The lifestyle of a modern person often leads to the development of many diseases. In particular, low physical activity, poor and irregular nutrition, and an unfavorable environmental environment negatively affect the body, which over time becomes difficult to maintain its normal functioning.
The digestive system, the main part of which is the gastrointestinal tract, is one of the vital human systems. Violation of any of its functions and the development of various pathologies negatively affects a person’s quality of life and leads to many health problems. Gastrointestinal diseases have characteristic symptoms that everyone should know about.
Gastrointestinal tract and causes of its pathologies
Gastrointestinal tract - as one mechanism
The human body is a complex mechanism consisting of many systems that function harmoniously and ensure its viability. The digestive system plays an important role in the life of any organism.
This is due to the fact that a person cannot live without food: with food, he receives everything he needs for normal life - proteins, carbohydrates, fats, various vitamins and other elements.
These particles not only play the role of “fuel”, filling the body with the necessary energy, but are also necessary as a building material that is used to restore and create new cells in all human organs and systems.
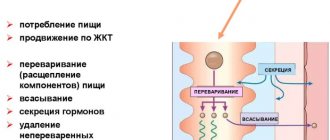
The gastrointestinal tract is part of the digestive system, with the help of which the body processes food entering through the mouth and esophagus, and receives from it all the useful and necessary components. The digestive system has several functions, including:
- motor-mechanical function that contributes to the grinding of food and its normal transportation through the intestines for further excretion
- secretory function - with its help, the necessary processing of crushed food particles is carried out using various enzymes, juices, and bile. Secretory function is necessary for the digestion process to proceed correctly and fully.
- absorption function, through which all necessary nutrients and fluids are absorbed
Gastrointestinal diseases are divided into 3 groups
Under the influence of many negative factors, disruptions in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract often occur, resulting in the emergence and development of diseases in this part of the human digestive system. The development of such pathologies can be provoked by the following reasons:
- poor nutrition. This reason includes: overeating, undereating, irregularity in food intake, excessive speed of its absorption, consumption of monotonous foods. A poorly balanced diet also plays an important role in the process of deteriorating digestion. Among other things, the gastrointestinal tract is negatively affected by harmful additives, dyes and preservatives, which are contained in many products.
- poor environmental condition. The digestive system is adversely affected by low-quality water, pesticides contained in products of plant origin, preservatives and other harmful substances found in products of animal origin.
- congenital predisposition to certain diseases
- side effects of certain medications
- violation of sanitary standards in the process of preparing and consuming food
- poor state of the nervous system: stress, overexertion
- harmful or simply difficult working conditions
- infectious diseases
- parasitic infestations
- endocrine system diseases
- bad habits
Due to the fact that this list of reasons is quite wide, the likelihood of one or another disease of the digestive system occurring is quite high. It is extremely important to pay attention to the state of your health and, if the slightest signs of disturbances in the functioning of the body appear, consult a doctor in a timely manner. This will help reduce the risk of developing serious diseases and their consequences.
How does an appointment with a gastroenterologist proceed?
First of all, the doctor will question you in detail about the symptoms that bother you, when the disease began, whether it is related to any food products, whether your relatives have the same problems, whether you had the same symptoms earlier in life, what other diseases you have, etc. etc. Also, the specialist will be interested in a list of medications taken against other diseases, since they can have side effects on the gastrointestinal tract.
After taking a thorough history, the doctor begins a physical examination of the patient. A phonendoscope is used for listening. The doctor determines the boundaries of the organs using the tapping method (percussion). The doctor will also feel the abdomen and check to see if it causes pain.
At the final stage of the first consultation, the doctor writes a list of tests and examinations that the patient needs to undergo to clarify the preliminary diagnosis. At the next consultation you will need to bring the results of these tests and examinations and, based on them, the doctor will draw up a complete picture and make a final diagnosis. The gastroenterologist will then prescribe a treatment regimen and observe what effect it has on a particular patient.
Common stomach diseases
One of the main organs is the stomach
The stomach is one of the main organs that is part of the gastrointestinal tract. So, in it, food is processed by gastric juice, as a result of which the digestion process begins.
Food exposed to gastric juice becomes more liquid. In this state, the crushed food is called chyme. After the stomach, chyme, through the lower sphincter of the organ, enters the following sections of the gastrointestinal tract. In addition to liquefying food, under the influence of digestive enzymes and gastric juice, protein decomposition occurs, so-called hydrolysis.
Also, the acidic environment of the stomach is an excellent barrier to a variety of pathogenic microorganisms. The organ itself is protected from aggressive hydrochloric acid by the mucous membrane. Stomach pathologies are divided into three groups:
- functional
- infectious
- inflammatory
The division is based on differences in the symptoms of different diseases. Each classification manifests itself in its own way, and the signs of diseases differ depending on the course of the disease and the degree of its neglect. The course of stomach diseases can be either acute or chronic.
As a rule, acute forms of organ diseases arise as a result of an infectious disease or poisoning by toxins. The chronic form is the result of the influence of negative factors over a long period of time. Serious stomach diseases, such as cancer, are difficult to treat. Their therapy depends on the timeliness of the patient seeking medical help.
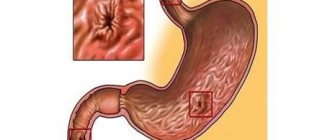
Due to the fact that many gastrointestinal diseases have very similar symptoms, an accurate diagnosis, on which the effectiveness of therapy directly depends, can only be made by a gastroenterologist. Among the diseases that affect the stomach, pathologies such as gastritis are the most common in terms of frequency of occurrence.
This disease manifests itself in the form of an inflammatory process that covers the mucous membrane of the organ. In most cases, gastritis manifests itself in a chronic form. Gastritis often causes the development of other gastric diseases. In case of gastritis, the patient may complain of the following symptoms:
- feeling of heaviness in the stomach
- vomit
- heartburn
- nausea
- belching
- pain in the stomach area
It is important to remember that many gastric pathologies, while occurring in remission, have virtually no signs of manifestation. However, destructive processes continue in the organ even when there are no symptoms.
Gastritis
There are many symptoms of gastrointestinal diseases!
In the case of gastritis, against the background of low acidity of the organ, various formations form on the lining of the stomach - tumors and polyps. Food is not digested sufficiently, the digestion process worsens, and the patient may suffer from anemia.
What to look for when choosing a gastroenterologist
A good gastroenterologist regularly takes advanced training courses and often has award certificates. A good sign is conducting scientific activities. The presence of a scientific degree indicates recognition of the doctor’s experience and professionalism by a special commission. If you need a gastroenterologist with an above-average level of qualifications, be sure to pay attention to a scientific degree.
The more experience the doctor has, the more reliable it is. It is better to choose a specialist who has at least 10 years of practical experience. The accumulated knowledge allows us to quickly make the correct diagnosis and better navigate treatment. This also affects the quality of hardware research and surgical operations, since this requires “training the hand” and the eye.
A good gastroenterologist will definitely ask about other diseases that the patient currently or previously suffered from. They can cause or be caused by gastrointestinal diseases. Also important is the attentiveness of the doctor, his desire to conscientiously understand the patient’s situation, explain the intricacies of diet and prevention, and answer all the patient’s questions.
Reviews on the Internet do not always directly correlate with the quality of the doctor, since they are often written for money. In practice, it happens that the higher a doctor’s salary, the more positive reviews he has on the Internet. Also, doctors from private clinics have more positive reviews than from public clinics, since the clinic’s management cares about the reputation of its employees.
Intestinal diseases and their signs
Poor nutrition is the main cause of gastrointestinal diseases
The basis of various intestinal diseases is inflammation, which can be acute, chronic or infectious. During the development of an inflammatory phenomenon, not only one part of the intestine can be affected, but several at once. Depending on the location of the inflammation, the disease has a specific name:
- enteritis
- appendicitis
- sigmoiditis
- proctitis
- colitis
- typhlitis
As a result of inflammation, the mucous membrane of the affected part of the intestine becomes hyperemic, edematous, and discharge of various types may be produced: hemorrhagic, serous or purulent. In especially severe cases, often bleeding ulcers develop. If the development of the ulcer is not stopped, it will eventually cause perforation of the affected area and subsequent development of peritonitis. Intestinal pathologies negatively affect its functions:
- Digestion worsens
- absorption of nutrients stops
- intestinal motility worsens
- there is an increase in mucous secretions
The main signs of pathologies are:
- pain in the abdominal area
- flatulence
- diarrhea
- constipation
- intestinal bleeding
- loss of appetite
Depending on the location of the disease in the intestinal region, it has a specific name. In general, the symptoms of all diseases are similar and the main one is the occurrence of pain.
How to prepare for an appointment with a gastroenterologist
Most often, no preparation is required for the first appointment with a gastroenterologist. After all, only there the doctor will make the first examination and determine the paradigm for further examination. But you will already need to prepare for the hardware examination procedures. Only in exceptional cases, before the first consultation, a gastroenterologist may prescribe a special diet before the examination, an enema or abstinence from food in the morning. If you want to do an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, then three days before it you need to exclude from your diet foods that cause flatulence: rye bread, legumes, cabbage, etc.
Contraindications
Contraindications are associated with the need to use a contrast agent and the risk of its spread beyond the intestinal lumen. Therefore they include:
- suspicion of gastrointestinal perforation;
- acute bloating of the colon (megacolon toxicum);
- biopsy of the intestinal wall in the previous 6 weeks;
- pregnancy;
- lack of cooperation with the patient;
- Research methodology;
- Double contrast method.
The esophagus and stomach are examined by fluoroscopy while swallowing a barite suspension. The effect of double contrast can be achieved thanks to an air bubble in the stomach, inviting the patient to change the position of the body (most often rotating around its axis). This allows the mucosa to be thoroughly coated with barite paste, making it easier to evaluate its surface.
Enteroclysis
Examination of the small intestine is carried out using a double contrast agent - enteroclysis. A solution of barite and methylcellulose (the carrier of barite in the intestine), which dilates the lumen and very accurately visualizes the mucosal folds, is injected through a tube inserted distal to the ligament of Treitz. The classic enteric cry is used less and less due to better visualization of the small bowel on CT and MRI.
Rectal enema
A rectal enema is the rectal administration of a barite suspension and air. The initial assessment is performed using fluoroscopy, and then a series of x-rays are taken in various positions of the body.
Symptoms
Diseases of the esophagus are characterized by the following symptoms:
- chest pain,
- difficulty swallowing,
- heartburn,
- nausea,
- belching.
Often the clinical picture is similar to manifestations of pathologies of other systems - respiratory, cardiovascular (dry cough, difficulty breathing, chest pain, shortness of breath).
If these symptoms occur, you should consult a gastroenterologist-hepatologist!
For chronic diseases of the stomach and duodenum, characteristic symptoms will be pain in the epigastric region (epigastric region). As a rule, they are associated with food intake. Stomach pathologies are characterized by the appearance of pain 15-20 minutes after eating. They last for several hours and may go away on their own. In diseases of the duodenum, pain begins 1.5-2 hours after eating.
With the development of tumors, pain is expressed in different ways: it can be associated or not associated with food. The development of malignant tumors of the stomach is characterized by pain not related to food (“hunger” pain, pain at night). Appetite is lost and significant weight loss occurs. An aversion to previously favorite foods appears. Sometimes - belching of undigested food.
Interpretation of the result
Signs of obstruction are fluid levels. If perforation is suspected, look for free air under the domes of the diaphragm or at the highest point of the abdominal wall (if the image was taken in a horizontal position). In the case of obstruction, performing additional projection in the supine position allows better assessment of bowel distension.
In cases other than perforation, obstruction or foreign body, plain imaging may reveal calcified structures (eg, renal deposits, vessel wall or bile duct calcification - but remember that only 30% of these are calcified).
Statistics
In Japan, among all operated patients with gastric cancer, patients with early cancer account for 50-55%. This is explained by the fact that categories of the population predisposed to stomach cancer undergo regular examination there. In Russia, from 60 to 90% of patients with newly diagnosed gastric cancer have stages III-IV, which determines the corresponding prognosis.
Our Center specializes in the diagnosis of early forms of malignant lesions of the gastrointestinal tract (esophagus, stomach, small intestine, colon) and their minimally invasive endoscopic treatment.
The special skills of our endoscopists allow us to identify tumors with a diameter of 1 mm and suspect their malignant nature, and timely surgical treatment using the endoscopic method allows us to cure the patient completely and in a timely manner.
During the endoscopic procedure, special techniques are used: chromoscopy, magnifying endoscopy, examination in a narrow spectrum of NBI light. This tactic undoubtedly improves the quality of histological verification, allows for targeted identification of foci of change and correct biopsy, which leads to an increase in the detection of various gastrointestinal pathologies, incl. oncological