What is a disease
Stomach pain due to high acidity is common.
Hyperacid gastritis, translated from Latin, roughly translates as follows: replenishment of the stomach, accompanied by increased acidity. If you remember school, biology, or rather, lectures on anatomy, then you know that hydrochloric acid and other digestive juices produced in the stomach are involved in the process of digesting food. But if acid is produced in excess of normal, it begins to destroy the walls of the stomach.
This is why high acidity causes harm to humans. The most “innocent” disease that can result from excess acid is gastritis, but the consequences will be much more serious if a stomach ulcer appears. If a patient diagnosed with gastritis has not completed the full course of treatment, then the disease is complicated by a stomach ulcer, which is not so easy to get rid of, and in advanced cases, surgical intervention, that is, surgery, is simply necessary.
Is it possible to achieve a full recovery?
The question is controversial.
The opinions of experts are divided among those who believe that timely, modern complex treatment can contribute to recovery and complete restoration of the gastric mucosa. But there are those who do not think so, saying that it is practically impossible. That the process is irreversible from a certain stage, when most of the gastric mucosa has atrophied. If the disease is in the initial stage, then the prognosis is quite optimistic. Here, first of all, timely antibacterial therapy to eradicate H. pylori plays a positive role. New generation drugs and modern treatment regimens are characterized by good and lasting results.
Symptoms
As a rule, the disease is accompanied by nagging, aching pain in the stomach. Experts call this pain “in the pit of the stomach”; in most cases, it is felt on an empty stomach. After eating, the pain dulls, but after 1.5-2 hours the pain resumes until food enters the stomach again.
Another characteristic symptom is heartburn; the patient has a burning sensation in the stomach or behind the sternum if acid enters the esophagus. If pain (burning) behind the sternum occurs suddenly, you should get a cardiogram, as this symptom may indicate an acute myocardial infarction.
Heartburn may appear after eating foods such as sour fruits, brown bread, halva, a variety of fresh baked goods, or after fried, fatty and smoked foods. Such a menu can lead to regular exacerbations of the disease. In addition, intense exercise can lead to excessive production of hydrochloric acid. In this case, the patient may feel heartburn in the upper abdomen.
Endogenous causes of gastritis
Inside the body, the following factors can lead to gastritis:
- genetic predisposition to gastrointestinal diseases;
- duodenal reflux;
- weakening of the protective function of cells at the level of the immune system;
- hormonal imbalances;
- automatic spread of pathologies affecting neighboring organs.
Duodenal reflux is the process of unhealthy passage of bile from the duodenum into the stomach. As a result, irritation of the gastric walls occurs and a change in the chemical composition of its acid. Most often, the pathology occurs first in the antrum of the stomach, and then affects the entire organ.
The weakening of the protective function of cells at the level of the immune system means that the cells cease to function normally. This leads to a number of separate pathological processes that also change the pH balance of gastric juice and irritate its walls. As a result, internal poisoning occurs, and the stomach begins to react negatively to the acidic environment of its own juice.
What else could indicate illness?
Helicobacter pylori as a cause of hyperacid gastritis
The gastroenterologist pays attention to symptoms such as:
- whitish or grayish coating on the tongue, and the tongue itself may be bright red;
- irritability and anxiety;
- nausea or vomiting after eating, but the same appetite;
- increased sweating;
- muscle spasms;
- constipation
At an appointment with a gastroenterologist, you should tell about all the symptoms so that the attending physician has the whole puzzle of the disease. After which the doctor will prescribe a urine and blood test and give a referral for intubation to determine the acidity of the gastric juice. This procedure is not pleasant, but it will allow you to determine the stage of the disease.
Complications of gastritis
If you do not take into account the doctor’s recommendations, inadequate treatment can cause serious consequences:
- Peptic ulcer disease. Most often it appears in the erosive form of the disease.
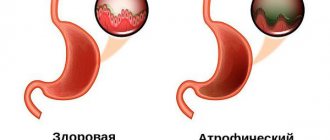
- Atrophic gastritis. Due to the low concentration of hydrochloric acid, the glands of the mucous membrane almost completely lose their ability to produce secretions and begin to be replaced by connective tissue. Refers to precancerous conditions.
- Gastric bleeding due to ulcers or erosions. It is characterized by shortness of breath, pale skin, weakness, the presence of blood in the vomit and black liquid stool. Refers to conditions requiring emergency medical care.
- Lack of vitamin B12 and folic acid. It occurs in the autoimmune form of the disease or in the advanced stage of atrophic gastritis, when the stomach glands stop producing the protein responsible for the absorption of vitamin B12.
- Anemia. It develops as a result of acute or chronic blood loss, as well as due to poor absorption of vitamin B12 from food by the body.
Gastritis and its treatment
Stress is not the only cause of increased acidity. Scientists in the last century identified the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, which causes the disease. After which, in addition to drugs that reduce acidity, patients were prescribed antibiotics, after which the symptoms of the disease began to subside.
When sick, patients must be prescribed a diet.
But it also happens that after some time the disease appears again, and with the same force. In this case, gastritis is considered chronic, which means that a person must adhere to a diet for life, and during an exacerbation of the disease, treatment is carried out according to the standard regimen. But, despite this, gastroenterologists do not recommend self-medication, even if you have studied your illness “in and out.” Chronic gastritis can lead to
Types of disease
Currently, there are several classifications of gastritis. Based on the nature and extent of the lesions, the following common forms of pathology are distinguished:
- Superficial is the safest form of gastritis, in which the mucous and inner lining of the stomach becomes inflamed.
- Chronic superficial - repeated inflammation of the mucous membrane. Chronic gastritis is characterized by periods of remission and exacerbation.
- Atrophic – a severe form of chronic gastritis, leading to atrophic changes in the mucosa.
- Erosive is a form of gastritis in which the inflammatory process is accompanied by the appearance of erosions (superficial damage).
- Anacidic - with low acidity, which is characterized by atrophy of gastric cells.
What can a patient do on his own?
A drug to reduce stomach acidity
Drug treatment is prescribed only by a doctor. But the patient can improve his condition on his own if he adheres to an appropriate diet. The diet for gastritis is very strict, as it is forbidden to include fatty, smoked and fried foods, fresh white bread, sour vegetables and fruits in your menu. In addition to the prohibited foods listed above, the diet suggests that the patient should drink little by little, but often, every 3-4 hours.
Causes of the disease
The most common cause of gastritis is infection with the bacteria Helicobacter pylori. These are one of the few microorganisms that can survive in the aggressive environment of gastric juice. Other causes of the disease usually include:
- The effect of chemical irritants (in particular, alcohol and some medications with prolonged use).
- Chronic stress.
- Parasitic infections.
- Autoimmune processes are damage to mucosal cells by cells of the immune system.
- Reflux of bile acids into the stomach (reflux gastritis).
- Identification of the etiological factor is important, since the treatment tactics of the disease depend on it.
What can you eat?
With this disease you are allowed to eat:
- milk noodle soups, creeps, in which you can add non-sour vegetables, exception
- cabbage;
- eggs in the form of an omelet or boiled soft-boiled;
- lean meat;
- vegetables, fish, steamed cutlets;
- compotes, jelly;
- milk at least 3 glasses per day;
- Vegetable fats and butter are useful for illness.
I follow the diet and all the doctor’s instructions, chronic gastritis will be under control.
Prevention
Prevention of gastritis consists of following the following recommendations:
- Balanced diet.
- Body weight control.
- Quitting bad habits (smoking, alcohol abuse).
- Control of emotional state (avoidance of stress).
- Timely treatment of gastrointestinal diseases.
For patients with chronic gastritis, it is important to follow the doctor’s recommendations to avoid exacerbations and relapses. For this purpose, such people need to visit a gastroenterologist twice a year.
Symptoms and course
Hypoacid gastritis may not manifest any abnormalities for a long time. The initial signs are:
- feeling of fullness, heaviness in the epigastric zone after eating, even in the absence of excess;
- pain occurs immediately after eating, is localized in the epigastrium, and can radiate to the hypochondrium;
- belching of rotten contents with an unpleasant odor;
- nausea;
- increased production of saliva in the mouth;
- metallic taste;
- rarely heartburn.
The nature of the pain is aching, dull, relieved by inducing vomiting
Secondary symptoms associated with damage to the intestines and other digestive organs include:
- alternating diarrhea and constipation;
- bloating of the intestines (flatulence) due to the activation of pathogenic flora and decay processes;
- hair loss and fragility;
- dry skin;
- increased fatigue, weakness;
- headache;
- tendency to lower blood pressure, palpitations;
- weight loss
It is noteworthy that the pain syndrome associated with acid deficiency is not associated with spastic contraction of the stomach muscles, but with its overstretching. It worsens with overeating, eating spicy foods, sauces, and fried foods. Secondary symptoms are caused by the formation of hypovitaminosis and anemia.
Exacerbations of gastritis with low acidity are observed in spring and autumn. They are provoked by alcohol intake, poor diet, and treatment of respiratory infections. Long periods of remission without clinical manifestations are possible.
Symptoms of chronic gastritis
Chronic gastritis
tends to cause chronic inflammation of the mucous membrane of the stomach walls. This form of gastritis most often develops under the influence of various negative external factors (various violations of proper nutrition, eating spicy or too hot food, eating dry food). Source: Ya.S. Zimmerman, Yu.A. Zakharova. Problematic issues of the doctrine of chronic gastritis // Clinical medicine, 2022, No. 95(1), pp. 8-14.
The most pronounced symptom of chronic gastritis is a feeling of some pressure and fullness after eating, nausea, heartburn, and loss of appetite.
How does the disease develop?
In the mechanism of acid formation disorders, the main role is played by the failure of adaptation of acid production to incoming food. As a result of dysfunction of the glandular epithelium, the supply of enzymes and food processing are delayed. The biochemical reactions that ensure the digestion process change qualitatively. Clinical symptoms appear that indicate gastric pathology.
A certain role is played by the decrease in the natural protection of glandular cells from the mucus-forming epithelium; this is facilitated by the entry into the stomach of too rough food and toxic substances
The initial overstrain of the parietal cells gradually leads to their death and atrophy. Therefore, gastroscopy reveals a picture of atrophic gastritis.
At the same time the following is violated:
- cell restoration process;
- formation of protective mucus;
- Insufficient blood supply is often detected against the background of hypertension and diabetes mellitus.
An important feature of chronic hypoacid gastritis is:
- primary damage to the fundus, where the acid-producing glands are most concentrated;
- rapid transition from their inflammation stage to atrophy;
- increased production of the gastrin enzyme due to the accumulation of undigested food (the more pronounced the atrophy, the higher the gastrin level);
- instead of new cells, connective tissue grows on the mucous membrane, which does not take any part in digestion;
- The gastric epithelium is partially replaced by intestinal cell types.
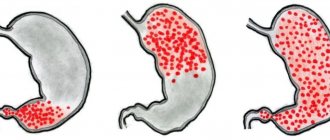
According to the results of fibrogastroscopic examination, 3 degrees of development of atrophic changes are distinguished:
- mild – about a tenth of the parietal cells are lost;
- medium - atrophic surface makes up from 10 to 20% of the stomach;
- severe - changes affect more than 20% of the glandular epithelium.