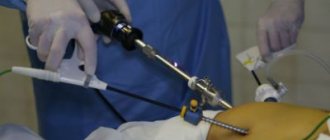
Gastric banding in Krasnodar tel. +79284177828 Regional Clinical Hospital No. 2
There are contraindications, consult a specialist. License FS 23-01-004528
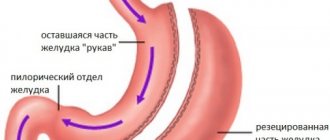
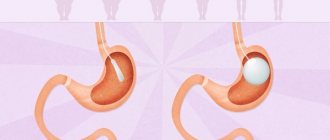
Compared to other surgical methods of treating obesity, gastric banding Banding preserves the integrity of the wall of the digestive tract. This method of surgical treatment of obesity makes it possible to regulate the rate of weight loss. The operation is reversible. That is, if necessary, the bandage can be removed. The purpose of the operation is to reduce the amount of food eaten, which leads to a decrease in calories received by a person. During the operation, a special ring is placed on the upper part of the stomach. Otherwise it is called a bandage (see figure).
The operation lasts on average 40 - 60 minutes. The stomach takes on the appearance of an hourglass. The volume of the upper part of the stomach is only about 20 milliliters. Food fills the upper part and satiation quickly occurs. A person can eat very little food at one time, which leads to weight loss. The ring, which is placed on the stomach, is a cuff that can be inflated through a special tube. The other end of the tube connects to a device or “port.” It is located under the skin of the abdomen. It is always possible to regulate the degree of narrowing of the ring on the stomach. It should be taken into account that such adjustment can be carried out 2 months after the operation. During this time, the ring should strengthen in the tissues. Gastric banding is performed laparoscopically and does not require an incision, just a few punctures. Weight loss begins almost immediately. Body weight loss after 3 months is about 10%, after a year up to 50% of excess weight. Overweight is considered body weight minus ideal weight. This operation is indicated for those patients whose BMI is 35 - 40 (the ratio of a person’s height to weight). Calculate BMI. With a BMI over 40, such an operation may not give the expected effect. In this case, gastropexy (suturing the stomach), draining gastrectomy, and gastric bypass are suitable.
Preparing for gastric banding
To install the bandage, go through a series of studies. The first is a mandatory consultation with an endocrinologist and a study of the patient’s hormonal levels. Secondly, it is imperative to perform a gastroscopy to assess the condition of the stomach. Third, you need to take a general blood test, determine your blood group, perform an ECG and fluorography. All these studies can be performed directly in the clinic. On the eve of gastric band installation, the patient is allowed a light meal; on the morning of the operation, drinking and eating are strictly prohibited.
After gastric band surgery
The patient is allowed to get up in the evening on the day of surgery. When bandaging the stomach, virtually no pain relief is required in the postoperative period. Liquid food is recommended for the first day. The patient is discharged 2–3 days after surgery. After installation of a gastric band, a special diet is required. Liquid and solid foods should not be taken together. You need to drink before meals or after 1.5 hours. Failure to comply with this condition will lead to a decrease in the effectiveness of the operation. The first gastric band adjustment is performed after two months.
Problems with gastric banding
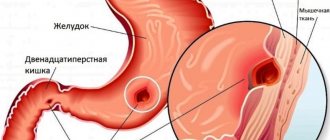
Like any other surgery, gastric banding carries a risk of complications. During the operation, bleeding is possible which in rare cases may require switching from laparoscopy to laparotomy (large incision). There may be injury to the wall of the stomach, which is not always determined during surgery and after surgery can lead to the development of an abscess or, in rare cases, general inflammation of the abdominal cavity. These complications require repeated operations. In the long-term postoperative period, after a year or more, it is possible for the band to fall into the stomach, sliding down the stomach, which leads to loss of its functions and sometimes to gastric obstruction (see figure). Also, unfortunately, the gastric band may lose its seal and become useless.
Disadvantages of Gastric Banding
Gastric banding has recently lost its leading position among bariatric surgeries, fusion resections and gastroplections. This is due to a number of disadvantages of this operation. The first is the need for constant adjustment of the bandage, which makes the patient “tied” to the clinic. Secondly, as experience was gained, complications began to appear during the operation of the gastric band, such as depressurization, migration into the lumen of the stomach, slipping, etc. Which also requires the patient to be within the reach of a specialized clinic. And the third is a smaller weight loss effect compared to other bariatric interventions.
The average price of gastric banding is 100,000 rubles. and ranges from 100,000 to 150,000 rubles. depending on the cost of the gastric band itself. Cost of gastric banding in Krasnodar.
Author: Ph.D. Siyukhov R.Sh.
The essence of the operation
First of all, you need to understand why you need a stomach band for weight loss.
The bandage, unlike the intragastric balloon, can be installed on the patient for life and does not require replacement over time. It is made of silicone and, if necessary, can be removed without any consequences for the stomach, if necessary. Today, manufacturers produce various types of bandages. Each of which is selected strictly individually, taking into account all the characteristics of the patient: the structure of his gastrointestinal tract, clinical data, and also based on the experience of a bariatric surgeon. As a rule, the patient is offered several bandage systems, then at the appointment the patient and the doctor choose the optimal one based on the advantages or disadvantages of each.
The bandage operates on the principles of a hydraulic system, which includes: a cuff, a connecting tube and a port. After the cuff is installed on the upper part of the stomach, it can be filled with an isotonic solution using a connecting tube. Through the port, which is part of the bandage system and is installed in front of the stomach under the skin, fluid flows into the connecting tube and from there into the cuff. The amount entering the port regulates the pressure in the cuff, thus increasing or decreasing the lumen in the stomach.
For each patient, the width of the lumen in the stomach is strictly individual and is adjusted empirically. Food that lingers in the upper part of the stomach (before the band) brings a faster feeling of fullness, putting pressure on its cardiac region. Thanks to this effect, the feeling of hunger is satisfied with much less food, in turn, a decrease in the amount of food leads to a decrease in calorie intake, which leads to gradual weight loss.
Preparation
Before placing a weight loss ring on the stomach, the patient must undergo an examination. It consists of consulting a surgeon, therapist, anesthesiologist, as well as passing:
- ECG;
- fluorography;
- gastroscopy;
- general urinalysis;
- general and biochemical blood tests;
- blood tests for HIV, syphilis, hepatitis, coagulation.
A week before the operation, the patient switches to a special diet (liquid food, exclusion of flour, sweet, fatty, meat), stops taking estrogen, aspirin and similar drugs, as well as those that affect blood clotting.
After midnight on the eve of the operation and up to it, you must refuse food and water.
Peculiarities
- Gastric banding is a surgical intervention, and like any surgical procedure, it requires preoperative preparation followed by hospitalization. The intervention lasts about 1 hour, hospitalization and recovery takes 2-3 days. After the initial adjustment of the pressure in the cuff and normalization of nutrition, the patient returns home, this usually happens on the 3rd day.
- Adjusting the pressure in the bandage system and monitoring the fastening of the cuff to the stomach wall takes time (about 2 months). After which, the patient comes to the procedure for adjusting the lumen of the stomach. Through a thin needle, a certain amount of saline is injected through a port into the cuff; the entire process takes no more than 15 minutes and is painless.
- Taking into account the characteristics of each patient, adjusting the pressure in the cuff is almost never instantaneous, and requires individual, repeated adjustments.
- ·For several days after surgery, the patient may experience a feeling of heaviness, retching, nausea, and pain in the epigastric region, which disappear within a few days.
- There are detailed rules for the patient’s nutrition after bariatric surgery, which the doctor or dietary nurse introduces to him. After adjusting the pressure in the cuff, you must strictly adhere to the nutritional rules, of which there are not many. The main rule is to limit liquid consumption for 1-1.5 hours before meals, since with liquid the food bolus penetrates more easily through the lumen of the bandage system. Drinking liquid is also not recommended earlier than 1-1.5 hours after eating.
Rehabilitation
This operation is low-traumatic and allows you to return to your normal life almost immediately. Patients are in the hospital for 1-3 days. After 5-7 days, the stitches are removed. Rehabilitation is almost painless and without complications.
On the first day, you need to limit the amount of liquid you drink. Then you can drink any unsweetened and non-carbonated drinks for three days. After this, you are allowed to drink any drinks, including low-fat milk, for two weeks.
Sometimes patients experience nausea. To prevent vomiting, medications are prescribed to relieve discomfort.
Three weeks after surgery, you can switch to liquid and puree foods. You are allowed to return to normal nutrition from the fifth week.
Three to four months after surgery, heavy physical labor and sports should be avoided.
Who is recommended for gastric banding?
Patients with a body mass index above 35-40 kg/m2 and the presence of concomitant diseases: diabetes mellitus, hypertension, varicose veins, arthrosis of the joints and other diseases.
The fight against obesity requires not only the patient’s motivation and interest in losing weight, but also forces the patient to completely reconsider his lifestyle and eating behavior, as well as strictly follow all doctor’s prescriptions. Installing a bandage will only help if you are strictly disciplined and follow all the doctor’s recommendations.
You can make an appointment and consultation with a bariatric surgeon at our Clinic by calling 676-25-25, or fill out an application on the website HERE and they will call you back.
Indications for the procedure
The indications for gastric banding are almost the same as for other bariatric surgeries. However, there are additional assumptions.
Patients are considered candidates for banding if they meet one of the following criteria:
- BMI ≥ 35;
- BMI = 30-34 in combination with one of the following obesity-related comorbidities: severe diabetes mellitus;
- Pickwick's syndrome;
- obesity-related cardiomyopathy;
- severe sleep apnea;
- osteoarthritis affecting lifestyle.
In February 2011, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) expanded the use of the gastric band system to patients with a BMI of 30–34 and any obesity-related comorbidities. In April 2013, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) joined these recommendations.
To be eligible, patients must have unsuccessfully attempted to lose weight through lifestyle or dietary changes.
One of the main indications was age under 25 or over 60 years.
The SAGES (Society of American Gastroenterology and Endoscopic Surgeons) guidelines note that well-selected patients over 60 years of age may benefit from gastric banding as well as adolescents.
The main benefit for older patients with this method is that vitamins, minerals and oral medications are absorbed as normal.
Shatsky rings - concept and prevalence
Food from the mouth enters the esophagus.
Food from the mouth passes into the esophagus, a hollow tube connecting the mouth and stomach. In the 20th century, benign neoplasms from mucous tissue at the esophagus-stomach border were described.
They reduce the lumen of the esophagus and retain the bolus. The pathology was named Shatsky's ring after the doctor who described this condition.
These neoplasms are observed in 6% of the planet's inhabitants. And often a person is unaware of the narrowing of the esophagus until difficulties begin with the passage of food. Esophageal stenosis can be acquired or congenital. The causes of this pathology have not been studied. The following are possible causes of esophageal stenosis:
- Reflux disease
- Surgical interventions on the esophagus and stomach
- Frequent attacks of vomiting
- Swallowing foreign objects
- Burns of the esophagus of various etiologies
- Infectious diseases
- Long period of stay of the probe in the esophagus
- Neoplasms in the esophagus and stomach of various origins
- In rare cases, these are consequences of radiation exposure or treatment with radiotherapy
- The causes of congenital pathology have not yet been studied.
Gastric resection
The first surgical method to solve this problem was vertical gastrectomy. This is a major abdominal surgery that was originally used to treat ulcers. Through a fairly large incision, the surgeon enters the abdominal cavity, cuts off part of the stomach, applies stitches and then closes the wound.
This type of gastric suturing has a number of obvious disadvantages:
- the operation is performed only under general anesthesia, which means it places a serious burden on the heart and kidneys;
- the integrity of the stomach itself is compromised, which is extremely undesirable;
- there is a high probability of infection of internal or external seams;
- after surgery, a long recovery period is required;
- for several months a person must follow a strict diet.
It is not surprising that very few people decided to have such a stomach reduction. And the surgeons themselves, without serious medical indications, performed it with great reluctance.
How the ring works
After a long fruitless search for a less traumatic way to shrink the stomach in order to lose weight, in the late 80s, the American doctor Lubomir Kuzmak proposed a very original solution to the problem. He was the first to come up with the idea of tightening the upper part of the stomach with an elastic silicone ring. And this idea worked!
In fact, the entire volume of the stomach was divided into two interconnected chambers. The volume of the top one is very small - no more than 20 ml. This is approximately two dessert spoons or four teaspoons. When the upper chamber is filled, a signal of saturation is sent to the person’s brain, and he no longer wants to eat more.
The food then gradually moves lower into the larger part of the stomach. And after a while the person wants to eat again. Thus, the patient is transferred to very small meals.
The daily volume of food eaten becomes approximately equal to the volume of the filled stomach. In 8-10 meals a person eats 20-30 ml of food.
Symptoms of the disease
Narrowing of the esophageal tube causes nausea.
In the initial stages of the disease or while the lumen of the ring is more than 2.5 cm, the patient may not feel discomfort. When the esophageal tube narrows to 1.5 cm, the following symptoms are observed:
- Difficulty swallowing
- Pain during the act of swallowing, behind the sternum
- Heaviness, feeling of pressure
- Nausea, vomiting
- Depressed, depressed state
- Weight loss
- Deterioration of skin and hair condition
- General malaise, signs of lack of vitamins and nutrients
If a large bolus of food enters and the esophagus is blocked, a person must induce vomiting in order to restore the patency of the organ. In severe cases, the doctor has to use an endoscope to alleviate the patient's suffering.
With congenital stenosis, a characteristic symptom is regurgitation of uncurdled milk. Additionally, there is increased salivation and mucus discharge from the nose. The diagnosis of “congenital stenosis” is confirmed with the introduction of complementary foods and solid foods.
Surgeries for diabetes and excess weight
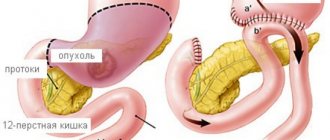
Interposition of the ileum
The technique involves transplanting a section of the ileum (the final section of the small intestine) into the jejunum (the initial section). At the same time, due to the early impact of food on the ileum, glucagon-like polypeptide-1 (GLP-1) is released earlier, which allows stimulating the production of its own insulin and achieving relief from the symptoms of type II diabetes mellitus.
This operation, unlike bypass operations, allows preserving the function of the entire small intestine, so it can be used in patients with relatively low weight, exclusively to eliminate the effects of diabetes mellitus II. The operation is performed laparoscopically.
pros
- Impact on all three hormonally active zones of the gastrointestinal tract
- Preservation of pyloric sphincter function
- Impact on all three hormonally active zones of the gastrointestinal tract
- Absence of malabsorptive syndrome
Minuses
- Technical difficulty
Advantages of banding in Belgium
- Gastric banding is performed less frequently than other bariatric surgeries. Therefore, not every European clinic has accumulated sufficient experience in its implementation. In Belgium, such operations are performed more often, thanks to the influx of patients from France, Great Britain and other EU countries, attracted by the reasonable prices of Belgian clinics. In this regard, in Belgium you can find a more experienced surgeon and have better guarantees of a good result.
- Use of reliable bandages with a high level of biocompatibility.
- Moderate cost of the operation compared to neighboring European countries and Israel.
Contraindications
This procedure is contraindicated in patients who cannot tolerate general anesthesia. It is also contraindicated in people with uncontrolled coagulopathy or in those at excessive surgical risk due to severe liver, lung, heart, and or vascular disease.
Relative contraindications include Prader-Willi syndrome, malignant hyperphagia, severe untreated psychiatric illness, pregnancy, cirrhotic diseases with portal hypertension, autoimmune connective tissue diseases, chronic inflammatory conditions and the need for chronic corticosteroid use.
Relative contraindications also include gastrointestinal disorders or infections and inability or unwillingness to follow dietary recommendations.
Possible complications
- infection
- bleeding
- tape erosion of the stomach
- esophageal distension
- vomit
- heartburn
- gastric perforation
- spleen injury
- mechanical failure of the tape or port
A retrospective review of 156 patients who underwent laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding over a four-year period reported an overall complication rate of 15.4% and a major complication rate of 3.2%. The authors noted that the procedure was associated with some complications, even when performed by a surgeon experienced in laparoscopic surgery.
Degrees of stenosis and diagnosis
Gastroscopy - will help determine the degree of passage of food.
Doctors distinguish 4 degrees of narrowing of the esophagus. The classification is based on the principle of passage of food and liquid through the esophagus:
- Grade 1 – sometimes there are problems when swallowing a bolus of food, pain in the stomach and esophagus is occasionally bothersome
- Stage 2 – semi-liquid foods, purees, thick dairy products pass
- Stage 3 – liquids only
- 4th degree – water and saliva do not pass through
The examination is carried out using 2 methods - x-ray and gastroscopy. X-ray with barium - allows you to visualize the passage of the contrast mass through the anatomical structures, the relief of the esophageal mucosa, and the linear dimensions of the tumor.
This method also helps to differentiate Shatsky’s rings from various protrusions of the walls of the esophagus and foreign objects. In preparation for the study, it is necessary to avoid eating for 8 hours.
It is advisable to perform fluoroscopy in the morning on an empty stomach. The procedure is carried out in real time. The duration of the examination of the esophagus is 40 minutes. After an x-ray, you should drink a large volume of water to remove barium sulfate from the body. Endoscopic examination allows you to identify and visualize Shatsky rings. The disadvantage of this method is that the endoscope tube cannot pass through the narrowing of the esophagus.