- home
- Coloproctology
- Sigmoid colon cancer
Sigmoid colon cancer
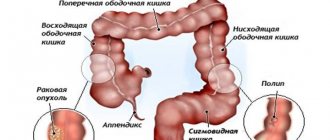
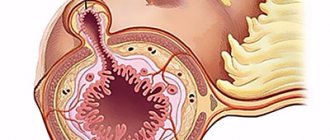
Sigmoid colon cancer is an oncological disease of part of the colon, in which a malignant tumor is formed from the epithelium of the mucous membrane. The sigmoid colon, located above the rectum, according to statistics, is one of the organs most often affected by cancer. Most of the oncologist's patients are people aged 45-65 years, with more cases among men.
Depending on the direction of growth, an exophytic form of cancer is distinguished - a formation on a thick stalk grows into the intestinal lumen, and endophytic cancer, when the process spreads along the intestinal wall. In this case, ulcerations appear, the lumen of the intestinal tube narrows, the movement of intestinal contents is difficult.
Tumors of this location also differ in histological structure. Adenocarcinoma is more common - its poorly differentiated variety has an unfavorable prognosis and is characterized by early metastasis. Signet ring cell carcinoma, which is less common, also has a poor prognosis.
Among the negative factors that can lead to illness:
- diverticula, benign polyps susceptible to malignancy;
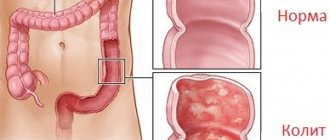
- diseases of the colon: colitis, Crohn's disease, atony, etc.
- digestive disorders: constipation, problems with peristalsis;
- alcohol abuse, smoking, unbalanced diet;
- some diseases: obesity, diabetes, etc.;
- hereditary predisposition.
Etiology and pathogenesis
Experts admit that it is hardly possible to identify a single, universal cause for sigmoid colon cancer. In most cases, we are talking about a combination of various unfavorable conditions.
One of the main factors in the appearance of this type of cancer is the characteristic location of the sigmoid colon itself. Located at the end of the large intestine, it practically passes into the rectum and ends at the anus. Accumulating in the sigmoid colon, feces are in contact for a long time with the mucous membrane, which absorbs toxins and carcinogens from them, which provoke the development of cancer.
The risk of developing the disease increases if a person has relatives with intestinal cancer in their family. Risk factors also include various chronic inflammatory diseases of the large intestine, such as Crohn's disease, chronic colitis, ulcerative colitis, and diverticulosis.
Often, chronic polyps in the large intestine can become malignant. Cancer of the sigmoid colon can develop against the background of a decrease in peristalsis - muscle contractility; this phenomenon can be age-related (senile), and also occurs as a result of a sedentary lifestyle, previous surgery, or long-term medication use.
An unbalanced diet (the predominance of products containing carcinogenic food additives), nicotine and alcohol abuse play a negative role.
Classification
Sigmoid colon cancer is classified according to the following factors:
| By the nature of the invasion | exophytic forms | the tumor spreads from the surface of the organ outward |
| edophytic forms | the tumor spreads inwards and invades the intestinal wall | |
| According to histological structure | adenocarcinomas | tumor of glandular tissue, occurs in 75-80% of all cases |
| mucinous adenocarcinoma | produced in mucous glands throughout the body | |
| signet ring cell carcinoma | the name is given according to the type of cells from which the neoplasm is formed | |
| undifferentiated cancer | a rare form of tumor, represented by undifferentiated cells (without any specific structural features that would indicate their belonging to a specific type of tissue) | |
| According to the international TNM system | T (tumor) | spread of the primary outbreak |
| Tis - cancer in situ | the tumor is limited to the mucous layer | |
| T1, T2, T3 | germination of the submucosa, muscular layer, the tumor spreads into the subserosal base | |
| T4 | tumor spread beyond the intestinal wall; Possible ingrowth into surrounding organs and tissues | |
| N (nodus) | metastasis to regional lymph nodes | |
| N0 | no lymph node involvement | |
| N1 | metastases in 1-3 lymph nodes | |
| N2 | damage to more than 3 lymph nodes | |
| M | presence of distant metastases | |
| M0 | no outbreaks | |
| M1 | metastases are determined in other organs (usually in the liver, less often in the lungs, brain, bones) |
Stages
The clinical course of sigmoid colon cancer involves four stages of development.
Stage 1. The tumor develops within the intestinal mucosa, its size does not exceed 15 mm, there are no metastases.
Stage 2. The size of the neoplasm exceeds 15 mm, but remains less than half the diameter of the intestine. This stage is divided into two subtypes:
- the tumor has not spread beyond the intestinal wall, no metastases have been identified;
- it grew into the intestinal wall with the possible appearance of single metastases.
Stage 3. The disease progresses, the tumor occupies more than half the diameter of the intestine. Here, too, there are differences in the two subtypes: metastases may be absent, or the neoplasm gives rise to their appearance in regional lymph nodes.
Stage 4. Multiple metastases grow into tissues and lymph nodes of both adjacent and distant organs.
Diet guidelines for colon cancer
The general principles of nutrition for tumors are divided into rules that apply to all oncology, and specifically a diet for intestinal tumors. When an oncological process develops in the human body, many organ systems undergo changes. This should be taken into account when choosing products for your daily diet.
First of all, the human immune system suffers, because cancer takes over all the attention of the “sentinel” cells of the immune system. Therefore, it is important to include natural plant immunomodulators and immunostimulants in the diet. These are sea buckthorn and rosehip berries, echinacea, decoctions and teas from St. John's wort.
Also, the immune system, when working hard, needs increased amounts of vitamins, minerals and amino acids. Therefore, it is important to eat foods rich in these elements.
The second important principle of nutrition for oncology is to take large amounts of alkaline foods. After all, the fact that tumors acidify the body’s environment is quite well known. To help the body cope with general acidification, you can drink alkaline mineral waters and eat durum wheat and other grains.
Nutritional rules specifically for tumors of the large intestine imply that the organ is affected by the neoplasm and functions with disturbances. Therefore, firstly, the diet should include something that is as easy as possible for the intestines and, if possible, free of chemical impurities.
In addition, an important factor is the patient’s drinking regimen. Due to the fact that during cancer, tissue metabolism accelerates, you should drink at least 2.5-3 liters of clean water daily. Otherwise, a lack of fluid in the body may occur, which will negatively affect both the functioning of the intestines and the functioning of the immune system.
Symptoms (signs)
Features of the symptoms of sigmoid colon cancer are the rather slow development of the disease; its clinical manifestations can appear only several years after the onset of malignant degeneration of cells.
Note! The likelihood of a complete recovery is high if oncological processes are detected in the early stages. But when nothing bothers the patient, he is in no hurry to undergo examination, and the disease progresses in a latent form.
In most cases, sigmoid colon cancer manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- the normal process of defecation is disrupted;
- stool may be delayed for several days, the intestines have to be emptied in several stages, constipation sometimes alternates with diarrhea;
- discharge from the anus may appear in the form of blood and mucus;
- a person develops weakness, increased fatigue, the skin turns pale (may acquire an earthy-gray tint);
- shortness of breath and palpitations are not excluded;
- sensations of discomfort from bloating, the appearance of pain in the left half and lower parts of the abdominal cavity.
As the tumor grows, symptoms progress: acute intestinal obstruction and bleeding from the tumor may appear. Classic manifestations of advanced sigmoid colon cancer are expressed by severe cramping pain, bloating, lack of passage of stool and gas, and vomiting.
Diagnostics
When a patient seeks medical help with complaints that, due to their symptoms, raise suspicion of sigmoid colon cancer, the doctor begins the examination with palpation of the abdomen and the intestine itself: a neoplasm of a certain size is detected in this way.
To confirm or refute the diagnosis, a complex of laboratory and endoscopic studies is used. It includes:
- stool occult blood test;
- general blood analysis;
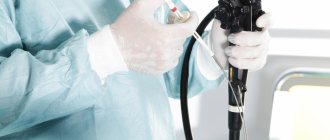
- examination of the lower intestine with a flexible endoscope (sigmoidoscopy);
- colonoscopy – examination of the entire colon;
- irrigoscopy - x-ray examination of the colon using a barium enema (performed if it is not possible to perform a colonoscopy);
- biopsy of a changed area of the mucous membrane or a whole polyp;
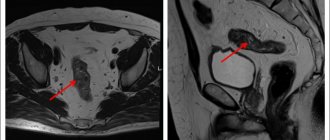
- Ultrasound or CT scan of the abdominal cavity and pelvis;
- X-ray of the lungs to determine the presence/absence of metastases;
- determination of tumor development using tumor markers - specific proteins that can be detected in blood and urine during laboratory tests.
In addition, according to indications, the doctor may prescribe additional examinations using endoscopic ultrasound, MRI of the abdominal cavity with contrast, PET-CT, diagnostic laparoscopy, scintigraphy of skeletal bones - this is a method for studying the metabolism of bone tissue.
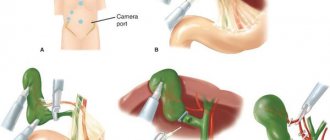
Progress of the operation
There are several methods for performing resection of the sigmoid colon; the choice directly depends on the nature and cause of the pathology. For example, a patient who has had a volvulus due to a congenital anomaly is indicated for an urgent operation according to Mikulicz or Hartmann. In the first case, the dead part of the intestine is excised, then the parts of the sigmoid are stitched in a special way and temporarily fixed on the abdominal wall. After 3-4 months, when the patient has recovered, a second operation is performed, during which the fistula is eliminated, and the intestine receives its pre-operative shape, only it becomes somewhat shorter.
According to Hartmann's method, after removing the atrophied section of the intestine, the passage hole is brought out. Such an intervention involves much less stress on the body, but it will be impossible to return to your usual lifestyle after it. Therefore, when the patient gets stronger, an operation to shape the intestine may be prescribed.
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
For neoplasms and polyps in the middle third of the sigma, the entire organ is removed. First, the surgeon removes the loops of intestine through an incision in the abdominal wall, performs an anastomosis and excises the affected area of the intestine. If the pathology allows you to “get by” by removing half of the sigma, then after excision the remaining parts are stitched together, which allows you to restore the natural functions of the intestine.
Treatment
Surgery is considered the most effective treatment for sigmoid colon cancer. In this case, as a rule, an integrated approach is used, including not only the surgical method, but also chemotherapy and radiotherapy.
Small cancerous tumors with clearly defined borders are removed along with part of the affected colon and nearby lymph nodes. After such an operation, the surgeon restores the integrity of the intestinal tube.
Tumors in stage IV cancer are most often removed along with the sigmoid colon, then a colostomy is performed - an artificially created anus by bringing the end of the colon out. In some cases, this is a temporary measure; sometimes the colostomy becomes permanent, and the patient wears a colostomy bag for the rest of his life.
Chemotherapy is used to kill cancer cells using drugs that can inhibit their ability to divide rapidly. The method can be effective even in advanced forms of the disease, and is used both before and after surgery.
At the same time, chemotherapy cannot be considered an alternative to surgery: it can only reduce the size of a cancer tumor and slow down its growth. It can be used as an independent therapeutic method when it comes to inoperable patients.
Radiotherapy, or radiation, also reduces the size of the tumor in the preoperative period, with its help it destroys cancer cells remaining at the border of healthy and diseased tissues.
Why is it better to perform sigmoid colon resection at the Swiss University Hospital?
- At the SwissClinic Center for Coloproctology, low-traumatic operations on the intestines have been carried out for more than 20 years; every month our surgeons perform about 120 surgical interventions, including high-tech and minimally invasive operations.
- More than 100 types of operations were developed by the doctors of our Center, some of them are performed only by us.
- In our coloproctology clinic, you can undergo all the necessary tests; if necessary, you can get advice from other specialists: gastroenterologist, endoscopist, gynecologist, urologist, etc.
- We have only modern equipment from leading companies, our staff includes experienced specialists of the highest category, many are known not only in the country, but also abroad, and the Center also welcomes foreign specialists.
- Our clinic is one of the few in the country where treatment is carried out in accordance with the best traditions of Western European clinics; we cooperate with famous university clinics in France, Germany, and Switzerland.
Forecast
The likelihood of successful treatment of patients with sigmoid colon cancer is directly dependent on the stage at which the disease was discovered.
After starting treatment at stage I, the prognosis for complete recovery is about 95%. If cancer is detected and treated at stage II, the five-year survival rate of patients is more than 90% in the absence of metastases and 83% with their appearance. The third stage corresponds to the following indicators: 59% of patients live after treatment for five years or more, if there are no metastases, when they are already present - 40%. After all treatment measures carried out, 8% of patients survive in stage IV.
Sample menu
For a patient diagnosed with colon cancer before treatment or after surgery, an approximate daily nutrition menu can be created as follows:
Breakfast
- oatmeal or other steamed porridge,
- fermented baked milk or natural yogurt,
- dried fruits, nuts, bran.
Afternoon snack
- apple, pear, banana
- half a glass of low-fat cottage cheese,
- not strong tea.
Dinner
- dietary soup (vegetable or chicken broth),
- whole grain bread
- rice or millet porridge with rabbit.
Complications
The organs to which metastases most often spread from sigmoid colon cancer are: liver, lungs, spine.
A cancerous tumor can grow into the rectum, bladder, uterus, nearby nerves, blood vessels, and also affect more distant organs.
Complications of this disease include:
- intestinal obstruction (complete or partial), which is caused by a gradual narrowing of the lumen of the affected intestine by the tissues of a growing malignant neoplasm;
- perforation of the intestinal wall with subsequent development of peritonitis (life-threatening inflammation of the peritoneum, it can be confused with manifestations characteristic of a perforated gastric ulcer or acute appendicitis);
- tumor growth into the tissue of adjacent organs;
- the formation of retroperitoneal abscesses (purulent inflammation localized in the retroperitoneal space), which are the result of microperforation of the affected intestinal wall or purulent inflammation of the retroperitoneal lymph nodes;
- the formation of thrombophlebitis (inflammation of the vein wall and the formation of a blood clot that closes its lumen) in the pelvic veins.
Prevention
Prevention measures include, first of all, the earliest possible detection of the disease. People aged 50 years or older are recommended to have a colonoscopy every 5 years and a stool occult blood test once a year. If there is a hereditary predisposition, these measures should be taken starting from the age of 40.
If polyps appear in the colon and sigmoid colon with a diameter of more than 1 cm, they must be removed immediately; if their size is smaller, regular monitoring by a doctor is recommended.
You should not delay treatment of any inflammatory bowel disease.
Giving up bad habits, an active lifestyle, and getting rid of excess weight play a positive role.
Note! No traditional medicine or “grandmother’s recipes” can cope with sigmoid colon cancer. The sooner you seek qualified medical help, the higher the chances of recovery.
Must-have products
A diet for colon cancer involves including a number of essential foods in the diet. All of them help in one way or another, if not directly fighting the tumor, then at least maintaining the human body in a state of intense immune function.
It is important to include foods rich in easily digestible protein in your diet. These include lactic acid products - kefir, fermented baked milk, natural yoghurts. Here you should pay attention to the presence of dyes and preservatives if the products are purchased in a supermarket. In addition, a lot of protein and amino acids are found in fish, nuts and cottage cheese.
To maintain immunity, it is recommended to eat foods that contain large amounts of vitamins and minerals. These are berries, bee products (unless there is an allergic reaction to them), fruits and vegetables, legumes. However, legumes should be consumed carefully, in small quantities, to avoid excessive gas formation.
An important element to maintaining a healthy immune system is taking enough natural antioxidants. They bind free radicals in the body and thus help suppress the tumor process. Antioxidants are found in bitter, sour and sharp-tasting foods - gooseberries, grapes, persimmons. There are also a lot of them in greens - parsley, dill, thyme, celery.
In many cancers, suppression of the function of the hematopoietic system is observed - anemia, leukopenia, and so on. This is also due to the use of cytotoxic treatments - chemotherapy and radiation therapy. Therefore, products that increase blood cells are recommended for consumption. This includes pomegranate juice, pumpkin seeds, red fish, and seafood in moderation.