Where is the dome of the cecum located?
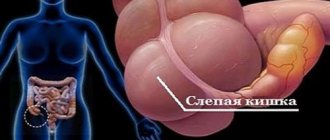
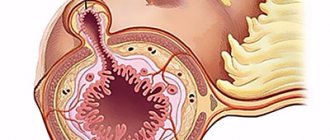
The cecum is the initial section of the large intestine. It is covered with peritoneum on all sides.
Located in the right iliac region, relatively short, from 1 to 10 cm long, from 5 to 9 cm wide. In very rare cases, this section of the large intestine is poorly defined, and the vermiform appendix extends slightly below the junction of the small intestine with the ascending colon.
The shape of the cecum varies, most often hemispherical. Rarer types: bay-shaped, conical, bag-shaped. The funnel-shaped form is rare and occurs when the growth of the cecum is delayed in the embryonic period; it represents a narrowing of the intestine from the base to the apex.
Appendix
The vermiform appendix arises from the medial posterior surface of the cecum, approximately 3 cm below the confluence of the small intestine. The average length of the appendix is 9 cm, its location directly depends on the location of the cecum, usually in the right iliac region.
If the cecum is located in a typical manner, then the vermiform appendix may be in the following positions:
- lateral (in a quarter of cases);
- medial (18%);
- downward (45%);
- behind in an ascending position (approximately 13%).
Ileocecal angle
The place where the ileum ends and the cecum begins is called the ileocecal angle, i.e. it includes the terminal part of the ileum, the cecum with the appendix and the ileocecal junction.
More often, the ileum “merges” into the cecum in its medial wall, forming a different angle: obtuse, acute, straight.
The ileocecal angle has a specific function - it works like a valve, which allows you to isolate the large and small intestines from each other and avoid backflow (reflux) of the contents of the large intestine into the small intestine. The cecum is well fixed to the posterior abdominal wall, which helps the doctor to easily find it and the appendix during surgery.
Topographically, the cecum is located slightly lower than the upper edge of the ileum, projected onto the anterior wall of the abdomen in the groin area on the right. The dome of the cecum is located 5 cm above the inguinal ligament. The dome of the cecum is directed towards the pelvis. The cecum almost never has a mesentery, in most cases it is covered with peritoneum and moves freely.
In rare cases, the cecum shares a mesentery with the ileum, which affects its pathological mobility.
Sometimes the posterior wall of the intestine is covered by the postcolic fascia and is not completely covered by the peritoneum. This fascia provides a tight fixation with the retroperitoneal tissue and parietal fascia. During operations on the cecum, such anatomy creates difficulties for its removal. The cecum is also connected to the parietal peritoneum by cecal folds.
In the area of the connection with the ileum, on the medial surface of the organ there is an ileo-intestinal papilla with an opening of the same name at the apex.
The papilla has a lower and upper lip and, together with the muscles of the terminal ileum, forms an anti-reflux valve mechanism - the Bauhinian valve.
Downward and posterior to it is the opening of the appendix, which is often closed by folds of the mucous membrane.
The cecum borders in front with the loops of the small intestine, on the right - with the lateral abdominal wall, below and behind - with the layers of the peritoneum and retroperitoneal tissue. The anterior wall adjoins the ureter on the right, between them there is the parietal peritoneum.
Functions
The wall of the cecum has the same structure as the walls of the large intestine. The mucous membrane has small folds: two are similar to valves and contain many muscle fibers and a single fold.
The mucous membrane contains Lieberkühn's glands and goblet cells.
The cecum takes part in the digestion process. Its immediate function is to absorb the liquid part of the chyme. However, she cannot be called irreplaceable. The vermiform appendix has more important functions: in its thickness there are many lymphoid follicles that protect the body from foreign agents. The appendix is a kind of depot of the immune system.
Diseases
Despite its small size, serious diseases often occur in the cecum.
Inflammation of the intestine or typhlitis, similar in symptoms to appendicitis. Probably the only difference is the time of onset of pain. With typhlitis, they begin to bother the patient several hours after eating, the pain is localized in the iliac region. Typhlitis must be differentiated from gynecological diseases, pathologies of the pelvic organs, and renal colic.
During the examination, the doctor pays attention to the following symptoms:
- on palpation, the cecum is dense and painful;
- bloating in the abdomen in general or on the right side;
- Auscultation of the presence of splashing noise.
For final confirmation of the disease, an X-ray contrast study and irrigoscopy are performed. The following changes are visible on the pictures: the folds of the mucous membrane are smoothed, the intestine is shortened, narrowed or expanded.
Typhlitis can lead to serious complications: paratyphlitis, mesadenitis, functional inferiority of the ileocecal valve.
This section of the intestine is susceptible to a disease such as adenocarcinoma. Moreover, the tumor is the most common among intestinal cancer pathologies.
- blood in the stool;
- general signs: weakness, fatigue;
- anemia;
- change in bowel movements at the usual time;
- a sharp drop in weight;
- bloating - flatulence;
- pain in the lower abdomen.
Treatment is carried out with surgical methods, chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
The prognosis is quite good: after radical treatment, 70% of patients live 5 years or more. As the stage of the process increases, survival rate decreases markedly.
Inflammatory diseases of the cecum include appendicitis.
Appendicitis has the following manifestations:
- Pain. The onset of pain in the epigastric region followed by its movement to the right iliac region is typical.
- Tension of the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Changing the stool. There may be diarrhea, but more often it is constipation.
- General symptoms (fever, weakness).
- Painful palpation of the abdomen.
- There are about 100 positive symptoms of appendicitis that can be determined by a doctor (Sitkovsky, Rovzing, etc.).
Treatment of appendicitis is surgical. It is important to apply in a timely manner, because... within 2-3 days the appendix fills with pus and its walls may rupture with the development of peritonitis.
The human intestine has several sections, each of which performs its own functions during the process of digestion, assimilation of food coma and evacuation of feces. One of them is the cecum.
Cecal dome
The cecum is located at the beginning of the large intestine, below the ileocecal valve, and due to its wide cavity it resembles a bag or dome. It is located in the abdominal cavity on the right, the symptoms associated with it also appear in the right side of the abdomen. The wide part of the dome of the cecum is directed towards the pelvis. It is connected laterally by a small passage to the ileum.
The cecum moves freely and is closed on all sides by the peritoneum, except for its posterior part, which is sometimes open. It is small - length up to 8 cm, width at the widest part - 5-9 cm. But most intestinal diseases, including cancer, are associated with it.
The appendix emerges from the cecum - a vermiform appendix connected to it by the mesentery, most often located in the right iliac fossa. The width of the appendix is 3-4 mm, the length can reach 12-13 cm.
Its exact location varies from person to person; there are cases when the appendix is located behind the cecum, covered by or outside the peritoneum.
The colon is located around it, and lymphoid tissue is present in the mucous membrane.
Source: https://shokomania.ru/kupol-slepoj-kishki-gde-nahoditsja/
Caecum: where it is located and how it hurts
The appearance resembles a pouch, reaching a length of 9 cm and a width of 8 cm, which fills the ileum of the large intestine on the right side.
Normally, it is surrounded on four sides by the peritoneum; this location is called intraperitoneal, but sometimes it is covered by it on three sides. The back wall is in contact with the muscles of the abdominal region. It takes a hemispherical shape, but there are cases where rare species are found - conical, bag-shaped.
Structure of the cecum
Represents the first section of the large intestine, starting immediately after the small intestine. In rare cases, it rises and takes place at the lower edge of the liver. On the front side it is covered with an omentum, in the bag of which pus accumulates in case of malfunctions.
Consists of the vermiform appendix (appendix) and the ileocecal valve. It takes part in the digestion of food, absorbing excess liquid from the food bolus, and the appendix performs a function that protects against foreign bodies.
The lower part of the body has a low pain threshold; pain in the cecum often seems insignificant, but the sensation is deceptive.
Appendix
Colloquially called the “vermiform appendix” due to its peculiar appearance, another version of the name “peritoneal tonsil”. When filled, the length reaches 15 cm, in diameter no more than 1 cm.
It is generally accepted that the appendix is a rudiment, but this belief is easily refuted by the fact: when the appendix is removed, a child has difficulty developing immunity and reproducing healthy microflora.
There is no method for treating the appendix; if inflammation is detected, the only solution is surgery to remove it. The location of the appendage varies depending on the anatomical structure of the intestine.
Function of the cecum
It occupies an important place in the structure of the intestines due to its direct participation in the digestion of the liquid component of food. This function cannot be called indispensable.
The work intersects with the functions of the colon, which easily plays a replacement role when the need arises.
Thanks to the liberkühn glands (crypts) located inside, which produce cells for villi, the surface of the intestine is lined with a mucous membrane that helps chyme move through the intestinal tract.
The appendix will not become a direct participant in digestion, but this does not diminish its “merits” in the functioning of the body. In the thickness of this process there are follicles that protect the internal environment of the body from the effects of foreign agents.
This is not just a container in the form of a “bag” for collecting garbage that cannot be digested, it is truly a guardian of human health. For centuries, Russian and foreign doctors have downplayed the importance of the appendix due to insufficient knowledge about the processes occurring inside.
But the importance of the immune function of the appendix is difficult to overestimate.
How does the cecum hurt?
It is a rare person who will be able to immediately determine where the blind part of the intestine is located and how it manifests itself, and what pain it causes. Normally there is no pain. The presence of discomfort indicates a clear disturbance in digestion or another internal process. Determining the diagnosis is 80% of success, so it is worth analyzing the disturbing symptoms.
Pain due to colitis
Colitis is common because it is easily provoked by the living conditions of the average person. Inflammation occurs, damaging the mucous membrane of the cecum. During an attack, the pain jerks from one place to another, and does not have the character of an easily established relationship in the area of manifestation. Causes:
- Infectious diseases;
- Drug intoxication (long course of antibiotics);
- Ulcers on the walls of the cecum;
- Weak blood flow in the intestines;
- Receiving a dose of radiation exposure;
- Dysbacteriosis;
- Worm infestation;
- Allergy;
- Causes of unknown origin - nonspecific colitis.
Pain due to appendicitis
Inflammation of the appendix is called appendicitis and exhibits pronounced symptoms:
- Acute pain in the navel area with transition to the right into the iliac region (intensified by tension in the abdominal wall through walking or coughing);
- Lack of appetite;
- Nausea, vomiting);
- Frequent painful urination;
- Severe chills;
- Low heart rate and low blood pressure.
The disease has an alarming symptom - a change in the color of the skin towards lightening, followed by the acquisition of a bluish tint. Peeling or profuse rashes may appear in several areas at once.
Crohn's disease
Granulomatosis affects the small intestine and gradually spreads to each section of the large intestine. The cecum hurts in a cramping manner, the pain is localized on the right side and occurs immediately after eating. Pain relief occurs after defecation.
Flatulence, diarrhea, the presence of blood in the stool and an increase in body temperature up to 38 degrees are recognized as pronounced symptoms. A long period of illness leads to weight loss.
The causes of the disease are not well understood; the most likely are genetic predisposition, activation of the body’s autoimmune activity, or the consequences of infections.
Pain due to diverticulosis of the cecum
Part of the intestinal wall protrudes due to poor nutrition, overeating, physical inactivity and obesity. These manifestations are easy to avoid for people with an active lifestyle.
With obesity, the risk of diverticulosis in the cecum increases many times. The left side of the abdomen is affected by pain that does not stop after defecation; the right half of the abdomen is affected.
The patient suffers from constipation, flatulence and a permanent increase in body temperature (from 37 to 38 degrees).
Cecal diverticulosis
Diverticula are divided into:
- Congenital (formed in the womb);
- Acquired (a direct consequence of a person’s lifestyle).
Pain in cecal cancer
A terrible disease of the cecum affects 10% of people. More often men suffer from the disease in this area. Cancer has not been sufficiently studied by official medicine; its sources cannot be stated with confidence. It is generally accepted that cancer is most often caused by:
- Food with excess amounts of animal proteins and refined fats;
- Presence of bad habits (drinking alcohol, smoking, drug addiction);
- Sedentary lifestyle (hypodynamia);
- Lifetime drug abuse;
- Constant emotional overstrain (stress);
- Work in hazardous production;
- Hereditary predisposition;
- Metabolic processes in the presence of excess body weight.
Symptoms of late stage cancer (third to fifth) are noticeable and severe. With cancer, a person feels constant pain in the stomach area, radiating to the right side, which can periodically change in character and intensity. Against the background of these factors, weight loss occurs and signs of intoxication appear. In the initial stages, the intestines may not hurt.
Since the disease is irreversible and rapid, you should consult a doctor if at least one symptom appears. Constant pain signals a deep and permanent malfunction in the body.
Diagnosis of cecal cancer is carried out using the methods of palpation (the intestines are felt), auscultation (the sounds of organ functioning are heard) or percussion (the area of the cecum is tapped).
These methods are ways to analyze the presence, size and condition of a tumor, fluid or sounds in the abdominal cavity.
Pain and troubles with the cecum can be easily avoided by following the principles of a healthy diet and lifestyle. It is important to prevent stagnation of feces and monitor the timeliness of bowel movements.
Source: https://GastroTract.ru/simptom/boli/slepaya-kishka.html
2. Reasons
The direct cause of cancer as such is a cellular mutation that is not recognized by the immune system and not destroyed in time, as a result of which an endless cycle of division and, accordingly, tumor growth is started - for this, a single immature cell is enough. The search for specific triggers (mandatory trigger conditions), methods of prevention and hypothetical ways to interrupt the oncological process constitute one of the main directions of modern science and go beyond the thematic scope of this article. As for risk factors, they have been identified in large numbers with high reliability and confirmed by large-scale studies on large regional and sociocultural samples.
For cancer of the cecum, these factors are not particularly specific (compared to cancer of other parts of the large intestine) and include the following:
- red meat that has undergone culinary processing (this is the wording used in the recent official WHO document, which classifies muscle-fibrous meat from large agricultural livestock as carcinogens), and some of the methods of “cooking” practiced today are much more dangerous than all other factors combined;
- age-related changes in tissues and weakening of intestinal peristalsis (the detection of cecal cancer increases stepwise from the age of 45, but since in most cases the late stage is diagnosed, the beginning of the age risk zone is considered to be 40 years);
- hereditary predisposition;
- the presence of chronic diseases and pathological conditions of the gastrointestinal tract (inflammatory, ulcerative, dyskinetic, benign neoplastic processes);
- environmental factors;
- the presence and activity of oncogenic viruses in the body (in particular, some subtypes of herpesvirus and human papillomavirus);
- smoking.
Visit our Oncology page
Cecal dome location photo
An appendix extends from the cecum, the length of which can reach 15 cm, but the diameter does not exceed 5 mm. As a rule, it lies in the area of the right iliac cavity. Inside, the process is lined with a mucous membrane, where there are large areas of accumulation of lymphoid tissue.
It is generally accepted that the appendage produces microorganisms necessary for the normal functioning of the intestine. The appendix also has a protective function, forming part of the mucasal immune system.
Malignant formations. Forecasts
Cecal carcinoma or malignant tumor of the cecum refers to oncopathological diseases of the large intestine. Cancer occurs in the lower part of the digestive system.
In most cases, a cancer begins with the formation of benign polyps in the gastrointestinal tract, which are pathological growths on the inner lining of the intestine.
Over the course of several years, polyposis may not manifest itself symptomatically, and the formation transforms into a malignant form.
If cancer is not detected in time, its cells can spread to the liver and lymph nodes.
If a patient is diagnosed with cecal cancer, the prognosis for successful treatment depends on many factors, including:
- Age.
- Localization of the tumor.
- The degree of damage to adjacent organs.
- Stage of development of the disease.
The most favorable prognosis accompanies the zero, first and second stages of cancer development. In 95% of cases, complete recovery is achieved by people under 50 years of age if they consult a doctor on time. Therefore, it is so important to seek medical help even at the slightest manifestation of discomfort.
If the diagnosis has confirmed that the tumor is at the third and fourth stages with extensive metastases in adjacent organs, the prognosis becomes disappointing.
Therapy comes down to three main options: surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy. The treatment method is developed taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient.
Radiation exposure and chemical drugs are necessary to destroy residual cancer cells after surgery, shrink the tumor before resection, or relieve symptoms as part of palliative therapy.
Tumor of the cecum
Benign and malignant formations, along with typhlitis, quite often affect the cecum. This section of the intestine accounts for 40% of reported cases of tumor development.
Symptoms
Manifestations of cancer are varied, they depend on the size of the pathological formation, the presence of complications, which can be manifested by concomitant diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Signs of cancer:
- frequent, prolonged dizziness;
- general weakness and weakness;
- tachycardia;
- changed color of stool;
- bleeding from the anus;
- aching pain in the lower right region of the peritoneum;
- rapid weight loss unexplained by other factors.
Structure
In terms of its external parameters, the cecum resembles a pouch and is located in the area of the right iliac cavity. The anterior surface is covered with an omentum, separating it from the abdominal wall.
At the border between the appendix and the intestine itself there is a sphincter that acts as a valve.
The Gerlach valve prevents the penetration of chyme (intestinal contents) into the lumen of the appendix.
Represents the first section of the large intestine, starting immediately after the small intestine. In rare cases, it rises and takes place at the lower edge of the liver. On the front side it is covered with an omentum, in the bag of which pus accumulates in case of malfunctions. Consists of the vermiform appendix (appendix) and the ileocecal valve.
Sections in the large intestine
Topography
Topographically, the cecum is located slightly lower than the upper edge of the ileum, projected onto the anterior wall of the abdomen in the groin area on the right. The dome of the cecum is located 5 cm above the inguinal ligament.
The dome of the cecum is directed towards the small pelvis. The cecum almost never has a mesentery, in most cases it is covered with peritoneum and moves freely.
In rare cases, the cecum shares a mesentery with the ileum, which affects its pathological mobility.
Sometimes the posterior wall of the intestine is covered by the postcolic fascia and is not completely covered by the peritoneum. This fascia provides a tight fixation with the retroperitoneal tissue and parietal fascia. During operations on the cecum, such anatomy creates difficulties for its removal. The cecum is also connected to the parietal peritoneum by cecal folds.
In the area of the connection with the ileum, on the medial surface of the organ there is an ileo-intestinal papilla with an opening of the same name at the apex.
The papilla has a lower and upper lip and, together with the muscles of the terminal ileum, forms an anti-reflux valve mechanism - the Bauhinian valve.
Downward and posterior to it is the opening of the appendix, which is often closed by folds of the mucous membrane.
The cecum borders in front with the loops of the small intestine, on the right - with the lateral abdominal wall, below and behind - with the layers of the peritoneum and retroperitoneal tissue. The anterior wall adjoins the ureter on the right, between them there is the parietal peritoneum.
4.Treatment
One of the key features of cecal cancer is that it is completely and relapse-free in almost all cases (various sources give estimates of 93-97%). However, this applies only to the initial stages - which makes early diagnosis a matter of vital importance - and does not apply to any non-medical practices, the only proven result of which is financial profit for some people and a suicidal waste of time for others.
Treatment is always intensive and combined and involves the use of all three main areas of modern oncology - surgery, radiation therapy and chemotherapy.
The dome of the cecum: role in the body, possible diseases
The dome of the cecum is directed towards the pelvis. Each person has different sizes. Length – 3-8 cm, width – 4-7 cm. Differs in mobility. It has important functions in digestion and the development of gastrointestinal diseases. The cecum is the beginning of the large intestine. The appendix extends from its dome.
Role in the body, functions
The cecum is often confused with the appendix. Although these organs are related, they are completely different. The appendix is a branch from the cecum, its shape resembles a worm. It is separated from the cecum by the sphincter. The length can be between 2-13 cm.
The cecum is responsible for processing fluid and absorbing it. It performs this function due to its structure. Consists of a large number of absorptive cells. In addition, it contains Lieberkühn glands. This is a hyperplastic organ. The appendix plays a more important role in the body. It protects it from foreign cells.
Signs of dysfunction of the cecum
The organ is not large in size, however, it is susceptible to the development of various diseases. Most often, inflammatory processes occur, appendix, cancer. Inflammation is accompanied by pain on the right side in the iliac region. The pain may spread to other organs and may be felt in the groin. The nature of the pain is sharp, acute, dull.
Signs of acute inflammation:
- strong pain;
- temperature rise to high levels;
- chills;
- headache, dizziness;
- nausea;
- weakness;
- diarrhea.
Chronic inflammation is not accompanied by pain. It can be provoked by physical activity, unhealthy diet, and alcohol abuse. In addition, flatulence, bloating, nausea, and lack of appetite occur.
Causes of disease development
The cecum often succumbs to inflammatory processes. The main reasons for their occurrence include:
- high consumption of fatty foods and flour;
- fiber deficiency;
- prolonged constipation;
- infectious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- dysbacteriosis;
- the presence of a food allergic reaction;
- decreased immunity;
- bad habits (especially alcoholism).
Oncological formations in the cecum are often found. Until now, doctors have not been able to determine the true cause of cancer. Predisposing factors include:
- genetic predisposition;
- work in environmentally polluted conditions (especially with high levels of radiation);
- constipation;
- long-term depression, frequent stress, nervous tension;
- presence of cecal polyps;
- old age, the results of aging of the body.
It is worth considering that the condition of the intestines is influenced by nutrition and emotional state. They are the initial cause of the development of diseases and pathologies of the digestive system.
Diseases of the cecum
The location and size of the cecum can be considered safe. Despite this, diseases of varying degrees of complexity arise. The most dangerous is cancer, the presence of malignant tumors. If you undergo examinations on time and start treatment, it can give a positive result.
Typhlitis
Typhlitis is an inflammation of this organ. Usually occurs due to the presence of infection. In some cases, inflammation can affect neighboring organs. Accompanied by severe complications if not treated in a timely manner. These include: necrosis and paratyphlitis. Manifests itself in acute and chronic forms.
Treatment of this disease is conservative. If an acute form occurs, the patient undergoes drug therapy in a hospital. It consists of taking the following medications: antibiotics, enzymes, antipyretics, anti-inflammatory. The patient is under the supervision of a doctor until complete recovery.
The chronic form with frequent relapses requires surgical intervention. If the disease is caused by fungi, the doctor will prescribe antifungal therapy.
Polyp
A polyp of the cecum most often occurs against the background of prolonged inflammation. In addition, there are the following reasons for the development of polyps:
- Alcohol abuse, unhealthy diet.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
- Ecological state of the environment.
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Congenital pathologies of the digestive organs.
- Having food allergies, gluten intolerance.
- Age-related changes (usually in people after 40 years).
Each person develops a polyp of the cecum for individual reasons. Most often this is associated with congenital pathologies and genetic predisposition. If a polyp is not detected in time, it can become a predisposing factor in the development of cancer.
The development of cancer in such cases is observed in more than 75% of patients. This is influenced by the shape and type of polyp. Therefore, if even one symptom of its development occurs, you should undergo diagnostics. It is worth noting that the presence of a polyp of any size requires surgical intervention.
Polyps are diagnosed using the following methods:
- irrigoscopy;
- colonoscopy;
- general and bacteriological analysis of stool;
- biopsy;
- CT scan;
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
After receiving the test results, doctors prescribe surgical treatment.
Adenocarcinoma
Pathology of the cecum, which is accompanied by a malignant formation. People over 50 years of age are at risk. Rarely occurs in young people and children. Causes of the disease:
- fiber deficiency;
- hereditary predisposition;
- age-related changes;
- papilloma virus;
- influence of chemicals;
- long-term use of medications;
- frequent stress;
- chronic constipation;
- polyps.
Even one factor can provoke the disease. Conservative treatment is not provided in this case. Surgical treatment is used in combination with chemical and radiation therapy. The patient's life depends on the stage of the disease.
Blastoma
This is a malignant formation of embryonic origin. Accompanied by tissue proliferation, which consists of deformed cells. Blastomas tend to penetrate tissues and damage blood vessels. The process of multiplication of metastases occurs.
Genetic predisposition significantly influences the development of this disease. The ecological state of the environment and radioactivity are of great importance.
Appendicitis
It develops against the background of infection by pathogenic microorganisms: enterococci, streptococci, staphylococci. This is a serious pathology that requires immediate treatment. Otherwise, peritonitis will develop.
The acute form requires urgent surgical intervention. The operation consists of removing the appendix. Characteristic symptoms are:
- sharp pain in the right groin;
- increased body temperature;
- vomit;
- severe weakness.
Even one such symptom requires diagnosis of the digestive system. Mild stages of appendicitis can be eliminated with conservative treatment. The patient is prescribed antispasmodics and antibiotics. In addition, you should follow a strict diet.
Disease Prevention
The causes of each disease of the cecum are interconnected. Basically, their development depends on nutrition. It should be complete, balanced, full of vitamins.
The diet should contain a large amount of fiber. For proper bowel function, it is beneficial to take fermented milk products daily.
Proper nutrition helps prevent constipation. Their presence is often caused by intestinal diseases. A healthy lifestyle is the best prevention of any disease, especially the digestive system.
Source: https://gastritam.net/bolezni/kupol-slepoj-kishki.html
Prevention
Preventive measures to prevent diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, including the cecum, are healthy, high-quality, regular nutrition, absence of bad habits, healthy active lifestyle, high-quality water, and lack of stress. Modern life, with its pace, rarely provides a person with the opportunity to easily implement such recommendations. Therefore, it is very important not to ignore preventive medical examinations, but at the first unpleasant symptoms and malaise, immediately contact a specialist so as not to waste time.
What is the dome of the cecum and what diseases can occur in it
The human intestine has several sections, each of which performs its own functions during the process of digestion, assimilation of food coma and evacuation of feces. One of them is the cecum.
Functions of the cecum
The main function of the cecum is the absorption of the liquid component from chyme - a semi-liquid lump consisting of semi-digested food, enzymes and acids of gastric juice, bile of exfoliated epithelium, and various microorganisms. The wall of the cecum is similar in structure to the large intestine.
The mucosa has small folds of muscle fibers; it contains goblet cells and Lieberkühn's glands - tube-shaped depressions of the epithelium that are important for normal intestinal motility. The role of the appendix is also very serious.
Its numerous follicles are protection against hostile foreign agents and perform a barrier function.
Polyps
Growths on the intestinal mucosa on a stalk in the form of a mushroom or loose structure are called polyps. These benign neoplasms are often localized in the cecum. Diagnosed during endoscopy using a colonoscope.
There are:
- adenomatous - can quickly increase in size, can cause intestinal obstruction, and develop into malignant;
- hyperplastic – small, there is no threat of growth and oncology;
- inflammatory – there is a danger of cancer, it contains numerous blood cells.
Symptoms appear only after the polyp grows strongly.
Usually this is an intense aching pain in the right side of the abdomen, closer to the groin area, inclusions of blood in the stool, bloating and hardening of the abdomen on the right, painful on palpation, anemia, weight loss, weakness.
The symptoms of the presence of a polyp in the cecum are associated with the obstruction caused by it and spasms as a result. In addition, polyps can become covered with ulcers and cause perforation of the intestinal wall. Hence the blood in the stool and anemia.
The nature of polyps is a genetic predisposition; the likelihood of their appearance is higher in people with chronic intestinal diseases, in those who have been eating incorrectly for a long time - dry food, irregularly, eating junk food.
Medicines are useless for treating polyps. They just need to be deleted. The method of surgical intervention depends on the location, size and number of tumors.
Small polyps are removed using a colonoscope, electrocoagulation or laser. In the case of multiple growths or a large polyp, part of the wall or intestine is removed.
The dome of the cecum is least often affected by polyps due to the peculiarities of its structure.
Cancer
In 40% of cases, patients with diseases of the cecum are diagnosed with cancer based on histology results. Malignant neoplasms of various natures and types do not manifest themselves in any way at first. The first symptom is the appearance of blood in the stool.
If this phenomenon is observed repeatedly, then urgent consultation with a doctor and further examination are necessary to make a diagnosis. Cancer can be successfully treated in the initial stages; in its advanced form, the prognosis is unfavorable.
Malignant neoplasms are studied in various ways:
- colonoscopy with biopsy;
- sigmoidoscopy;
- MRI.
This is necessary to find out the extent of the lesion, location, and size of the tumor. Surgery is then performed to remove the tumor, adjacent affected lymph nodes and some soft tissue.
To prevent relapse, courses of radiation and chemotherapy are carried out. If the operation no longer produces results or is impossible, only a course of chemotherapy is prescribed.
It can prolong the life of a cancer patient and somewhat improve its quality.
In the later stages of cancer, pain appears, the patient quickly loses weight, and with metastases in the liver, obstructive jaundice occurs. Therefore, you should not delay a visit to the doctor if symptoms of any disease of the cecum appear.