The main causes of the disease include:
- Infectious. The occurrence of the disease occurs due to infection with intestinal infections (for example, salmonella, candida);
- Non-infectious. Chronic colitis appears against the background of other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, becomes a consequence of self-administration of laxatives with non-compliance with the dosage, poor diet or food allergies, and a tendency to constipation.
Nutrition for chronic colitis is an important part of drug therapy.
A properly selected diet and diet significantly reduces treatment time, prevents relapses and improves intestinal motility.
Basic nutritional recommendations include: dividing the daily amount of food into 6-7 meals, strictly following the list of prohibited and permitted foods.
Sigmoiditis: causes and symptoms
The sigmoid colon got its name from its shape.
Among inflammatory bowel diseases, sigmoiditis is the leader in the frequency of occurrence. This is due to the structural features of this section of the intestine. The sigmoid colon is curved and is located directly in front of the rectum. Most often, fecal retention occurs in the sigmoid colon, causing it to become inflamed.
In addition to long-term fecal retention, there are several main causes of sigmoiditis:
- Intestinal infections. Various bacteria, entering the intestines, begin to multiply and release toxins. They destroy the intestinal mucosa, provoke the development of dysbiosis, the appearance of ulcers and erosions. The sigmoid colon is the most vulnerable in this regard.
- Dysbacteriosis. With dysbiosis, many parts of the intestine are affected, including the sigmoid colon. Pathogenic flora begins to prevail over beneficial bacteria, which provokes an inflammatory process.
- Intestinal ischemia. With ischemia, the circulatory process is disrupted. Plaques form in the vessels, which prevent blood from flowing freely to the tissues. Some intestinal tissue dies. Necrotic areas cause inflammation of all parts of the intestine.
- Radiation sickness. With radiation sickness, all tissues and organs are affected. Healthy cells are destroyed by free radicals.
Sigmoiditis does not have a clearly defined list of symptoms, since it has many forms and varieties. But some signs appear invariably with any form of sigmoiditis. The disease is accompanied by pain in the abdominal area. They usually occur on the left, but can spread further and radiate to the leg.
Irritable bowel causes upset bowel movements. More often it is diarrhea, less often - constipation. Usually the patient suffers from frequent urge to defecate and loose stools. Sometimes you may notice streaks of blood or mucus in the stool. Pain may occur before and after bowel movements. Patients also noted nausea, flatulence, rumbling in the stomach, and unpleasant belching.
If the disease is not treated, the patient's condition will worsen. Body weight will decrease, due to chronic diarrhea, dehydration and vitamin deficiency will appear. The inflamed sigmoid colon can even grow together with nearby organs, which is fraught with various complications.
Diseases
Where is the colon located and how does it hurt? First of all, a person who has inflammation of this part of the organ will feel pain in the lower abdomen and discomfort in the anus.
In addition, other signs of pathology may be observed:
- regular constipation;
- discharge of pus from the anus;
- the presence of blood impurities in the stool;
- flatulence;
- painful urge to defecate;
- loose stool.
If a person has pain in the upper, transverse, descending colon, symptoms of pathology may also indicate iron deficiency anemia. This occurs due to the formation of bleeding ulcers or erosions in the affected organ.
Diseases of the colon occur for the following reasons:
- lifestyle errors: physical inactivity, overeating, abuse of fatty foods;
- hypotension;
- chronic constipation;
- abuse of dietary supplements of dubious quality;
- long-term treatment with antibiotics.
The colon, the symptoms of inflammation of which cannot be ignored, is susceptible to many diseases, including the formation of a malignant tumor.
Hirschsprung's disease
This is a hereditary pathology that manifests itself in a person in infancy or early childhood.
A person with this disease suffers from prolonged constipation, which can last over several weeks.
In this case, enemas and laxatives are useless. However, constipation in Hirschsprung's disease alternates with debilitating diarrhea.
All these disorders of the functioning of the digestive system occur due to ganglion cells of the colon.
The parts of the intestine located above it hypertrophy due to constant contractions, which is why the intestines cease to empty themselves. With this disease, a person is indicated for surgery to remove hypertrophied parts of the organ.
Diverticulosis
The disease can be either congenital or acquired. Diverticulosis is a disease that is accompanied by protrusion of sections of the intestinal mucosa through its muscular layer. This is accompanied by the formation of sac-like formations in which feces can accumulate, which can provoke inflammation of the organ mucosa.
Typical symptoms of diverticulosis include lower abdominal pain, nausea, diarrhea and vomiting. Ignoring treatment for diverticulosis can lead to such serious consequences as organ obstruction, phlegmon and peritonitis.
Polyposis
A disease accompanied by the formation of growths on the mucous membrane of the organ, the size of which ranges from several millimeters to several centimeters.
Polyps are dangerous because they can degenerate into malignant neoplasms, that is, provoke intestinal cancer.
Symptoms of the disease include problems with defecation, since growths in the lumen of the organ interfere with the free movement and exit of feces.
If the polyps are large, the patient may suffer from hemorrhages inside the organ. Polyposis is treated surgically, as well as using cytostatic drugs.
Oncology
Often, inflammation of the colon, the symptoms and treatment of which is extremely important, leads to cancer of this part of the intestine. Oncologists consider colon cancer the least dangerous type of cancer of the gastrointestinal tract. However, the threat of this disease to human life lies in the fact that the symptoms of the disease resemble signs of a disorder in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
So, the patient suffers from symptoms such as diarrhea, pain and colic in the lower abdomen, slight discharge of blood and mucus during bowel movements. But as the disease progresses, symptoms such as anemia and prolonged constipation, caused by a narrowing of the lumen of the colon, increase.
In this case, cancer is treated surgically: the affected part of the organ is removed along with part of the mesentery and nearby lymph nodes.
If metastases occur after surgery, a course of chemotherapy is given.
In the first stages of the disease, the prognosis for patient survival is 70%, but in the last stages of cancer the probability of death is at least 80%.
Possible symptoms of colon cancer cannot be ignored, because timely consultation with a doctor will allow treatment of the disease to begin as early as possible.
What to do if you have inflammation of the sigmoid colon? Symptoms and treatment
Where is it located and how does it hurt?
sigmoid colon
- important information for those who suffer from abdominal pain and bowel disorders
.
Considering human anatomy, pain with sigmoiditis ( inflammation of the sigmoid colon
) occur
in the lower left part of the abdomen
.
But this section of the intestine is quite mobile, so pain can occur in any part.
This complicates the correct diagnosis and makes it difficult to choose the right treatment tactics.
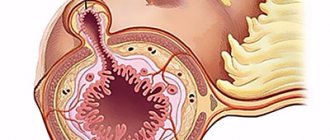
Sigmoid colon: what is it and where is it located?
This part of the intestine is S-shaped
(the name comes from the Latin letter sigma).
It is located in the lower part of the intestine, connecting the descending colon (part of the large intestine) and the rectum.
The length of this section varies for each person, ranging from 10 to 65-65 cm.
The average is 40 cm. The mesenteric ligament provides mobility to the sigmoid colon, so it can change location.
Active digestion of food no longer occurs in the sigmoid. Here, the consumed liquid and electrolytes dissolved in it are absorbed, and feces are formed.
The anatomy of the sigmoid colon is designed in such a way that if the digestive system malfunctions, feces do not move in the opposite direction.
In the presence of certain factors (decreased peristalsis, sedentary lifestyle), feces can stagnate in this section, causing inflammation of the sigmoid colon.
Sigmoid colon hurts: what are the causes?
It is extremely rare that diseases of this part of the intestine occur independently. More often they develop against the background of existing acute or chronic inflammation of the digestive system, especially the large intestine.
Other causes of sigmoid colon diseases include:
- Congenital features. The human intestine has a convoluted shape, but the number of curves varies. The more there are, the more difficult it is for food and feces to move through it. Stagnant processes occur more often; long stay of feces in the intestines leads to inflammation and general intoxication.
- Inflammatory processes in the intestines, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, duodenal ulcer or any other part.
- Dysbacteriosis.
- Chronic constipation of various etiologies.
- In women, inflammation of the sigmoid colon occurs during pregnancy due to increased pressure of the uterus on the intestines. Sigmoiditis also occurs against the background of inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs. It is in this section that adhesions most often occur.
- Impaired blood supply to the intestines, decreased vascular tone, increased blood density, high blood cholesterol levels.
- Abdominal injuries.
- Abdominal surgery, which could result in damage to the intestines.
- Ionizing radiation, which causes cell degeneration.
Diseases of the sigmoid colon: types, symptoms and treatment
Sigmoiditis is the most common disease of the sigmoid colon. This is an inflammation of the mucous membrane, in which the functionality deteriorates and the motility of this part of the intestine decreases. Inflammation from this section can move downwards, causing inflammation of the rectum, hemorrhoids and other troubles.
There are several types of sigmoiditis:
- Catarrhal
. In this case, the inflammatory process covers only the superficial layer of the mucosa. The symptoms are mild, this form often does not cause serious complications, and with proper and timely treatment, this disease can be eliminated forever. - Erosive
. This is the second stage of the disease, in which the mucosal defect is more serious. Foci of inflammation form on it - erosions, which often bleed. The damage penetrates deep into the mucous membrane, causing pain in the person’s lower left abdomen. - Ulcerative
. At this stage, all layers of the mucous membrane are damaged, and sometimes inflammation also affects the muscle layers. Ulcers that form on the intestines and bleed can lead to severe bleeding. - Perisigmoiditis
. This form of the disease leads to through-and-through damage to the intestine, as a result of which the inflammation “spreads” to the abdominal cavity. Adhesive processes develop. Adhesion is the fusion of intestinal loops, due to which motility is significantly reduced, and inflammation rapidly spreads.
Depending on the spread of the inflammatory process, there are:
- Proctosigmoiditis (sigmoproctitis) is an inflammation of the sigmoid colon and large intestine.
- Rectosigmoiditis is a disease that affects both the sigmoid and rectum.
Bowel bending in this section occurs much more often than in sections of the small intestine.
This happens because the sigmoid region is very mobile.
There are two forms of this disease: acute and chronic
. Acute is characterized by severe paroxysmal pain and obstruction.
In the chronic form, the sigmoid colon does not hurt much, but constipation and intestinal atony develop gradually.
Diverticulosis
- an inflammatory process that covers the sigmoid colon and the sphincter connecting it to the rectum. Occurs due to poor circulation and stagnation of feces. Characterized by stool retention and severe pain in the left side of the abdomen.
Dolichosigma
– a disease that can occur at any age. This is an excessive lengthening of the sigmoid colon or its mesentery, which reduces intestinal motility and functionality of this section.
Sigmoid colon cancer is a malignant tumor, one of the causes of intestinal cancer. Treatment in this case is carried out surgically. In the early stages, the disease can be cured.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
The NetGastritu project was created with the goal of providing people with accurate and up-to-date information on medical topics. Articles are written by professionals and, unfortunately, development costs slow down the development of the project. If you want to support us, use the form below.
Let's make the world a better place together. Thank you for your attention.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
Symptoms of diseases of the sigmoid colon
Diseases of this part of the intestine are easily confused with other gastrointestinal ailments. The most characteristic signs of sigmoid colon pathology:
- violation of bowel movements - constipation or tendency to diarrhea;
- abdominal pain, which often occurs after bowel movements. The lower left part of the abdomen, where the sigmoid colon is located, hurts;
- bloating, feeling of fullness;
- belching, which sometimes ends in vomiting;
- loss of appetite;
- weakness, apathy, which arise as a result of intoxication of the body;
- weight loss.
Pain in the intestine can vary in intensity. Severe pain may indicate an acute inflammatory process or a long period of pathology. Moderate pain indicates low-grade inflammation. In both cases, the patient requires evaluation and treatment to prevent significant deterioration.
What diagnostics are needed?
If your stomach hurts quite often, you need to undergo a comprehensive examination, including checking the sigmoid colon. To do this, you need to contact a gastroenterologist who will perform palpation and prescribe additional diagnostic procedures.
In the presence of inflammation, the hard sigmoid colon is palpated, the pain intensifies and radiates to the left hypochondrium.
But with increased mobility, the palpation method is not reliable: you will need to examine the intestines more carefully - using ultrasound and x-rays.
These methods will allow you to detect displacement, determine the length of the sigmoid intestine, determine how many centimeters it differs from the norm, whether there are areas of expansion or narrowing, as well as the degree of damage to the mucosa.
Treatment of diseases of the sigmoid colon
Surgical treatment is used in the presence of tumors, obstruction or severe bending. Other intestinal problems are treated with medication.
Treatment of sigmoiditis with medications is carried out on an outpatient basis
.
Severe deterioration requires hospitalization, often for surgery. Sigmoiditis in the early stages (from catarrhal to ulcerative) is well treated if good modern drugs are used.
To treat inflammation of the sigmoid colon, use:
- antibiotics that will help eliminate bacterial inflammation;
- adsorbents that will help bind and remove toxins;
- antispasmodics to relieve spasms of the intestinal muscles (No-Shpa, Spazmalgon);
- antihistamines to reduce swelling;
- digestive enzymes - for faster and more thorough digestion of food;
- probiotics that normalize microflora;
- anti-inflammatory medications.
Most medications are taken in the form of tablets and capsules.
But some anti-inflammatory, bowel cleansing agents are used rectally - in the form of suppositories or therapeutic enemas.
Treatment with suppositories helps prevent hemorrhoids and some other complications.
Video - Sigmoid colon and its diseases
Treatment with folk remedies at home
Treatment of sigmoiditis with alternative medicine can be carried out, but only if the diagnosis is confirmed and the localization of inflammation is accurately determined. For this, herbal decoctions are used:
- plantain (anti-inflammatory and hemostatic effect);
- chamomile;
- rosehip.
You can use these components either individually or as part of a mixture (in equal proportions).
Separately, plantain decoction (a tablespoon of dry crushed leaves per liter of water) is especially effective when the patient has a tendency to diarrhea.
A decoction of watermelon rinds is used to treat inflammation of the colon and sigmoid colon.
100 grams of dried peels are poured into 0.5 liters of boiling water, boiled for 15 minutes, then drunk during the day in 3 doses.
Diet for sigmoiditis
to treat
intestinal diseases while following a therapeutic diet.
Its goal is to reduce the load on the intestines during an inflammatory disease, while maintaining normal motility.
Avoid foods that are difficult for the digestive system: fatty foods, fried and smoked foods, salty and sour foods, spicy foods, caffeine-containing drinks, alcohol.
It is necessary to exclude baked goods and sweets, as they increase fermentation.
Recommended:
- low-fat fermented milk products;
- rice;
- boiled or steamed vegetables;
- boiled potatoes;
- lean meat and fish, steamed;
- liquid soups with low-fat broth.
In case of acute illness, it is enough to adhere to the diet until complete recovery. Chronic inflammatory process requires constant adjustment of diet.
Let's like and subscribe to the channel. Thank you for your attention!
Symptoms of sigmoiditis
In acute cases, a catarrhal process is usually observed. Patients complain of severe cramping pain in the left half of the abdomen, often radiating to the left leg and lower back. Patients with sigmoiditis experience nausea, vomiting, rumbling, bloating and stool disorders in combination with frequent false urges. The stool becomes foul-smelling, mucus and streaks of blood appear in it. When proctitis and sigmoiditis are combined, mucus and blood may be discharged without impurities of feces.
Signs of intoxication are revealed: weakness, weakness, hyperthermia, headache. When palpating the abdomen of a patient with sigmoiditis, pain is detected in the projection of the sigmoid colon. Rectal examination reveals thickening of the affected part of the intestine. In its clinical manifestations, acute sigmoiditis resembles appendicitis or peritiphlitis, but the pain is localized not in the right, but in the left iliac region. With an atypical location of the sigmoid colon, the localization of pain may change, which sometimes causes diagnostic difficulties.
Severe forms of ulcerative sigmoiditis tend to have a subacute or chronic course. There is a violation of the general condition, weakness, intoxication, intestinal discomfort, stool disorders and false urges. Characterized by persistent diarrhea. The stool of patients with sigmoiditis is liquid, foul-smelling, and the color resembles meat slop. In severe forms of the disease, the spread of the inflammatory process with the development of perisigmoiditis is often observed.
The clinical picture of perisigmoiditis does not differ from the manifestations of ordinary sigmoiditis. As a result of inflammatory damage to the peritoneum, adhesions gradually form in the abdominal cavity. Adhesive disease with sigmoiditis usually proceeds favorably. There are nagging pains that intensify after physical activity, bloating, a feeling of fullness in the abdomen and a tendency to constipation. In some cases, with sigmoiditis complicated by adhesive disease, symptoms of intestinal obstruction may be observed: increasing pain, vomiting, lack of stool, hyperthermia and leukocytosis.
Exacerbation of chronic sigmoiditis usually occurs against the background of diet disorders, consumption of alcoholic beverages, acute infections (influenza, ARVI), general physical or mental fatigue. The severity of symptoms can vary significantly - from slight pain and slight increase in stool to full-blown manifestations resembling acute sigmoiditis. Diarrhea is often combined with constipation. Patients complain of a feeling of fullness in the abdomen and pain radiating to the leg, perineum and lower back. With a prolonged course of sigmoiditis, sleep disturbances, fatigue and increased irritability are possible due to constant discomfort in the abdomen.
Colitis
Colitis is an inflammatory process that occurs in the inner mucous membrane of the colon.
Causes of colitis:
- various intestinal bacteria, fungi, viruses, infections (salmonellosis and dysentery are prime examples);
- long-term use of antibiotics, laxatives, antipsychotics;
- poor blood supply to the intestines (mainly in older people);
- improper diet (monotonous food, high consumption of flour and meat, spicy foods and alcoholic beverages);
- radiation exposure;
- dysbacteriosis;
- allergic reaction to food;
- poisoning with heavy metals and arsenic;
- worms;
- genetic predisposition;
- wrong lifestyle;
- excessive physical and psychological stress.
Main types, causes and symptoms of colitis:
- 1 Ulcerative - ulcers form on the walls of the colon, and the patient may feel severe pain on the left side of the abdomen, there are constant temperature fluctuations, frequent constipation, and sometimes pain in the joints occurs.
If you do not respond to the symptoms, then after a while bleeding from the rectum or bloody purulent discharge will appear. - 2 Spasmodic - bloated abdomen, diarrhea or constipation, gas, abdominal pain. This disorder occurs against a background of nervous experiences and stress.
- 3 Pseudomembranous - its symptoms depend on the form of the course.
The mild form occurs due to dysbiosis, which has formed due to prolonged use of antibiotics, and manifests itself in the form of diarrhea. After finishing taking the pills, the stool becomes normal. Moderate and severe forms are characterized by diarrhea even after stopping antibiotics. At the same time, mucus, blood, elevated temperature appear in the stool, the patient is in a weak and broken state, and the patient often vomits. In addition to stomach disorders, cardiovascular disorders also occur. - 4 Enterocolitis - can be infectious or non-infectious. Symptoms: nausea, bloating, white coating appears on the tongue. If this is infectious enterocolitis, then blood is added to the stool, and symptoms of poisoning appear (severe headache, aching bones, severe weakness).
- 5 Ischemic - occurs due to insufficient blood supply to the colon, manifests itself in pain in the left side of the abdomen, intestinal obstruction, then peritonitis appears, over time the patient loses weight.
Forms of colitis:
- acute - often has a simultaneous course with inflammation of the small intestine and stomach (gastritis), the causative agents are often microorganisms (dysenteric, salmonella, streptococci and staphylococci);
- chronic – occurs due to poor nutrition over many years.
In case of severe exacerbation, it is necessary to fast for 2-3 days (in this case, the patient should drink at least one and a half liters of water per day, maybe tea), then he must go on a special diet (depending on the symptoms, the duration of the diet can be from 2 weeks up to several months).
And only then can you return to your normal diet.
Healthy foods and dishes include:
- vegetable purees and cutlets, greens, boiled cabbage (cauliflower), zucchini, pumpkin (and it is useful to drink the water in which it was boiled);
- rice, semolina, oatmeal;
- freshly squeezed juices, tea, compotes, decoctions made from currants, rose hips, various jelly;
- jam, fruit (boiled), homemade jelly;
- fermented milk products, namely: non-acidic sour cream, low-fat kefir, yogurt, milk, grated cottage cheese;
- olive and butter;
- meat and fish of low-fat varieties, steamed or boiled;
- eggs (boiled and no more than one per day);
- bread (white, gray wheat, crackers), biscuit (dry), cookies and baked goods.
The number of meals should be at least 4, but no more than 6 per day.
Traditional medicine for colitis
To normalize the condition, it is necessary to drink decoctions of nettle leaves, mint, chamomile flowers, burnet roots, sage leaves, bird cherry fruits, alder catkins, smokewort (all dosages must be observed, since this plant is considered poisonous), wormwood, oregano, St. John's wort, from seeds cumin. In case of severe diarrhea, drink a decoction of small petals (popularly the herb is called “shut up the goose”).
In addition to herbal medicine, you also need to give enemas, which are prepared with the addition of onion and garlic juice, aloe, and infusions of orange and pomegranate skins.
Dangerous and harmful products for colitis
- fatty meat and fish;
- alcoholic drinks;
- all flour products made from shortbread and puff pastry;
- all sodas;
- coffee;
- legumes;
- barley and pearl barley porridge, millet, pasta;
- mushrooms, radishes with radishes;
- sauces, marinades, smoked meats, spices, pickles;
- seasonings;
- freshly baked bakery products;
- sausage, canned food, frankfurters;
- vegetables and fruits that have not undergone heat treatment;
- store-bought sweets;
- fried, too salty, fatty, spicy foods.
Causes
Inflammation of the sigmoid colon develops under the influence of the following factors:
- Causative agents of intestinal infections;
- Dysbacteriosis;
- Inflammatory diseases of nonspecific nature;
- Insufficient blood supply to the intestines (ischemia);
- Radiation sickness
Group of intestinal infections
Among diseases of infectious origin, dysentery, food toxic infections and amoebiasis are of primary importance. Most pathogens can produce toxins that differ in their tropism and type of action.
It is with shigellosis that the pathogen induces damage to epithelial cells, which leads to a decrease in the functional area of the hollow organ. The main mechanism of transmission is fecal-oral, and the source of infection is often a sick person or carrier.
The greatest danger to the patient is latent/erased forms of infectious intestinal lesions.
The incubation period of the disease and the severity of the clinical picture depend on the amount of incoming pathogen and the characteristics of the organism.
Dysbacteriosis
Inflammation of the sigmoid colon can occur due to disruption of the microflora in this section. The ratio of saprophytic bacteria depends on the state of a person’s immunity, as well as previous diseases. The following nosological units are of great importance:
- Shigellosis;
- Salmonella;
- Food poisoning infections (FTI);
- Parasitosis (amoebiasis, giardiasis).
The trigger factor for dysbiosis in inflammation of the sigmoid colon is considered to be long-term use of antibacterial drugs, the spectrum of action of which also covers representatives of one’s own microflora.
In maintaining the correct balance, diet and the presence of bad habits play a role. Addiction to alcoholic beverages and smoking, frequent consumption of poor-quality food causes changes in the conditions of the internal environment of the body.
Nonspecific inflammation
Sigmoiditis as a manifestation of nonspecific intestinal diseases may be one of the first pathological signs. These primarily include the following:
- Nonspecific ulcerative colitis;
- Crohn's disease.
The true causes and mechanism of development of these diseases are unknown to this day. Moreover, they manifest more often in people in the age group from 20 to 40 years. Inflammatory changes occur more often in the distal parts of the colon, so sigmoiditis is a characteristic manifestation.
Today, most researchers are inclined to believe that these diseases are of an autoimmune nature. People with a hereditary predisposition are at risk.
Ischemic command
The sigmoid colon has its own characteristics of blood supply, so in case of insufficiency, only this section is affected. The main reason for this is atherosclerosis. Manifestations develop gradually, reaching their peak after 60 years.
In this case, patients report complaints of extraintestinal symptoms of vascular damage in the form of one of the variants of coronary heart disease (angina pectoris, cardiosclerosis, history of heart attack) or cerebral insufficiency.
In more rare cases, the sigmoid colon is affected due to ischemia arising for the following reasons:
- In utero anomalies in the formation of vessels of the sigmoid colon;
- Diffuse connective tissue diseases;
- Compression of blood vessels from the outside by a tumor, enlarged lymph nodes;
- Spikes.
Chronic insufficiency of blood supply (hypoxia) can subsequently cause a secondary infection or narrowing of the intestinal lumen due to the proliferation of connective tissue with the formation of scars.
Radiation sickness
Chronic sigmoiditis can be a manifestation of radiation sickness, which is typical primarily for workers of hazardous enterprises and people injured as a result of the Chernobyl accident (liquidators, displaced persons, evacuated residents).
It should be taken into account that this form of the disease can occur in the long term - several months or even years after radiation exposure.
Inflammation of the sigmoid colon occurs as a side effect of radiation therapy in cancer patients with malignant lesions of formations in the pelvis (rectum, bladder, prostate, ovaries) or a metastatic process in the lymph nodes.
Proctosigmoiditis
Proctosigmoiditis is an inflammatory process in the rectum and sigmoid colon.
Causes of proctosigmoiditis:
- as a manifestation of Crohn's disease, ulcerative colin;
- infectious – causative agents of dysentery, campylobacter, chlamydia, herpes viruses and cytomegalovirus;
- causative agents of venereal diseases - gonorrhea and syphilis;
- antibiotic treatment;
- chemical, thermal and radiation burns of the rectum;
- frequent enemas and subaqueous baths (colon hydrotherapy);
- helminthic infestation (roundworms, pinworms, etc.);
- rough prostate massage and anal sex.
According to the clinical course, there are 2 forms of proctosigmoiditis:
Acute proctosigmoiditis.
Characterized by a sudden onset, accompanied by a rise in body temperature and chills. Tenesmus (false urge to evacuate) due to constipation and a feeling of heaviness in the rectum, a strong burning sensation in the rectum are disturbing.
Chronic proctosigmoiditis.
More common than acute. Has an imperceptible onset or is a continuation of an acute one.
There are practically no general symptoms, since intestinal functions are preserved. Local symptoms predominate: itching, burning and/or a feeling of wetness in the anus, mucous and mucopurulent discharge from the rectum, which intensifies with errors in the diet (spicy foods, alcohol).
- With a long course of proctosigmoiditis (more than 3 months), the color of the skin around the anus changes (hyperpigmentation, weeping eczema appears in the anus, skin folds and anal papillae in the anus hypertrophy.
- Diagnosis of proctosigmoiditis: includes sigmoidoscopy and rectoscopy (not used in acute cases), biopsy of the rectal mucosa and bacteriological examination of a smear from the rectal wall.
- It is necessary to differentiate or distinguish between proctosigmoiditis and ulcerative colitis, polyps and cancer of the rectum or sigmoid colon.
- Treatment.
- 1. eliminating the cause of proctosigmoiditis;
- 2. diet:
- in case of acute proctosigmoiditis, exclude spicy, sour, salty foods, alcohol, raw fruits and vegetables, juices, all sweets and chocolate. It is recommended to consume a large amount of liquid (up to 2 liters per day), semolina, rice porridge, meat broth, pureed vegetable soup, boiled meat, boiled fish, steamed low-fat cutlets, cottage cheese with sour cream, cranberry jelly, yesterday's white bread.
- The diet for chronic proctosigmoiditis is the same as for acute proctosigmoiditis. It is allowed to introduce boiled eggs, kefir, and moderate amounts of carrots, cabbage, potatoes, apples, plums, and strawberries into the diet.
3. Local treatment of proctosigmoiditis consists of:
- if clinically necessary, taking sulfonamides (salofalk, sulfosalazine);
- medicinal microenemas with chamomile decoction with 0.3%-0.5% collargol solution for two weeks;
- correction of intestinal microflora;
- If there is itching, ointments Ultraproct, Proctosedyl, Sinalar, Celistoderm, Posterizan forte, etc. can be used topically.
- Prognosis: acute proctosigmoiditis with proper treatment ends in recovery.
- Chronic proctosigmoiditis can periodically worsen in the form of discomfort and itching in the anus, usually after errors in diet.
- Be healthy, take care of yourself!
Treatment of pathology
Treatment depends on the test results.
Diet is the basis for the treatment of digestive disorders, so special attention is paid to this point. Nutrition must be balanced and properly composed, the menu is compiled taking into account the stage and form of the disease
Subtleties should be discussed with your doctor. The second method is drug therapy, tailored to the form in which the disease occurs. The doctor will explain to the patient why sigmoiditis is dangerous, how it is treated, and the doctor selects the medications. Medicines will help you quickly and permanently cope with the disease. But both methods should be used simultaneously for best effect. Folk remedies are used only with the permission of a doctor, as is heating, which is actively used in the treatment of sigmoiditis.
Sigmoiditis is a disease that may not manifest itself for a long time, but it makes unpleasant adjustments to a person’s life. Diagnosis is aimed at the causes of the pathology. Only based on the results of a complete examination, the doctor prescribes therapy, which consists of diet, medication, and alternative medicine.
How inflammation of the sigmoid intestine is characterized and what are the causes of the pathology - more details in the video:
Diseases affecting the sigmoid colon are described in the video:
Diet for sigmoiditis
Abnormal stool is one of the symptoms of sigmoiditis
Nutritional therapy is of primary importance in the treatment of sigmoiditis, regardless of the reasons that provoked this disease. Diets 4-4b are the main ones for sigmoiditis. The nature of nutrition can also be adjusted depending on the type and severity of the disease.
If the patient has severe diarrhea, it is recommended to undergo therapeutic fasting for 1-3 days. During this time, strong unsweetened tea, rose hip decoction, etc. are allowed to be consumed. Afterwards, they switch to diet 4. If the manifestations of inflammation decrease, the patient is allowed to expand the diet to options 4b and 4c.
The basis of nutrition for sigmoiditis is the consumption of the right amount of nutrients necessary for the body, primarily proteins, microelements, vitamins and electrolytes. Diet 4 involves reducing carbohydrates and fats to the lower limit of the daily norm; diets 4b and 4c assume the presence of all necessary substances in normal quantities.
Salt can be consumed in limited quantities - 8-10 g, which is the lower limit of the norm, and all dishes that contain mechanical, chemical or thermal irritants. That is, it is not allowed to eat food that is too cold - below 15 degrees Celsius, or hot food. Table 4 requires mandatory wiping of food. In options 4b and 4c this requirement is reduced.
The basis of the diet for sigmoiditis is eating small portions 5-6 times a day. It is not allowed to consume foods that contribute to the process of fermentation and putrefaction in the intestines. Such products include non-dietary meat and coarse plant fiber.
Chronic sigmoiditis during the period of remission involves the consumption of foods rich in fiber, which include beets, cookies, bread with bran, dried apricots, juices from vegetables and fruits, carrots, prunes, pumpkin.
If the patient has a tendency to constipation, he is prescribed wheat or rye bran. To achieve a therapeutic effect, add a tablespoon of bran to a glass of boiled water and leave for 30 minutes. Next, the water is drained, and the remaining mass is consumed with porridge, cottage cheese or in its pure form. The maximum dose of bran per day can be 6-8 tablespoons, provided there is no diarrhea or pain.
Persistent remission allows you to switch to general nutrition. It is not allowed to consume only fatty meat, canned food, smoked meats, spicy and salty foods, alcoholic beverages and baked goods. In case of exacerbation of the process after the introduction of a general diet, you should return to the use of diet 4c.
Chronic sigmoiditis during an exacerbation involves the appointment of the same diet as for acute sigmoiditis. If the disease is severe and the patient loses more than 15% of body weight, he is prescribed parenteral nutrition, in which all the necessary substances, as well as glucose solution, amino acids, protein compounds, fat emulsions enter the body through a catheter inserted into the subclavian vein .
If you are interested in seeing how the operation to remove the sigmoid colon is performed, watch the video on YouTube.
Sigmoiditis implies an inflammatory process that occurs in the sigmoid colon. Simply put, a lesion occurs in the final sections of the intestine located in the large intestine.
The sigmoid colon is most vulnerable to inflammatory processes, since it is physiologically designed in such a way that long-term stagnation of the masses located in the intestine is formed in this area, awaiting the formation of fecal waste from them.
Sigmoiditis quite often occurs accompanied by colitis or proctitis. Moreover, this disease has practically no symptoms that separately characterize the presence of sigmoiditis. It is noteworthy that sigmoiditis can occur even in acute and chronic forms.
How to eat properly with chronic colitis
- What not to eat if you have chronic colitis
- For chronic colitis, it is not recommended to consume fatty meats and poultry, smoked sausages and fish delicacies, saturated fatty broths, fried foods, foods high in fat, soft baked goods and pastries, vegetables and fruits, which have a direct effect on the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. intestinal tract (legumes, cucumbers, onions, garlic, radishes, grapes, plums, apricots and others), pepper, horseradish, mustard, wasabi, other hot and salty sauces.
- What can you eat if you have chronic colitis?
For chronic colitis, it is recommended to adhere to the list of products according to dietary table No. 4.3. In particular, patients can eat low-fat meats, poultry and fish, low-fat broths, cereal-based cereals (with the exception of pearl barley and millet), low-fat fermented milk products, vegetables and fruits, berries, dried bread, low-fat cookies, and yeast-free bread.
It is very important to follow the correct preparation and processing regime for products.
Meat, fish and poultry are allowed only when boiled in water or steamed, eggs are best consumed in the form of a steamed omelet, it is advisable to dry bread before eating and, of course, all fruits, vegetables and berries must undergo appropriate processing to prevent infections from entering the body. The diet should contain a large amount of fiber and dietary fiber.
Menu for every day (sample version)
- First breakfast:
Oatmeal with water and diluted milk, fresh cottage cheese, crackers and tea. - Second breakfast:
low-fat cheese or protein omelet, tea. - Lunch:
Soup containing cereals or noodles in a weak meat or vegetable broth, steamed meatballs, vegetable puree and lingonberry broth. - Afternoon snack:
Kissel. - Dinner:
Boiled meat or fish, buckwheat porridge, apple compote. - Late dinner:
Kefir or fermented baked milk, cookies.
Compliance with the correct regimen and diet is the basis of therapy in the treatment of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Treatment of chronic colitis in a sanatorium will allow you not only to strictly follow all nutritional recommendations, but also to undergo a number of physiotherapeutic procedures to promote a speedy recovery.
“The right choice of a sanatorium is a significant step towards maintaining and increasing health. “Gorny” is a resort complex that combines the experience and knowledge of Russian and Soviet balneology.
The presence of modern medical equipment and innovative installations, the professionalism of the staff and love for their work will serve as the key to extending longevity,” - the head physician of the sanatorium, Alexander Olegovich Karaulov.
Treatment of sigmoiditis
If sigmoiditis is not accompanied by perforating complications and does not require emergency surgical intervention, its therapy begins with the prescription of diet No. 4.
Diet number 4 according to Pevzner helps reduce fermentation processes in the colon, stimulates the regeneration of the mucous membrane and the growth of beneficial microflora. The diet implies the following rules:
- daily calorie intake – 1400-1700 kcal;
- ratio of proteins, fats and carbohydrates (BJU) – 120 g/50 g/140 g per day;
- number of meals per day – 5-6;
- maintaining an adequate drinking regime - from 1500 to 2000 ml of clean water per day;
- The preferred method of processing food is steaming. Food is served warm and pureed;
- complete exclusion from the diet of easily digestible carbohydrates (honey, sugar, jam, chocolate and candies, baked goods, white bread, bananas, grapes, carbonated drinks);
- sources of proteins and fats - cottage cheese with a fat content of at least 5%, egg whites, chicken, lean meats (veal, beef) and fish (burbot, river perch);
- the diet excludes foods high in extractive substances (citrus fruits, coffee, radishes, garlic, spinach);
- to stimulate peristalsis, bran, gray bread, and decoctions of sage seeds can be used;
- sources of carbohydrates are oatmeal and buckwheat porridge, potatoes, sprouted wheat seeds, decoction of flax seeds and corn silk.
This diet includes many restrictions, therefore, to avoid nutritional deficiencies of vitamins and microelements, patients are prescribed a complex of multivitamins, and the duration of this diet does not exceed 10 days.
Drug therapy for sigmoiditis includes:
- Antibiotic therapy. The drugs of choice are intestinal antiseptics that minimally affect the composition of the microflora - Nifuroxazide, Ersefuril, Enterofuril, Intetrix. Drugs of this group are prescribed for a course of 7 days.
- During the period of antimicrobial treatment, probiotics are prescribed - drugs in this group contain lactobacilli (Bactistatin, Bifidumbacterin).
- To relieve pain, antispasmodics are used that have a positive effect on peristalsis and bowel emptying - No-shpa, Spazgan, Duspatalin.
- In case of profuse diarrhea, they resort to infusion-transfusion therapy with saline solution and the use of oral rehydrating agents - Regidron, Trihydron.
Low FODMAP: Recommended Diet for IBS
III. Stages of the low FODMAP
Stage 1. Exclusion of prohibited products . It is necessary to strictly follow the principles of the diet with the exclusion of foods rich in FODMAP substances from the diet (a list of “prohibited” and “allowed” foods with an indication of the amount is given here). The exclusion period for prohibited foods is usually 3-6 weeks. However, with the correct selection of a therapeutic diet and its strict adherence to it, an improvement in well-being can be observed already in the first week.
It is very important that during the period of exclusion of prohibited foods the diet remains varied. The formation of the menu within Stage 1 of the diet should be based on the principles of rational nutrition. So, for example, the number of servings of vegetables in the daily diet should be at least 5, milk and fermented milk products (allowed by the diet) 2-3 servings per day, fruits - 2 servings, cereals and products made from them - 6-7 servings.
“Serving” sizes vary both within one food group and between groups. For example, for most vegetables, one serving is usually 75 g. In the dairy and milk substitutes group, 1 serving is 1 cup (250 ml) milk, 3/4 cup (200 ml) dairy products, 2 pieces of hard cheese, 1/2 cup (120 g) soft cheese or cottage cheese. One serving of fruit corresponds to an average of 100-150 g of fresh fruit (1 banana, 1 pear, 1 orange or 2 tangerines, 2 kiwi) or 30-40 g of dried fruit or 1/2 cup of juice. In the cereal group, one serving is 1 piece of bread (40 g), half a cup of cooked cereals and pasta (75-120 g), 4 tablespoons of cereal and muesli.
Breakfast may include the following items:
- Porridges from permitted cereals (buckwheat in the form of prodel, corn, rice and millet cereals, oatmeal in the form of flakes, quinoa) - with water or with lactose-free, rice, soy, almond milk. You can add to porridge: permitted berries and fruits, butter or vegetable oil, sugar (1 tsp).
- Natural, protein omelettes. You can add to the omelette: permitted greens, permitted vegetables (for example, carrots, broccoli florets, etc.).
- Scrambled eggs with the possible addition of some vegetables (tomatoes), bacon. You cannot add onions or mushrooms.
- Cheese (allowed by the diet and in the allowed quantity), lactose-free milk or dairy products - 1 serving.
- Bread made from rice, corn, flaxseed flour in the form of toast, including with baked tomatoes or hard cheese. You can use bread labeled "Low FODMAP". Quantity - 1 piece.
- Vegetable fritters (eg zucchini, potatoes, carrots).
- Pancakes or pancakes made from buckwheat, corn, flaxseed, and rice flour.
- Dishes from meat, poultry and fish - any, including those familiar to you. It should be remembered that according to a balanced diet, you should limit the consumption of processed red meat products (sausages, sausages, ham).
- 1 standard serving of Phase 1 permitted fruit
- Salads from allowed vegetables
- Smoothies using lactose-free, rice, soy, almond milk and allowed fruits and berries
Dinner and supper:
- First courses with meat, fish, poultry with the addition of permitted vegetables (potatoes, carrots, broccoli, green beans, etc.) and cereals.
- Any dish made from meat, fish, poultry, seafood - they do not contain FODMAP carbohydrates. You can use permitted spices, seasonings, seeds (for example, sesame), fruits (citrus fruits, pineapple, etc.) to improve the taste of meat dishes.
- Any side dishes from permitted vegetables, cereals (salads, vegetable stews, pasta/pasta, cereals, etc.).
- 1 standard serving of Stage 1 permitted fruit per meal
- Bread made from rice, corn, flaxseed flour in the form of toast, including with baked tomatoes or hard cheese. You can use bread labeled "Low FODMAP". Quantity - 1 piece per meal.
- Allowed drinks
Stage 2. Diet expansion . If the effect of diet therapy is achieved (disappearance or significant reduction of disease symptoms), it is recommended to gradually introduce foods high in FODMAP substances into the diet. At this stage, those FODMAP foods that cause symptoms are clarified, and the acceptable amount of these foods in the diet is determined. If there is no effect from the low-FODMAP diet (if strictly followed for 6 weeks), the patient can return to their usual diet after consulting their doctor. If the effect of the diet occurred before the period planned by the doctor expired (for example, after 3 weeks instead of 4-6), the expansion of the diet can be started earlier.
This is the most important stage of diet therapy. The decision to move to the second stage is made after consultation with the attending physician who prescribed the diet. Properly performed dietary expansion will allow you to select well-tolerated foods. What does right mean? Let's try to figure it out.
As mentioned above, FODMAP substances include 5 different carbohydrates. Some products contain only one type of carbohydrate (for example, milk contains only lactose), while others contain several (a striking example is watermelon, which contains fructose, fructans and mannitol). In order to establish a response to a specific FODMAP carbohydrate, it is advisable to first expand the diet to foods containing only one of the listed carbohydrates. For example, start with dairy products to eliminate lactose intolerance. Then - with honey (a source of fructose). Mannitol is found in mushrooms, and sorbitol is found in fresh avocado and peach. Fructans, other than some fruits (melon, etc.), are the only FODMAP carbohydrate in fresh onions, red onions and garlic. Galactans are present in significant quantities in almonds.
Usually, if there is poor tolerance to a certain carbohydrate (lactose, fructose, etc.), similar symptoms will be observed when eating other foods containing this carbohydrate.
You should not start expanding your diet with foods containing several carbohydrates. For example, an apple contains fructose and sorbitol, so when symptoms appear, it will be impossible to determine which carbohydrate the intestines are reacting to.
It takes 3 days to introduce one product.
Day 1 – use a small portion of the product. Since the response to FODMAP carbohydrates can vary from patient to patient and is usually dependent on the amount consumed, it is recommended to start with half the recommended serving. This could be, for example, 100 ml of yogurt. Since yogurt contains lactose, lactose tolerance is assessed in this case. If symptoms (bloating, loose stools, increased abdominal pain) appear after eating 100 ml of yogurt, this may indicate intolerance to even small amounts of lactose. You should try another product with the same carbohydrate after 3 days. If there are no symptoms when consuming a small portion, continue to evaluate the tolerability of a regular portion of the product on day 2.
Day 2 – use a standard portion of the product. Standard serving sizes for vegetables, fruits, grains and dairy products have been described above, with more detailed information provided in the food tables. On the second day, you should eat a standard portion (for example, 200 ml of yogurt) and evaluate your symptoms. If you experience bloating, increased abdominal pain, loose stools or other unpleasant sensations, the test on day 3 is not performed. After 3 days, you can try another product with the same carbohydrate.
Day 3 – consume a large portion of the product. If the usual portion is well tolerated, you can evaluate the tolerance of a larger amount of the product on the third day. For example, drink 400 yogurt per meal (double portion). The presence of symptoms will indicate that such large quantities should not be consumed. If there are no symptoms after three days, the tolerability of other products from the same group should be assessed. For example, to assess lactose tolerance, this could be cottage cheese, sour cream, cream, milk (cow, goat).
Each new product is evaluated according to the above scheme (day 1-2-3). If the patient wants to establish the exact amount of a product that he can tolerate (for example, what will happen if he eats 50 ml of yogurt?), then this assessment can be carried out additionally. There should be 3 days between tests with two different products in order to completely eliminate the influence of the previous test on the subsequent one.
After analyzing the tolerance of various products within one group (for example, the group of milk and fermented milk products), you can move on to assessing other carbohydrates. Try a fructose tolerance test with honey and mango. The next food group to evaluate is, for example, lentils, hazelnuts and almonds (containing only galactans). Pomegranate, grapefruit, melon and some other fruits, garlic and onions will help assess your fructan tolerance. Sorbitol is found in peach, apricot, avocado, and blackberry. Mannitol is found in large quantities in mushrooms (champignons, porcini mushrooms), as well as in cauliflower.
Next, it will be possible to assess the tolerance of foods with a complex carbohydrate composition (may contain 2-3 FODMAP carbohydrates). The testing principle is the same: day 1-2-3.
Record your symptoms after trying new foods and different servings of those foods!
Example:
| Product name | Test day | Symptoms after eating the product |
| 100 ml yogurt for breakfast | Day 1 | No symptoms |
| 200 ml yogurt for breakfast | Day 2 | Gas formation 30 minutes after breakfast lasting 3 hours |
| No test performed | Day 3 | ——- |
In order to understand which carbohydrate is contained in large quantities in a particular product, use the table.
What to do with those products whose tolerance you have already assessed as good? If you are absolutely sure that there are no symptoms, you can introduce this product into the diet in the amount that was well tolerated (or less). This product should be included in a meal in which subsequent testing will not be performed.
Stage 3. Individualization of the diet . The end result of the diet is a personalized diet that excludes only those FODMAP foods that cause symptoms. This allows the patient to maintain dietary diversity and prevents “avoidant” behavior in everyday life (for example, refusing to visit cafes and restaurants for fear of eating something “wrong”).
Basic principles of diet for diverticulosis of the sigmoid colon
- The transition to a therapeutic diet should not occur in one day, but gradually. First, introduce foods rich in plant fiber during breakfast, replacing them with foods that contain less dietary fiber. After a few days, change the composition of lunch in the same way, and after some time, start dinner.
- Since the body of different people will react differently to the same amount of plant fiber, do not try to tie your menu to mathematical calculations of the total fiber content in the diet. Act intuitively, focusing on your own well-being.
- Despite the fact that meat, fish, eggs and other animal products do not contain dietary fiber, they cannot be completely excluded from the diet when planning a diet for diverticulosis of the sigmoid colon. A competent healing table should involve a combination of plant and animal foods, for example, meat with buckwheat or scrambled eggs with vegetable salad.
- Train yourself to drink at least 8 glasses of water a day every day. Since dietary fiber absorbs water like a sponge, the stool of patients who consume sufficient fiber will remain soft. But if you drink little liquid at the same time, the effect may be exactly the opposite - the feces will become dense, and its passage will be difficult.
- Meals should not be too large, but their number should be increased to 4-6 times a day.
Diet for colitis - easy nutrition in all respects
Ekaterina Golubovskaya
TS/Fotobank.ru
Colitis is inflammation in the intestines. There are different degrees of inflammation - acute and chronic. In any case, you will have to follow a special diet that can significantly alleviate the painful symptoms of colitis.
Modern doctors agree that food does not greatly affect the development of colitis, but a special diet for colitis can still significantly alleviate the course of the disease and protect against acute attacks. especially if one of the manifestations of the disease is diarrhea (diarrhea or bear sickness). It is important to know what to avoid during colitis, and what, on the contrary, should be included in the diet.
Insoluble fiber is very harmful for colitis. Its sources include whole grain products (whole grain bread, pasta, cereal flakes and others), sweet corn, cabbage, grape and apple peels.
Insoluble fiber tends to not completely dissolve in the intestines and attaches to the walls of the inflamed colon. This factor only aggravates the situation and can cause an attack of colitis.
Accordingly, such products should be excluded from the diet for any form of colitis.
But soluble fiber, on the contrary, is beneficial for the intestines and is included in the diet for colitis (both ulcerative and intestinal). It has the ability to soften stool and improve intestinal motility.
Soluble fiber can be found in fruits and vegetables (potatoes, carrots, apples and pears without peel), white rice and oatmeal.
In therapeutic diet 3 - a special diet that is prescribed to patients with intestinal diseases - fiber also plays a key role.
Diet for colitis must include fish oil and fatty sea fish. It is best to get fish oil from food rather than from capsules, as it is much easier to absorb.
The diet for colitis does not prohibit dairy products, but it limits them. An excess of these foods in the diet may worsen the patient's condition. Therefore, it is recommended to consume no more than 100g of dairy products per day.
Diet options for colitis
Since colitis can develop differently in everyone, the principles of diet for colitis also differ. For example, a diet for chronic colitis, constant diarrhea, constipation, abdominal pain, flatulence, etc.
Diet for non-acute attacks of chronic colitis
The purpose of such a diet is to restore the motor and secretory functions of the intestine. Such a diet can be called complete with some restrictions on the consumption of milk, coarse fiber, spicy foods and spices. Meals on this diet are designed for 5-6 meals.
Diet for chronic colitis and constipation
The daily diet contains sufficient amounts of proteins and carbohydrates, and the amount of fat is increased by vegetable oils. This diet for colitis recommends eating beets, carrots, prunes, figs, dates, and apricots. Meals are also divided into 5-6 meals.
Diet for chronic colitis and diarrhea
The goal of the diet is to reduce fermentation processes in the intestines and spare it as much as possible, both chemically and mechanically. The diet limits the consumption of fats and carbohydrates and excludes pickles, spices, milk, fiber and smoked foods from the diet. The number of meals remains the same - 5-6 times a day.
Diet for acute colitis
All dishes are only boiled or steamed, and then pureed. Soups should also be pureed, the grains in them should be boiled, and the vegetables should be finely chopped. It is also allowed to cook baked dishes without a hard crust. Meals are also divided into 5-6 meals.
Any diet for colitis should be purely individual and based on the signs and course of the disease. At the first signs of colitis, consult a doctor immediately so as not to spread the disease.
Treatment of the sigmoid colon
Inflammatory processes can be suppressed with medication, while structural changes in the department require surgical intervention. Before treating the sigmoid colon, it is necessary to identify the etiology of the pathological process and promptly eliminate the main provoking factor from the patient’s life. Then remove the pain with painkillers, proceed to intensive therapy, supplemented by a therapeutic diet and physiotherapeutic procedures for medical reasons.
Conservative therapy
Drug treatment is aimed at removing the cause and consequences of inflammation, and is additionally monitored by clinical methods. The intensive therapy regimen involves a combination of representatives of several pharmacological groups to enhance the overall therapeutic effect. This:
- antispasmodics to relax smooth muscles: Spazmalgon, No-shpa;
- enzyme-containing preparations: Mezim, Creon, Festal;
- antibiotics to kill bacteria: representatives of the fluoroquinolone group;
- antihistamines against allergic reactions: Fenistil, Suprastin, Tavegil;
- immunosuppressants: Daclimusa, Cyclosporine, Azathioprine;
- anti-inflammatory drugs: Prednisolone and its analogues;
- adsorbents to prevent stomach ulcers: Smecta;
- probiotics to normalize intestinal microflora (Enterol, Linex);
- enemas, rectal suppositories with a favorable prognosis for the disease.
- multivitamin complexes to restore the immune system after long-term treatment of the sigmoid colon with medications.
Surgical methods of treatment
If conservative methods are ineffective, doctors recommend a radical approach to the problem. The patient requires surgery on the sigmoid colon with preliminary radiation therapy. Such surgical intervention is appropriate for oncology of the sigmoid colon. First, its size is reduced by an acceptable dose of radiation, and then completely removed. An additional course of chemotherapy and radiotherapy is necessary to prevent the spread of metastases to healthy parts of the digestive system. For polyps, resection of the pathological focus is recommended.