- home
- Gastroenterology
- Treatment of gallstones
Treatment of gallstones is a complex and multi-stage process that requires the use of high-tech medical equipment, the best medications, and the involvement of real professionals in the field of gastroenterology. All these components are available in our clinic.
What is gallstone disease
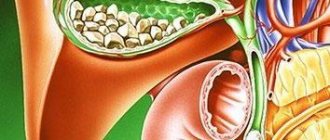
Gallstone disease is a pathology in which stones form in the gallbladder.
Cholelithiasis (cholelithiasis) is a pathology in which stones form in the gallbladder or duct. The size of the stones can range from a couple of millimeters to several centimeters.
The causes of the disease include the consumption of foods that contain a high content of animal fat and protein. Due to the uncontrolled consumption of these products, a person’s cholesterol level in bile goes through the roof, which leads to poor performance of functions and stagnation.
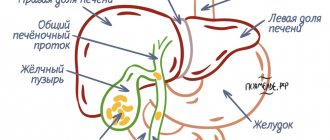
Bile is a liquid found in the cavity of the gallbladder, which is responsible for the breakdown and digestion of food. The gallbladder is located next to the liver, which produces bile, namely its component - the pigment bilubin. The second main component of bile fluid is cholesterol, the excess of which provokes the development of cholelithiasis.
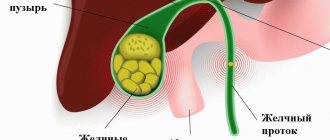
Due to long-term stagnation of bile, cholesterol precipitates, from which the so-called “sand” is formed, the particles of which join each other and form stones (calculi). Small stones (1-2 mm) are able to pass through the bile ducts on their own, while larger stones are a gallstone disease that requires therapeutic intervention.
What foods dissolve gallstones?
causes gallstones?
The bile produced goes into the gallbladder, a small organ located under the liver. Bile juice is a complex substance that contains bilirubin and cholesterol.
With elevated cholesterol levels, it is deposited on blood vessels in the form of cholesterol plaques, negatively affecting the functioning of many organs and systems. An excess of the substance in the body increases its concentration in bile and makes it very viscous. This makes it difficult to evacuate bile from the bladder cavity and leads to its crystallization. At this stage, “sand” is formed. Over time, grains of sand join together and form concrements (stones).
The main causes of calculous cholecystitis include:
- inflammatory processes in the gallbladder;
- poor nutrition;
- the use of certain medications, including hormonal ones;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (gastrointestinal tract), diabetes mellitus, cirrhosis of the liver;
- alcohol abuse;
- heredity;
- obesity;
- pregnancy and multiple births in women.
Psychosomatics plays an important role - studies have found that the development of cholelithiasis is influenced by stress, and the disease more often develops in people with emotional lability and prone to depression.
Types of stones
Bile consists of various components that affect the composition of the formations. The following types of stones are distinguished:
- cholesterol - characterized by small size and round shape;
- bilirubin - small in size, localized both in the gallbladder and in the ducts;
- mixed - consist of a pigmented center and a cholesterol shell.
Sometimes there are calcareous stones, which contain a lot of calcium.
Symptoms of the disease
Often cholelithiasis occurs secretly and does not manifest itself for a long time. Symptoms begin to appear when the formations reach large sizes or block the bile ducts. In such cases, the disease manifests itself as an attack of biliary colic, which lasts from 10 minutes to several hours.
Its signs:
- pain in the right hypochondrium, which often radiates under the shoulder blade, into the back, into the shoulder;
- nausea, vomiting;
- bitterness in the mouth;
- temperature increase.
Depending on the size of the stones and their location, symptoms can be either muted or pronounced.
Blockage of the bile ducts is manifested by yellowing of the skin, sclera and mucous membranes, itching, dark urine and light-colored feces.
Therapeutic diet
Compliance with a diet for cholelithiasis is one of the important components of bile duct therapy. By adhering to the recommended diet, you can improve your condition, reduce bile stagnation, eliminate malfunctions of the gallbladder, liver, intestines, and reduce the risk of colic. If you have gallstones, you need foods rich in fiber, vitamins and magnesium.
Most useful:
- lean meats and fish;
- slightly dried bread;
- vegetable broth soups;
- low-fat dairy products;
- boiled or baked vegetables;
- non-acidic berries and fruits;
- vegetable oil (olive, corn).
An infusion of rose hips, which has a moderate choleretic effect, will be beneficial.
Patients with calculous cholecystitis should avoid fried, fatty foods, marinades, pickles, smoked foods, coffee, and alcohol. Among vegetables, it is not recommended to eat onions and green onions, sorrel, garlic, and radishes.
Is it possible to dissolve stones with products?
Removing stones is the job of surgeons. But in some cases, certain products help get rid of them. They should be used with caution and only after consulting a doctor.
It is believed that cholesterol stones can be affected. They have a soft structure and are more pliable than bilirubin. Products that break up stones turn them into sand, which then flows out through the channels without much difficulty.
You can use traditional methods to dissolve stones if:
- no exacerbation;
- diet is followed;
- do not drink alcohol-containing drinks;
- the stones are immobile and small in size.
What foods dissolve gallstones:
- Apple juice and apple cider vinegar. Apples contain acid that softens gallstones, and vinegar controls the formation of cholesterol. Add a tablespoon of vinegar to a glass of freshly squeezed juice and take it once a day.
- Beetroot decoction . This root vegetable enhances the outflow of bile and is able to reduce the size of formations. The beets are boiled for 5-6 hours until the liquid acquires a thick consistency. The decoction is taken 3 times a day, ½ cup.
- Lemon juice. It dissolves stones and promotes their removal. The juice of three lemons is diluted with 3 liters of water and consumed throughout the day every 2 hours. The course of treatment is a week.
Many patients try to use traditional methods to avoid surgery. But do not forget that decoctions and infusions often cause increased secretion of bile, which can lead to migration of formations into the ducts. The result of this process will be blockage of the bile ducts, which will require urgent surgical intervention.
Sources
“Eating, Diet, & Nutrition for Gallstones”, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, USA https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/gallstones/eating-diet-nutrition
"Gallstones: Overview", National Health Service UK https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/gallstones/
"Gallstones", University of California, Department of Surgery, San Francisco https://surgery.ucsf.edu/conditions—procedures/gallstones.aspx
Symptoms of cholelithiasis
Heartburn can be a symptom of cholelithiasis.
Often, a person is not aware of the presence of cholelithiasis until the sudden onset of symptoms that require immediate action. List of common symptoms of this disease:
- acute pain in the right hypochondrium;
- a sharp attack of biliary colic;
- heartburn;
- nausea and vomiting;
- bloating;
- high temperature;
- yellowness of the skin.
Neglect of the disease can provoke the following complications:
- gallbladder infection;
- narrowing of the bile ducts;
- the formation of chronic inflammatory processes leading to diseases such as hepatitis, cholecystitis, duodenitis, pancreatitis.
Dissolving stones with medications
Allohol is a drug that stimulates the production of bile fluid.
This method of treatment is effective only for cholesterol stones, for calcareous and pigment stones, alas, this method does not work. The following medications can be used:
- Bile acid analogues: Henofalk, Henochol, Ursosan, etc.
- Drugs that stimulate contraction of the gallbladder and the production of bile fluid: Cholasas, Allohol, Lyobil, Zixorin, etc.
Disadvantages of drug therapy:
- when you stop taking medications, often (10-70% of cases) the disease returns again, as cholesterol levels rise again;
- side effects are observed in the form of diarrhea and changes in liver tests (AST, ALT);
- the course of treatment is long, medications are taken for at least half a year, sometimes up to three years;
- high cost of medicines.
Contraindications to drug treatment:
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract: peptic ulcers, gastritis;
- kidney diseases;
- obesity;
- pregnancy period.
Authorized Products
- Butter, olive, corn, flaxseed, sunflower oil. The ratio of animal and vegetable fats should be 1:1. A prerequisite is that all oils are introduced into the finished dish in their natural form. It is natural vegetable oils that have not undergone heat treatment that cause the production of cholecystokinin , which stimulates the formation of bile.
- Wheat bread with bran, rye. Only stale bread is allowed; biscuits, whole grain bread and bran bread are allowed. For the whole day: 150 g of wheat bread and 100 g of rye bread are allowed.
- Soups with vegetable broths (from cereals, vegetables or noodles). You can eat borscht and cabbage soup, beetroot soup, and fruit soups.
- Lean beef, rabbit, chicken, veal. You can boil them and make beef stroganoff from boiled meat; you can bake them after boiling. Serve in pieces or chopped (steamed or baked meatballs, cutlets, meatballs and quenelles).
- Baked lean fish, fish stuffed with vegetables, steamed and baked fish cutlets, soufflés and quenelles.
- Cereal dishes include crumbly porridges made from rice, buckwheat and oatmeal, viscous semolina, and pasta.
- Fermented milk products should be chosen as low-fat. It is recommended to consume low-fat cottage cheese daily (in its natural form and as part of dishes). Milk and sour cream are added only to dishes.
- Eggs are allowed to be eaten as an omelet or soft-boiled.
- Various vegetables in baked, boiled or stewed form, salads from fresh vegetables with vegetable oil, vegetable caviar, puree of carrots, pumpkin, green peas. Mainly the diet should contain cabbage of all varieties (if poor tolerance is limited to fresh white cabbage), beets and carrots, pumpkin, dill, parsley.
- Sour cream, vegetable and milk sauces are allowed. You can bake fish, meat and vegetables with sauces.
- Fruits and berries should be chosen that are not acidic and consumed fresh and in the form of compotes, jelly, fruit drinks, and infusions.
- Sweets are limited - marmalade, honey, jam, sugar (30 g per day).
- Drinks: rosehip infusion, vegetable juices, weak tea (preferably with milk), bran decoction, still mineral water.
Table of permitted products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| eggplant | 1,2 | 0,1 | 4,5 | 24 |
| zucchini | 0,6 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 24 |
| cabbage | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,7 | 27 |
| broccoli | 3,0 | 0,4 | 5,2 | 28 |
| Brussels sprouts | 4,8 | 0,0 | 8,0 | 43 |
| cauliflower | 2,5 | 0,3 | 5,4 | 30 |
| carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
| cucumbers | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,8 | 15 |
| salad pepper | 1,3 | 0,0 | 5,3 | 27 |
| parsley | 3,7 | 0,4 | 7,6 | 47 |
| iceberg lettuce | 0,9 | 0,1 | 1,8 | 14 |
| tomatoes | 0,6 | 0,2 | 4,2 | 20 |
| pumpkin | 1,3 | 0,3 | 7,7 | 28 |
| dill | 2,5 | 0,5 | 6,3 | 38 |
Fruits | ||||
| bananas | 1,5 | 0,2 | 21,8 | 95 |
| apples | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 47 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| raisin | 2,9 | 0,6 | 66,0 | 264 |
| dried figs | 3,1 | 0,8 | 57,9 | 257 |
| dried apricots | 5,2 | 0,3 | 51,0 | 215 |
| dried apricots | 5,0 | 0,4 | 50,6 | 213 |
| prunes | 2,3 | 0,7 | 57,5 | 231 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| buckwheat (kernel) | 12,6 | 3,3 | 62,1 | 313 |
| oat groats | 12,3 | 6,1 | 59,5 | 342 |
| pearl barley | 9,3 | 1,1 | 73,7 | 320 |
| rice | 6,7 | 0,7 | 78,9 | 344 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| pasta | 10,4 | 1,1 | 69,7 | 337 |
| noodles | 12,0 | 3,7 | 60,1 | 322 |
| buckwheat noodles | 14,7 | 0,9 | 70,5 | 348 |
Bakery products | ||||
| bran bread | 7,5 | 1,3 | 45,2 | 227 |
| whole grain bread | 10,1 | 2,3 | 57,1 | 295 |
Confectionery | ||||
| jam | 0,3 | 0,2 | 63,0 | 263 |
| jelly | 2,7 | 0,0 | 17,9 | 79 |
| marshmallows | 0,8 | 0,0 | 78,5 | 304 |
| milk candies | 2,7 | 4,3 | 82,3 | 364 |
| fondant candies | 2,2 | 4,6 | 83,6 | 369 |
| fruit and berry marmalade | 0,4 | 0,0 | 76,6 | 293 |
| paste | 0,5 | 0,0 | 80,8 | 310 |
| Maria cookies | 8,7 | 8,8 | 70,9 | 400 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| honey | 0,8 | 0,0 | 81,5 | 329 |
| sugar | 0,0 | 0,0 | 99,7 | 398 |
Dairy | ||||
| kefir 1.5% | 3,3 | 1,5 | 3,6 | 41 |
| Ryazhenka | 2,8 | 4,0 | 4,2 | 67 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cottage cheese | 17,2 | 5,0 | 1,8 | 121 |
| cottage cheese 1% | 16,3 | 1,0 | 1,3 | 79 |
Meat products | ||||
| beef | 18,9 | 19,4 | 0,0 | 187 |
| rabbit | 21,0 | 8,0 | 0,0 | 156 |
Bird | ||||
| boiled chicken breast | 29,8 | 1,8 | 0,5 | 137 |
| boiled chicken drumstick | 27,0 | 5,6 | 0,0 | 158 |
| boiled turkey fillet | 25,0 | 1,0 | — | 130 |
Eggs | ||||
| chicken eggs | 12,7 | 10,9 | 0,7 | 157 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| flounder | 16,5 | 1,8 | 0,0 | 83 |
| pollock | 15,9 | 0,9 | 0,0 | 72 |
| cod | 17,7 | 0,7 | — | 78 |
| hake | 16,6 | 2,2 | 0,0 | 86 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| butter | 0,5 | 82,5 | 0,8 | 748 |
| corn oil | 0,0 | 99,9 | 0,0 | 899 |
| linseed oil | 0,0 | 99,8 | 0,0 | 898 |
| olive oil | 0,0 | 99,8 | 0,0 | 898 |
| sunflower oil | 0,0 | 99,9 | 0,0 | 899 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| mineral water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| green tea | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| apricot juice | 0,9 | 0,1 | 9,0 | 38 |
| carrot juice | 1,1 | 0,1 | 6,4 | 28 |
| peach juice | 0,9 | 0,1 | 9,5 | 40 |
| plum juice | 0,8 | 0,0 | 9,6 | 39 |
| tomato juice | 1,1 | 0,2 | 3,8 | 21 |
| pumpkin juice | 0,0 | 0,0 | 9,0 | 38 |
| rose hip juice | 0,1 | 0,0 | 17,6 | 70 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Crushing stones using ultrasound
Ultrasound crushing of stones is used if the patient has no more than four stones.
This method is used if the patient has no more than four stones, up to 3 cm in size, that do not contain calcareous impurities.
The principle of operation is to expose the stones to high pressure and vibrations of a regenerated shock wave, in order to crush the resulting stones to a size not exceeding 3 mm.
Next, small stones are excreted through the bile ducts into the duodenum. Disadvantages of ultrasonic crushing:
- there is a possibility of blockage of the bile ducts due to vibration waves;
- sharp stones can damage the walls of the gallbladder.
Contraindications:
- poor blood clotting;
- pregnancy period;
- inflammatory processes and chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract: pancreatitis, peptic ulcers, cholecystitis.
Laser crushing of stones
Access to the gallbladder is through a puncture on the anterior abdominal wall. The laser beam is delivered directly to the affected area and splits the existing stones. The duration of the procedure is no more than 20 minutes.
Contraindications:
- The patient's weight exceeds 120 kg;
- Age over 60 years;
- Severe general condition.
Flaws:
- The likelihood of a burn to the mucous membrane, which in the future can lead to the development of an ulcer;
- Injury to the walls of the gallbladder by sharp edges of stones and obstruction of the bile ducts;
- The need for special equipment.
Method of contact chemical cholelitholysis
This method fights all types of stones, regardless of composition, quantity and size. The primary goal of contact chemical cholelitholysis is to preserve the gallbladder. The method can be applied at any stage of symptomatic or asymptomatic disease.
How the procedure is carried out: using ultrasound control, a catheter is inserted into the patient’s gallbladder through the skin and liver, through which a dissolving liquid (mainly methyl trebutyl ether) is slowly injected. Experts have confirmed that the gallbladder is resistant to the cytotoxic effects of this solvent.
The disadvantages of this method include invasiveness (invasion into the patient’s body).
The most common folk methods
Traditional medicine has accumulated many recipes that are used to treat gallstone disease. Various means can be used to dissolve stones, remove them along with bile, relieve pain and inflammation, and improve the general condition of the patient. Properly selected folk remedies can soften stones, break them into smaller fragments and remove them from the gallbladder.
Any medicine, even natural, has contraindications. Therefore, before using traditional methods, you should consult your doctor. The selected product must be used strictly according to the instructions, observing the dosage and regimen.
Many folk remedies can alleviate the patient’s condition, you just need to choose the right one
Chicken bile
This remedy is considered the most effective for dissolving even large stones. After all, chickens swallow ordinary pebbles, which they need for digestion. And then they dissolve with the help of bile. But this method is quite expensive, since bile from one chicken is enough for 2 days, and you need to take it for 2–4 weeks.
For treatment, you need to buy a fresh and not very fatty chicken carcass. Carefully cut out the gallbladder and collect its contents with a syringe. Take 20 drops per day. This is done like this: roll 10 balls of bread crumb, drop 2 drops of bile into each. They need to be swallowed every 2 hours throughout the day. The remaining bile is stored in the refrigerator.
Raisin
With the help of raisins, you can both treat existing gallstone disease and prevent the formation of new stones. This product helps relax the smooth muscles of the bile ducts and accelerates the excretion of bile. But for this it is better to use red raisins.
To prepare this medicine, you need to pour 100 g of raisins in a glass of boiling water in a thermos in the evening. After a day, eat the resulting mass. You need to wash down the raisins with a glass of mineral water in which a spoonful of Holosas syrup is dissolved. Then you need to lie on the heating pad with your right side. This procedure should be carried out every 2 days, 10 times in total.
The following remedy is also effective for cleansing the gallbladder and intestines: mix 50 g of raisins and hay and boil in one and a half liters of water. Leave overnight, then strain and add 100 ml of Holosas syrup. Drink half a glass in the morning half an hour before breakfast.
Potato
What can you eat if you have gallstones?
Potato decoction can be used to introduce sand and small pebbles from the gallbladder. It is best to make it from whole potatoes. You don't need to clean it, just cut out the eyes. Pour half a kilogram of potatoes into 3 liters of water and cook over low heat for several hours. Then make puree without draining the water. After settling, a liquid forms on top, which must be drained and consumed as medicine. You need to drink 2 tablespoons half an hour before each meal.
You can prepare the medicine in another way. Wash regular potato peelings well and cook for 5-10 minutes. After straining, drink 2 glasses throughout the day. This remedy also has a choleretic effect.
Olive oil
This product is considered the most effective choleretic agent. The oil helps remove excess bile from the bladder, prevents stagnation, and also reduces the amount of cholesterol. This allows you to soften the stones and prevent their formation. For treatment, it is better to use unrefined virgin oil. Start taking it with half a teaspoon, as it can cause nausea.
Use of medicinal herbs
This is the main method of traditional medicine. Various medicinal herbs are used for stagnation of bile, cholecystitis, and the presence of small stones. You need to use decoctions and infusions of herbs for 2–4 weeks, then take a break.
There are many effective recipes, so everyone can choose the one that suits them best:
- You need to rinse and squeeze the juice from the wheatgrass. Dilute it with water 1:1 and boil for several minutes. Take a glass a day.
- St. John's wort decoction is taken half a glass half an hour before each meal.
- Wild strawberries are also useful for improving the flow of bile. Take the juice from its berries, 4 tablespoons in the morning, as well as a decoction of the leaves, half a glass before meals. It is useful to make tea from twigs, dry berries and leaves. It has a choleretic effect and increases the amount of bile acids in bile, which prevent the hardening of stones.
- Decoctions of mint and oregano can also be used as tea. They have a mild choleretic effect.
- You can drink a teaspoon of fresh celandine juice. Just be sure to dilute it with water.
- The following mixture effectively dissolves stones: mix mint, immortelle, knotweed, nettle, chamomile and rose hips in equal parts. Boil a tablespoon of the mixture for 10 minutes in a glass of water. Take a tablespoon half an hour before each meal.
Decoctions of medicinal herbs are most effective for gallstone disease.
Cholecystectomy and laparoscopic cholecystectomy
Laparoscopy and laparotomy in this case mean removal of the gallbladder along with the stones it contains. A laparoscope is a tube with a video camera that is inserted into one of several incisions in the abdominal cavity (3-4 are made during surgery). Next, the gallbladder is removed through a small hole (up to 1.5 cm in diameter). Advantages of laparoscopy:
- short recovery period;
- low cost;
- no large scars.
Laparoscopy
Laparoscopy is performed under general anesthesia. Stones are removed using trocars (metal guides) that are inserted into incisions in the abdomen. The peritoneum is filled with carbon dioxide, and a device tube is inserted into one of the incisions to transmit the image to the monitor screen. Based on the image, the doctor finds and removes the stones. After the operation is completed, staples are applied to the ducts and vessels of the gallbladder. The operation lasts about an hour, hospital stay is 1 week.
The indication for laparoscopy is calculous cholecystitis.
Contraindications:
- Obesity;
- The stones are too large;
- The presence of adhesions after surgical interventions;
- Gallbladder abscess,
- Diseases of the heart and respiratory system.
Cholecystectomy
Both laparoscopy and laparotomy in this case involve removal of the gallbladder itself. Surgical treatment is indicated for large stones and frequent relapses, which are accompanied by severe pain, high fever and various complications.
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy
During laparoscopic cholecystectomy, gallstones are removed along with the bladder through a small incision up to 1.5 cm in diameter on the anterior surface of the abdomen. A total of 3-4 such incisions are made. A laparoscope (a small tube with a video camera) is inserted through another incision to monitor the operation. The advantages of laparoscopy over abdominal surgery are a short recovery period, absence of noticeable scars and lower cost.
Cavity open surgery
If the stones are too large, surgery is performed.
Surgeons resort to this method in case of gallstone diseases with severe complications, when the stones are too large or in the presence of dangerous inflammatory processes.
The operation is performed through a large incision with a diameter of up to 30 cm, running from the right hypochondrium to the navel. Flaws:
- mandatory anesthesia;
- high invasiveness;
- possibility of infection;
- risk of bleeding;
- Possible death (in case of emergency surgery).
Reasons why the gallbladder should not be removed:
- impaired motility of the muscles of the duodenum;
- bile changes its consistency and does not protect the organ as effectively from pathogenic organisms;
- bile acid irritates the mucous layers and, as a result, diseases are possible: gastritis, duodenitis, colitis, etc.;
- the functions of secondary absorption of bile are disrupted and it is quickly eliminated from the body, which negatively affects the digestion process;
- the appearance of pain in the right hypochondrium, bitterness and metallic taste in the mouth.
Removing the gallbladder does not guarantee the absence of cholelithiasis, since stones can also form in the bile ducts.
Before resorting to cholecystectomy, you need to try to get rid of the problem using more gentle methods, and only when their ineffectiveness is confirmed, then operate.
Fully or partially limited products
- Extractive dishes (broths), spicy vegetables and herbs with a high content of essential oils: horseradish, parsnips, celery, onions, garlic, shallots, katran, oregano, marjoram, savory, rosemary, basil, radishes, turnips, radish.
- Fatty meat and fish, goose and duck meat, smoked meats, fish caviar, salted fish, refractory fats and lard, sausages, all types of canned food.
- By-products (internal organs of animals due to their high cholesterol content).
- Hard-boiled and fried eggs, which are difficult to digest.
- Fresh bread, pastry, fried pastries (pies, pancakes, pancakes), cakes, pastries, puff pastry.
- Whole fat milk and cream.
- Hot sauces.
- Carbonated and alcoholic drinks, coffee, chocolate, cocoa.
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| canned vegetables | 1,5 | 0,2 | 5,5 | 30 |
| swede | 1,2 | 0,1 | 7,7 | 37 |
| peas | 6,0 | 0,0 | 9,0 | 60 |
| bulb onions | 1,4 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 41 |
| chickpeas | 19,0 | 6,0 | 61,0 | 364 |
| radish | 1,2 | 0,1 | 3,4 | 19 |
| white radish | 1,4 | 0,0 | 4,1 | 21 |
| beans | 7,8 | 0,5 | 21,5 | 123 |
| horseradish | 3,2 | 0,4 | 10,5 | 56 |
| garlic | 6,5 | 0,5 | 29,9 | 143 |
| spinach | 2,9 | 0,3 | 2,0 | 22 |
| sorrel | 1,5 | 0,3 | 2,9 | 19 |
Berries | ||||
| grape | 0,6 | 0,2 | 16,8 | 65 |
Mushrooms | ||||
| mushrooms | 3,5 | 2,0 | 2,5 | 30 |
| marinated mushrooms | 2,2 | 0,4 | 0,0 | 20 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| nuts | 15,0 | 40,0 | 20,0 | 500 |
| almond | 18,6 | 57,7 | 16,2 | 645 |
Snacks | ||||
| potato chips | 5,5 | 30,0 | 53,0 | 520 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| vareniki | 7,6 | 2,3 | 18,7 | 155 |
| dumplings | 11,9 | 12,4 | 29,0 | 275 |
Bakery products | ||||
| buns | 7,9 | 9,4 | 55,5 | 339 |
Confectionery | ||||
| pastry cream | 0,2 | 26,0 | 16,5 | 300 |
| shortbread dough | 6,5 | 21,6 | 49,9 | 403 |
Ice cream | ||||
| ice cream | 3,7 | 6,9 | 22,1 | 189 |
Chocolate | ||||
| chocolate | 5,4 | 35,3 | 56,5 | 544 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| mustard | 5,7 | 6,4 | 22,0 | 162 |
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
Dairy | ||||
| milk 4.5% | 3,1 | 4,5 | 4,7 | 72 |
| cream 35% (fat) | 2,5 | 35,0 | 3,0 | 337 |
| whipped cream | 3,2 | 22,2 | 12,5 | 257 |
Meat products | ||||
| fatty pork | 11,4 | 49,3 | 0,0 | 489 |
| salo | 2,4 | 89,0 | 0,0 | 797 |
| bacon | 23,0 | 45,0 | 0,0 | 500 |
Sausages | ||||
| smoked sausage | 9,9 | 63,2 | 0,3 | 608 |
Bird | ||||
| smoked chicken | 27,5 | 8,2 | 0,0 | 184 |
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| smoked duck | 19,0 | 28,4 | 0,0 | 337 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Eggs | ||||
| hard-boiled chicken eggs | 12,9 | 11,6 | 0,8 | 160 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
| black caviar | 28,0 | 9,7 | 0,0 | 203 |
| salmon caviar granular | 32,0 | 15,0 | 0,0 | 263 |
| salmon | 19,8 | 6,3 | 0,0 | 142 |
| canned fish | 17,5 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 88 |
| salmon | 21,6 | 6,0 | — | 140 |
| trout | 19,2 | 2,1 | — | 97 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| animal fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
Alcoholic drinks | ||||
| whiskey | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,4 | 235 |
| vodka | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,1 | 235 |
| cognac | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,1 | 239 |
| liquor | 0,3 | 1,1 | 17,2 | 242 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| cola | 0,0 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 42 |
| instant coffee dry | 15,0 | 3,5 | 0,0 | 94 |
| sprite | 0,1 | 0,0 | 7,0 | 29 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||