Causes of bezoar
This pathology can occur for several reasons. The most common cause of stomach stone formation is the ingestion of particles and objects, both organic and synthetic. Here is a list of possible reasons:
- Mental disorders, neurological disorders and mental retardation, as well as schizophrenia, neuroses and some types of obsessive-compulsive disorders. Anything that can cause uncontrolled absorption of various objects and substances (plasticine, glue, paper, hair, nails, etc.).
- Disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, a decrease in the amount of hydrochloric acid and insufficiently fast digestion of food with a slowdown in its evacuation further into the duodenum. The development of Candida fungi can provoke the formation of bezoars of a fungal nature.
- Previous surgical interventions and disruption of postoperative rehabilitation reduce the secretion of enzymes and the secretory function of the body, and this in turn provokes a long digestion of products and the formation of undigested lumps.
- Malnutrition and problems with the oral cavity and teeth. Poor nutrition, insufficient chewing of rough food, swallowing pieces of bones and plant seeds provokes the formation of bezoars.
How is anesthesia used during the procedure?
Endoscopic examination is performed using short-acting agents that are quickly eliminated from the body. They cause slight relaxation and drowsiness.
An injection of contrast agent is given intravenously immediately before endoscopy. The patient is asked to lie on his left side, the endoscope tube is inserted through the mouth and the examination begins. The study is carried out in a hospital setting. The endoscopy procedure is painless and comfortable. A sore throat goes away within 30 minutes.
During endoscopy of the bile ducts and pancreatic ducts, local anesthesia with a special aerosol is used to numb the mouth and pharynx, relieve discomfort and improve breathing when installing an optical device. The doctor directs the endoscope (the diameter of the endoscope is like a small piece of sugar) through the mouth and pharynx - into the esophagus, stomach, and into the duodenal papilla - the lumen of the duodenum. The monitor screen shows the real condition of the bile ducts and pancreatic duct: cysts, stones, inflammation, narrowing, cicatricial stenosis or neoplasm. Based on the examination, the endoscopist makes an accurate diagnosis. According to indications, successful treatment is carried out (95% success).
Endoscopic examinations can be performed while the patient is sleeping. A sleeping pill is administered intravenously under the supervision of an anesthesiologist. For invasive surgery (in certain cases), general anesthesia may be used.
30 minutes after endoscopy of the bile ducts and pancreatic ducts, patients return to normal life.
Types of stomach stones
Bezoars have several varieties, different composition and density, it all depends on the method of formation. What formations are most common:
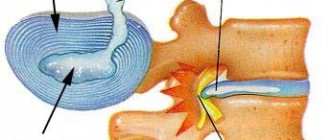
Trichobezoar is a calculus formed by hair that enters the stomach during neurotic and mental disorders, which are accompanied by the habit of gnawing the ends of hair.
Phytobenzoar – this type of gastric stone is most often diagnosed. It is formed when the seeds, tough skins, seeds and skins of fruits, vegetables and fruits are ingested. Gradually, a lump forms, which becomes covered with mucus and fats, becomes harder and increases in size.
Stibobesoar is a fatty calculus that appears with excessive consumption of animal fats, lamb meat, lard and lard. Over time, a dense lump of fat mass forms in the stomach.
Lactobesoars are a feature of premature or weakened infants who are fed artificial high-lactose formulas with a high casein content.
Bezoars of embryonic origin - such stones are formed in utero and most often look like cysts or teratomas with elements of the dermis and other particles.
Shellacobesoars are a special type of calculus formed by chemicals such as paints and varnishes that enter the stomach and react chemically with water and gastric juice.
There are several other types of stomach stones that are rare and are formed by consuming threads, wool, poorly digestible medications, resin and other items.
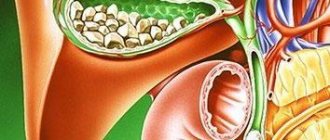
removal of stones from bile ducts
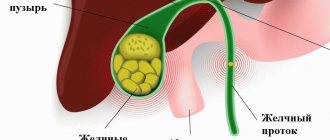
Please note that using intraluminal endoscopy we remove stones from the bile ducts , stones from the gallbladder are removed along with the bladder in general surgical departments.
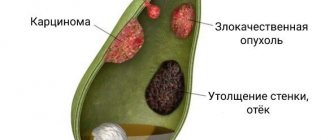
Stones in the bile ducts of the liver are formed due to cholelithiasis. It should be understood that cholelithiasis is a chronic disease with a disruption of the normal metabolism of bile acids, and after removal of the gallbladder with stones (in medical terms - cholecystectomy for calculous cholecystitis), the cholelithiasis itself will remain. There remains a metabolic disorder, which leads to the formation of new stones in the main bile ducts. The resulting stones block the normal bile outflow - the patient’s eyes (the whites of the eyes first) and then the patient’s skin visually acquires a yellowish tint - they turn yellow, the right side hurts, the urine darkens to the color of “black tea” or “dark beer”, and the feces, on the contrary, become light (to a light gray tint) – a condition develops, which doctors call “obstructive jaundice”. Obstructive jaundice is called because the obstruction of bile outflow is purely mechanical, i.e. there is a mechanical obstacle to the normal flow of bile. Mechanical jaundice is also called jaundice, which develops with tumors of the bile ducts or the head of the pancreas, when the tumor compresses the lumen of the bile duct and blocks the normal mechanism of bile outflow. The condition is dangerous for the body and, if appropriate measures are not taken, leads to death. The correct diagnosis in a number of cases can be difficult, since it is also necessary to exclude viral hepatitis, which also occurs with jaundice. Therefore, we need competent surgeons and an Ultrasound Diagnostics specialist above the average level to prescribe the necessary tests, make the correct diagnosis and choose the right operation that will correct the situation and not harm the patient.
For 10-20 years now, major traumatic abdominal surgeries for gallstones have become a thing of the past. They were replaced by a low-traumatic (in medical terms - minimally invasive) Endoscopic Retrograde CholangioPancreatography ( ERCP ): a procedure that combines the capabilities of endoscopic examination with a special flexible endoscope-duodenoscope (like the instrument used for gastroscopy) and x-ray examination. Bile duct stone removal or bile duct stone removal is done through the mouth. ERCP with removal of gallstones in the Central Clinical Hospital, as in any state medical facility. institution, performed by an endoscopist or surgeon certified in flexible endoscopy. After the diagnostic part of the procedure, when the cause of the bile outflow disorder has been clarified, an experienced doctor can remove stones from the bile ducts using special stone-grasping instruments directly through the working channel of the duodenoscope itself, connected to the exit from the bile ducts into the lumen of the duodenum. Sometimes, for this purpose, the actual place where the common bile duct exits into the intestine—the bile papilla—is expanded or incised. Stones do not fit into the lumen of the endoscopic apparatus, since they are usually much larger than its diameter, and they are left in the lumen of the intestine, from where they subsequently easily come out with food and feces.
Risks.
The most common complications when performing ERCP for surgical (therapeutic) purposes are bleeding and the development of inflammation of the pancreas, which develop with a frequency of 3-10% and 3-15%, respectively (according to various authors and statisticians with large samples, i.e. 1000 patients or more). Perforation of the duodenal wall and other complications are observed in experienced hands no more often than in 1-2% of all cases. It should be noted that the incidence of allergic reactions to the contrast agent used during ERCP is negligible. In our clinic over the past 5 years, we have not observed a single similar reaction, but descriptions of cases are given in the medical literature. Mortality with surgical ERCP performed by an experienced specialist does not exceed 1%.
Alternative treatments.
ERCP is currently the “gold” standard in the treatment of bile duct stones. Surgical operations, both open and laparoscopic, to remove stones from the bile ducts are accompanied by a high incidence of complications and mortality, reaching 25% in elderly patients. Percutaneous manipulations to remove stones lead to the leaving of stones or their fragments in the bile ducts and, as a consequence, to a relapse of obstructive jaundice.
Question: An ultrasound found a stone in the common bile duct, the duct is not dilated, the stone is small - no more than 5 mm. Should I do an ERCP and remove it or can I wait?
Answer: If stones in the bile ducts are detected by ultrasound by chance and have not yet caused obstructive jaundice, they should be removed and this must be done urgently. It is small stones that are often the most dangerous, because... wedged at the exit of the bile ducts can cause severe complications, even fatal.
Question: Small stones have been found in the gallbladder on ultrasound for several years. Pain began in the right hypochondrium. Ultrasound and MRI revealed a stone in the cystic duct. Is it possible to remove it through an endoscope without major surgery?
Answer: “common bile duct” and “cystic duct” are different things. Endoscopic intraluminal stone removal is possible from the common bile duct. In the described situation, it is necessary to remove the gallbladder with small stones laparoscopically; at the same time, a stone from the cystic duct can also be removed. If it cannot be captured during the operation and it slips into the common bile duct, then it can easily be removed endoscopically with ERCP (either directly during the operation, or 1-2 days after it in the second stage).
If you have any questions, you can get clarification by calling:
European Medical Center (EMC) - 8 (495) 933-66-55 ext. 45-05 and 42-41.
Central Clinical Hospital (CDB) - 8 (495) 530-03-96 during working hours from 09.00 to 17.00 and on weekdays.
With commercial payment, the cost of treatment depends on the severity and complexity of the case, the average final price consists of the cost of the operation itself (for example, ERCP with removal of a stone from the bile duct - from 35 thousand rubles), the cost of quite expensive disposable imported (mainly Japanese or American) consumables and the number of days spent in the hospital.
If you want to undergo treatment with us under insurance, please check with your supervisor for details.
To determine the optimal tactics, a preliminary consultation , for which you can sign up by calling the numbers listed in the section making an appointment .
Our advantages:
* Experienced doctors who perform endoscopic manipulations and operations on a daily basis. Thanks to our experience and excellent equipment in operating rooms, we avoid complications, and if they do occur, we know how to deal with them without harm to the patient’s health. Therefore, you will not find bad reviews about our work on independent sites. Doctors performing manipulations on the bile ducts completed an internship at one of the best clinics in Japan (Ariake Cancer center, Cancer Institute Hospital of JFCR, Tokyo).
* Friendly and polite nursing staff , trained and working daily with VIP level patients.
* The best equipment . We use endoscopic equipment of the highest (expert) class from a recognized leader in the production of medical video equipment - the Olympus company (Japan) with the ability to digitally zoom and examine in a narrow spectrum of light, allowing us to see early cancer with an area of 1 mm (not a typo - a millimeter!).
* No hidden markups , as, for example, in a number of medical centers or some state clinics with cunning “modern managers”, where after research they will tell you that you owe another 200-300 thousand rubles. for used “consumables”. With us, the price of an endoscopic instrument or consumable is, as a rule, known and understood even before the manipulation begins. We discuss all price issues with you before the start of manipulations.
* Excellent food and comfortable accommodation. Important things if you have to stay in the hospital for several days. Nutrition has been a positive “fad” of the Central Clinical Hospital since Soviet times. Central Clinical Hospital is famous for its delicious and varied menu. The linen on the beds is colored, and not “sick white” - another opportunity not to feel sick. You can choose accommodation from 3 to a single room; at your request, a two-room “suite” is available.
* Double control. The quality of patient treatment and the quality of compliance with the sanitary and epidemiological regime are constantly monitored. Moreover, in private medical centers, sanitary and epidemiological stations control not only sterility - compliance with standards and the quality of treatment itself in private medical centers is strictly controlled by insurance companies ! And in the case of the Central Clinical Hospital, this control is double. Firstly, the Central Clinical Hospital is a medical government structure - the level of medical care we provide and the compliance of the treatment provided with established standards is controlled by government agencies and inspectors from insurance (CHI) companies, as in other public hospitals. But the hospital is still part of the structure of the Presidential Administration. Therefore, the activities are also monitored by the inspection bodies of the Administration. The result is double control of the level of treatment we provide. Double control of epidemiological safety, i.e. sterility of equipment and instruments, while the controlling sanitary and epidemiological stations (there are also two of them - state and administrative) carry out tests and cultures for sterility independently of each other.
the information on this page is an original author's product,
Unauthorized copying and posting will result in sanctions from search engines.
Diagnosis of gastric bezoar
The complexity of this disease is expressed in the absence of specific symptoms. Discomfort in the abdomen, a feeling of heaviness and satiety with a small amount of food rarely forces a person to consult a doctor. However, with timely detection, the risk of complications and the need for surgical intervention is reduced.
To make a correct diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo a number of examinations:
- Consultation and examination by a gastroenterologist. Determining the possible causes of the disease, collecting a complete history and physical examination, prescribing further studies.
- X-ray of the stomach with contrast. Allows you to detect a foreign body or formation in the stomach. Its shape, size and location.
- Fibrogastroduodenoscopy. The most reliable way of research. During the procedure, a specialist may take a particle of the formation to conduct additional research.
- Additionally, an ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity may be prescribed.
If necessary, the gastroenterologist may prescribe additional studies to determine the general condition of the body and prescribe a more accurate treatment regimen.
Why is endoscopy performed?
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography is performed for differential diagnosis of patency of the biliary tract and pancreatic ducts (narrowing of the ducts, tumors, stones, etc.). In the treatment of diseases of the gallbladder and pancreas (cyst, tumor, polyps, etc.) and for hidden bleeding, anemia, Crohn's disease, etc. Endoscopic examination allows you to identify changes in the bile ducts and pancreatic ducts, indicate the exact location of the lesion, and take a biopsy or urgently operate.