The article was prepared by a specialist for informational purposes only. We urge you not to self-medicate. When the first symptoms appear, consult a doctor.
Pyloric stenosis (pyloric stenosis) is a complication of gastric ulcer, in which the lumen in this area of the digestive tract narrows and the passage of food into the intestines from the stomach is disrupted.
Over time, this pathology leads to the development of severe disorders in the body and changes in homeostasis. Such stenosis occurs in adults and is only acquired.
Pyloric stenosis, causes of development
Pyloric stenosis is a pathological condition
The main cause is considered to be a scar that appears after the ulcerative surface has healed. Such scars consist of connective tissue; they greatly reduce the mobility of the stomach wall, as they tighten it. Stenosis also occurs as a result of the growth of a cancerous tumor inside the stomach wall.
As a result, food stagnates in the stomach. After all, it cannot fully move through the digestive tract. In order to somehow remove food from the stomach, the body provokes the growth of muscle tissue. This leads to compensation for the condition of stenosis.
But the hypertrophied layer of the stomach is also unable to cope with the existing loads. Therefore, the stomach gradually stretches due to the significant volume of stomach contents. The accumulated food still stagnates. Multiplying microbes provoke active fermentation and decomposition.
Tests and diagnosis of pyloric stenosis in newborns
Diagnosis of pyloric stenosis in newborns and infants includes:
- Characteristic complaints of parents and medical history.
- X-ray examination. It is carried out in two stages. The first stage is a survey X-ray of the abdominal organs, performed with the child in an upright position. The stomach is found distended with air and contents. Its bottom is located below the navel and even at the level of the pelvic bones. There is less gas in the intestines than usual. Decisive in diagnosis is X-ray contrast examination, which is carried out at the second stage after plain radiography. Barium x-ray is useful only to rule out or confirm pyloric stenosis if there is any doubt. barium suspension with glucose solution or milk (50-60 ml of milk + 2 teaspoons of barium suspension) is used as a contrast agent The contrast agent is injected into the stomach through a thin catheter. After the contrast is administered, a series of images are taken after 20 minutes and 3 hours, if necessary - after 6 hours and 24 hours. The child should be in an upright position during the examination. If after 3 hours there is more than half of the contrast agent in the stomach, this is the main radiological criterion for pyloric stenosis. With pyloric stenosis, barium remains in the stomach for more than 24 hours without vomiting during this time. The second radiological sign of pyloric stenosis is “segmented” peristalsis of the stomach. On a lateral X-ray, the narrowed pyloric canal appears beak-shaped—a symptom of “antral beak.” X-ray examination is used to select one or another tactic of surgical intervention. Pylorospasm is also diagnosed x-ray - in this case, the pyloric patency is not impaired, but the stomach empties from the contrast after 3-6 hours.
- Ultrasonography. Reveals symptoms characteristic of pyloric stenosis: elongation of the pylorus (it has a length of more than 20 mm), thickening of the muscle layer (more than 4 mm) and narrowing of the lumen of the canal.
- Esophagogastroduodenoscopy is used to a limited extent at such an early age - only to clarify the diagnosis. The endoscopic method should be used as a final examination after radiography and ultrasound. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy reveals an overstretched stomach with pronounced folding of the mucous membrane in the antrum. Stenosis of the pyloric canal of varying severity is noted; the pyloric canal does not open when inflated with air. There is also no possibility of penetration into the duodenum even after the administration of atropine .
Main stages of the disease
The first stage is compensated pyloric stenosis. The passage is slightly narrowed. The patient feels a feeling of heaviness and fullness in the stomach after eating. A sour belch appears. Vomiting makes you feel better for a short period of time. The condition can be called satisfactory.
The second stage is the stage of subcompensation. An unpleasant feeling of fullness in the stomach is accompanied by pain, heaviness, and belching. Vomiting can even occur while eating. After vomiting, the person feels a little better. After some time, the person loses weight significantly.
If you palpate the abdomen, you can feel a splash in the navel area.
The third stage is the stage of decompensation. At this stage, the stomach stretches, and exhaustion only intensifies. Added to this is dehydration. Frequent vomiting does not provide adequate relief. The vomit contains remnants of food eaten many days ago. Therefore, the contents of the vomit emit a terrible smell.
List of sources
- Nagornaya N.V., Limarenko M.P., Bordyugova E.V. Rational therapy of functional gastrointestinal disorders in young children. News of medicine and pharmacy. 2008. 16(255) - pp. 14-15.
- Khavkin A.I. Functional disorders of the gastrointestinal tract in young children. M., 2000. 71 p.
- Zaprudnov A. M. Handbook of pediatric gastroenterology. M., 1995. pp. 25–26.
- Botvinyev O.K. Turina I.E. Barmaver S.Z. Difficulties in diagnosing congenital pyloric stenosis in children. Russian pediatric journal. 2000.-N 6.-P.45-46.
- Vasilyeva, N.P. Possibilities of echography in congenital pyloric stenosis / N.P. Vasilyeva, M.Kh. Arslanova, T.M. Shakhmaeva // Ultrasound diagnostics. – 1997. – No. 4. – P. 11.
Congenital pyloric stenosis
Symptoms of pyloric stenosis - characteristic
In children, this disease is exclusively congenital. Its hereditary nature is often determined. In this case, connective tissue grows in the area of the excretory section. Boys are susceptible to this pathology four times more often than girls.
This disorder is the main cause of gastric obstruction in infancy. The disease makes itself felt very early, literally in the second to fourth weeks. Severe vomiting is noteworthy. Such fountain vomiting happens very often. If the operation is performed on time, everything ends well. Therefore, an accurate and correct diagnosis is of great importance.
Prevention
Prevention of the disease has not been developed, but taking into account risk factors, it can be assumed that the following general measures will be effective:
- A rational and balanced diet for a pregnant woman, including folic acid , vitamins and microelements.
- Minimizing stressful situations and psycho-emotional stress during pregnancy.
- Compliance with the work and rest schedule of a pregnant woman.
- Observation at the antenatal clinic to identify pregnancy pathologies.
- Normalization of the child's feeding regimen in order to eliminate overfeeding and regurgitation.
- Creating a prosperous environment for the child.
- For adults with pylorospasm, it is important to eliminate psycho-emotional stress and stress, and establish adequate sleep and rest.
Causes of development of esophageal stenosis
The cause of this disease is a developmental defect in the prenatal state. This pathology can be noticed already from the first days of a newborn’s life. The baby spits up milk quite persistently. If the stenosis is small, then it may not be noticed during the breastfeeding stage, but when solid food begins to be introduced, it makes itself felt.
If the stenosis is acquired, it is also characterized by a narrowing of the lumen. Obstruction of the esophagus is associated with one of the following reasons:
- the presence of scars that appear as a result of diseases such as peptic ulcers, gastroesophageal reflux disease, infectious and inflammatory lesions of the stomach;
- traumatic lesions of the esophagus, burns;
- neoplasms of the esophagus or adjacent tissues;
- enlarged lymph nodes, aortic aneurysm, abnormal arrangement of blood vessels.
Pathogenesis
From a pathogenetic point of view, it is associated with hypertrophy of the circular muscles of the pylorus and partial muscle hyperplasia. In the prenatal period, partial excessive growth of the stomach anlage occurs from the mesenchyme in the pyloric region, from which the muscle elements differentiate. However, hypertrophy of the muscle layer develops postnatally. The anterior and upper walls of the exit section are the most thickened, as a result of which the pylorus takes on the shape of a spindle. From the beginning, the child does not experience inflammation or swelling of the pyloric mucosa. The addition of mucosal edema to the existing hypertrophy and hyperplasia of the pyloric muscles is manifested by increasing obstruction of the pyloric region.
Many believe that a spastic component is added (that is, spasm is secondary); some authors argue that spasm and hypertrophy appear simultaneously. Among the causes of spasm and hypertrophy are the immaturity of the autonomic regulation of gastric function. The visceral organ is under the control of regulatory influences. The pathogenesis of spasm is due to disruption of interactions between the diseased organ and regulatory systems. From the side of the narrowed pylorus, signals enter the cerebral cortex, and in response, return impulses go to the pylorus. The cerebral cortex constantly receives signals that disrupt its regulatory function. A vicious circle is created: impulses from the center disrupt the function of the gatekeeper, and impulses from it to the center deepen the damage to the regulatory system. Breaking the chain restores normal relationships.
Pylorospasm is associated with increased tone of the sympathetic nervous system. The resulting prolonged spasm of the pylorus muscles makes it difficult to empty the stomach. Hypertonicity can be caused by fetal hypoxia , posthypoxic encephalopathy , increased intracranial pressure and hydrocephalic syndrome .
Signs of esophageal stenosis
There are several signs by which esophageal stenosis can be diagnosed, these traditionally include the following:
- unpleasant pain when eating, and the pain is felt as the food moves in the esophagus;
- salivation is constantly observed;
- one feels nauseated, often vomiting and belching.
There are several degrees of damage to esophageal stenosis:
- First degree. Problems arise from time to time when swallowing solid foods. In general, the condition is satisfactory.
- Second degree. Food can pass through the esophagus only in semi-liquid form.
- Third degree. Only liquid food can pass through the esophagus.
- Fourth degree. It is very difficult to swallow even saliva and water.
Diet
Diet table No. 1
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after 3 weeks
- Terms: 2 months or more
- Cost of products: 1500 - 1600 rubles. in Week
The nutrition of children was discussed above; for adults with pylorospasm, mechanically and chemically gentle nutrition is recommended. Food should be taken warm. Avoid hot and cold foods rich in fiber. It is not advisable to consume spicy foods and seasonings, coffee, carbonated drinks, which can intensify the spasm. Table No. 1 meets all requirements .
Reflection of the disease in the picture of laboratory data and ECG
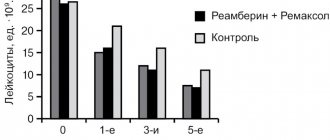
In a general blood test, anemia (normochromic or hypochromic) may be observed. This is due to the depletion of the body’s intake of various nutrients and valuable substances, especially iron. The number of red blood cells increases when repeated vomiting occurs and the body becomes dehydrated. Dehydration also causes the blood to thicken. This increases hemoglobin and may increase ESR.
In the biochemical blood test, the content of protein and albumin was reduced. Repeated vomiting also shows signs of dehydration. We are talking about electrolyte disturbances: hyponatremia, hypochloremia, hypokalemia, hypocalcemia. Sometimes the amount of iron decreases. Hypochloremia leads to an increase in urea levels in the blood.
According to the ECG results, changes in the myocardium of a diffuse nature are observed: the amplitude of the T wave in several leads decreases. If the electrolyte composition of the blood is disturbed, this will be reflected in the ECG accordingly. If hypocalcemia is present, there will be a prolongation of the electrical systole of the ventricles - the QT interval, sometimes a shortening of the PQ interval and a decrease in the amplitude of the T wave.
Hypokalemia gives a decreasing amplitude of the T wave or shows the formation of a biphasic (±) or negative asymmetrical T wave. An increase in the amplitude of the U wave can also be observed. Sometimes there is a lengthening of the electrical systole of the ventricles - the QT interval; The ST segment moves horizontally below the isoline.
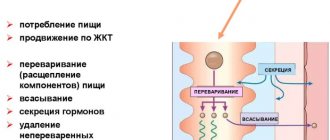
Digestive system, how does it work? Watch the video:
Forecast
Pylorospasm with age, as the nervous system improves, regurgitation is reduced, vomiting disappears by 5-6 months. Vomiting in some children may resume with a fever, a cold, or after a conflict situation.
Pyloric stenosis can be treated with surgery. Pyloromyotomy shows good long-term results: children develop well, and X-ray control indicates normal gastric function and good emptying. There are no relapses after the operation. Mortality with proper surgical treatment is minimal - it is observed only among patients who are operated on late and their death is associated with exhaustion and its attendant complications.
Rekomed - Choosing a clinic for treatment abroad
The Rekomed company will help you choose a clinic and a doctor, organize a trip for consultation, diagnosis, treatment or surgery. We will provide all coordination services for you and will help in solving organizational issues throughout the treatment. It is important to note that payment for treatment is always made directly to the clinic’s cash desk at the clinic’s prices.
Contact us by phone or use the “doctor” form to send your request.
doctor
| Rating | 2560 views | Recommend to friends | Roman KM |
Where to treat “Pyloric stenosis”?
North Estonian Regional Hospital
J.Sütiste tee 19, 13419 Tallinn View on map
0 positive review 0 negative review
The structure of the North-Estonian Regional Hospital includes the largest oncology center with a nuclear medicine department and a cardiology center with cardiac surgery and invasive cardiology departments. The multidisciplinary medical center has 7 clinical departments: anesthesiology, diagnostics, surgery, psychiatry, oncology, hematology, and an internal medicine clinic. The full range of medical services is provided with the exception of ophthalmology, pediatrics and obstetrics. Read more >>>
Cheongsim International Medical Center
267-177, Misari-ro, Seorak-myeon, Gapyeong-gun, Gyeonggi-do, Korea View on map
1 positive review 0 negative review
International medical practice combines Western and Eastern methods and approaches to the treatment of vomiting. Thus, modern technologies are favorably combined with oriental subtleties, and acupuncture, all kinds of moxibustion and preparations based on plant extracts significantly speed up recovery. Read more >>>
University Hospital Hamburg-Eppendorf
Martinistr. 52, Hamburg, Germany View on map
0 positive review 0 negative review
University Hospital Hamburg-Eppendorf (German: Universitätsklinikum Hamburg-Eppendorf) is a medical center in the North of Germany, located in the Eppendorf district of Hamburg. Read more >>>
Clinics of the Ludwig Maximilian University in Munich
Marchioninistraße 15, Munich, Germany View on map
0 positive review 1 negative review
The Medical Center is a modern multidisciplinary center, where advanced experience, the best medical traditions and modern equipment are optimally combined... Read more >>>
Goethe University Hospital
Theodor-Stern-Kai 7, Frankfurt am Main, Germany View on map
0 positive review 0 negative review
History of the clinic at the University. Johann Wolfgang Goethe (Goethe-Universitat Frankfurt am Main) is inextricably linked with the history of the educational institution itself, which will celebrate its 100th anniversary in 2014. University Clinic Read more>>>
Charite Clinic
Charitestraße 1, 10117 Berlin, Germany View on map
0 positive review 0 negative review
One of the oldest medical institutions in Germany, the Charite Clinic was founded in 1710. The level of this university hospital, which in addition to providing medical care also offers fundamental training for doctors and scientists, is extremely high. Read more >>>
University Hospital Dusseldorf
Moorenstr. 5, Düsseldorf, Germany View on map
0 positive review 0 negative review
The participation of the University Hospital of Düsseldorf in various international medical projects allows the application of progressive techniques in practice, which makes treatment even more effective. Read more >>>
Medical
Kiryat Hadassah, Jerusalem, Israel View on map
0 positive review 0 negative review
Medical is a multidisciplinary clinic located in two buildings. The center has inpatient departments equipped with modern equipment, a department for outpatient treatment, and an emergency room. Read more >>>
Medical Center named after. Rabin
Petah Tiqwa, Israel View on map
2 positive review 0 negative review
Multidisciplinary medical institution - medical center named after. Rabin, this is one of the best clinics in Israel. The center unites six specialized clinics, which allows it to provide high-quality medical services in all areas. Children's clinic "Schneider", located on the territory of the medical center named after. Rabin, Read more >>>
Clinic "Assuta"
Tel-Aviv, Israel View on map
0 positive review 0 negative review
The Assuta Private Clinic, one of the most popular medical institutions in Israel, was founded in Tel Aviv in 1934 by Dr. Ben-Zion Harel, his son and repatriated doctors from Germany. Now this is a whole network of private clinics: 4 hospitals, medical complexes More >>>
Medical
Ramat Gan, Israel View on map
0 positive review 0 negative review
The Medical Center is the largest medical institution not only in Israel, but throughout the Middle East. The center has 1,700 beds for hospitalization, and the medical team is about 900 highly qualified Read more >>>
Teknon Medical Center
Vilana 12, Barcelona, Spain View on map
0 positive review 0 negative review
Medical is one of the best private clinics, which is known not only on the Mediterranean coast, but also far beyond its borders. This clinic is accredited by JCI (Joint Commission International), Read more >>>
Genolier Clinic Group
Route du Muids 3, 1272 Genolier, Switzerland View on map
0 positive review 0 negative review
Genolier Swiss Medical Network - Group of clinics "Genolier" - twelve specialized medical institutions that are located in different municipalities of Switzerland, but united by high quality of service and equipped with the most modern equipment. Read more >>>
Group of private clinics Hirslanden
Witellikerstrasse 40, 8032 Zürich, Switzerland View on map
0 positive review 0 negative review
At the Hirslanden Clinic, all conditions have been created for patients to undergo a detailed examination of the whole body; it has the best diagnostic facilities with the most modern equipment. Only after a thorough examination can we talk about drawing up a treatment plan. Read more >>>
University Hospital Quiron Madrid
Calle Diego de Velázquez, Madrid View on map
0 positive review 0 negative review
The Quirón Madrid University Hospital is a prestigious private multidisciplinary medical institution. The level of service in the clinic meets international standards, which is confirmed by ISO certification. Read more >>>
University Hospital in Krakow
ul. Kopernika 36, 31-501 Kraków View on map
0 positive review 0 negative review
The University Clinic is a large-scale medical center with multifaceted activities in the field of health care. In 2012, the clinic was awarded a CSQ certificate for the well-functioning work of the team and the high quality of medical care provided in accordance with the requirements of the international standard ISO 9001:2008. Read more >>>
Raffles Hospital
Raffles Hospital, 585 N Bridge Rd, View on map
0 positive review 2 negative review
Raffles Hospital is conveniently located in the center of Singapore. The clinic provides a full range of medical services, providing an individual approach, and uses modern medical technologies. Read more >>>
Debrecen University Medical Center
Nagyerdei krt. 98. Debrecen Hungary View on map
0 positive review 0 negative review
The Debrecen University Medical Center was created and opened on the basis of an educational institution founded back in 1921. Today, in this hospital, everyone can undergo diagnostics using the latest modern equipment, as well as receive a course of qualified treatment and rehabilitation at the highest European level, which ensures the equipment of the center and the professionalism of its doctors. Read more >>>
Private Clinic Döbling
A-1190 Vienna, Heiligenstädter Straße 55-63 View on map
0 positive review 0 negative review
Privatklinik Dobling - The private clinic "Döbling" was founded in 1941 and is located in the very center of Vienna. The windows of the clinic building offer a beautiful view of the city, which only contributes to the comfortable state of mind of its patients. Read more >>>
Vienna private clinic
A-1090 Vienna | Pelikangasse 15 View on map
0 positive review 0 negative review
The Vienna private clinic is located in the very center of the city, not far from the largest European hospital, AKH. The clinic building resembles an old mansion, behind the facade of which there is a multidisciplinary medical center equipped with the latest technology. The clinic offers its patients comfortable conditions that are not inferior to living conditions in luxury hotels. Read more >>>
Mayo Clinic
4500 San Pablo Road Jacksonville, FL View on map
0 positive review 0 negative review
The clinic's activities are based on an integrated approach to treatment methods. The clinic allocates large funds for the development of scientific methodological rules and for the organization of large-scale clinical studies. More than 40% of the clinic’s total budget goes to finance developments that are put into practice and have a resounding success in the global medical community. Read more >>>
Bangkok Clinic in Pattaya
301 Moo 6 Sukhumvit Road, Km. 143, Banglamung, Chonburi, Thailand View on map
0 positive review 0 negative review
The Bangkok Clinic in Pattaya is a superbly equipped modern medical center on the East Coast. This is a multidisciplinary clinic where you can take advantage of medical services covering almost all areas of medicine: from emergency care to aesthetic and plastic surgery services, all at the highest level. Read more >>>
Bangpakok International Hospital 9
362 Rama II Rd, Chom Thong, (Jomthong) Bangkok 10150 View on map
0 positive review 0 negative review
Bangpakok 9 International Hospital / Bangpakok 9 International Hospital is known far beyond Thailand. A wide range of medical services are provided here, as this clinic is multidisciplinary. The clinic was founded relatively recently, in 2003, but during this time many patients have used its services and received qualified assistance in the treatment of various diseases. Read more >>>
Acibadem Maslak Clinic
Büyükdere Cad. No:40, Maslak Sarıyer, 34457 Istanbul View on map
1 positive review 0 negative review
Acibadem Maslak, an Istanbul clinic with a wide range of medical services, is part of the famous Turkish medical group Acibadem Healthcare Group. The clinic began its work in 2009. Read more >>>
University Hospital Zurich
Rämistrasse 100, 8006 Zürich View on map
0 positive review 0 negative review
The University Hospital of Zurich is one of the best and largest medical centers in Switzerland. It was here that the computed tomography procedure was first performed. The clinic works closely with the Zurich Federal Institute and is its clinical base, which opens up broad prospects for research in the field of medicine and the search for advanced technologies and the latest methods for the treatment of various diseases. Read more >>>
Diagnosis
The diagnosis is established on the basis of a characteristic symptom complex, the results of gastric probing, gastroscopy, roentgenol, data and study of the motor function of the stomach. An important role in P.'s diagnosis is played by gastroscopy (see), with the help of which one can determine the cause of the disease (ulcer, tumor, scar), as well as accurately determine the diameter of the narrowed pylorus.
The task of rentgenol, research comes down to P.’s detection, clarification of its origin and assessment of the degree of compensation of stenosis. To fill the pylorus more densely with a contrast mass, it is necessary to resort to polypositional examination, in particular lateroscopy (see Polypositional examination). Facilitates diagnosis and double contrast of the stomach - barium and air. In order to differentiate organic narrowing of the pylorus and pylorospasm (see), Pharmakol is used. samples.
The narrowing caused by a malignant tumor is rigid, its contours are uneven with filling defects. With P. of another etiology, the contours of the narrowing are smooth, and variability of the narrowed area is observed on serial photographs.
Rice. 2. X-ray of the stomach of a patient with cicatricial pyloric stenosis due to peptic ulcer: the stomach is dilated, hypotonic, contains mucus (1), the pylorus is sharply narrowed (2).
In the phase of P.'s compensation, the stomach is of normal size or slightly enlarged, evacuation is not delayed or lasts 8-12 hours, its peristalsis is deep and enhanced. In the subcompensation phase, the stomach is enlarged in size, contains liquid on an empty stomach, peristalsis is weakened, and emptying is delayed for up to 24 hours. Decompensation is manifested by the expansion of the stomach, which contains a lot of fluid, mucus, food debris, and is hypotonic, as a result of which the contrast mass sinks to the bottom of the stomach, forming a bowl shape with a horizontal level (Fig. 2). Peristalsis is weakened, and waves of antiperistalsis are sometimes visible. With repeated studies after 24 hours or more, retention of the contrast agent is observed in the stomach.