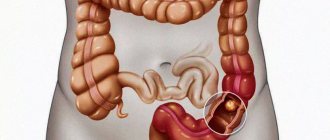
The sigmoid colon is part of the large intestine. Due to its curved shape, it often becomes inflamed and experiences great stress due to intestinal pressure, which leads to the formation of diverticula, protrusions in the intestinal wall.
Diverticula themselves are not fatal, but the likelihood of serious complications is very high, so it is important to identify them early and begin treatment. Diverticula can occur in people at any age, but they are much more common in people over 50 years of age. How to diagnose and treat sigmoid colon diverticulum?
Anatomy and physiology of diverticulum
A diverticulum is a hernia-like growth, the size of which ranges from 5 millimeters to 10 centimeters. The neck of the formation is narrow, the length is on average 3 millimeters. The diverticulum cavity is enlarged and resembles an apple in appearance. Single and multiple diverticula are diagnosed. Multiple formations are difficult to treat and, as a rule, are removed through surgery.
The pathology is called diverticulosis or diverticular disease. In old age, most of the population suffers from proctological disease. Intestinal growths form due to age-related changes. In most cases, patients are not aware of the development of the disease, since there are no symptoms, and diverticulosis does not manifest itself in any way in the early stages . Feces get stuck in the diverticulum pocket, after which the mucous membrane becomes thinner and weakened. Bleeding and inflammation begin.
If an inflammatory process is observed, we are talking about diverticulitis. If there is no inflammation, the disease is called diverticulosis.
Prognosis and prevention
You can avoid the formation of diverticula of the sigmoid colon by adhering to proper nutrition: this disease practically does not occur in those countries where people mainly eat vegetables, fruits and cereals. The diet should consist of foods rich in fiber. First of all, you need porridge (oatmeal, buckwheat, wheat), fruits, raw and boiled vegetables. You should also pay more attention to moderate exercise.
Due to the fact that 80% of patients with diverticula of the sigmoid colon are asymptomatic, the prognosis for this disease is quite favorable. It worsens with age, as atrophic changes in the intestinal walls begin to progress. A less favorable prognosis for complications such as abscess, peritonitis, perforation of diverticula of the sigmoid colon.
Types of diverticula
There are the following types of diverticula:
- Congenital (true) diverticula are an anomaly that develops in a person in utero. With this pathology, protrusion of all layers of the intestine is observed.
- Acquired (false) diverticula - pathology caused by age-related changes. Formed next to blood vessels. There is protrusion of the mucous and submucosal layer of the intestine. The outer shell of connective tissue is not subject to deformation.
Where do diverticula form? In most cases, neoplasms are diagnosed in the large intestine. Diverticula are found in the sigmoid colon and the left half of the colon. That is why the most common pathology is considered to be diverticulitis of the sigmoid colon.
It is extremely rare that neoplasms appear in the small intestine. Diverticula are found in the esophagus, stomach, bladder and urinary tract, bile ducts.
Symptoms of diverticulitis
There are no specific signs of diverticulitis, as such. The symptoms of the pathology are similar to an attack of appendicitis, renal colic and gynecological pathologies. That is why an accurate diagnosis will require a comprehensive examination using laboratory and instrumental methods.
You should pay attention to the following symptoms:
- Bloody impurities in the stool - the inflammatory process of the diverticulum is accompanied by bleeding erosions in the cavity of the formations. At the initial stage, the abundance of discharge is not strong. The patient notices blood on underwear, on toilet paper, in stool. The discharge increases with pushing. In some cases, the diverticulum bursts and breaks into the intestinal lumen. In such situations, acute pain is present.
- Temperature increase. During the inflammatory process in the intestines, special components are released into the blood, namely pyrogens. They affect the thermoregulation of internal organs, so body temperature rises. The body's defenses are activated and begin to fight inflammation.
Common symptoms include decreased appetite, nausea and vomiting, lethargy, belching, flatulence and bloating. Diverticula become inflamed, the body is poisoned by harmful substances, so the signs of intoxication are clearly pronounced.
Intestinal diverticulosis: symptoms, complications, treatment
Surgeon Nishimenko A.O.
Surgical department No. 1
Intestinal diverticula are saccular protrusions of the wall of the large, less often small intestine, of a congenital or acquired nature.
Pronounced symptoms in most patients suffering from colonic diverticulosis are usually absent or coincide with the symptoms of other intestinal diseases. However, the incidence of diverticulosis has been found to increase as the patient's age increases. The frequency of pathology among people under 40 years of age is 10%, and among people over 80 years of age – 50-60%. In Europe, diverticular disease is found in every 10th resident under 40 years of age, after 60 - in every third, and in every second after 75 years.
Symptoms of the disease are associated with the location of the diverticula. In Western countries, during diagnosis, diverticula are most often found in the distal parts of the large intestine - 90%, of which 50-60% fall on the sigmoid colon and only 10% on the first parts of the colon. No diverticula were found in the rectum.
Clinical manifestations of diverticular disease of the sigmoid colon and large intestine
All of the above reasons are the cause of intestinal dysfunction and lead to the gradual development of symptoms of diverticulosis and its complications:
- chronic and acute intestinal obstruction;
- internal and external (rare) fistulas;
- formation of infiltrate;
- perforation of the intestinal walls;
- bleeding;
- diverticulitis (inflammation of diverticulum).
The disease is characterized by a progressive nature with clinical symptoms, the severity of which depends on the patient’s compliance with recommendations regarding nutrition and diet, the patient’s age, the presence of concomitant diseases, the location of diverticula, complications of diverticular disease, and the duration of the disease.
The most common type is uncomplicated diverticulosis of the large intestine. It is present in almost 80% of patients with this pathology. For a long time it was believed that this form of the disease occurs without symptoms, but recent studies have shown that in 85% of patients, even single diverticula in the colon cause clinical manifestations, the severity of which varies on a purely individual basis.
In this case, the clinical signs of the disease are nonspecific. Most often, the patient does not seek help at all, and if he does, he is diagnosed with large intestinal dyskinesia, chronic colitis, dysbacteriosis, etc., since doctors often misinterpret the symptoms.
The main and most common symptoms of colon diverticulosis are:
- unstable, periodically recurring pain of a spasmodic, paroxysmal or aching dull nature, which is localized in the left, middle or lower abdomen. It is generally accepted that the appearance of pain is caused by impaired intestinal motility and increased internal pressure;
- the pain may subside on its own after several hours or intensify after eating;
- pain may appear that resembles an attack of appendicitis (in the lower right section), even if the localization of the diverticulum is on the left side, in the sigmoid colon;
- sometimes the pain radiates to the lumbar region, anus, sacrum, buttock or groin area;
- complete disappearance of pain or partial reduction may be observed after defecation or passage of gas.
In addition to the main manifestations of diverticular disease of the large intestine, general symptoms may develop, which are also characteristic of intestinal dysfunction:
- a feeling of incomplete emptying after defecation (very often a concomitant sign of diverticulum in the sigmoid colon);
- repeated acts of defecation or false urges;
- significant discharge of gases, bloating;
- copious mucous discharge;
- constipation followed by diarrhea;
- persistent constipation
The main thing in the treatment of uncomplicated forms of diverticulosis is a proper diet, which includes foods rich in dietary fiber. Based on the latest research, eating the “right” food in patients with asymptomatic disease is a measure to prevent the occurrence of complications and progression of the disease. Some researchers even claim that using such a diet leads to regression of diverticula.
Dietary or dietary fibers are plant fibrous substances of varying structure and composition that the intestines cannot digest and, accordingly, cannot adsorb. Based on a caloric intake of 2500 kcal per day, the daily intake of such fiber should be 30 grams. Most plant fiber contains alginates, lingin, hemicellulose, cellulose, pectin and indigestible polysaccharides. The main property of these substances is the binding of water located in the intestinal lumen, which helps accelerate the removal of toxins and feces from the body, reduces intraintestinal pressure, and increases the volume of chyme.
In addition, insoluble dietary fiber, which covers 6-9% of the body's energy needs, also creates additional surface in the intestines, which serves to fix and accommodate beneficial intestinal bacteria. Fiber is an acceptable environment for these bacteria, so they begin to actively multiply and accordingly improve the intestinal ability to suppress pathogenic flora.
It becomes clear why dietary products that contain bran are a useful food in the presence of intestinal diverticulosis. Coarsely ground wheat bran is most effective in increasing the volume of chyme and reducing intraintestinal pressure. They are introduced into the diet gradually over a period of 2 weeks to one month. The daily norm is from 5-10 to 20-30 grams. To prepare, you need to pour a glass of boiling water over the daily dose of bran and leave for 30-40 minutes, after which the water is drained. Bran brewed in this way can be added to soups, porridges, fermented milk products and vegetable dishes.
During the first month of such a diet, if you have intestinal diverticulosis, pain in the abdomen may increase. Therefore, during this period it is recommended to use antispasmodic drugs, for example, Mebeverine or No-shpu 20-30 minutes before meals in the morning, and in the evening - Bucopan, Meteospasmil 400 mg each. Effective sources of dietary fiber are also the preparations “Psyllium”, “Solgar”, “Ispagol”, “Fiberlex”, “Mukofalk”, which consist of the shell of the seeds of the oval plantain, which grows in the arid regions of India, Pakistan, and the Mediterranean. The seed shell of this type of plantain contains a high concentration of mucous components, which is why the drug is classified as a soft dietary fiber.
Nutrition for patients with intestinal diverticulosis should include:
- baked vegetables (if tolerated);
- dairy products;
- vegetable soups cooked in meat broth;
- vegetable casseroles;
- crumbly porridge from buckwheat and wheat with vegetable oil;
- bread made from wholemeal white flour or bran.
It is advisable to exclude foods that delay and astringent peristalsis from the diet. These include:
- chocolate, cocoa, red wine;
- strong tea, coffee, jelly;
- rice and semolina porridge;
- pasta;
- bread and flour of the highest quality.
Dietary fiber is a means of preventing and treating colon diverticulosis. If there are no complications of the disease, it is recommended to constantly adhere to this diet, with the exception of summer and autumn, when the daily diet is saturated with a sufficient amount of greens, fruits and vegetables.
If the disease progresses during therapy, hospitalization is required
If no improvement is observed within 3 days of treatment, the patient must be hospitalized, further treatment tactics and its correction must be determined. Additional diagnostics are also performed and infusion therapy is prescribed - saline solutions, glucose solution, and the need for surgical intervention is determined.
In what cases is surgery necessary?
If the patient has already suffered 2 attacks of diverticulosis, then, according to the latest study, it is necessary to undergo planned surgical intervention. The fact is that subsequent repeated attacks are poorly amenable to drug treatment and in most cases ends with perforation of the intestinal wall and the development of peritonitis. In addition, patients over 40 years of age, even after a single attack of diverculitis, should be consulted for surgery.
Surgical treatment consists of resection (removal) of the intestinal area damaged by diverticula. Indications for the operation are as follows:
- opening of an abscess with the development of internal or external intestinal fistula;
- perforation of the diverticulum with the development of peritonitis and phlegmon of the retroperitoneal area;
- progressive intestinal obstruction;
- heavy bleeding.
Each specific case individually determines the scope of surgical intervention. In some cases, during emergency surgery, the surgeon must remove the colon in an unnatural way (through the abdominal wall). Only timely contact with a coloproctologist and gastroenterologist, in combination with adequate therapy, and, if necessary, planned surgical intervention, can improve the prognosis of the disease. In 80% of cases, the course of diverticulosis passes without complications; in case of complications, the risk of relapse in the future is 25%.
Diagnosis of diverticulitis
Which doctor should I contact in case of intestinal problems?
A proctologist treats proctological pathologies. The therapist can also refer the patient to a urologist, gynecologist and other specialized specialists. It is recommended to consult a gastroenterologist who treats the digestive system. The patient will be referred for tests and diagnostic tests.
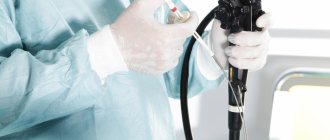
A colonoscopy is performed to diagnose the intestines. The inner surface of the colon is examined using an endoscope. The device is equipped with a narrow tube that is inserted into the anus. A small camera is attached to the end of the tube, which transmits the image to the monitor screen. The endoscopist identifies changes in the intestinal mucosa and takes material for a biopsy, if necessary.
Indications for colonoscopy
Colonoscopy is performed if there is a suspicion of cancer, ulcer or diverticulitis. Diagnostic testing also helps to diagnose the cause of internal intestinal bleeding, gastrointestinal disorders, and inflammation of the colon.
Colonoscopy is performed to detect deformation of the mouth of the diverticulum, an inflammatory or infectious process. The screen clearly demonstrates the presence of redness, swelling, and dilated blood vessels. The procedure determines the location of bleeding and determines the intensity.
X-ray contrast examination of the intestines
Irrigoscopy or X-ray contrast examination of the intestine allows you to take an X-ray and see the outline of the large intestine. It is carried out in equipped diagnostic rooms. In order to see the outlines of the internal organs, the patient is injected with a contrast liquid. We are talking about a solution of barium sulfate. As a rule, the contrast agent is administered through an enema or by ingestion.
The endoscopist takes pictures in a lying and standing position to observe the functioning of the internal organs in different situations.
Indications for irrigoscopy
The following indications for irrigoscopy are distinguished:
- bleeding from the anus;
- pain in the intestines;
- mucous or purulent discharge from the intestines;
- problems with bowel movements;
It is recommended to perform irrigoscopy if colonoscopy does not give accurate results. X-ray diagnostics reveal various symptoms of diverticulitis. The size of the formations in diameter does not exceed 10 centimeters. If the protrusions are single, it is much easier to cure the pathology. Multiple protrusions extend beyond the contour of the intestine. In the presence of inflammation, the edges of the diverticula have irregularities.
When a diverticulum ruptures, a fistula forms on the surface of the intestine. This complication is demonstrated both during irrigoscopy and colonoscopy. Often, during inflammation, adhesions form from the connective tissue, which affect the narrowing of the intestines.
Folk remedies
The following folk remedies are recommended to help normalize stools and restore intestinal function:
- Carrot seed powder (to do this, you need to thoroughly grind the carrot seeds and consume this powder several times a day (2-3), with a sufficient amount of water - 200-300 ml).
- Sauerkraut brine or radish juice (drink a few tablespoons after meals, 1-2 times a day).
- Infusion of aloe leaves (approximately 150 g of crushed leaves, pour 300 g of honey, leave the resulting mixture for 24 hours, strain and take a tablespoon an hour before meals).
- Flaxseed oil 1 tablespoon on an empty stomach daily.
- Mint tea (add 2-3 mint leaves to regular tea).
Indications for laparoscopy
The following indications for manipulation are distinguished:
- suspicion of ectopic pregnancy in women;
- suspicion of intestinal cancer;
- acute pain in the intestines;
- suspicion of acute intestinal obstruction;
- bleeding into the abdominal cavity caused by a ruptured diverticulum.
During laparoscopy, the doctor diagnoses the presence of growths on the outer wall of the intestine. On the surface of the diverticulum it is easy to see the condition of the blood vessels.
Complications
The development of the disease is fraught with abscess formation, and the abscess can break into the abdominal cavity. The subsidence of symptoms does not in all cases lead to the final resorption of the infiltrate; in this case, hardening of the mesentery and surrounding tissues occurs, which can result in a tumor of the abdominal cavity.
Repeated attacks of diverticulitis can lead to adhesions of the intestine with neighboring organs. Here the abscess has the ability to open into the bladder, vagina, urethra, small intestine, and fistulas are formed. However, perforation of a sigmoid colon diverticulum into the free abdominal cavity can have quite tragic consequences, since peritonitis develops and rapidly progresses.
Intestinal bleeding in this disease cannot be called profuse, however, it is so pronounced that it is quickly noticed by both the patient and doctors. Its hidden forms usually manifest themselves in anemia. Since it is quite difficult to recognize the causes of all these symptoms, a comprehensive study is used. In addition to the clinical manifestations of the disease, the results of essential X-ray and endoscopic examinations are also taken into account.
Treatment of diverticulitis
The treatment plan is drawn up individually for each patient. Elimination of the disease is carried out in hospital or at home. Hospitalization is indicated for exacerbation of chronic diverticulitis, in the presence of severe pain. Treatment is carried out in a hospital if the following symptoms are present:
- elevated temperature;
- signs of peritoneal irritation;
- increased number of leukocytes 15x 109/l;
- inability to take food by mouth;
- elderly age;
- the presence of concomitant diseases or complications;
The patient must be treated with medications. In most cases, surgical removal is performed.
Chemotherapy treatment of sigmoid colon cancer
Chemotherapy for sigmoid colon cancer can be used as part of a combination treatment. In addition, it can be used as an independent method of therapy for unresectable tumors or when it is impossible to perform surgery due to general contraindications.
As part of combination treatment, adjuvant chemotherapy is performed. The feasibility of its use is determined based on the stage of the tumor and the results of an urgent intraoperative examination of the removed intestinal fragment for the presence of malignant cells.
As part of adjuvant chemotherapy, fluoropyrimidine therapy (5-fluorouracil, then 5 FU) is used together with 3rd generation platinum drugs (oxaliplatin). If the patient develops severe complications from two-component regimens, therapy is continued with fluoropyrimidines in monotherapy. The goal of adjuvant chemotherapy is to destroy remaining tumor cells and prevent relapses of the disease.
Independent chemotherapy is palliative in nature and is aimed at containing the tumor process, prolonging the patient’s life and improving its quality.
In addition to regimens with oxaliplatin and 5-FU, regimens with irinotecan are used. Treatment may be supplemented with targeted drugs. In the absence of BRAF and RAS mutations, cetuximab and panitumumab are used. Bevacizumab can be prescribed regardless of the presence of mutations, but it is effective only in conjunction with cytostatic therapy. Cetuximab and panitumumab can be used as 3rd line monotherapy.