Sigmoid colon cancer often does not manifest clinical symptoms for a long time. For this reason, the diagnosis is often made at a late stage of the tumor process. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital recommend that even with minor manifestations of intestinal discomfort, immediately seek help.
At the Yusupov Hospital, oncologists use the latest methods for diagnosing diseases of the sigmoid colon. Patients are examined using the latest equipment from leading global manufacturers. Laboratory technicians examine blood, feces and other biological materials using high-quality reagents, which allows you to obtain accurate test results.
Surgeons at the Oncology Clinic masterfully perform traditional and innovative surgical interventions. Chemotherapists prescribe patients the most effective antitumor drugs that have minimal side effects. Radiologists conduct radiation therapy with modern devices that allow them to target the pathological focus without damaging the tissue surrounding the tumor.
Causes of tumors
Sigmoid colon cancer originates from glandular epithelial cells. Accounts for 34% of the total number of colorectal cancer cases. In 60% of cases, a malignant tumor is detected in patients aged 40-60 years. Men suffer 1.5 times more often than women.
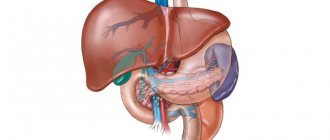
The high probability of developing sigmoid colon cancer is due to the characteristics of the organ. The sigmoid colon is located on the left side of the abdomen, above the rectum. It has an S-shape. If the movement of contents through the intestines slows down, it remains in the sigmoid colon for a long time. This increases the time of contact of toxic food processing products with the organ mucosa.
Sigmoid colon cancer can develop under the influence of the following unfavorable factors:
- Unbalanced diet - eating large amounts of fatty and meat foods, insufficient consumption of fruits and vegetables, foods rich in fiber;
- Compounded heredity - the risk of developing a malignant neoplasm increases if close relatives had sigmoid colon cancer;
- Chronic inflammatory processes in the intestines - nonspecific ulcerative colitis, diverticulosis, Crohn's disease;
- A sedentary lifestyle, as a result of which the evacuation of intestinal contents slows down;
- Multiple intestinal polyps, which are prone to degeneration into a malignant tumor; Constipation, in which the mucous membrane not only comes into contact with carcinogens for a long time, but is also injured by the solid contents of the intestine;
- Age-related intestinal atony.
Smoking, alcohol abuse, and consumption of foods containing carcinogenic food additives lead to the development of sigmoid colon cancer.
Make an appointment
Epidemiology
Applicable to Russia and the former USSR, one can note the rapid increase in the incidence of diverticular disease. In 1970, the incidence of the disease did not exceed 2-3 per 100 thousand population. In 1979, this number increased almost 6 times. According to data published by the State Research Center in 2002, the number of diverticulosis detected during X-ray examination was 14.2% of all coloproctological patients, and already in 2012 this figure doubled and amounted to 28.8%.
The growth of this disease is clearly visible along with the process of industrialization and urbanization due to changes in people’s way of life, lifestyle and nutrition. A decrease in the amount of dietary fiber consumed, a large amount of carbohydrate foods and consumption of red meat led to a significant jump in cases of diverticulosis.
In contrast, in developing agricultural countries, diverticular disease is characterized by isolated cases, which is determined by the nature of the diet, which includes a significant amount of plant foods.
The aging of society is another reason for the increase in the incidence of diverticular disease. It is noted that under the age of 40 years, the risk of developing diverticulosis varies between 5-10%. Whereas at the age of 60 years, the percentage of detected cases of the disease is already 30%, and by the age of 80 it exceeds 66%.
Thus, diverticular disease was, is and remains a serious problem posing difficult challenges for doctors and patients.
To understand the term diverticular disease, a brief description of the anatomy of the colon is necessary.
Classification
Taking into account the characteristics of tumor growth, oncologists distinguish two types of sigmoid colon cancer: exophytic and endophytic. Exophytic tumors grow into the intestinal lumen. They are protruding nodes on a thick stalk. As the pathological process progresses, sigmoid colon cancer often ulcerates. Bleeding and infection occurs.
Endophytic cancer of the sigmoid colon grows predominantly deep into the intestine. The tumor spreads along the intestinal wall and can cover the intestine circularly. In its center, areas of ulceration appear. Due to the circular growth of sigmoid colon cancer, the intestinal lumen narrows and the movement of feces becomes difficult. This type of growth is most characteristic of sigmoid colon cancer.
Histologists distinguish three types of sigmoid colon cancer:
- Adenocarcinoma originates from glandular epithelial cells. It can be highly differentiated, moderately differentiated and poorly differentiated;
- Mucous (mucosal) adenocarcinoma is a type of poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma, represented by mucinous cells that secrete large amounts of mucus. The tumor grows quickly and metastasizes early;
- Signet ring cell carcinoma of the sigmoid colon is represented by atypical signet ring-shaped cells, which are formed as a result of intracellular accumulation of mucin, pushing the cell nuclei to the periphery. The tumor is aggressive and has an unfavorable course.
Cancer of the recto-sigmoid colon is represented by two forms: scirrhus and adenocarcinoma.
Stages
Oncologists distinguish 4 stages of sigmoid colon cancer:
In the first stage of the tumor, the size of the tumor does not exceed two centimeters. The tumor is located within the submucosal layer or mucosa. Regional lymph nodes are not affected by atypical cells.
In the case of the second A stage of cancer, the tumor occupies less than half the circumference of the intestine and does not grow into the wall. There are no metastases in the lymph nodes and internal organs. A cancerous tumor at stage 2B is located in the intestinal wall, but does not extend beyond its boundaries. Oncologists detect metastases in the lymph nodes. There are no distant metastases.
With stage 3A sigmoid colon cancer, the size of the tumor exceeds half the circumference of the intestine. There are no atypical cells in the regional lymph nodes. In stage 3B tumors, regional lymph nodes are affected by metastases.
The tumor in stage 4 cancer blocks the lumen of the sigmoid colon. Hematogenous metastases are detected in other organs. In stage 4 sigmoid colon cancer, nearby organs are affected, and enterovesical fistulas and conglomerates are formed.
Symptoms
At first, sigmoid colon cancer is often asymptomatic or minimally symptomatic, which complicates timely diagnosis. As the tumor progresses, it spreads to nearby organs, giving regional and hematogenous metastases (to the liver, lungs, spine, and less often to other organs).
In the lower part of the intestine - the sigmoid colon - feces are finally formed, water and nutrients are absorbed. With improper nutrition, feces are retained in this segment of the large intestine. The accumulated feces presses on the intestinal walls, as a result of which blood circulation is disrupted and toxic substances enter the body through the walls of the sigmoid colon. Constant constipation negatively affects the entire body. As a result of stagnation of intestinal contents, precancerous diseases, malignant tumors of the sigmoid colon, develop.
For quite a long time, a tumor of the sigmoid colon does not manifest clinical symptoms, which complicates timely diagnosis. The first symptom of sigmoid colon cancer is intestinal discomfort. At first it occurs periodically, and with the growth of the tumor it becomes more pronounced. Later stages of sigmoid colon cancer are manifested by the following symptoms:
- Flatulence, belching, nausea, constipation or diarrhea, pain;
- The appearance of streaks of mucus and blood in the stool;
- Intense, dull or cramping pain that does not depend on food intake;
- Development of intestinal obstruction;
- Abdominal abscess, bleeding, peritonitis (inflammation of the peritoneum).
Patients have diarrhea alternating with constipation. Doctors are often able to palpate a tumor-like formation in the left half of the abdomen. Sometimes the first manifestation of the tumor process is the development of intestinal obstruction. As the tumor progresses, it spreads to nearby organs, giving regional and hematogenous metastases (to the liver, lungs, spine, and less often to other organs).
In patients with sigmoid colon cancer, doctors identify the following symptoms:
- Weakness;
- Fatigue;
- Pale or grayish skin tone;
- Hyperthermia;
- Loss of weight and appetite due to cancer intoxication.
With the development of intestinal obstruction, paroxysmal cramping pain occurs, which is repeated every 10-15 minutes, bloating, gas and stool retention are noted. Possible vomiting. If the intestinal wall is destroyed, peritonitis develops. Stage 4 sigmoid colon cancer with liver metastases is manifested by cachexia (cancer exhaustion), anemia (anemia), jaundice and liver enlargement. When hematogenous metastases appear, symptoms appear that indicate dysfunction of the affected organs.
Make an appointment
General characteristics of the disease
Proctitis is a disease of the sigmoid colon.
To draw correct conclusions about the condition of the sigmoid colon, it is necessary to conduct an examination of the processes that occur inside it. It is necessary to study the physiological and anatomical components of the sigmoid colon.
As everyone knows, the intestine has a thick section and a thin section. Each of them is responsible for performing a specific function.
The thin section is responsible for digesting food and absorbing nutrients, while the thick section supplies the blood with water, glucose, vitamins and amino acids. Fecal matter also forms in the large intestine.
To study sigmoiditis, we need the large intestine. This is where the rectum and colon are located. The terminal portion of the colon is shaped like the letter S, hence the name sigmoid.
Taking as a basis the physiological, anatomical characteristics and the presence of the nearby rectum, we can conclude that sigmoiditis in isolation is quite rare. If it occurs, it is most often in the final section of the gastrointestinal tract.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of a sigmoid colon tumor is made by oncologists at the Yusupov Hospital taking into account the medical history, complaints, objective examination data and the results of additional studies. The most informative methods for sigmoid colon cancer are endoscopic methods (sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy). They allow you to visually assess the volume and location of the tumor and take material for subsequent histological examination.
In the process of examining patients with suspected sigmoid colon cancer, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital use irrigoscopy (X-ray examination using a barium suspension) and stool analysis for occult blood. To detail the stage of the tumor process, magnetic resonance and computed tomography are performed. All instrumental research methods are performed using the latest equipment from leading manufacturers in the USA, Japan and European countries.
Other diagnostic techniques are used to detect metastases:
- Ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs;
- X-ray of the spine;
- Chest X-ray.
Oncologists at the Yusupov Hospital make the final diagnosis based on the results of histological examination. Differential diagnosis of malignant neoplasms of the sigmoid colon is carried out with precancerous and inflammatory bowel diseases, fixed tumors of the retroperitoneal space and mobile neoplasms of the mesentery.
Examination methods
When interviewing a patient, it is necessary to establish previous diseases, the nature of abdominal pain, their connection with food intake, time of day, frequency of bowel movements, and features of feces. When examining the abdomen (see) in a patient with S.'s pathology, one can see increased intestinal motility (with obstruction), protrusion of the abdominal wall (with large tumors, especially in exhausted patients). When palpating the anterior abdominal wall, a pathologically altered S. can be identified. Among the instrumental methods used are endoscopic (see Colonoscopy, Peritoneoscopy, Sigmoidoscopy) and X-ray examination (see Angiography, Irrigoscopy).
Complex therapy
Oncologists at the Yusupov Hospital provide combined treatment for malignant tumors of the sigmoid colon.
It includes surgery, radiotherapy and chemotherapy. The leading role is given to surgical treatment, which is aimed at radical removal of the tumor. The extent of surgical intervention depends on the extent of sigmoid colon cancer. In the early stages of the disease, endoscopic techniques are used in some cases. For this purpose, resection of the sigmoid colon is used. In case of widespread tumor processes, surgeons perform resection of the sigmoid colon with a section of the mesentery and nearby lymph nodes. The affected area of the sigmoid colon is removed along with five centimeters of intact intestine located above and below the tumor. Surgery for sigmoid colon cancer can be one-stage or two-stage. When performing one-stage operations after tumor removal, the surgeon restores intestinal continuity by performing an anastomosis. In advanced cases, the intestine is resected and a colostomy is formed. The integrity of the intestine is restored several months after the first operation.
Surgery can be typical, combined, extended or combined. A typical operation involves resection of the area of intestine containing the tumor. A combined treatment method is used if it is necessary to perform surgery on the cancer-affected segment of the intestine and other organs into which the tumor has grown. Extended surgery is performed when the tumor grows or there are synchronous neoplasms. A combined operation involves removing the affected segment of the intestine along with other organs due to concomitant diseases.
In the presence of cancer metastases, doctors at the oncology clinic administer chemotherapy. Treatment with antitumor drugs for sigmoid colon cancer after surgery is used with caution - in some cases it can cause negative results. Most often, the use of chemotherapy is advisable for inoperable tumors - it helps to reduce the size of the tumor. Sigmoid colon cancer does not respond well to radiation treatment. Radioactive rays can damage normal tissue, so this method is not used to treat sigmoid colon cancer.
In advanced cases of cancer, palliative therapy is carried out to reduce pain and ensure intestinal patency. Sometimes emergency surgery is performed for sigmoid colon cancer. They are aimed at sanitizing the abdominal cavity in case of peritonitis and eliminating intestinal obstruction.
Planned surgical treatment of diverticulosis
As a rule, after a single attack of diverticulitis, surgical treatment is not indicated, but may be recommended for persons under 45 years of age. The decision to perform an operation is made individually.
After successful conservative treatment of two or more episodes of diverticulitis, elective surgery is recommended. The indications for elective surgery are limited by the high anesthetic and surgical risks identified during examination of the patient.
Elective surgical treatment is mandatory after conservative treatment of complicated diverticulitis.
Planned surgical treatment is indicated in the presence of fistulas.
Nutrition after surgery
After surgery on the sigmoid colon, patients at the Yusupov Hospital are provided with dietary nutrition. The chefs prepare dishes from quality ingredients. They contain a sufficient amount of vitamins and minerals. The menu includes kefir, yogurt, bifido products, fresh vegetables and fruits. All dishes are prepared using gentle technologies: steamed, boiled, baked in the oven or grilled. If indicated, the food is crushed. Patients eat regularly, in small portions.
During the rehabilitation process, the patient should follow certain rules:
- eat only fresh foods;
- products must contain a sufficient complex of vitamins and minerals;
- reduce meat consumption to a minimum;
- consume kefir, yogurt, and bifido products more often;
- eat more fresh vegetables and fruits;
- include cereal porridges and products made from wholemeal flour with bran in the menu;
- periodically include boiled or steamed sea fish in the menu;
- Take food in crushed form, chew thoroughly;
- do not overeat, eat small meals and regularly.
Rehabilitation period
It is worth understanding that removing part of the intestine affects the functions of the gastrointestinal tract as a whole. Therefore, during the recovery period, it is important to follow all medical instructions regarding nutrition. Initially, the diet will contain exclusively liquid dishes, then mashed potatoes, cereals, and solid foods will be gradually added. All food should be easily digestible.
In the first 10 days after the operation, a particularly strict diet is indicated, then boiled fish and chicken are gradually added to the diet. Adding new foods is quite similar to feeding a baby for the first time - it takes a couple of days to test the body's reaction to them. On average, it takes 1.5-2 months for the intestines to adapt to “new conditions”.
More fresh and relevant information about health on our Telegram channel. Subscribe: https://t.me/foodandhealthru
We will be grateful if you use the buttons:
Forecast
The survival prognosis of patients with sigmoid colon cancer depends on the histological type of the tumor, the level of cell differentiation, the prevalence of the malignant process, the presence of concomitant diseases and the age of the patient.
The average five-year survival rate is 65.2%. A more optimistic prognosis after surgery for adenocarcinoma of the sigmoid colon, since the tumor grows slowly and practically does not metastasize. When sigmoid colon cancer of the first stage is detected, 93.2% of patients overcome the five-year mark, the second - 82.5%, the third - 59.5%. 8.1% of patients with stage 4 sigmoid colon cancer survive up to five years. Therefore, consult a doctor when the first signs of intestinal dysfunction appear.
To establish an accurate diagnosis in the early stages of sigmoid colon cancer, when the first signs of intestinal disorders appear, call the Yusupov Hospital. After a comprehensive examination, if the diagnosis is confirmed, oncologists will provide adequate therapy. After treatment, doctors at the oncology clinic conduct clinical observation, the purpose of which is the timely detection and treatment of early metastases. This makes it possible to improve the quality and increase the life expectancy of patients diagnosed with sigmoid colon cancer.
Make an appointment
Possible complications
Possible complications:
- bleeding due to inadequate hemostasis;
- failure of postoperative wound sutures or anastomosis;
- infectious complications (life-threatening conditions such as peritonitis and sepsis may develop);
- dynamic intestinal obstruction (intestinal paresis);
- adhesive disease;
- postoperative hernia.
A sigmoidectomy is a major surgical procedure. However, if the operation is performed correctly by qualified surgeons and the patient follows all recommendations, it is possible to achieve a good quality of life for the patient after resection.