therapist, surgeon, and infectious disease specialist. Diagnosis is possible after differential diagnosis to exclude other inflammatory processes in the intestines, such as paraproctitis, ulcerative colitis, as well as infectious diseases - dysbacteriosis, dysentery, cholera.
Diagnostics includes the following studies:
Diet for acute colitis. General rules
The task of the diet for colitis is to provide nutrition for impaired digestion, that is, mechanical and chemical sparing of the digestive tract, reducing the inflammatory reaction.
The main task is to eliminate fermentation and putrefaction in the intestines and normalize its functions and the functions of other organs of the gastrointestinal tract.
According to the Pevzner diet table, for colitis, diet No. 4 is prescribed in case of a sharp exacerbation of the disease or No. 4b in case of a subsiding process or in case of a mild exacerbation.
The treatment table for colitis has a reduced energy value (limiting the consumption of fats and carbohydrates, but with a normal amount of protein), and is equal to 2170-2480 Kcal.
Diet composition:
- protein content – 85-90g, of which 60-65% are animal;
- carbohydrates 300-350 g;
- table salt – 8-10g.
Diet
The diet for colitis of any stage is fractional, 5-6 times a day and in small portions. Due to this principle of diet, the mechanical load on the digestive tract, and, in particular, on the intestines, is reduced, and food is easier to digest and assimilate. The last meal should be no later than 3 hours before bedtime.
Food temperature
Dishes should not be too cold or hot so as not to irritate the gastrointestinal mucosa. The optimal food temperature is 15-60°C.
Cooking
All dishes should be boiled, steamed or baked, but without a hard crust. In addition, food is served pureed or chopped. This way, the intestines have time to break down foods into nutrients that are absorbed into the blood - this achieves mechanical sparing.
Plant fiber
The amount of plant fiber in the diet for colitis is reduced, since, firstly, it does not linger in the intestines, that is, it increases the frequency of bowel movements (and colitis is usually accompanied by diarrhea), and, secondly, it irritates the intestinal mucosa, which so inflamed.
Salt
The salt content in food for colitis is slightly reduced, to 10g. Excessively salty foods irritate the digestive tract.
Free liquid
Free fluid intake should be at least 1.5-2 liters per day. In this way, hydrochloric acid is diluted in the stomach and the volume of fluid lost during diarrhea is replenished.
Alcohol
Alcohol should be avoided, especially during periods of exacerbation of the disease. Alcohol irritates the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines, aggravates inflammation in the colon, stimulates the production of pancreatic enzymes and the release of bile, which aggravates the disease.
How to treat sigmoiditis
Painful sensations as a symptom of sigmoiditis
Treatment of sigmoiditis is carried out based on the causes of its occurrence. In case of sigmoiditis as a result of intestinal infections, treatment is based on antibacterial therapy with drugs such as Biseptol, Cefran, Tetracycline, Ampicillin.
It is mandatory to prevent dysbiosis with Bifidobac, Lactobacterin, etc. If the disease is chronic, the patient is also prescribed intestinal antiseptics, such as Smecta or Intetrix.
Sigmoiditis, provoked by nonspecific inflammatory bowel diseases, is treated with anti-inflammatory drugs that have an effect on the underlying disease: Sulfasalazine, Salazoperidazine, Prednisolone.
General intoxication processes are eliminated by infusion therapy. For this purpose, solutions of glucose, blood plasma and, if necessary, treatment of anemia, iron preparations are used. In order to restore normal microflora, bacterial medications and preparations are also prescribed.
Treatment of ischemic sigmoiditis has the same features as the treatment of sigmoiditis caused by nonspecific diseases. If therapy does not bring the desired effect, surgery may be prescribed to plasticize the vessels that feed the intestines.
In addition, the patient is prescribed a special diet 4, the peculiarity of which is the exclusion of smoked, fried, spicy foods, alcohol from the diet and minimizing the consumption of fats, salt and carbohydrates. Also a prerequisite for the diet is chopping food before eating it.
Most often, treatment of sigmoiditis is long-term and can last from 1 to 3 months with 1-2 courses of medical therapy.
Fully or partially limited products
Exclude from the diet during diarrhea and exacerbation:
- Fiber-rich foods (seeds, fruits, bread with seeds, vegetables, bran, whole grains).
- Fresh bread, dried fruits, honey, pastries, jam, sweets.
- Rich broths, fatty fish and meat, since fatty foods enhance peristalsis.
- Barley, corn and pearl barley porridge, legumes.
- Whole milk, milk soups, sour cream and cream. During the period of improvement, milk is consumed in diluted form or in dishes (omelettes, soufflés, casseroles, puddings).
- Kvass, cocoa and coffee with milk, carbonated drinks.
- Alcohol.
- Fried and hard boiled eggs.
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| vegetables legumes | 9,1 | 1,6 | 27,0 | 168 |
| swede | 1,2 | 0,1 | 7,7 | 37 |
| cucumbers | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,8 | 15 |
| parsnip | 1,4 | 0,5 | 9,2 | 47 |
| parsley (root) | 1,5 | 0,6 | 10,1 | 49 |
| radish | 1,2 | 0,1 | 3,4 | 19 |
| white radish | 1,4 | 0,0 | 4,1 | 21 |
| turnip | 1,5 | 0,1 | 6,2 | 30 |
| celery | 0,9 | 0,1 | 2,1 | 12 |
| horseradish | 3,2 | 0,4 | 10,5 | 56 |
| garlic | 6,5 | 0,5 | 29,9 | 143 |
| spinach | 2,9 | 0,3 | 2,0 | 22 |
| sorrel | 1,5 | 0,3 | 2,9 | 19 |
Fruits | ||||
| bananas | 1,5 | 0,2 | 21,8 | 95 |
| melon | 0,6 | 0,3 | 7,4 | 33 |
Berries | ||||
| grape | 0,6 | 0,2 | 16,8 | 65 |
Mushrooms | ||||
| mushrooms | 3,5 | 2,0 | 2,5 | 30 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| dried fruits | 2,3 | 0,6 | 68,2 | 286 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| pearl barley | 9,3 | 1,1 | 73,7 | 320 |
| Wheat groats | 11,5 | 1,3 | 62,0 | 316 |
| millet cereal | 11,5 | 3,3 | 69,3 | 348 |
| barley grits | 10,4 | 1,3 | 66,3 | 324 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| pasta | 10,4 | 1,1 | 69,7 | 337 |
Bakery products | ||||
| vysivkovy bread | 9,0 | 2,2 | 36,0 | 217 |
| Old Russian grain bread | 9,6 | 2,7 | 47,1 | 252 |
| Rye bread | 6,6 | 1,2 | 34,2 | 165 |
Confectionery | ||||
| candies | 4,3 | 19,8 | 67,5 | 453 |
| Kurabye cookies | 6,7 | 25,8 | 64,6 | 516 |
| butter cookies | 10,4 | 5,2 | 76,8 | 458 |
Ice cream | ||||
| ice cream | 3,7 | 6,9 | 22,1 | 189 |
Cakes | ||||
| cake | 4,4 | 23,4 | 45,2 | 407 |
Chocolate | ||||
| chocolate | 5,4 | 35,3 | 56,5 | 544 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| seasonings | 7,0 | 1,9 | 26,0 | 149 |
| mustard | 5,7 | 6,4 | 22,0 | 162 |
Meat products | ||||
| pork | 16,0 | 21,6 | 0,0 | 259 |
Sausages | ||||
| dry-cured sausage | 24,1 | 38,3 | 1,0 | 455 |
Bird | ||||
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| dried fish | 17,5 | 4,6 | 0,0 | 139 |
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
| Red caviar | 32,0 | 15,0 | 0,0 | 263 |
| black caviar | 28,0 | 9,7 | 0,0 | 203 |
| canned fish | 17,5 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 88 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| animal fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| bread kvass | 0,2 | 0,0 | 5,2 | 27 |
| black tea | 20,0 | 5,1 | 6,9 | 152 |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| apricot juice | 0,9 | 0,1 | 9,0 | 38 |
| grape juice | 0,3 | 0,0 | 14,0 | 54 |
| plum juice | 0,8 | 0,0 | 9,6 | 39 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Prognosis and complications
With proper treatment of sigmoiditis, in most cases it is possible to achieve complete recovery, but it should be understood that the treatment process is long and is accompanied by a lot of dietary restrictions.
If left untreated, inflammation may spread to adjacent sections of the intestine, most often to the rectum (proctitis).
Also, as inflammation progresses, the tightness of the intestine may become compromised, resulting in peritonitis - inflammation of the abdominal cavity, requiring extensive surgical intervention.